Microbe Mission
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
What is a Microbe?
A microbe is a tiny organism that the naked eye cannot see. Microbes involve many organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and other organisms.
a microscopic form of life including bacterial, archaeal, fungal, and protozoal cells
What are Eukaryotes?
Eukaryotas are cells that have a nucleus, and organelles that have different functions(like the mitochondria, which produces energy).
Eukaryotas can include simple organisms like protozoa. Human cells are Eukaryotas!
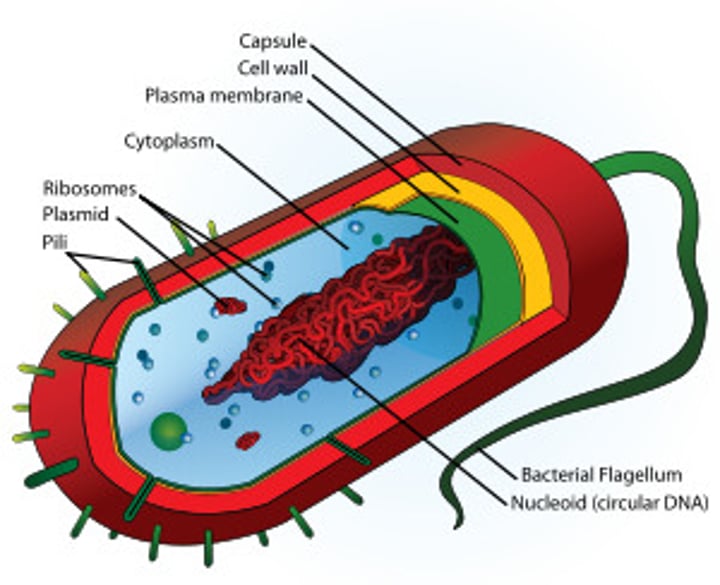
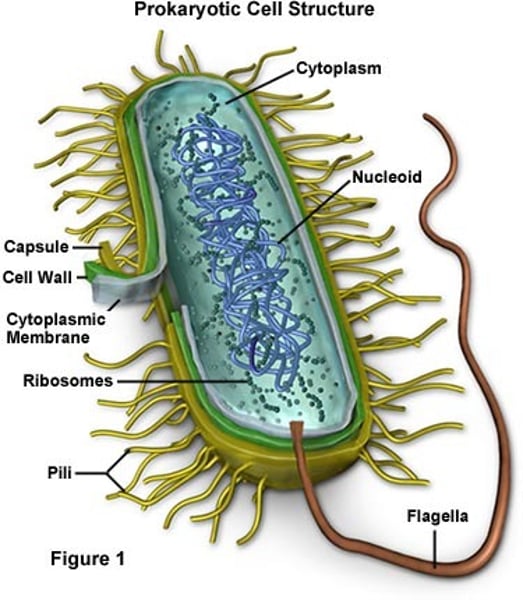
What does it mean to be Prokaryotic?
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. They do have a cell membrane, and cytoplasm which contains all of the genetic material.
Bacteria are the only Prokaryotes.
What are Bacteria?
Bacteria are a type of Prokaryote that can be found all over the place. Most bacteria are helpful, or have no effects at all. But some can have a devastating effect on humans, and other animals. Bacteria get around by many means of movement. Some have flagella, and some get around by cilia. Bacteria comes in many shapes and forms. Scientists have discovered thousands of different species, and that's only 1% of the entire bacteria population!
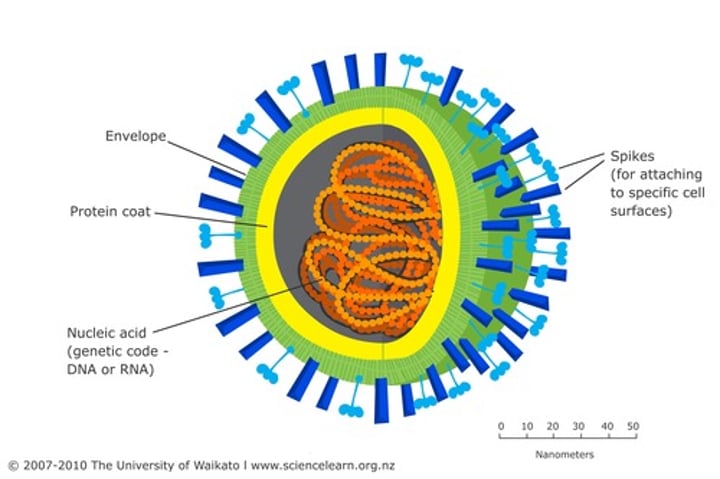
What is a virus?
A virus is a non-living particle that needs a host to survive and reproduce. Viruses cause a variety of different diseases, such as the flu, polio, and many different diseases. Viruses reproduce by invading other cells and changing the function of the infected cell into producing more viruses so the disease can spread.
Parts of a Microbe: Cell Membrane
Most to all Microbes have a semi-permeable cell membrane that encases the organism in a protective layer.
In Eukaryotic cells, the cell membrane goes through osmosis, diffusion, or active transport. Some Eukaryotes(plant cells) also have a rigid layer on the outside called the cell wall.
In Prokaryotic cells, the cell membrane acts like a wall against outside and alien objects. It also acts to grip surfaces or to maintain proper homeostasis of the prokaryote.
In viruses, the outside coat is just a coat of protein with protrusions that latch onto cells that the virus plans to invade.
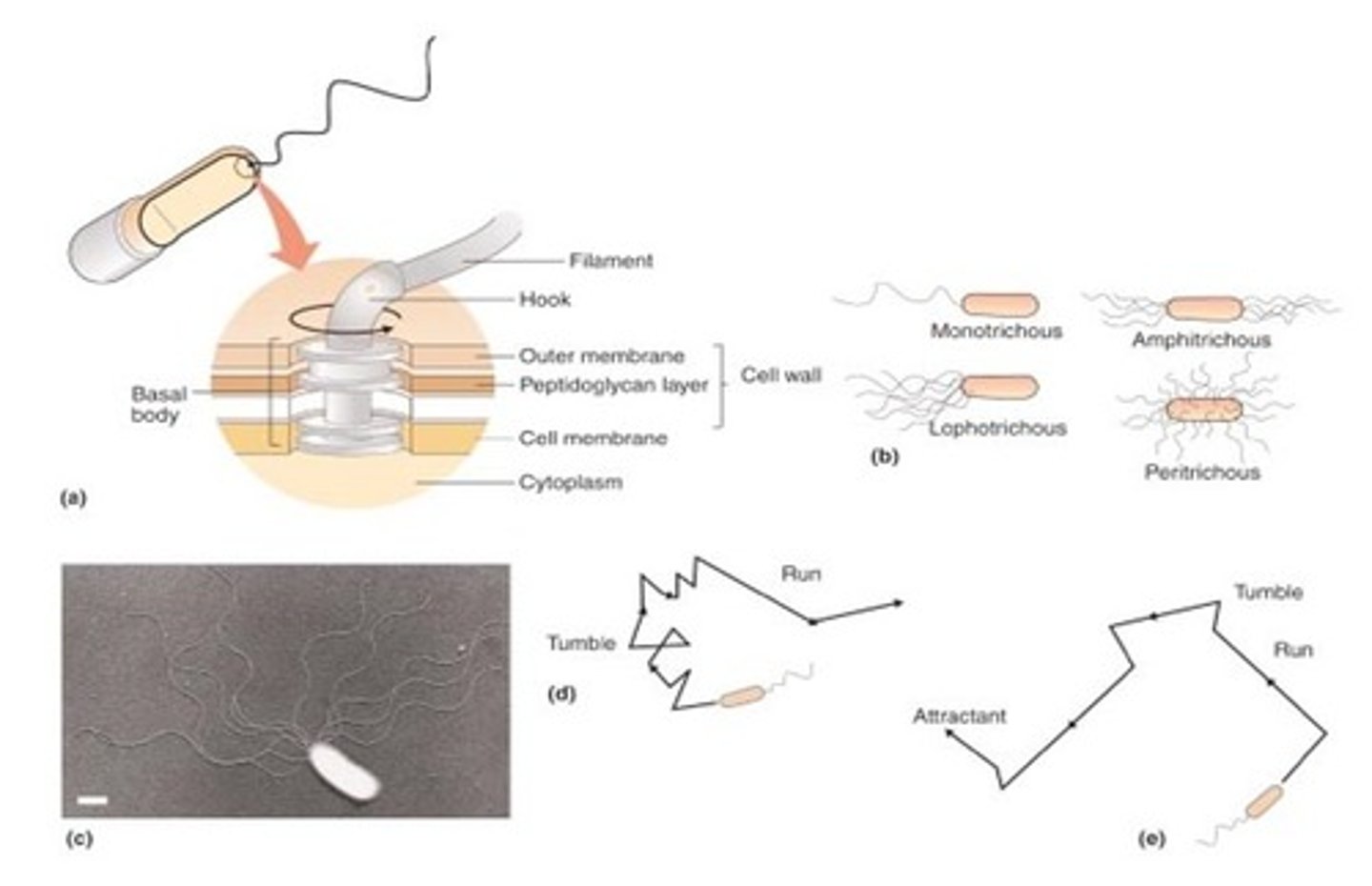
Prokaryotic Movements: Flagella
Flagella are long filaments that rotate around to propel bacteria. Flagella bacteria usually live in liquid environment, and use flagella for their means of movement.
Prokaryotic Movements: Cilia
Cilia
Anaerobic Bacteria
These are the bacteria who do not use oxygen to produce food. They are much like those at the beginning of Earth's history.
