BMS 501 Practical Study Guide
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
how do you calculate total magnification of an object being observed under a light microscope?
objective magnification (10x, 40x, 100x) X ocular magnification (10x)
orange
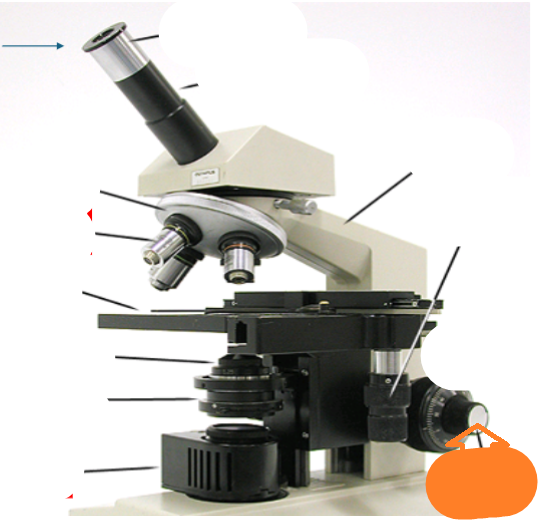
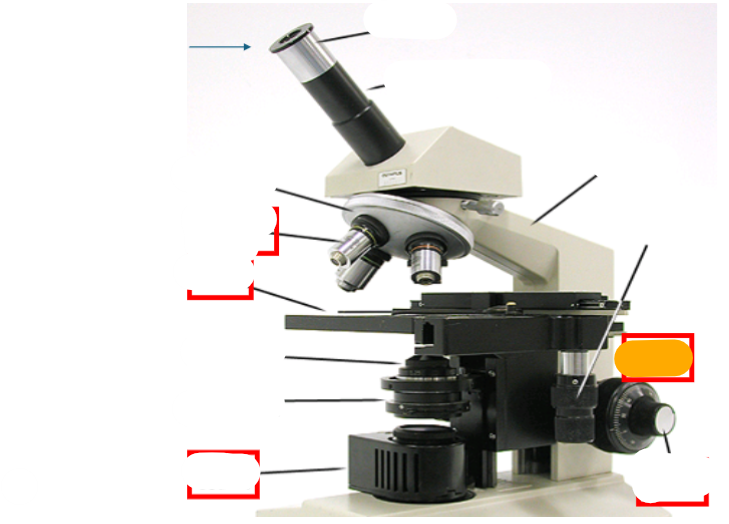
fine focus
orange
course focus
orange
coaxial stage controls
orange
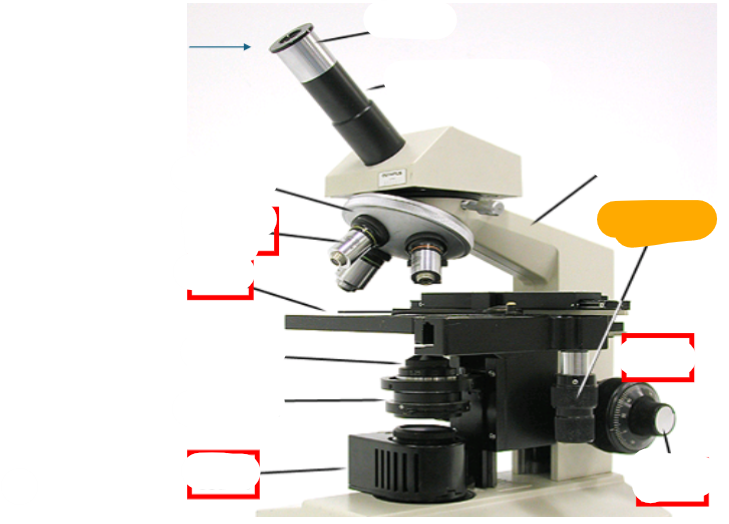
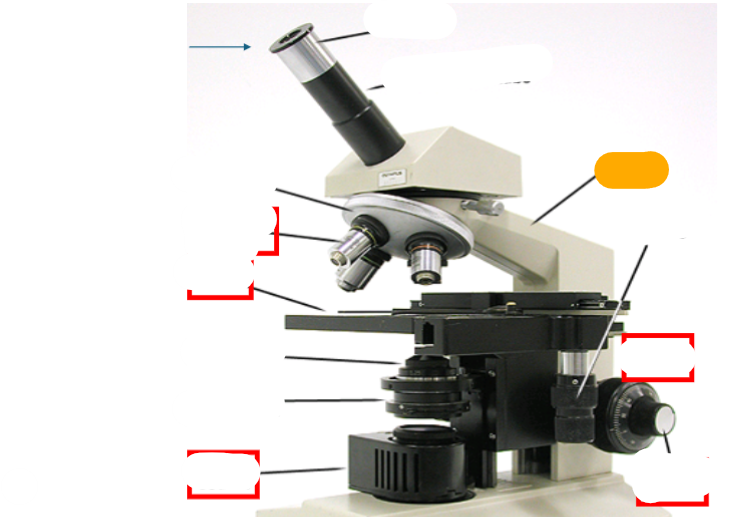
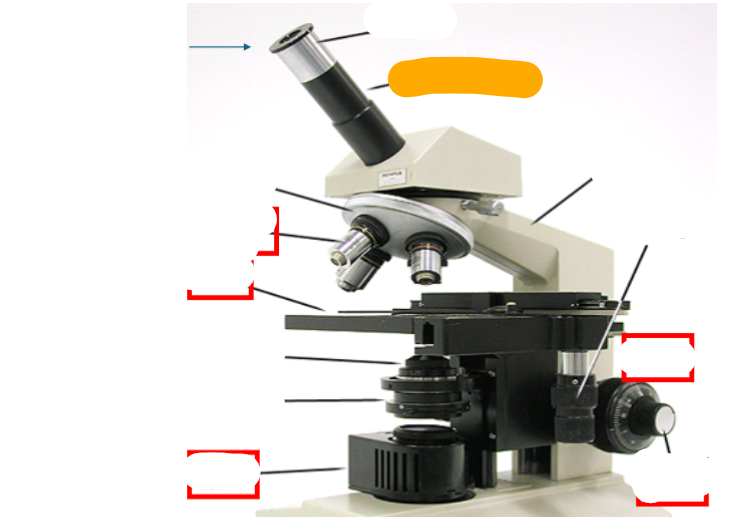
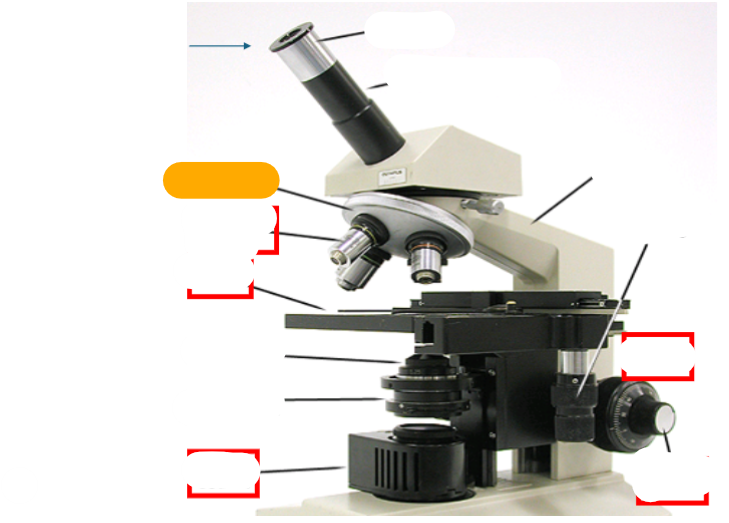
neck
orange
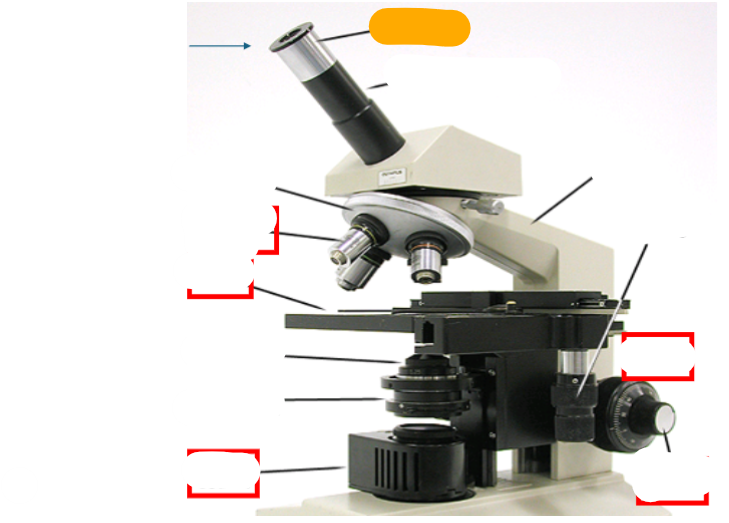
observation tube
orange
eyepiece
where is the ocular lens located in a microscope
in the eyepiece
orange
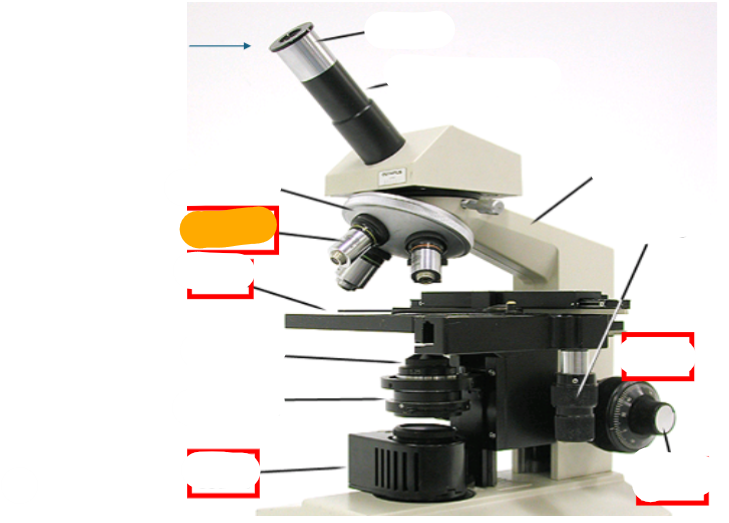
nosepiece
orange
objective lens
