IB HL Bio Unit 3 - Macromolecule Terms
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
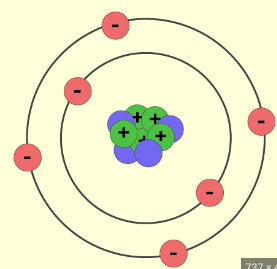
Carbon
Tetravalent element that serves as the building block of life. Present in all four Macromolecules
Organic (Carbon) Chemistry
The study of compounds containing carbon
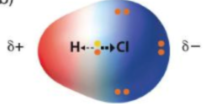
Polar Covalent Bonds
A Covalent Bond where the two atoms have different electronegativities, resulting on unequal pulls on the electrons
One side = (+) while the other is (-)
Nonpolar covalent bonds
A Covalent Bond where the two atoms have the same/close electronegativities, resulting in an equal pull on the electrons.

Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract shared electrons
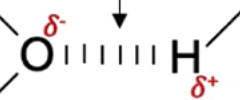
Hydrogen Bond
A polar bond between hydrogen and another atom
Valence Electrons
Electrons that occupy the outer-most shell of an atom
Valence
The number of covalent bonds an atom can form
Tetravalence
The ability to form 4 covalent bonds total - why carbon is the “backbone for life”
Hydrocarbon
A compound of only carbon and hydrogen
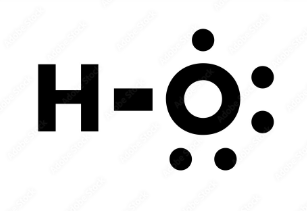
Hydroxyl
Functional Group (OH)
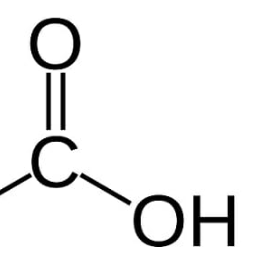
Carboxyl
Functional Group (COOH)
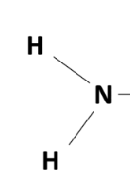
Amino
Functional Group (NH2)
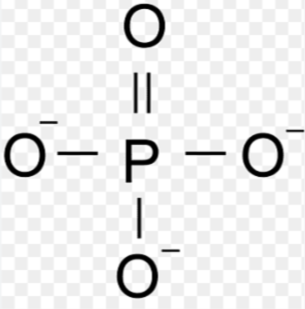
Phosphate
Functional Group (PO4 3-)
Macromolecules
Nucleic Acids, Lipids, Proteins, Carbohydrates
Metabolism
Chemical reactions in a cell
Anabolic
an Endergonic Metabolic pathway that synthesizes Polymers from Monomers through dehydration synthesis
Endergonic
stores/requires energy
Condensation reaction
Takes place during anabolic pathways - takes out water to combine molecules