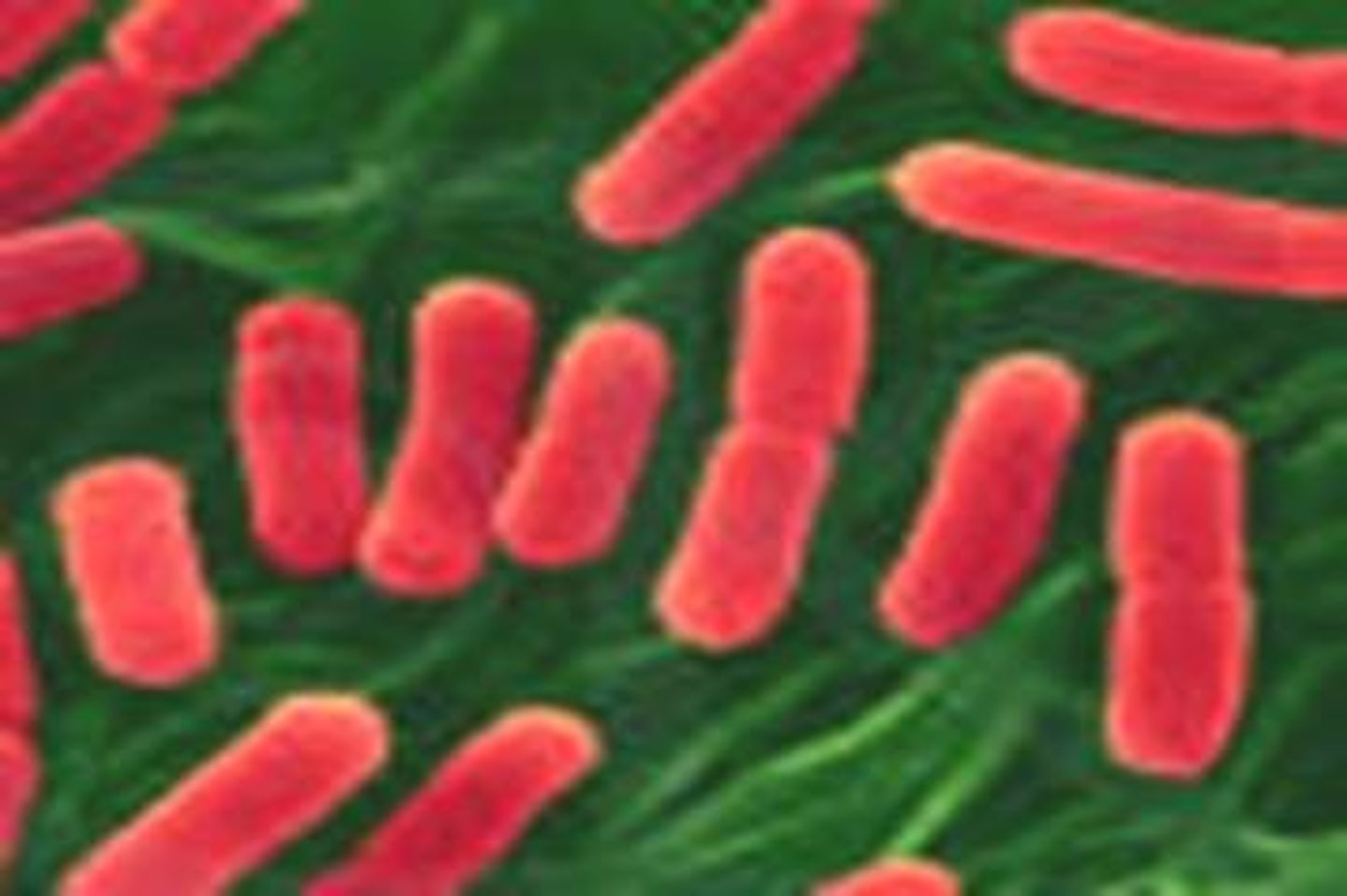
Aerobic Bacteria
These are the bacteria who do use oxygen to produce food. They are the present day bacteria.
Photosynthetic Bacteria
These are the bacteria who use photosynthesis to produce their food. They use the sun's energy to do their food processing. They are living with the Aerobic Bacteria- and have been living after the Anaerobic Bacteria.
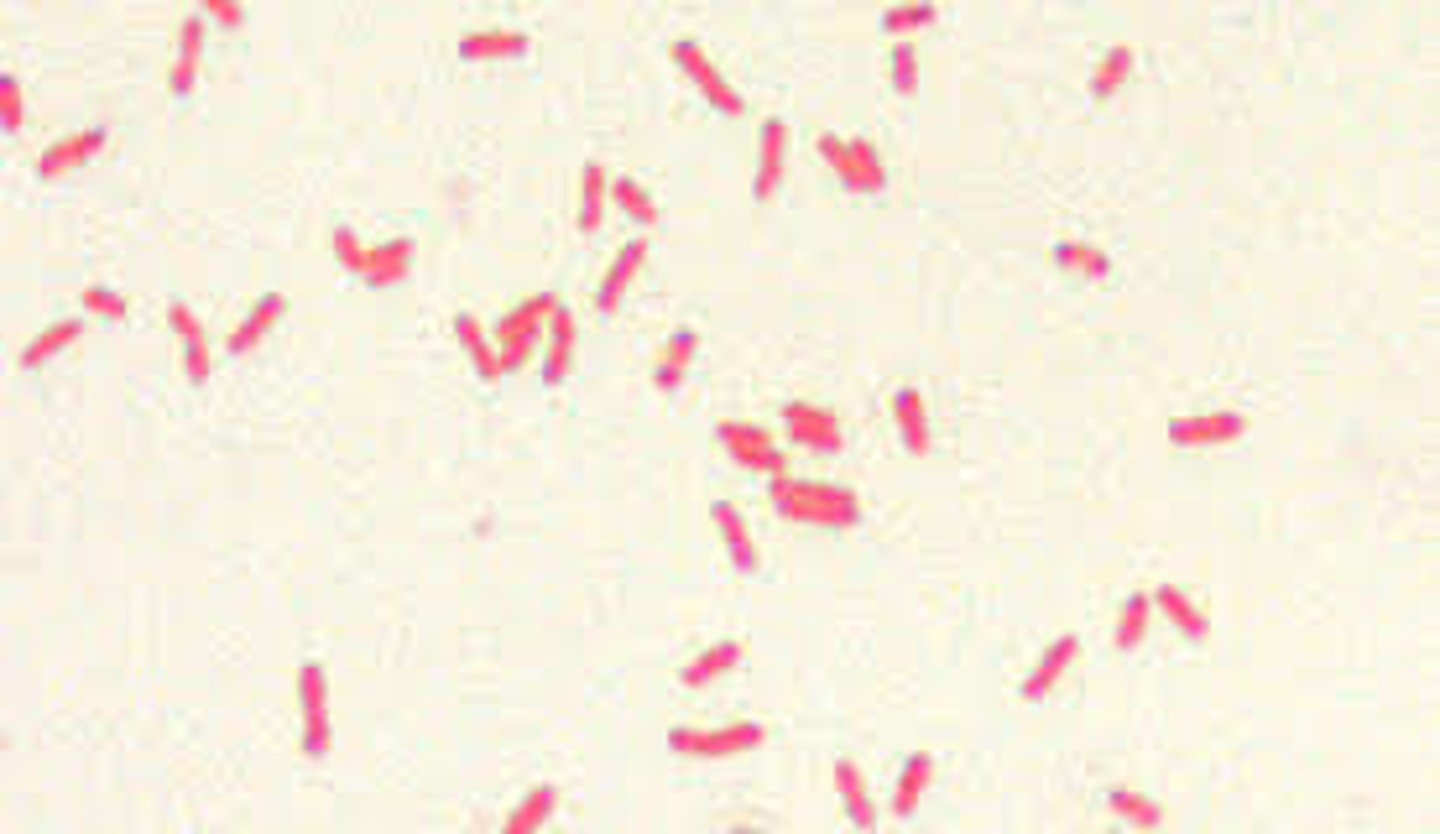
Bacilli Bacteria
Anaerobic, Rod-shaped bacteria that is mainly found in soil and water. May cause Food Poisoning, and Anthrax.
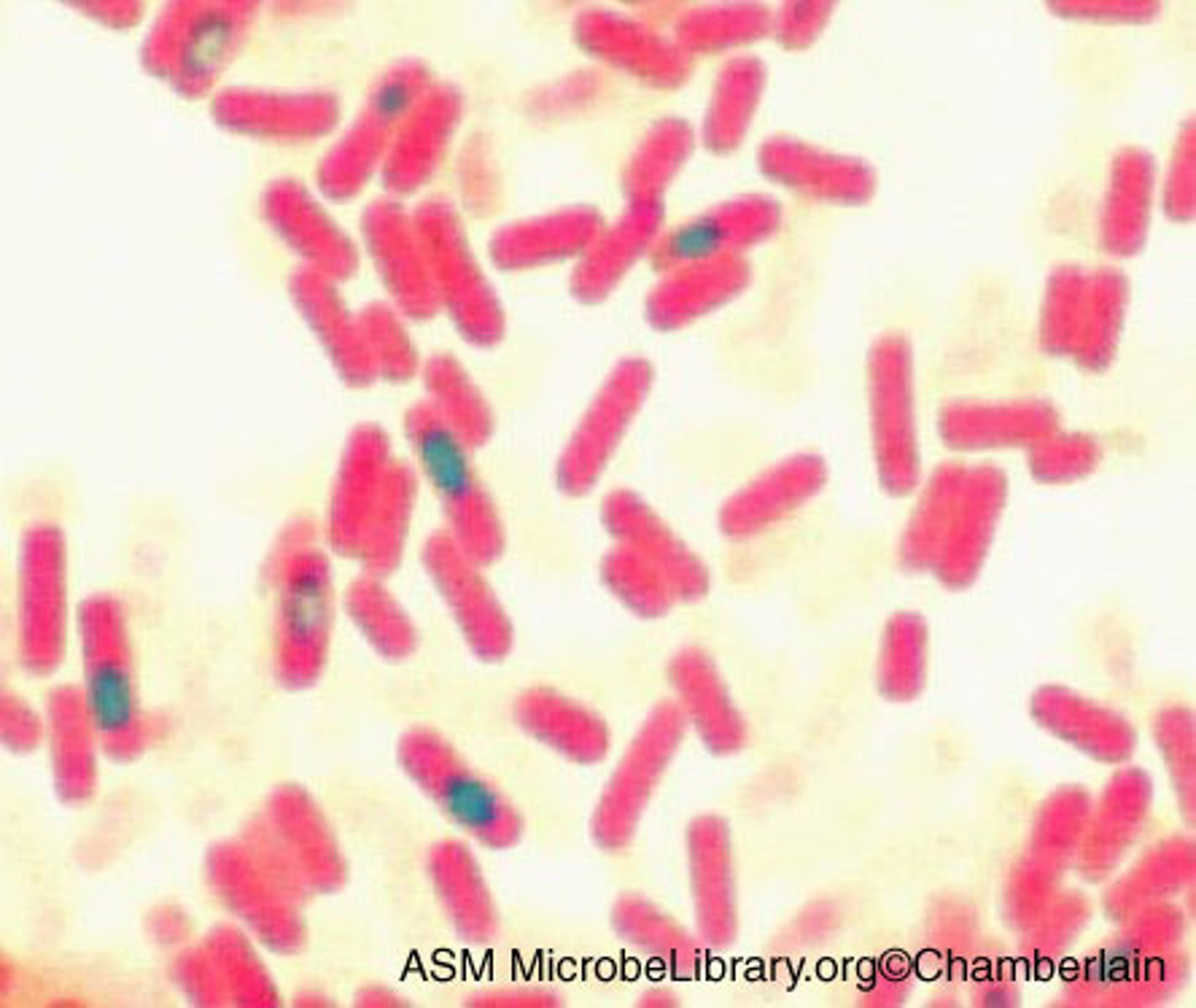
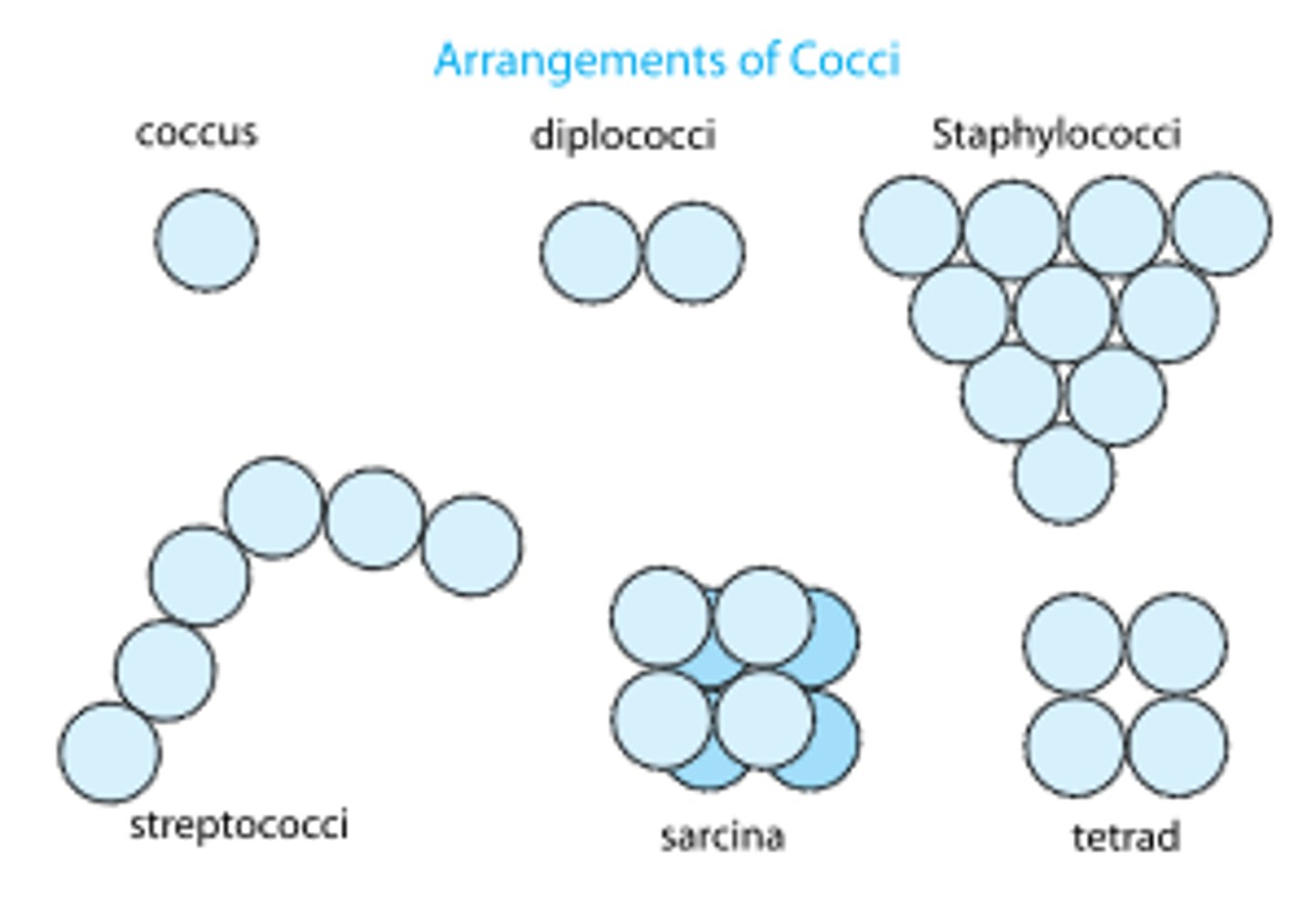
Cocci Bacteria
Any bacteria that is rounded, circular. Can be found almost anywhere, and many good types are found in humans. It may cause skin irritations, and sometimes serious diseases.