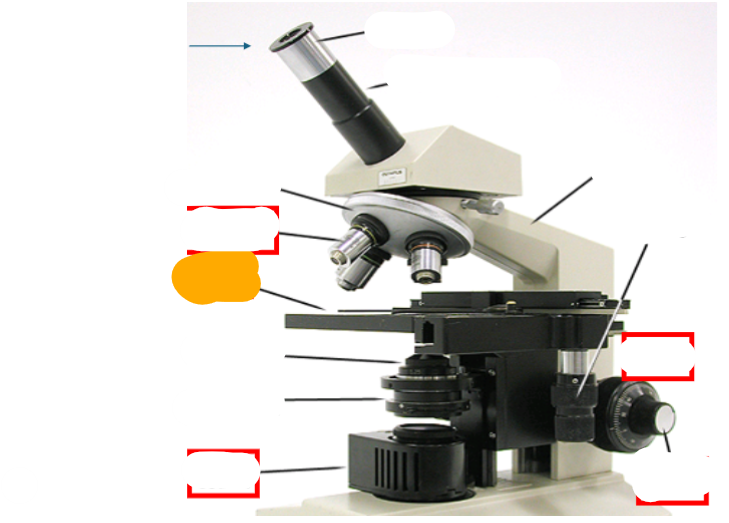
orange
stage
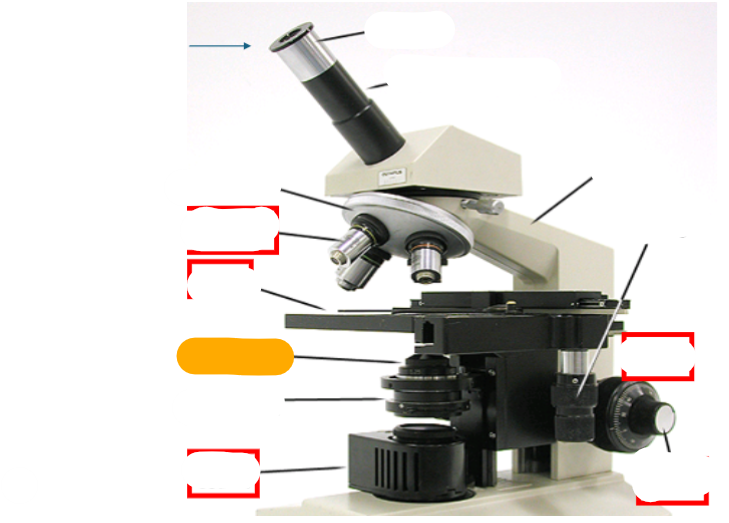
orange
condenser lens
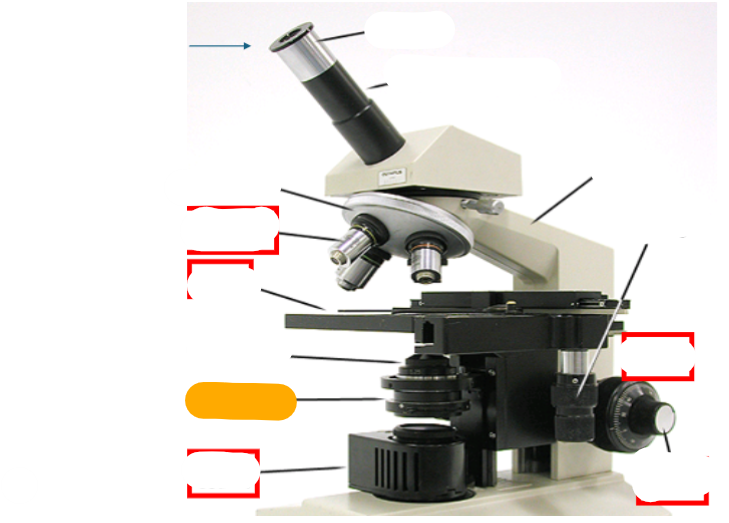
orange
iris diaphragm
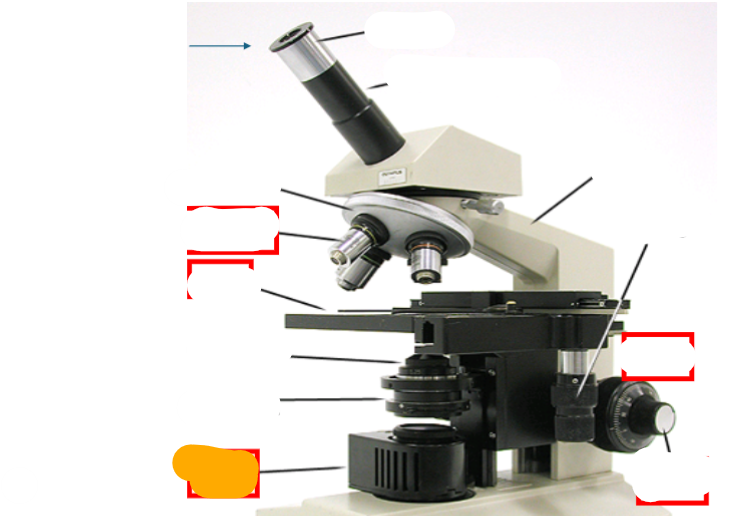
orange
light source
Which is properly written?
Escherichia coli or Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
How do you shorten an organisms name? Use Escherichia coli as an example
E. coli
simple stain
coloring cells to see shapes
Gram stains
differentially coloring cells to see shapes and determine Gram class
Endospore stains
differentially coloring to see if the species makes spores
what type of cell wall do Gram-negative cells have?
thin peptidoglycan layer
what type of cell wall do Gram-positive cells have?
thick peptidoglycan layer