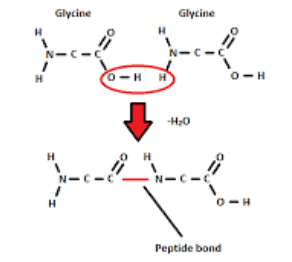
Catabolic
an Exergonic Metabolic pathway that breaks down Polymers into Monomers through hydrolysis
Exergonic
releases energy
Hydrolysis
Takes place during catabolic pathways - inserts water to break apart molecules
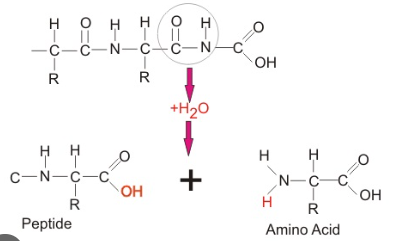
Monomer
individual molecules that make up a polymer
Polymer
A large molecule consisting of monomers
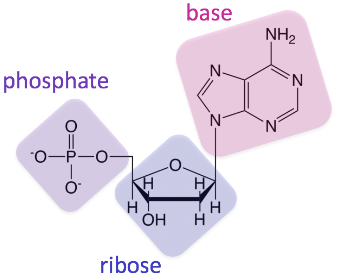
Nucleic Acid Elements
CHONP (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorous)
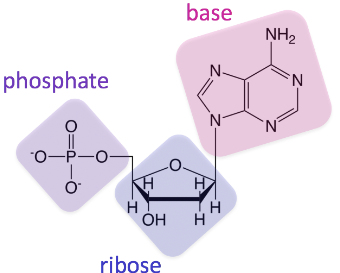
Nucleic Acid Monomer
Nucleotide
Nucleic Acid Polymer
Polynucleotide
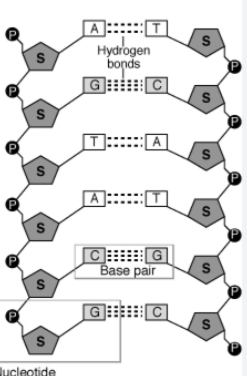
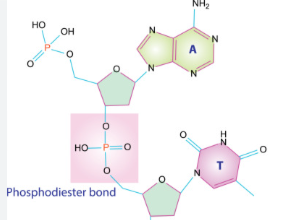
Nucleic Acid Bond
Phosphodiester Bond
Proteins Elements
CHON (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen - SOMETIMES SULFUR)
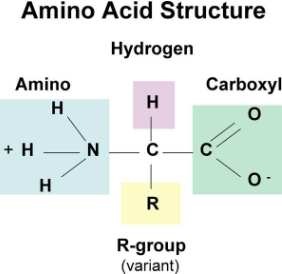
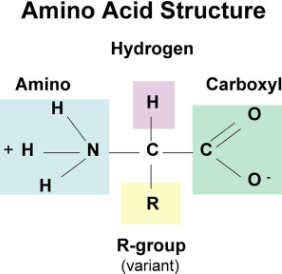
Proteins Monomer
Amino Acids
Proteins Polymer
Polypeptides - there are 20 total
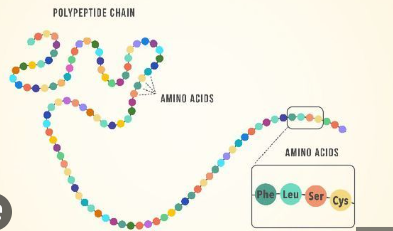
Proteins Bond
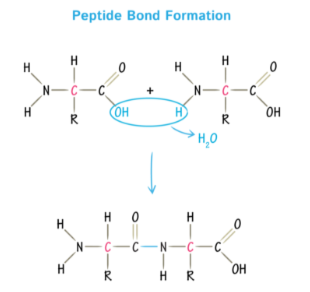
Peptide Bond
Carbohydrates Elements
CHO
Carbohydrates ratio
1:2:1
Carbohydrates Monomer
Monosaccharide - simple sugars
Carbohydrates Polymer
Polysaccharide - complex carbs
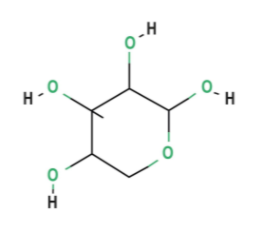
Pentose
5 carbons - ex. Ribose
Hexose
6 carbons - ex. Glucose, Galactose, Fructose
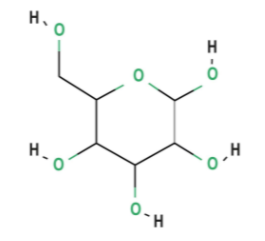
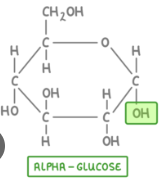
Alpha Glucose
-OH is below the ring
Alpha Glucose glycosidic linkages are more easily digested by humans
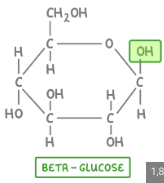
Beta Glucose
-OH is above the ring
humans cannot break beta glucose glycosidic linkages = pass through as fiber.