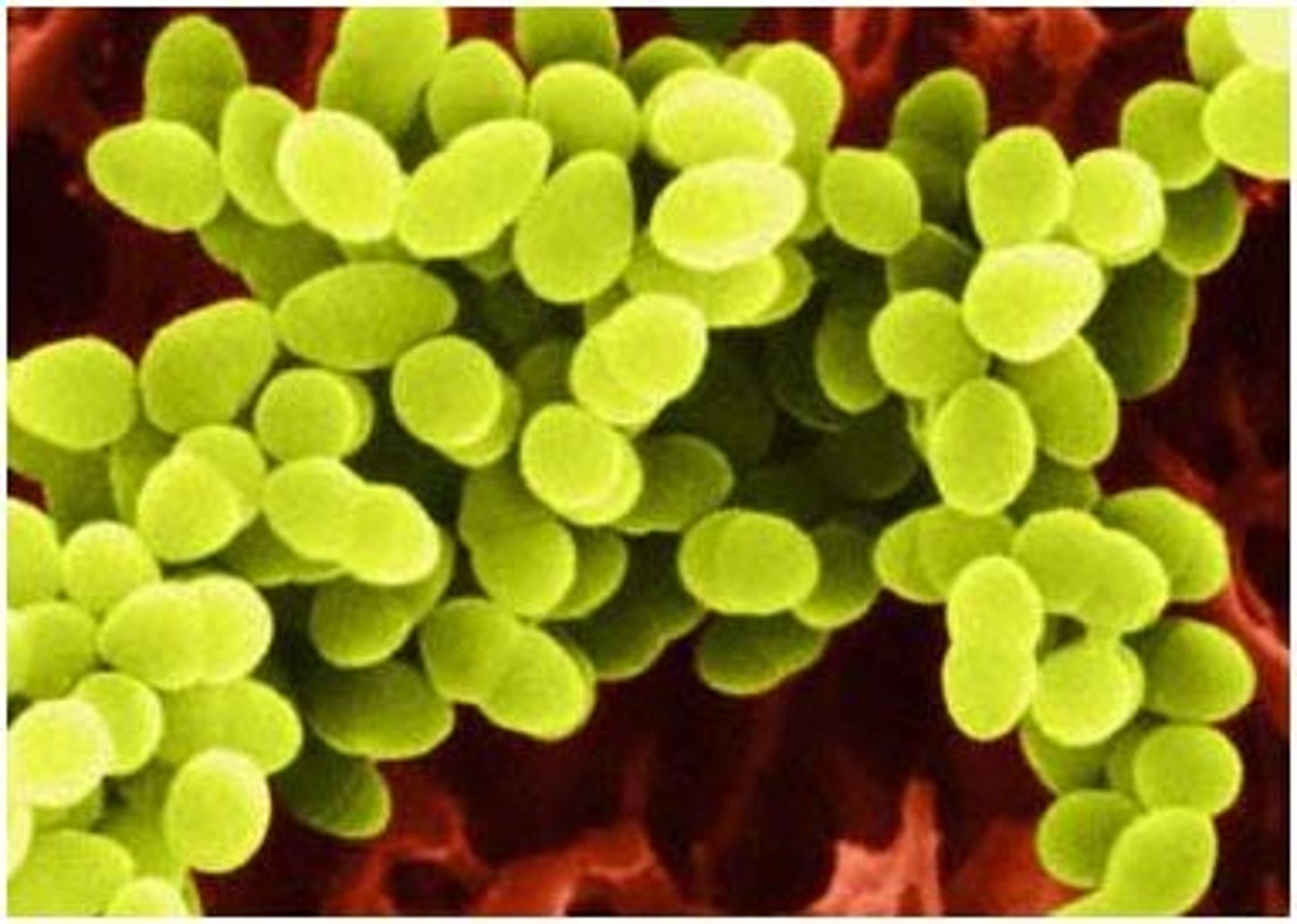
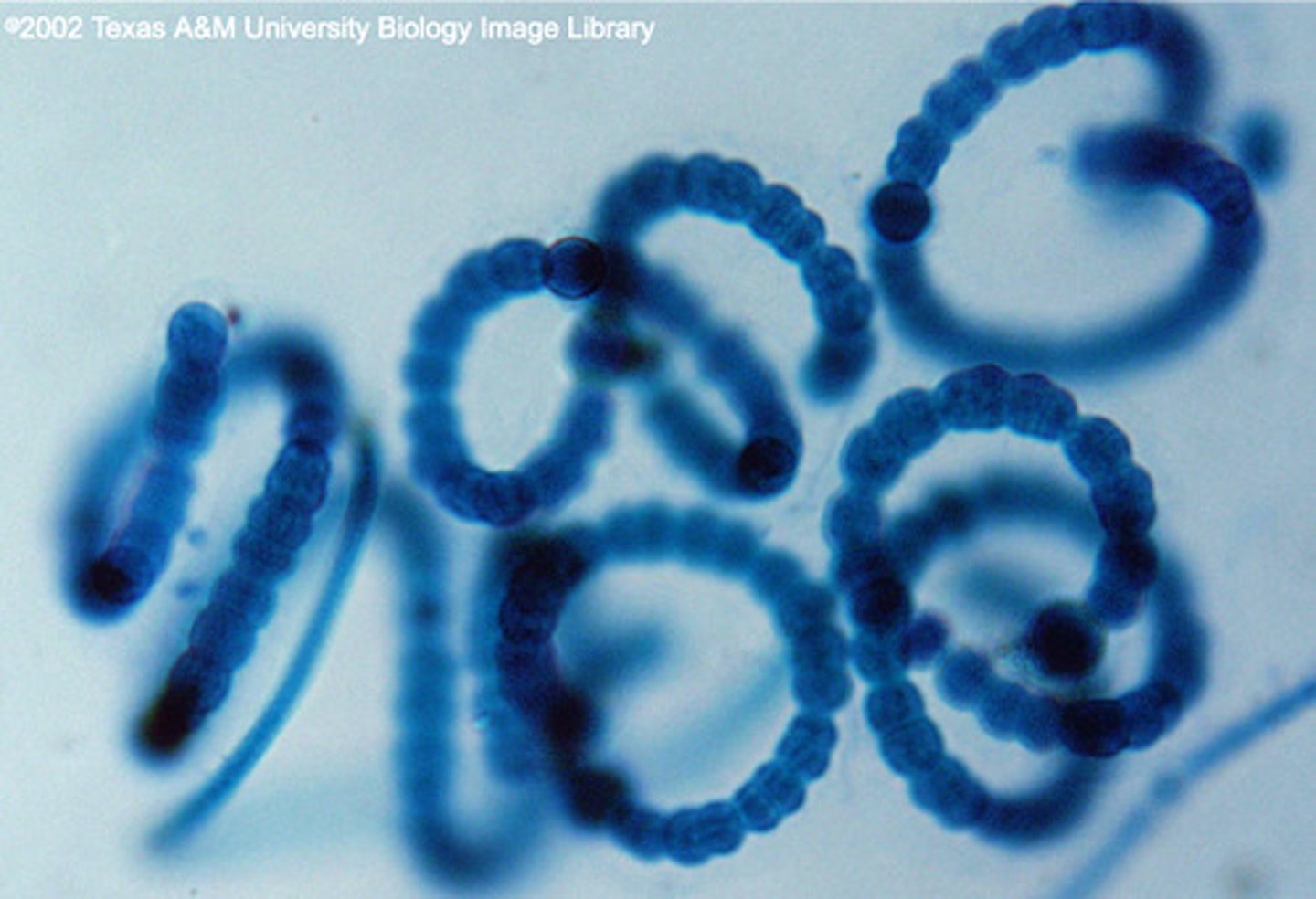
Spirillum Bacteria
Corkscrew-shaped, lives mainly in water due to it's shape. May cause rat-bite infection.