Staphylococci morphology
cocci in grape-like clusters
Bacilli morphology
rods, spore-forming
Clostridia
Rods, spore formers
Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli, klebsiella, salmonella, shigella) morphology
rods
mycobacteria morphology
rods, weakly gram positive
acid fast stain positive
what color is Gram-negative in a gram stain
pink
what color is Gram-positive in a gram stain
purple
first step of gram staining
put crystal violet (primary stain) on the slide for 1 minute
second step of gram staining
put Gram’s iodine (mordant) on the slide for 1 minute
third step of gram staining
put acetone alcohol (decolorizer) on the slide for less than 5 seconds
fourth step of gram staining
put safranin (Counterstain) on the slide for 1 minute
why do Gram-negative bacteria result in a pink appearance in a Gram stain
because they have a thin peptidoglycan layer which allows for the decolorizer to get rid of the purple color from the crystal violet, then they get stained pink with the safranin
why do Gram-positive bacteria show up purple in a gram stain
because they have a thick peptidoglycan layer preventing the decolorizer from ridding the cells of the purple crystal violet stain
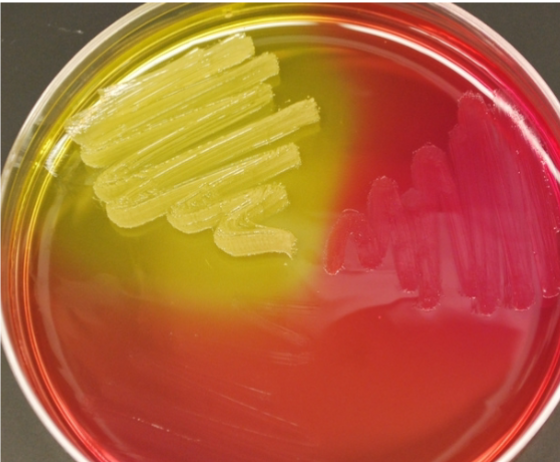
what plate is this
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
is Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) plates selective or differential
selective and differential
selective for Gram positive bacteria
differential for fermentation of the sugar mannitol using phenol red as an indicator
what does a positive MSA plate look like?