but COWS have a symbiotic relationship with stomach bacteria that can break down beta glucose bonds (cellulose)
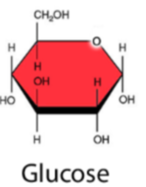
Glucose function
POLAR (lots of OH bonds) - soluable in water = transported through blood plasma
STABLE (ring form) - great material for building polysaccharides like Starch, Glycogen, and Cellulose
OXIDIZED - ATP energy for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration
When Glucose is oxidized to create ATP energy for the cell
Polysaccharides Function
Energy storage (ex. Starch and Glycogen) and Structural building material (ex. Cellulose and Chitin)
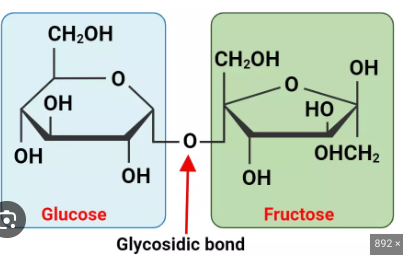
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharides joined through condensation reaction with Glycosidic Linkages
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
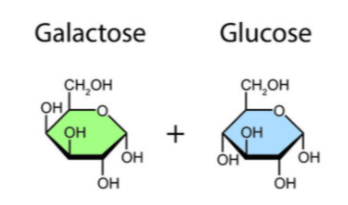
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
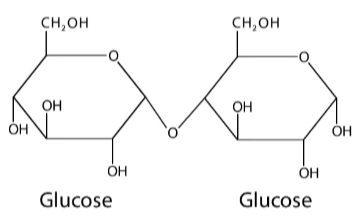
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose
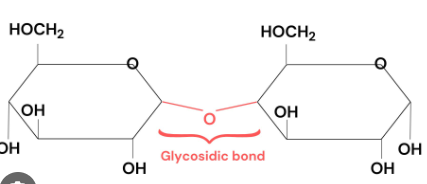
Glycosidic Linkage
covalent bond formed with condensation reaction connected with an oxygen
4 major Polysaccharides
Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose, Chitin
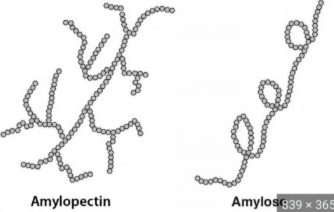
Starch
FUNCTION - Energy Storage
FOUND IN - Plants
MONOMER - alpha glucose - Amylose (linear/coiled polysaccharide) + Amylopectin (very branched polysaccharide - BETTER FOR ENERGY STORAGE)
SOLUBILITY - large molecule = relatively insoluble
Glycogen
FUNCTION - Energy Storage
FOUND IN - Animals - large amounts in liver + muscles in humans
MONOMER - alpha glucose - highly branched
SOLUBILITY - relatively insoluble
Cellulose
FUNCTION - Structural Material
FOUND IN - Plants - cell walls
MONOMER - beta glucose - linear
BONDS - linked with hydrogen bonds to form bundles called cellulose microfibrils
Chitin
FUNCTION - Structural Material
FOUND IN - Fungi - cell walls, and Anthropods - exoskeleton
MONOMER - modified glucose
Also used as surgical thread
Glycoproteins
A sugar-protein molecule embedded in cell membrane as “ID Tag"
cellular recognition/communication
receptors/secretion of chemical signals
structural support
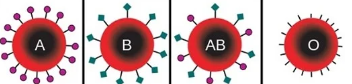
Ex. ABO Blood Groups
work as antigens
Glycoproteins - ABO Blood Groups
prescence of specific glycoproteins - determines ABO blood typing system
Lipids Elements
CHO (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen) - VERY little O compared to C
Lipids Unifying Properties
No real monomers/polymers
Defined by Hydrophobic properties as they have long hydrocarbon chains and little Oxygen
Hydrophobic
insoluble/repels water - nonpolar
Hydrophilic
soluble/”likes” water - polar
Amphipathic
Contains both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the structure
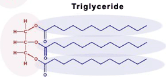
Lipids Triglycerides
Fats and Oils - made of two building blocks (NOT MONOMERS) - one glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains connected by Ester Linkages
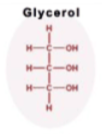
Glycerol