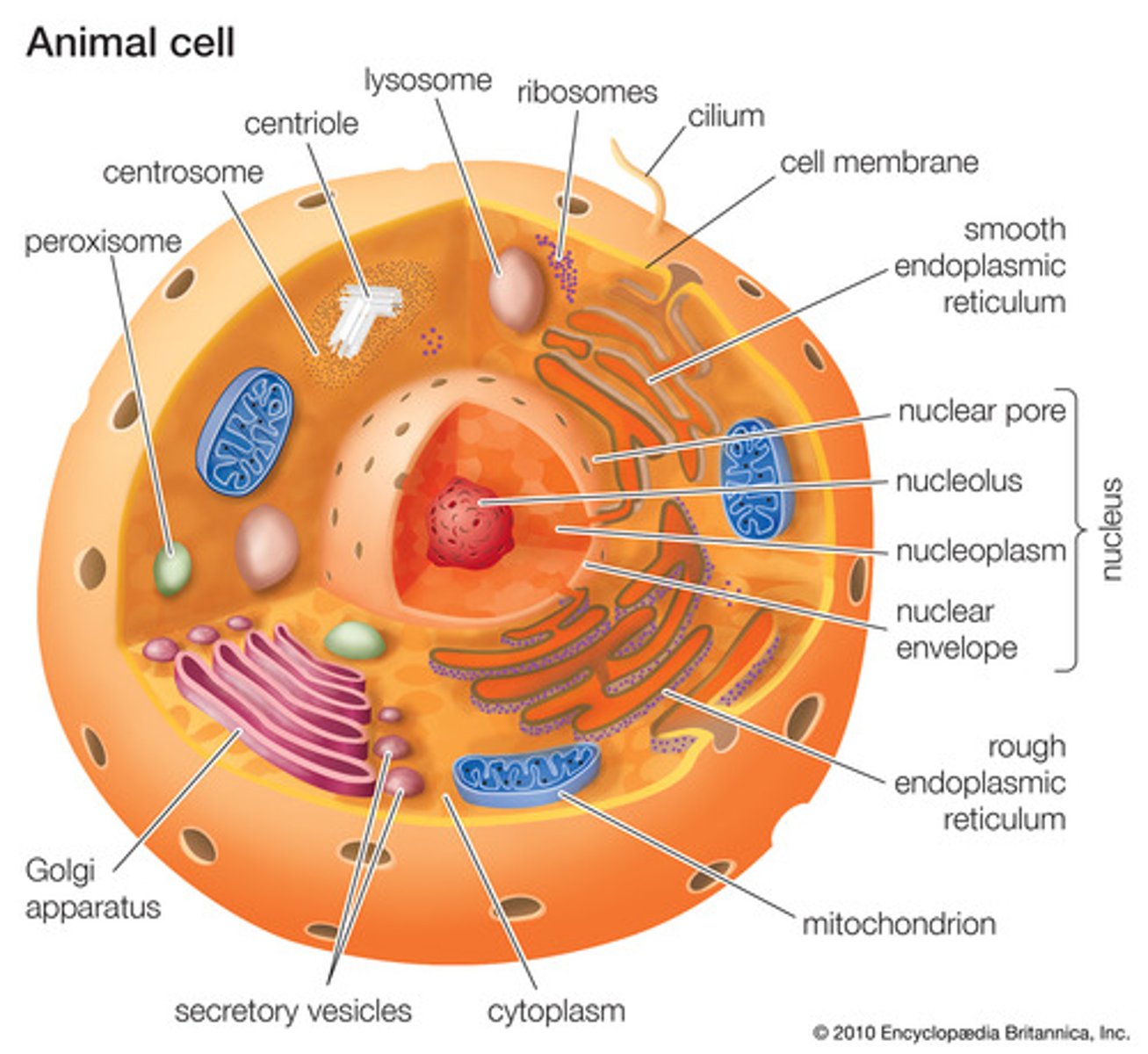
Animal Cell(Eukaryotes)
An animal cell has many different forms, depending on it's job in an organism. Each one has a cell membrane, cytoplasm, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum(E.R.), the nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, and vacuoles.
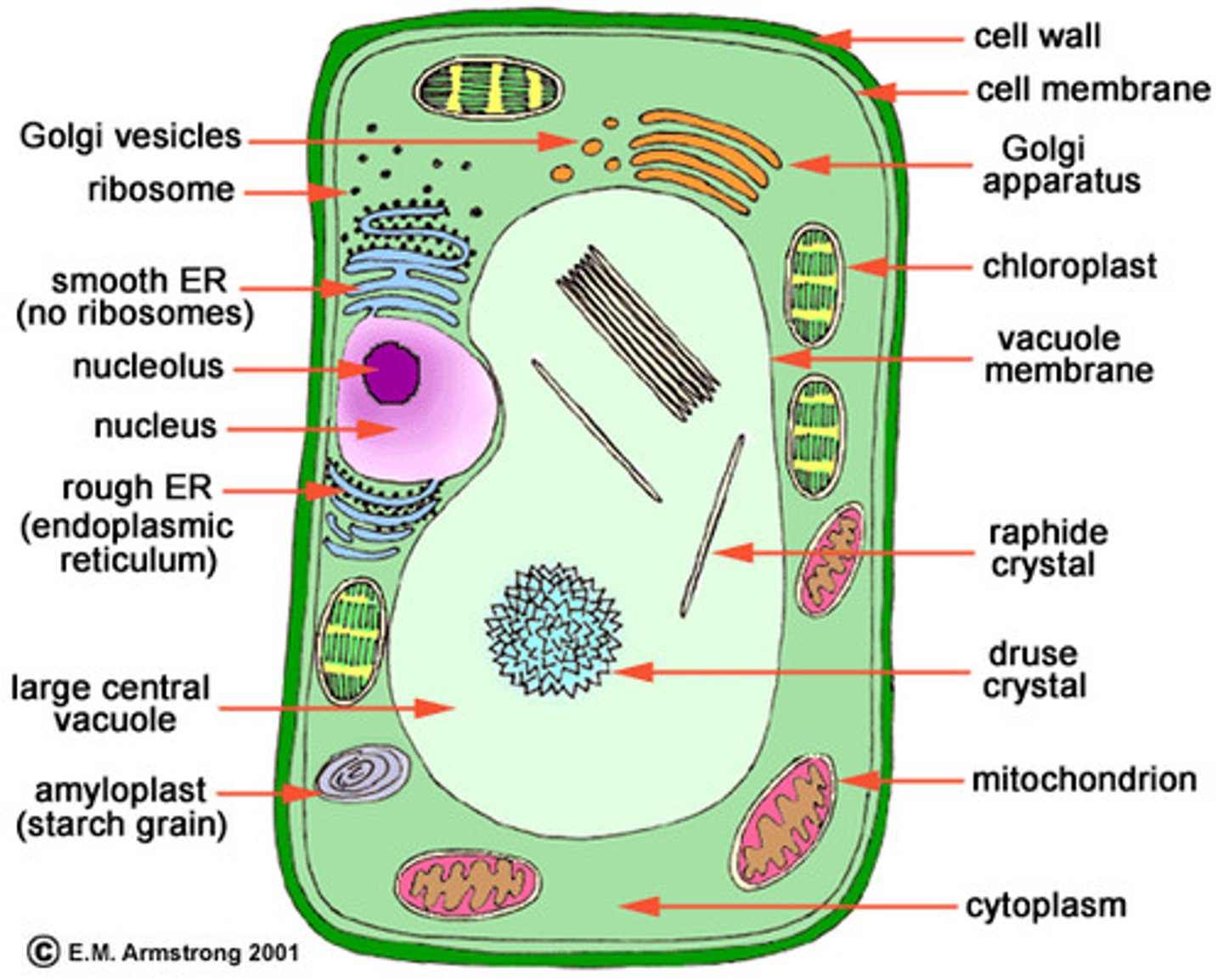
Plant Cell(Eukaryotes)
A plant cell is usually box-shaped, and has a tough cell wall on the outer edge of the cell membrane. Then there's the large central vacuole, and the cytoplasm, the E.R., the Golgi Apparatus, the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
Kingdom Anamalia
Includes mammals, reptiles, birds, and is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.
Kingdom Plantae
Includes plants, and is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.

Kingdom Fungi
Includes Fungi and is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.

Kingdom Protista
Includes Protozoans, and any single-celled eukaryotes (except yeast). It is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.

Kingdom Monera
Includes Bacteria, and unicellular organisms, in is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.
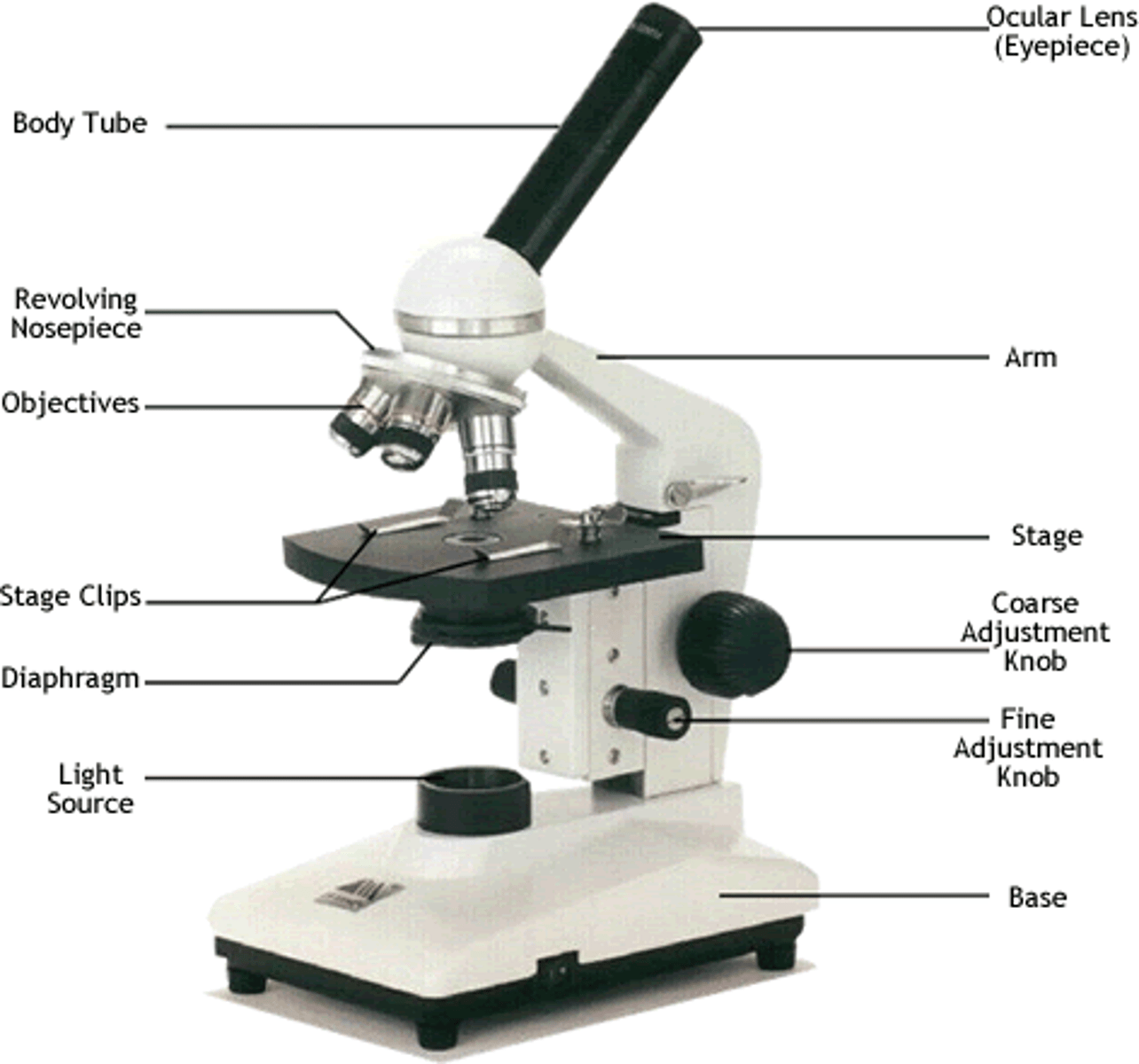
Bright Field Microscope
uses the visible light source under the stage to produce a clear image. The Diaphragm adjusts the amount of light entering the stage. It consists of three objectives- the scanning power(usually 4x-6x), the low power(10-12x), and high power(40x).
