Quiz 2: Dimensional Analysis and Atomic Structure
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
4.98 mg = ? grams
4.98 mg x 1g/1000 mg = 0.00498 g
1.7 x 10^3 Ms = ? seconds
1.7 x 10^3 Ms x 1s/(1 x 10^6 Ms) = 0.00175 s
What are the 2 temperature Conversion Formulas?
T (k) = T (degrees C) + 273.15
T (degrees C) = (5/9) [T (degrees F) - 32]
Temperature Conversions:
70 degrees F = ? degrees C
(5/9)(70-32) = 21 degrees C
Temperature Conversions:
45.73 degrees C = ? Kelvin
45.73 degrees C + 273.15 = 318.88 K
SI Unit Conversions:
0.10 m^3 = ? mL
0.10 m^3 x (100 cm/1 m)^3 x 1 mL/1 cm^3 = 1.0 x 10^5 mL
True or False:
The atom is not indestructible
True
What are the three Subatomic Particles you need to know?
1. Electrons
2. Neutrons
3. Protons
What charge does each subatomic particle have?
Electrons - 1-
Neutrons - no charge
Protons - 1+
What makes up the Atomic Number?
The number of Protons
_____________ and ____________ are known as Nucleons because they are inside the nucleus
- Protons
- Neutrons
_____________ spread out over a large volume due to repulsion
Electrons
_______________ are outside the nucleus occupying orbitals
Electrons
All _____________ of an atom comes from the electron cloud
Volume
_______________ are atoms with the same protons but different neutrons
Isotopes
How do you know if an atom is Neutral?
- There is no charge on the nuclide symbol
- Protons = Electrons
Draw the Nuclide Symbol Format
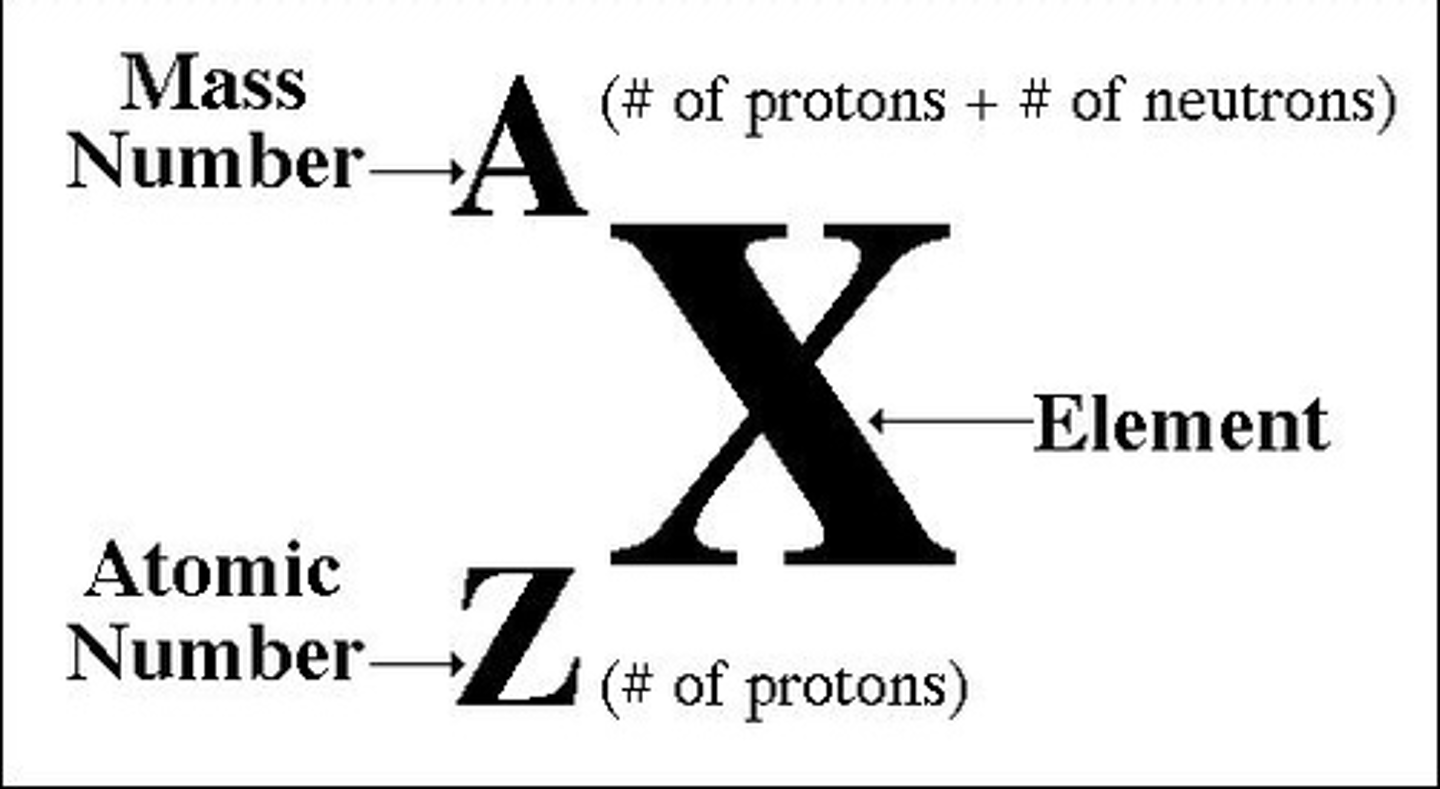
How many protons, neutrons and electrons does
235
U
92 have?