phenol red (pink color) turns yellow when mannitol salt is fermented
what does a negative MSA plate look like?
phenol red (pink color) remains red-orange in color due to the fact that mannitol sugar is not fermented
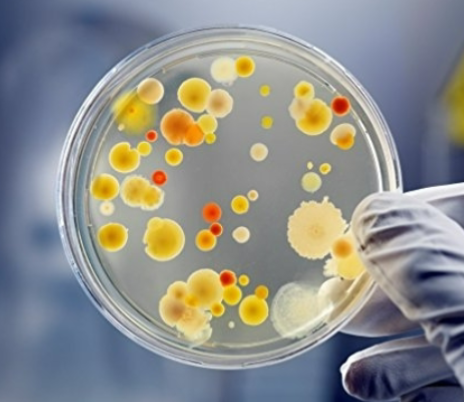
what plate is this
Nutrient Agar (NA)
is nutrient agar (NA) plates selective or differential
neither they allow growth of many organisms, does not exclude or distinguish

what plate is this?
Blood Agar Plate (BAP)
how can you differentiate between a Blood Agar Plate (BAP) and Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) plate?
a MSA plate will appear reddish-pink and a BAP will have a darker red color
are blood agar plates (BAP) selective or differential
differential only
what does alpha hemolysis mean on a BAP
bacteria can partially breakdown blood
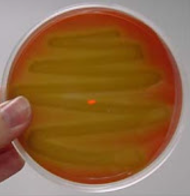
what result on a BAP plate is this
alpha hemolysis
what does beta hemolysis on a BAP mean
bacteria can completely breakdown blood
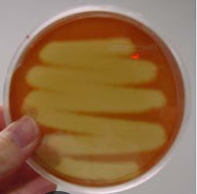
what result on a BAP plate is this
beta hemolysis
what does Gamma hemolysis on a BAP plate mean
bacteria cannot breakdown blood
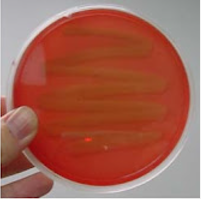
what result on a BAP plate is this
gamma hemolysis
Are bile esculin slants (BES) selective or differential
selective and differential
selective for gram positive species due to bile salts
differentiates species by esculin hydrolysis

what result of a BES test is this
positive
it can hydrolyze esculin

what result of a BES test is this
negative
it cannot hydrolyze esculin

what test is this?
Bile Esculin Slant (BES)
is a catalase test selective or differential?
differential based on the bacteria’s ability to produce the enzyme catalase

is this catalase result positive or negative?
negative
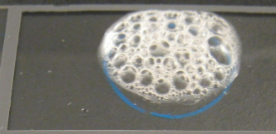
is this catalase result positive or negative?
positive
what does a positive catalase test result mean?
it can produce catalase
does Streptococcus agalactiae grow on MSA plates
no it doesn’t grow
what is aseptic technique?
methods of working free of microbial contamination
why is aseptic technique important?
prevents culture/specimen contamination
prevents contamination of yourself/others/environment
what does aseptic technique include
safely dispensing culture media
flame-sterilizing instruments
proper labeling, handling, and storing
practicing correct hand hygiene and workspace disinfection
what is selective media
only permits the growth of certain type of bacteria
inhibits other types of bacteria in many ways including: salt content, high/low pH, antibiotics
what is differential media
allows visually differentiation between two or more kinds of bacteria due to chemical reactions in the media
more than one type of bacteria can grow on the plate
How do you properly label plates and tubes
initials/lab section/type of media/what is on it/date
where do you label a plate
on the bottom, not the lid
what is the first step to a quadrant streak
flame an inoculating loop, wait for it to cool, collect a loopful of the bacteria and spread it across 1/4th of the plate
what is the second step of a four quadrant streak
flame the inoculating loop, wait for it to cool and then drag some bacteria from the first quadrant and streak it into another 1/4th of the plate
what is the third step of a quadrant streak?