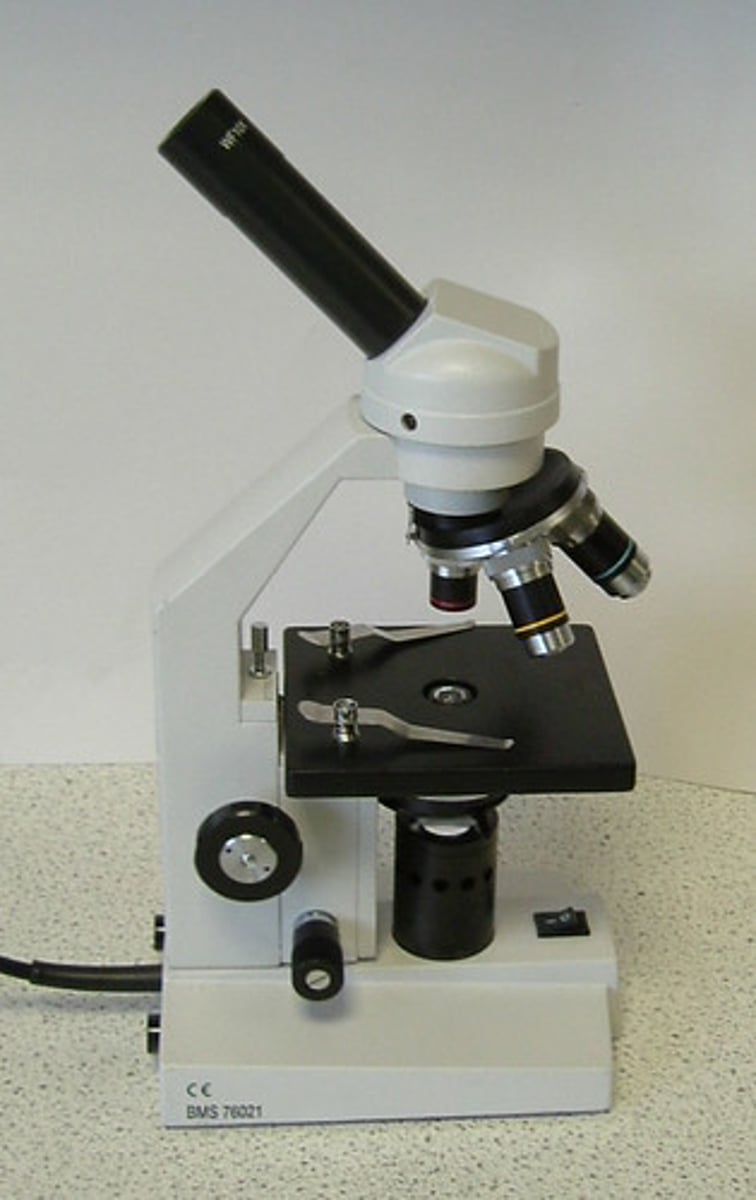

Dark Field Microscope
Illumination comes from the sides, thus making the background appear dark, and the organism on the slide appear light(bright).
Phase Contrast Microscope
an optical-microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. Phase shifts themselves are invisible, but become visible when shown as brightness variations.
Differential-Interference Microscope
Optical Microscopy used to enhance or create contrast in transparent, unstained organisms.
Fluorescence Microscope
an optical microscope that uses fluorescence and phosphorescence instead of, or in addition to, reflection and absorption to look at organisms on a slide.
Up to 2000x magnification
Confocal Microscope
A microscope used for increasing the optical resolution and contrast that eliminates out-of-focus light.
Up to 2000x magnification
Transmission Electron Microscope(TEM)
A form of electron microscopy in which an image is derived from electrons that have passed through the specimen, in particular one in which the whole image is formed at once rather than by scanning.
Up to 100,000x magnification
Scanning Electron Microscope(SEM)
An electron microscope in which the surface of a specimen is scanned by a beam of electrons that are reflected to form an image.
An instrument that bounces electrons off objects to create a three-dimensional image that is more highly magnified than possible through a light microscope.
up to 650,000x magnification
1 meter equals how many millimeters?
1000 millimeters
1 millimeter equals how many micrometers?
1000 micrometers
1 micrometer equals how many nanometers?
1000 nanometers
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The ocular
The eyepiece in which you see through. This has a magnification of 10x.
magnifies the image formed by the objective.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The nosepiece
The nosepiece supports the objectives
holds the objectives.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The objectives
The objectives magnify the item on the slide either: A. Scanning power, which usually ranges from 4x to 6x; B. Low power, which usually ranges from 10x to 12x; C. High power, which usually is 40x
lenses that receive the light from the field of view and form the first image.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The Stage Clips
Holds the slide down to the stage.
supports the slide and the specimen.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The Stage
Holds the slide.
hold the slide in place.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: Coarse Adjustment
Adjusts the Stage greatly. Used only on SCANNING POWER!
used for initial or low power adjustment.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: Fine Adjustment
Adjusts the stage finely. Used on High and Low power
used for fine tuning & high power focusing.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The Base
Keeps the Microscope steady and is the "base" for everything.
foundation which supports the scope & keeps it stable.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The Diaphragm
Controls how much light illuminates the organism/slide.
controls the amount of light reaching the specimen.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The Light Source
It is the light source that lights up the specimen
source of light.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The Arm
Holds the Objectives, the Nosepiece, the Ocular, and the Body Tube.
supports the ocular, objectives and body tube.
Parts of a Bright Field Microscope: The Body Tube
The tube between the ocular and the nosepiece/objectives.
tube or barrel between the ocular and the objectives.
What is the Largest Classification of organisms?
Kingdom, example, the human. We are kingdom Animalia.

What is after a Kingdom?(Classification of organisms)
Phylum, example, the human. We are Phylum chordates.
What is after a Phylum?(Classification of organisms)
Class, example, the human. We are class Mamalia.
What is after a Class?(Classification of organisms)
Order, example, the human. We are order Primates.
What is after an Order?(Classification of organisms)
Family, example, the human. We are Family Hominids.
What is after a Family?(Classification of organisms)
Genus, example, the human. We are Genus Homo.
What is after a Genus?(Classification of organisms)
Species, example, we are Homo Sapiens.
How are organisms Classified, largest to smallest?
Kingdom to Phylum to Class to Order to Family to Genus to Species.
What is AIDS?
An autoimmune disease that affects the immune system.
Symptoms: Fever, Sore-throat, Fatigue, Weight Loss, Sweats, and infection. There may also be pain in the abdominal areas, as well as persistent diarrhea, and/or watery diarrhea. Opportunistic infection, headache, oral thrush, pneumonia, red blotches, severe unintentional weight loss, skin rash, or swollen lymph nodes may also occur.
What is Dengue Fever?
It is transmitted by mosquitoes, and it causes high fever, around 104 to 105 degrees. Skin Rash, Headaches, joint pain, and pain in general may also occur. It originated in Tropical or/and Subtropical Areas.
What is Mononucleosis?
Symptoms: Fatigue, sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, swollen tonsils, headaches, skin rash, and swollen spleen.
What is Viral Encephalitis?
Leads to High temperature, Headache, sensitivity to light, general malaise, stiff neck, stiff back, vomiting, changes to personality, confusion, memory loss, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
What is Mad Cow disease?
A disease caused by prion. Prion are abnormal protein packs that are not viruses or bacteria. This prion originates in cows, and when a person eats the infected cow's meat, the prion infects the human as well. Prion are highly resistant to heat, pressure, and other extreme conditions. The prion causes major brain deterioration, and other harmful brain damage.
Acellular
Does not have any cellular components; they may not metabolize, or reproduce by themselves. A virus is acellular because they must invade a host cell to reproduce, and cannot grow on it's own.