- 92 protons
- 235 - 92 = 143 neutrons
- 92 electrons
How many protons, neutrons and electrons does
235 3 +
U
92 have?
- 92 protons
- 235 - 92 = 143 neutrons
- 92 - 3 = 89 electrons
How many protons, neutrons and electrons does
235 3 -
U
92 have?
- 92 protons
- 235 - 92 = 143 neutrons
- 92 + 3 = 95 electrons
Periodic Table:
1. rows represent ____________
2. columns represent ____________
1. periods
2. Groups (18)
Period Table:
How many groups are there and how many are Main (representative) groups and how many are Transitional metals (elements)?
- 18
- 1-2 and 13-18
- 3-12
Period Table:
The separate rows on the bottom are the ____________ and _____________.
They are the ____________ metals
- Lanthanides
- Actinides
- Inner transition
What are the 2 types of Ions?
1. Anions (1-)
2. Cations (1+)
What is the difference between Cations and Anions?
- Cations are positively charged ion, loses electrons
- Anions are negatively charged ion, gains electrons
Which groups identify as cations and which groups identify as anions?
Group 1
Group 2
Group 3
Group 4
Group 13
Group 15
Group 16
Group 17
- Groups 1-4 and 13 are Cations
- Groups 15-17 are anions
Positive Ions (Cations): What is the charge of each group?
Group 1
Group 2
Group 3
Group 4
Group 13
1+
2+
3+
4+
3+
Negative Ions (Anions): What is the charge of each group?
Group 15
Group 16
Group 17
3-
2-
1-
Group __________ consists of Alkali metals
1
Group _________ consists of Alkali earth metals
2
Group __________ consists of Noble gases
18
Group ___________ consists of Halogens
17
Fine the Average Atomic Mass:
10
B → 19.9% 10.0129 amu
11
B → 80.1% 11.0093 amu
(0.199)(10.0129) + (0.801)(11.0093) = 10.811 amu
Fine the Average Atomic Mass:
25
Mg → 78.99% 23.985 amu
25
Mg → 10.00% 24.986 amu
26
Mg → 11.01% 25.983 amu
(0.7899)(23.985) + (0.1)(24.986) + (0.1101)(25.983) = 24.305 amu
63
Cu → 69.17% 62.9396 amu
Average atomic mass = 63.546
What is missing? __Cu
100% - 69.17% = 30.83%
63.546 amu = (0.6917)(62.9396) + (0.3083)(x)
x = 64.929 amu → round up to 65
65
C
Most elements are ____________ while only 20 elements are ________________
- metals
- nonmetals
____________ lack metallic properties
Nonmetals
Metals are defined by their metallic properties. What are these 5 properties?
1. Metallic luster (shiny)
2. Conducts heat/electricity
3. Malleable (can be hammered into sheets)
4. Ductile (can be drawn into wires)
5. Usually hard (ex. steel)
What are metalloids and how do they compare and contrast to metals?
- In between metals and nonmetals (ex. silicon)
- Semiconductors → conduct electricity/heat but not well
(ex. Electronics, solar cells, LEDS)
What is the SI base unit for
1. Mass
2. Length
3. Temperature
4. Time
5. Quantity of a substance
1. kg (kilogram)
2. m (meters)
3. K (kevin)
4. s (seconds)
5. mol (mole)
What is the value for each SI unit
1. G (giga) = 10^9
2. M (mega) = 10^6
3. k (kilo) = 10^3
4. h (hecto) = 10^2
5. da (deka) = 10
6. d (deci) = 10^-1
7. c (centi) = 10^-2
8. m (milli) = 10^-3
9. cursive M (micro) = 10^-6
10. n (nano) = 10^-9
11. p (pico) = 10^-12