flame the inoculating loop and wait for it to cool, drag some bacteria from quadrant 2 and spread it onto another 1/4th of the plate
what is the fourth step of a quadrant streak?
flame the inoculating loop, wait for it to cool and spread some bacteria from quadrant 3 into the final 1/4th of the plate and spread it
acid-fast staining
stains thick, waxy lipid walls
what does a pink mean in an acid-fast stain
acid fast positive
what does a blue result in an acid-fast stain mean
counterstained aka negative
diagnosis and treatment of Candida
microscopic analysis of vaginal discharge reveals budding yeast or yeast in hyphal form
yeast can also be identified by culture methods
first-line treatments: antifungal azole drugs
how many tapeworms infect humans
6 tapeworms
ex: Taenia saginata from beef and Diphyllobothrium latum from fish
Bill Nye discovered a new bacterial species that he named named Sciencius guyus! After growing a culture overnight at 37°C, he spread 3 CFU plates, 100uL on each. The 10-3 plate has 3149 colonies; the 10-4 plate has 229 colonies; the 10-5 plate has 15 colonies. What is the CFU/mL of the culture?
2.29 × 107 CFU/mL
An E. coli outbreak was traced by epidemiologists back to a batch of infected lettuce. Approximately 20,000 heads of lettuce had been sold from the crop, and there were 127 reported illnesses and 6 reported deaths. Laboratory testing on the lettuce revealed an average number of 50 cells of E. coli bacteria present on a given plant. Approximate the ID50 and LD50 of the E. coli strain, assuming each head of lettuce was eaten by 1 person. Use Scientific notation
ID50 = 3.9 x 103 cells
LD50 = 8.3 x 104 cells
ID50: 10,000 (half of population)/127 (amount of people sick) = 78.74 × 50 (amount of cells) = 3,937 cells = 3.9 × 103 cells
LD50: 10,000 (half of population)/6 (amount of people dead) = 1,666.66 × 50 (amount of cells) = 83,333 cells = 8.3 x 104 cells
how are O2 requirements tested
thioglycolate tubes
obligate aerobe
needs oxygen to live, breaks down sugars using it
absolute dependence on oxygen use in metabolism
can effectively manage reactive oxygen species

obligate anaerobe
dies in presence of oxygen (doesn’t use it, can’t detoxify it)
has no dependence on oxygen use in metabolism → not used
cannot effectively manage reactive oxygen species
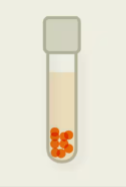
microaerophile
can only stand oxygen in low concentrations
uses small amounts of oxygen in metabolism
can effectively manage reactive oxygen species but only in small amounts

aerotolerant anaerobe
doesn’t use oxygen, but doesn’t die when exposed to it (Can detoxify it!)
oxygen is not used in metabolism, but can live in the presence of it
can effectively manage reactive oxygen species

facultative anaerobe
prefers oxygen, but can do anaerobic respiration and detoxify oxygen when needed
prefers using oxygen for metabolism but can survive without it
can effectively manage reactive oxygen species

where does Bordetella pertussis infect
lungs
whooping cough
where does mycobacterium tuberculosis infect
lungs
where does mycoplasma pneumoniae infect
lungs
what are common ventilator-associated pneumonias
Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and MRSA
where does Borrelia burgdorferi infect
blood and lymph
lyme disease
where does Treponema pallidum infect
blood and lymph
syphilis
where does Yersinia pestis infect
blood and lymph
plague
where does Staphylococcus aureus infect
skin
staph infections → wound infection, scalded skin syndrome, CAUTIs, pneumonia, sepsis
where does Propionibacterium acnes infect
skin
where does Helicobacter pylori infect
stomach
ulcers
where does Clostridioides difficile infect
large intestine
where does Salmonella species infect
large intestine
extreme thermophiles
grow in 65-120 degrees C
thermophiles
grow in 40-75 degrees C
mesophiles
grow in 10-50 degrees C
human body temperature
psychrotrophs
grow in 0 to 30 degrees C
psychrophiles
grow in -20 to 10 degrees C
Are Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) slants selective or differential
differential based on ability to ferment lactose, sucrose and glucose