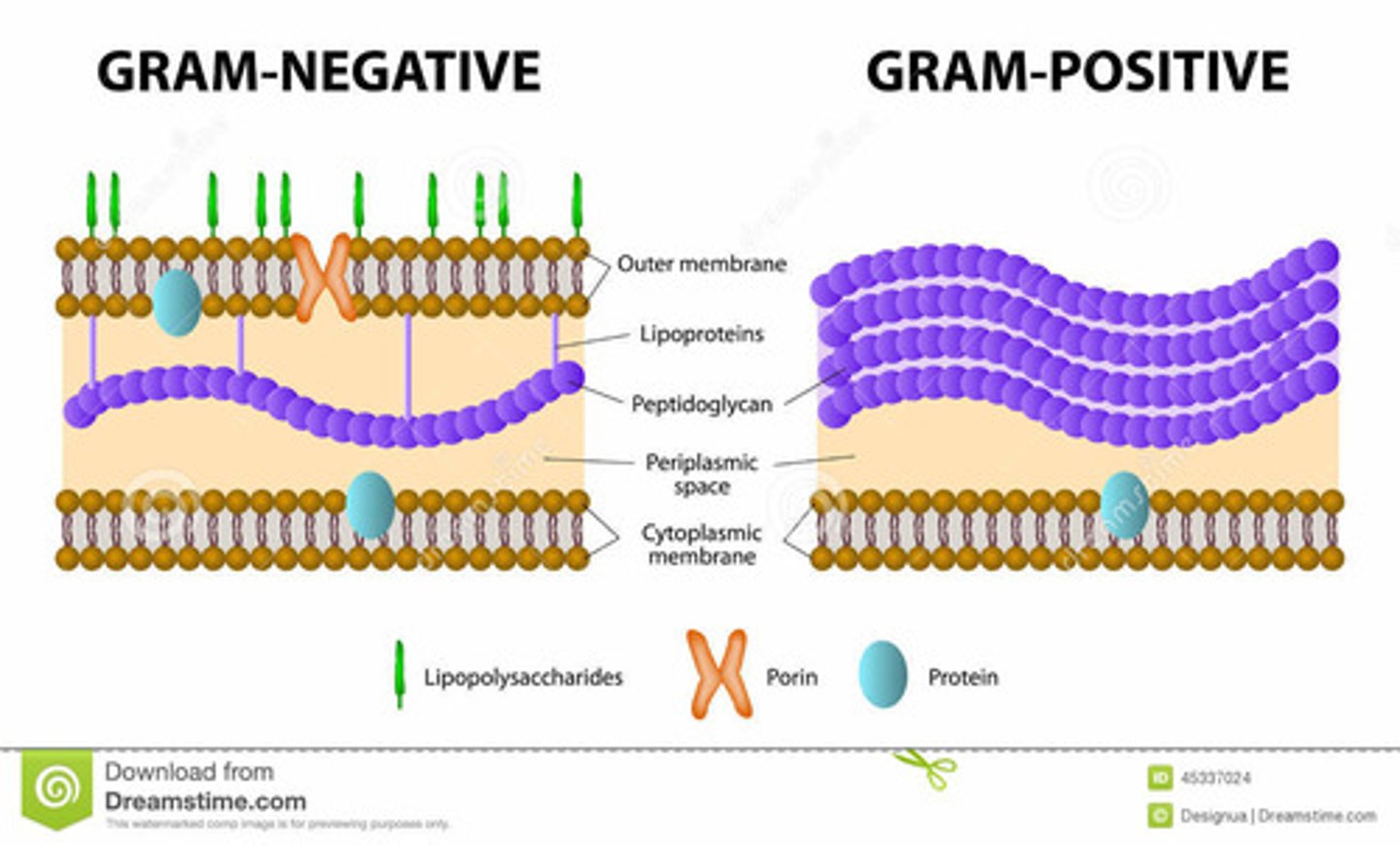
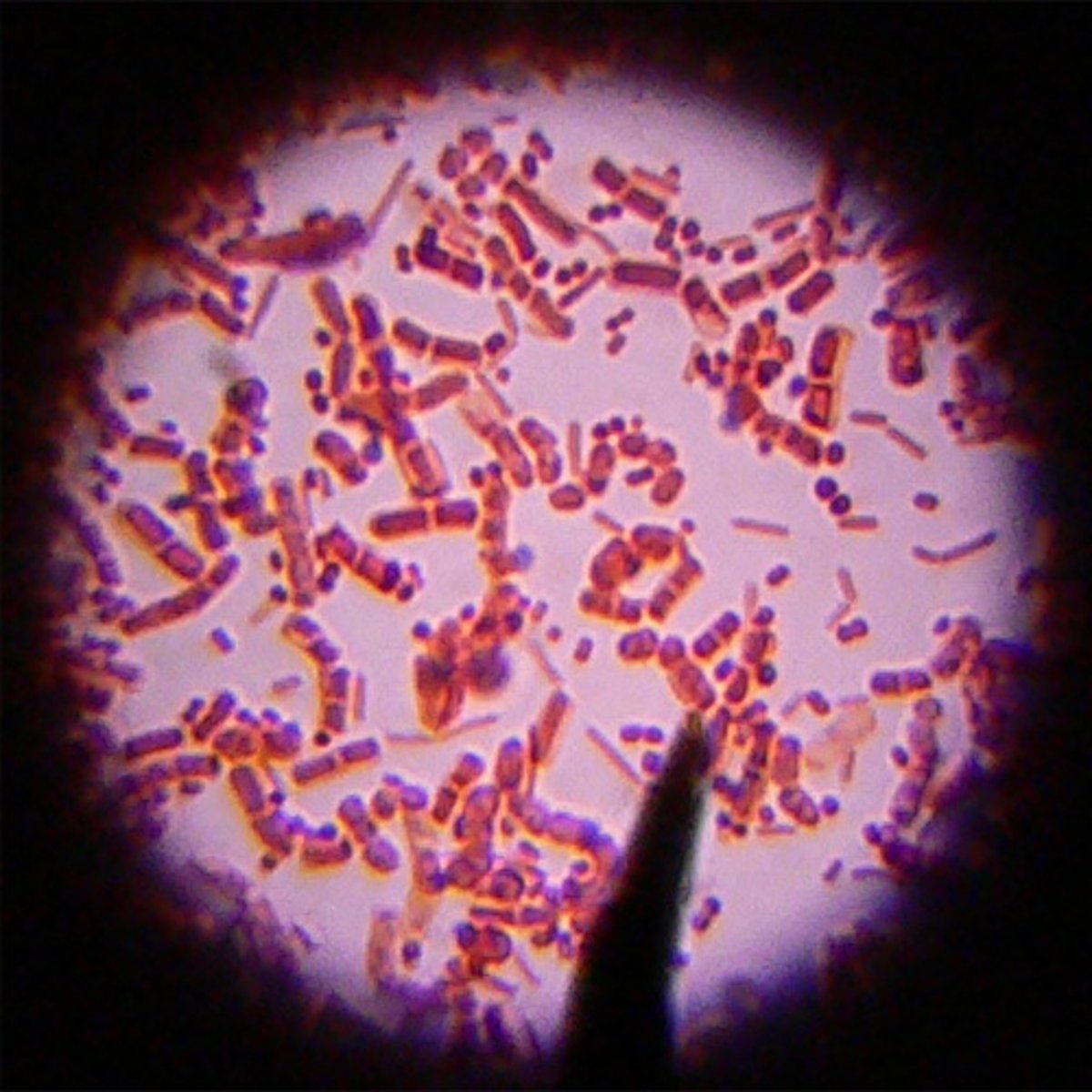
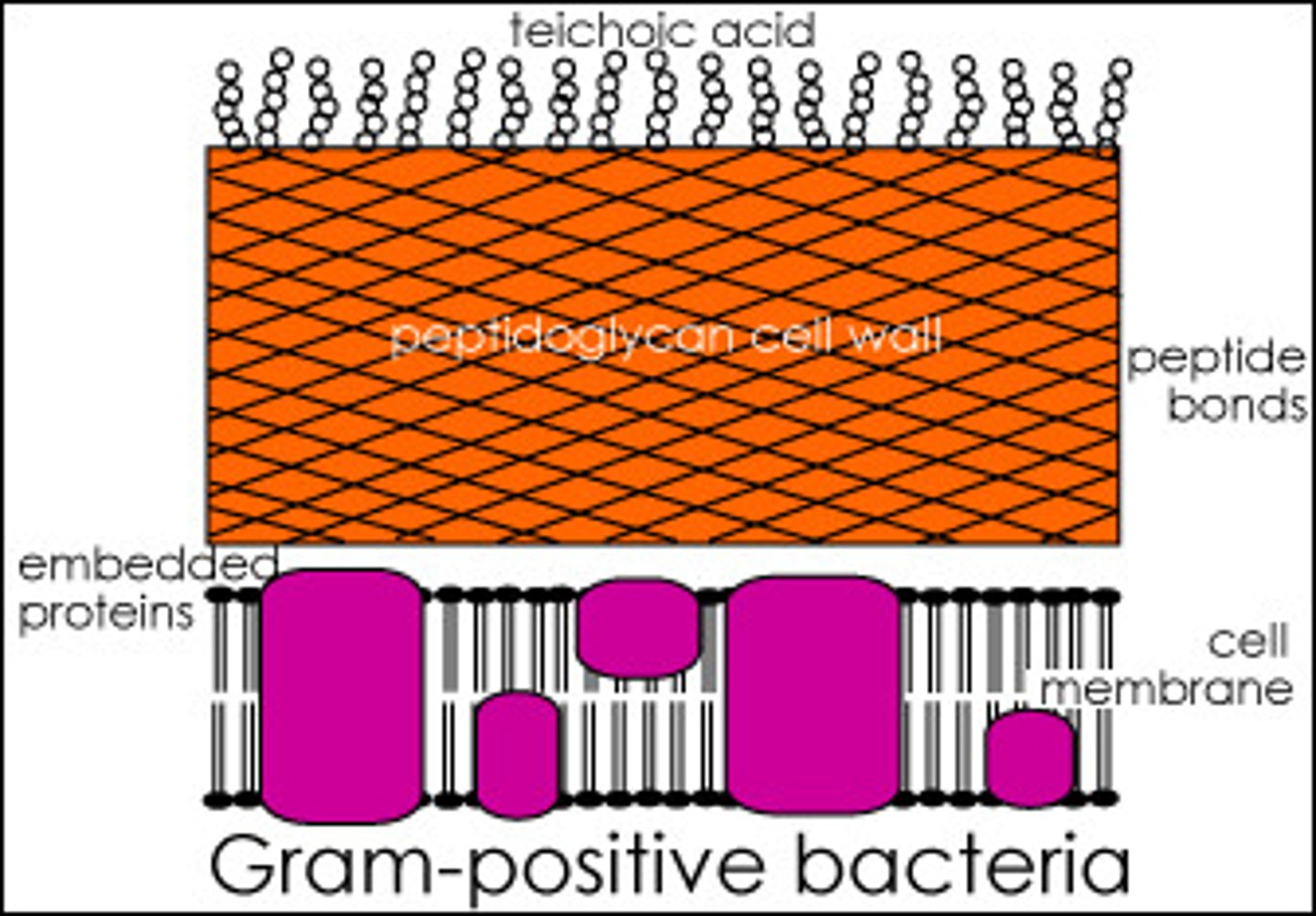
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Bacteria that give the positive result for the gram stain test. After being stained with the violet dye, these bacteria look to be purple. This is because they have a thick cell wall composed of peptidoglycan.
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Bacteria that retain a red-pink color. These bacteria have a thin membrane of peptidoglycan, sandwiched between an outer membrane and an inner membrane.
Cellular
Composed of cells and organelles.
What is Chickenpox?
A highly contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster
virus (VZV). It causes a blister-like rash, itching, tiredness, and fever. The rash appears first on the stomach, back and face and can spread over the entire body causing between 250 and 500 itchy blisters. Chickenpox can be serious, especially in babies, adults, and people with weakened immune systems. The best way to prevent chickenpox is to get the chickenpox vaccine.
What is Influenza?
Influenza (flu) is a viral infection. The flu is usually caused by influenza viruses A and B. There are different strains of the flu virus every year.
People often use the term "flu" to describe any kind of mild illness, such as a cold or a stomach virus, that has symptoms like the flu. But the real flu is different. Flu symptoms are usually worse than a cold and last longer. The flu usually does not cause vomiting or diarrhea in adults. Most flu outbreaks happen in late fall and winter. Because symptoms may not start for a couple of days, you may pass the flu to someone before you know you have it.
What is Measles?
Measles starts with fever, runny nose, cough, red eyes, and sore throat. It's followed by a rash that spreads over the body. Measles virus is highly contagious virus and spreads through the air through coughing and sneezing. The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine protects against measles.
What is Ebola?
