music theory :3
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Major Pentatonic Scale
remove the 4 and 7 from key signature scale
Minor Pentatonic Scale
remove the 2 and 6 from key signature scale
Blues Scale
remove 2 and 6 and repeat 5 and lower it
Chromatic Scale
go up by semitones each time with # and down by semitones each time with b
Whole Tone Scale
go up by whole tones for an octave
I Don’t Particularly Like Modes A Lot
Ionian (+), Dorian (-), Phrygian (-), Lydian (+), Mixolydian (+), Aeolian (-), Locrian (-)
Ionian
major scale
Dorian
minor scale and raise the 6
Phrygian
minor scale and lower the 2
Lydian
major scale and raise the 4
Mixolydian
major scale then lower the 7
Aeolian
minor scale
Locrian
minor scale, lower the 2 and 5
Determining modes
Starting note, then find the key. Find the note of the key and count up from ionian until the end of scale
Minor Triads
lower the third
Diminished Triads
lower the third and fifth
Augmented Triads:
raise the fifth

5/3

6/3
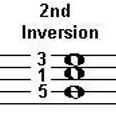
6/4
Who funded Classical Era
royal courts in 1750-1820
Diatonic Melodies
melodies using notes within a single scale
Modern Orchestra
string section, winds in pairs, percussion section
Key Characteristics of Classical Era
Use of homophonic textures.
Development of sonata form
Expansion of the orchestra, symphony/concerto
Importance of the piano as a solo instrument.
Focus on instrumental music, especially symphonies and string quartets.
Cleaner sound
Typical Multi Movement Work Structure
Movement 1 – Fast: Sonata Form
• Movement 2 – Slow: a broad a b a form is common; sometimes a theme-variation
• Movement 3 – Dance; usually a minuet and trio, or later, a scherzo and trio; omitted in most three movement structures
• Movement 4 – Fast: usually a rondo; sometimes sonata Form
Primary singing genre in classical time period
opera
Recitative
provided narrative to the story
Aria
provides commentary or feelings to the plot
A typical first movement in sonata form included three components
• Exposition – presents the primary theme in the tonic key, followed by a secondary theme in a contrasting key, sometimes in a contrasting mood
• Development – composer’s imagination could flourish. This music was based on the prior material but there would be drastic modifications using Tonal centres, dynamics, rhythms, harmonies, and tempos
• Recapitulation – provided a return to stability; a return to the tonic key, and the primary theme
ROMANTIC ERA Time Period
1810-1920
Absolute music
music created for its own sake, not a funded purpose
Program music
music created to depict moods, images, stories, or characters
Homophonic
musical tension and to intensify emotion
Lieder
Arts songs short and poetic. Centered around keyboard
Characteristics of Romantic Era
Experimentation with rhythm and meter (more syncopation, tempo changes, hybrid meters)
Opera and Ballet become an important part
Emotion Took Over in composers
absolute and program music
FRANZ JOSEPH HAYDEN - Classical
Mentor to Mozart
Taught Beethoven
Helped make Classical music more popular across Europe
Especially in England, as well as France, Spain, and Italy
WOLFGANG MOZART - Classical
Child prodigy
Came from Austrian aristocracy
His father was a court musician
Struggled financially
Wrote over 600 compositions
Died at 35
LUDWIG VAN BEETHOVEN - Classical
Bridged the Classical and Romantic eras
Studied with Joseph Haydn
Famous for powerful, emotional music
Became deaf
Wrote 9 symphonies
Johannes Brahms - Romantic
Born in Germany
Composer and pianist
Friends with Robert and Clara Schumann
Fell in love with Clara Schuman but very loyal to Robert
Music is passionate, introspective, and full of lyrical melodies
Frederic Chopin - Romantic
Born and educated in Poland but spent professional life in Paris
Frequent use of rubato
Elaborate, decorative melodie
Pyotr I’yich Tchaikovsky - Romantic
Russian composer
Created Swan Lake,Sleeping Beauty, Nutcracker, and Romeo and Juliet
thick, lush texture of the Romantic period orchestra
Giuseppe Verdi - Romantic
Greatest Italian opera figure, national hero
Famous in America
Librettos were usually unhappy with tragic endings
Richard Wagner - Romantic
German opera composer
Fled Germany and moved to Switzerland
Operas were more symphonic in nature – powerful brass instrument