A 3-carbon alcohol w/ 3 Carboxyl groups (COH)
each -OH group is a location for the fatty acid to attach to in Triglycerides
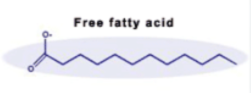
Fatty Acids
Long Hydrocarbon chains that are either Saturated, Monounsaturated, Polyunsaturated, or Trans-unsaturated, connecting to Glycerol in Triglycerides
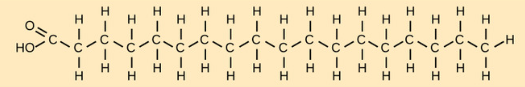
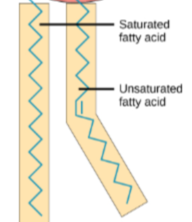
Saturated Fatty Acid (fats)
BONDS: All single bonds = linear w/ no kinks = easily packed together
MELTING POINT: high, solid at room temp
FOUND IN: mammals (lard)
Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
One double-bonded carbon in the hydrocarbon chain that creates a bent configuration
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid
2+ double-bonded carbons in the hydrocarbon chain that create multiple bends in the configuration
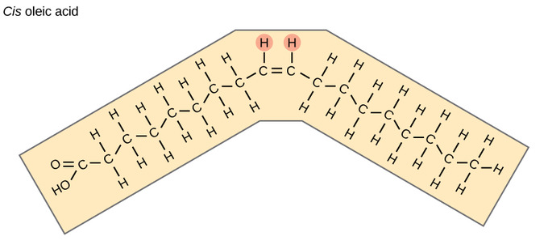
Cis-unsaturated Fatty Acid (oils)
BONDS: double bonds = bent configuration
MELTING POINT: low, liquid at room temp
FOUND IN: fish and plants (ex. olive oil)
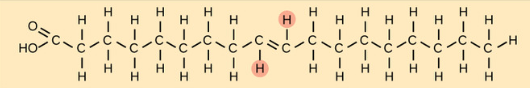
Trans-unsaturated Fatty Acid (trans fats)
An unnatural, factory-produced formation of a fatty acid that undergoes hydrogenation to put both hydrogens on an unsaturated fatty acid on the different sides, removing kinks and making them function more similarly to saturated fatty acids but can increase cholesterol
Lipids Fats and Oils Functions
Longer-term energy storage than carbohydrates
Insulation to reduce heat loss
Protection/cushioning/support of internal organs
Mammals store Fats in adipose tissue
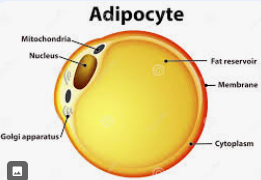
Adipose Tissue
Cell comprised mostly of a fat reservoir that is broken down to provide atp energy for the endotherms
Endotherms
Regulate body temp - requires constant energy from fats in adipose tissue
Lipid storage in plants and seeds
A greater amount of fats and oils provide energy for the seed when photosynthesis is unavailable
Phospholipids
Provides flexibility as part of the phospholipid bilayer of cells comprised of one glycerol and phosphate with two fatty acid tails, bonded with ester linkages
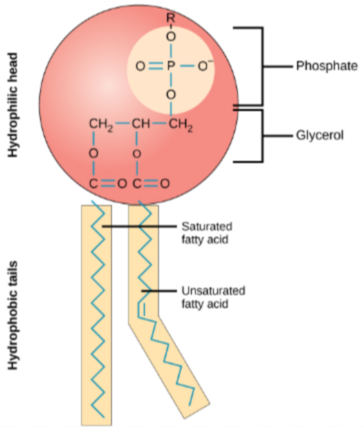
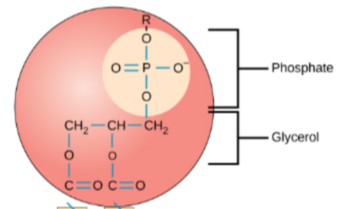
Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head
A glycerol and a phosphate
“loves” water
faces the outside of the phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid Hydrophobic Tails
Two fatty acid tails - saturated and unsaturated
“hates” water
on the middle of the phospholipid bilayer
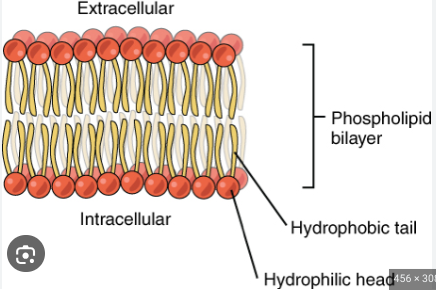
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two layers of Phospholipids that form the cell membrane and provide flexibility
Hydrophilic heads face the aqueous environments on the inside and outside of cells
Hydrophobic tails remain in between the two heads, away from both aqueous environments
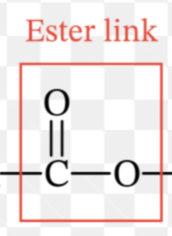
Ester Linkage
Part of Lipids - covalent bond between a hydrogen and acidic hydroxyl group
Lipids Steroids
4 fused hydrocarbon rings
different functional groups are added to ring framework to give different properties.