Ebola, previously known as Ebola hemorrhagic fever, is a rare and deadly disease caused by infection with one of the Ebola virus species. Ebola can cause disease in humans and nonhuman primates (monkeys, gorillas, and chimpanzees).
light microscope
light passes through lenses (through specimen, through objective lens, to eyepiece) to magnify objects
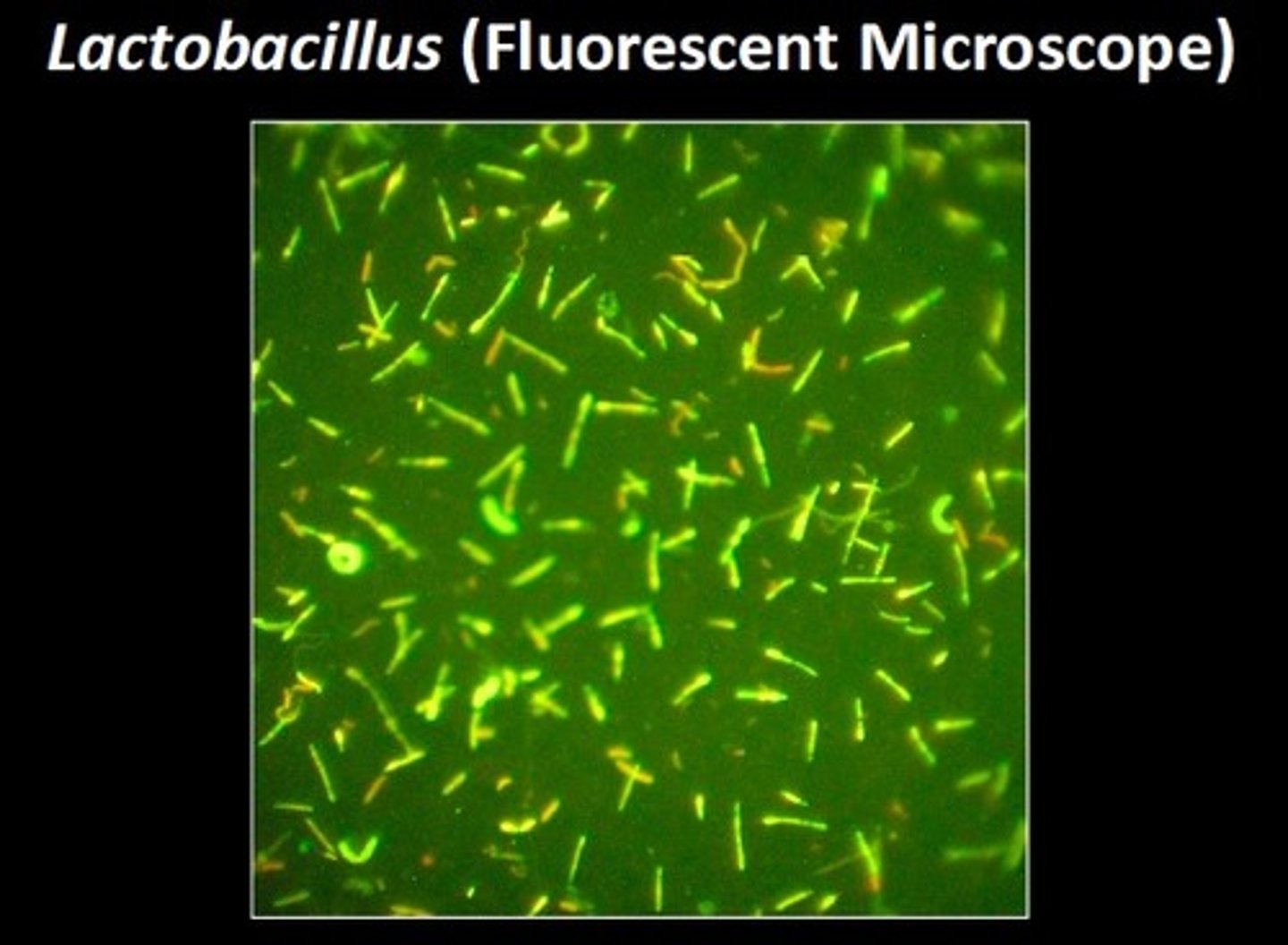
fluorescence microscope
light of known bandwidth excites a fluorescent molecule in a sample, which is detected when it emits light of a longer wavelength
scanning electron microscope
electron beam magnifies objects (up to 2 million times)
transmission electron microscope
electron beam passes through thin specimens
3 Domains
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea
3. Eukaryote
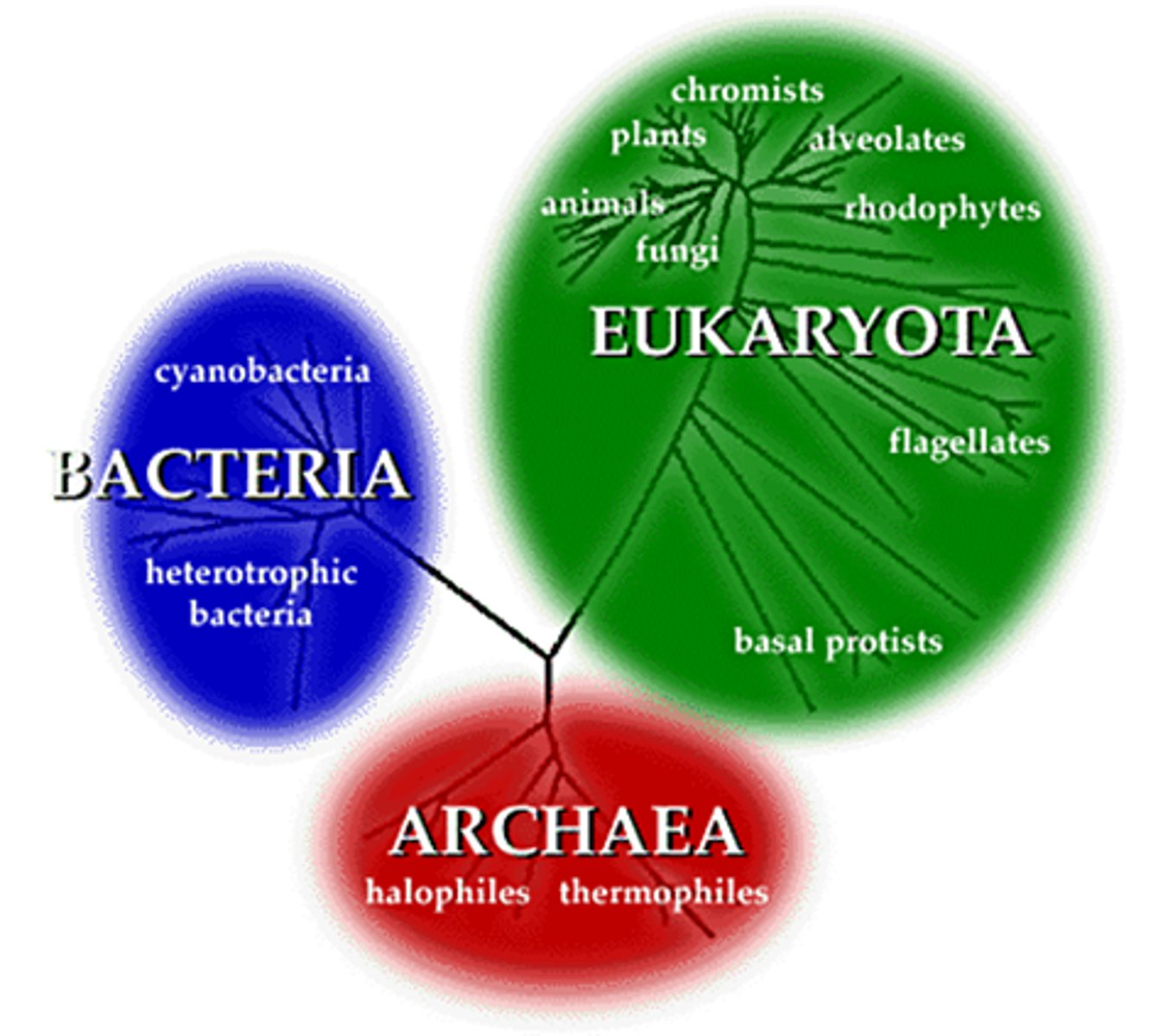
Microbe
microorganism observed by a microscope
prion (proteinaceous infectious particle)
a protein that can infect a neuron, cause cell death, and be transmitted from one cell to another
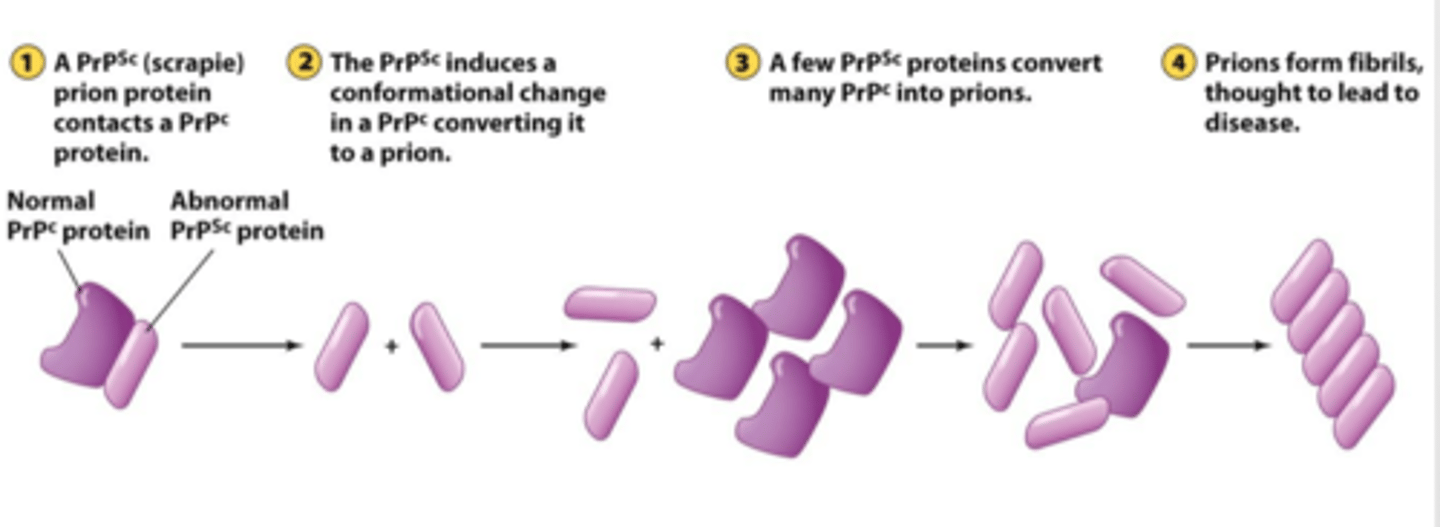
mutant prion protein
altered secondary structure (PrP^Sc)