Hydrophobic and insoluble = can pass through cell membrane
low proportion of oxygen to carbon
Cholesterol
Part of animal cell membranes
reduces permeability of cell membrane by reducing fluidity @ higher temperatures
increases permeability of cell membrane by increasing fluidity @ lower temperatures
also modified into other steroids (hormones)
Hormones
controls a wide range of physiological functions
modified cholesterol molecules
hydrophobic = easily pass through cell membrane to give cell instructions
ex. testosterone + oestrogen (estrogen)
Lipids Waxes
Diverse lipids that are typically long hydrocarbon chains
Melt @ low temperature (think candle)
energy storage
Used to “water proof” due to hydrophobic tendencies
ex. waxy sheath on plants to control evaporation and hydration
Proteins functions
enzymes (lactase)
hormones (insulin)
transport (haemoglobin)
structure (collagen)
movement (actin)
storage (ovalbunim)
defense (antibodies)
receptors (rhodopsin)
Proteins elements
CHON (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen) plus additional side chain elements
Proteins Monomer
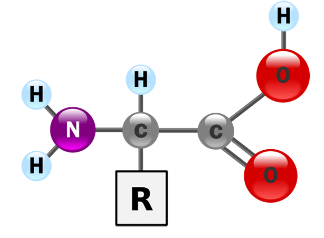
Amino Acid
Amino Group (NH2)
Carboxyl group (COOH)
Alpha carbon
Side chain/R group
Proteins Non-essential Amino Acids
Humans are able to make non-essential amino acids from other amino acids
Proteins Essential Amino Acids
Humans are unable to make essential amino acids = must be from food
*Vegan/Vegetarian Issues - best source of essential amino acids = animal proteins (beef, poultry, eggs), and restricting these is risky
Proteins Dipeptide
Two Amino Acids held together via a peptide bond
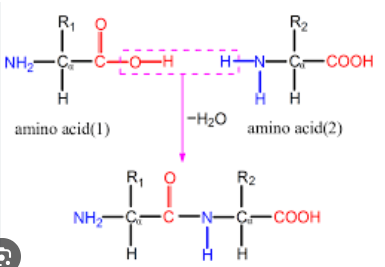
Proteins Peptide Bond
Resulting from a condensation reaction connecting the carboxyl group with the amino group by removing a water molecule
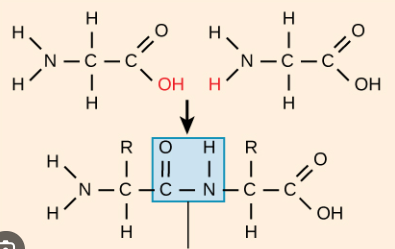
Proteins Side Chain
Variable - Provides property to amino acid. 20 different side chains = 20 different amino acids
Nonpolar side chain = hydrophobic
Polar side chain = hydrophilic
Charged side chain = hydrophobic, acidic or basic
Proteins Polypeptide
Chains of amino acids linked by Peptide bonds, with a c-terminus (carboxyl end) and n-terminus (amino end) and an N-C-C backbone
Protein vs. Polypeptide
A Polypeptide is a chain of 3+ amino acids, and is the polymer of proteins, which are 1 or more polypeptides
Lysozyme
An enzyme in tears and saliva able to kill certain bacteria
Glucagon
a hormone that raises blood sugar levels (opposite to insulin)
Myoglobin
An oxygen-binding protein in muscles
Alpha-nuerotoxins
Group of neurotoxins found in snake venom
Conjugated Proteins
Contains a non-protein component
ex. Haemoglobin and Glycoproteins
Non-Conjugated Proteins
Contains only polypeptides (ex. insulin and collagen)
Integral Proteins
Embedded into the phospholipid bilayer of a cell membrane, with the hydrophobic side chain embedded into the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids
Fibrous Proteins
Long, skinny, simple strands of repeating structure
strength + stability (structural support)
Insoluble in water
ex. Collagen
Globular Proteins
spherical and complex with irregular folds
soluble in water
found in enzymes, transporters, and regulators
ex. Insulin