enters neuron, acts to change the normal protein to the mutant protein
amyloid
tightly packed clump of mutant prion proteins
prions + disease
associated with class of diseases called Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
characterized by loss of motor control, dementia, paralysis, wasting and eventually death; neurodegenerative
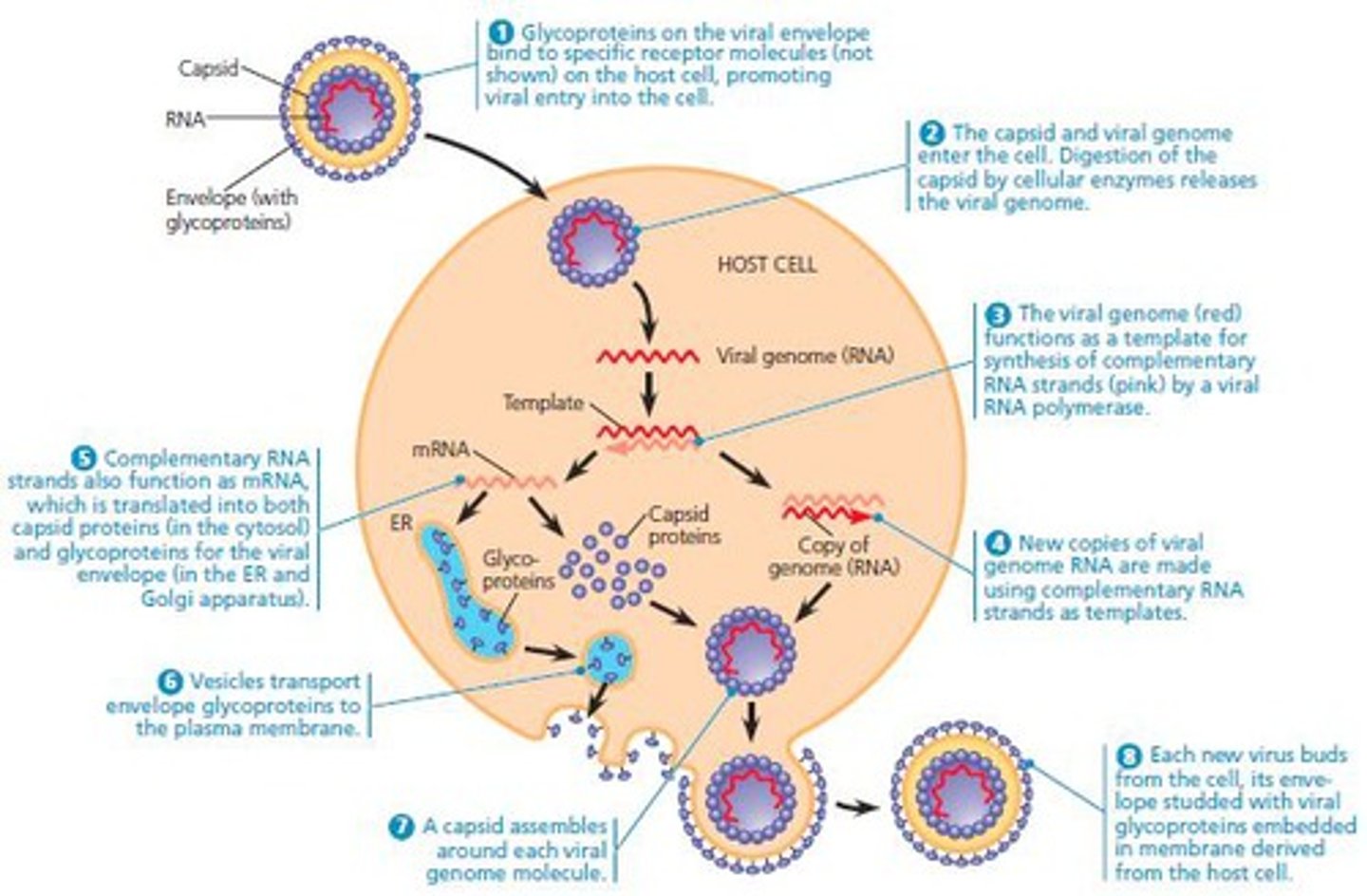
virus
an infective agent smaller than bacteria that consists of a tiny bundle of genetic material carried in a shell called the viral coat, and is able to multiply only within the living cells of a host
components of a virus
consists of a piece of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) encased in protein and in some cases a membrane-like envelope
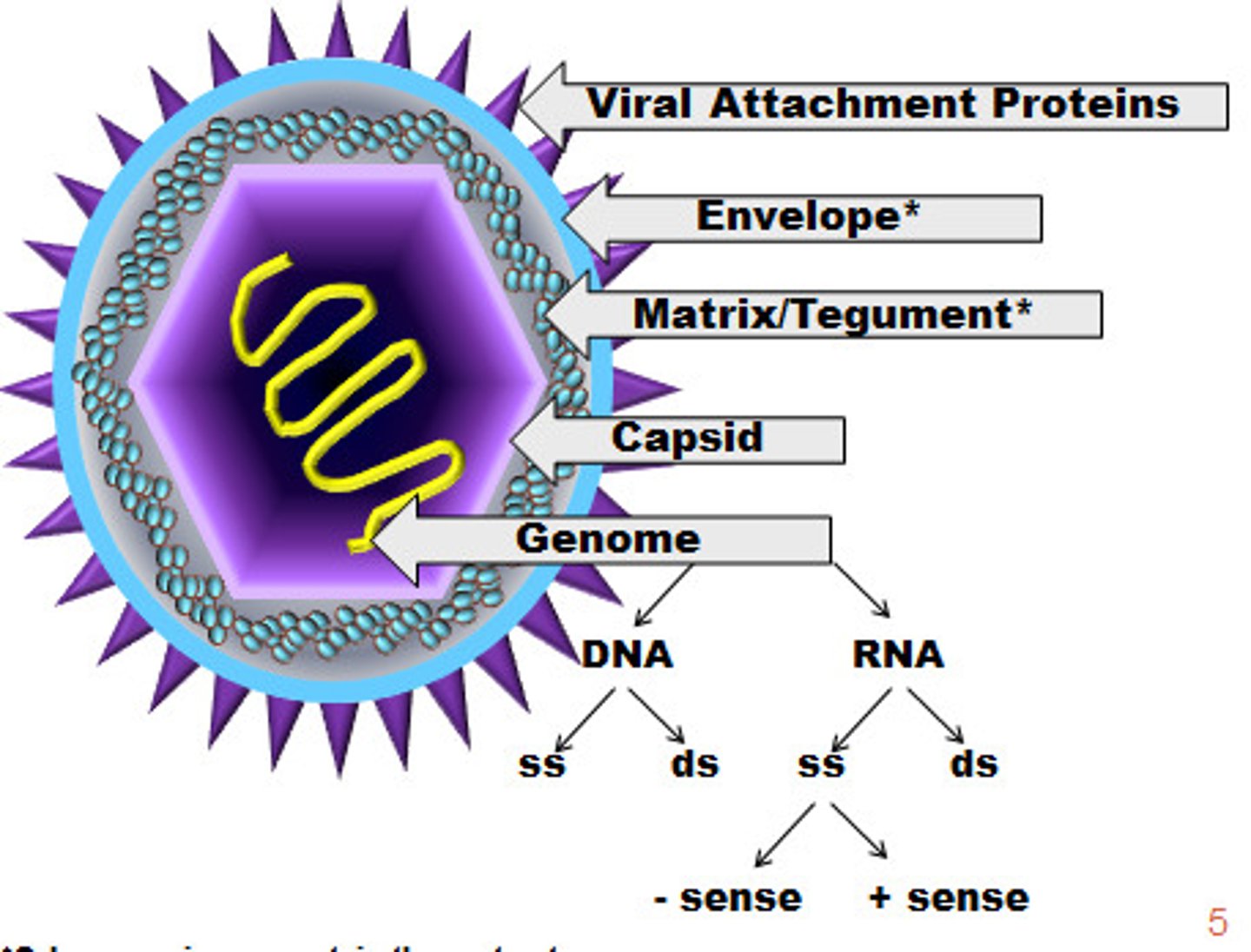
viral genome
the nucleic acid in virus encodes for this
it is the nucleic acid that codes for the viral genes
viral capsid
the protein shell, which may or may not contain viral enzymes
function: acts to package the nucleic acids so they can be delivered to a new host cell
nucleocapsid
viral genome + viral capsid
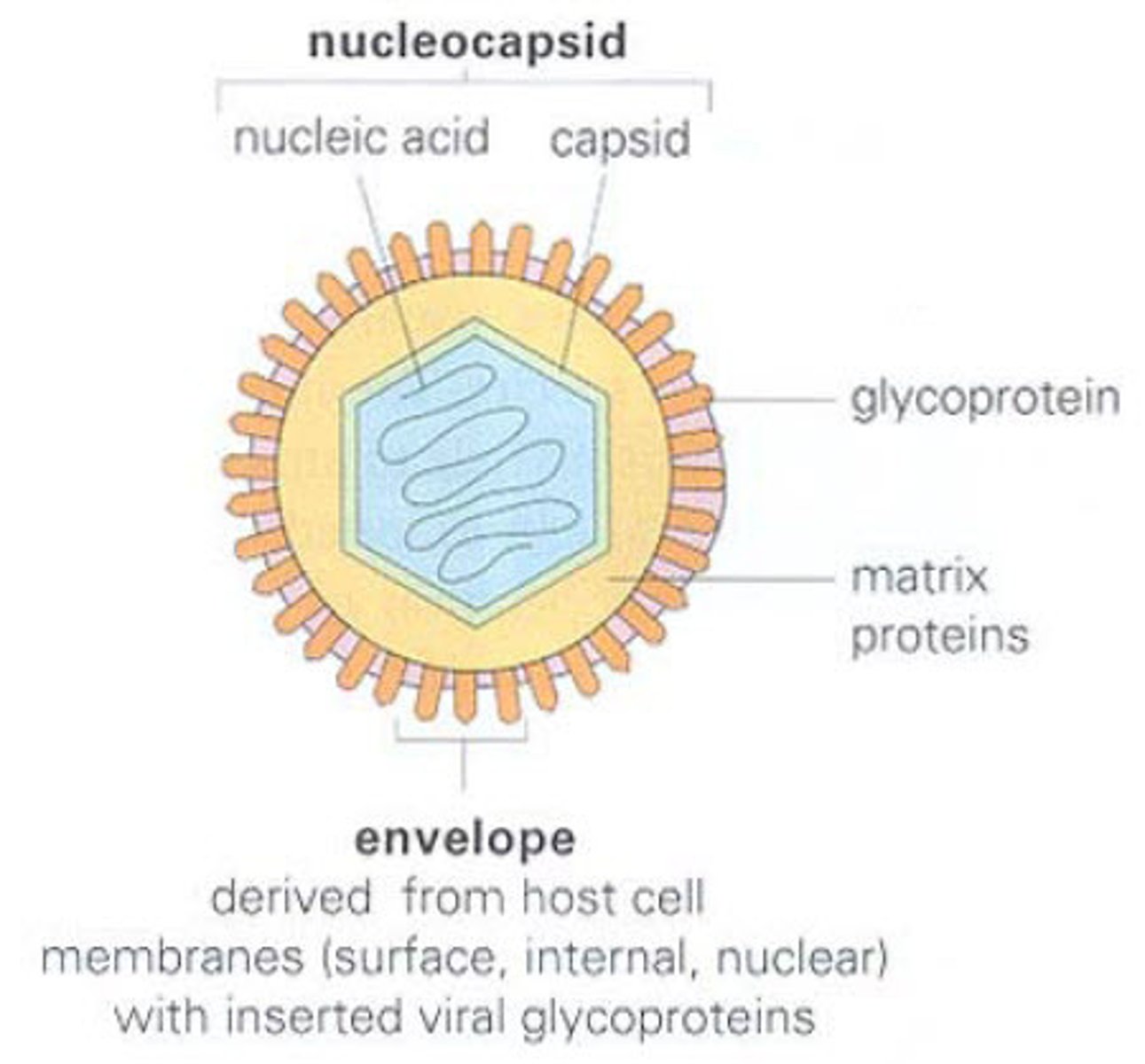
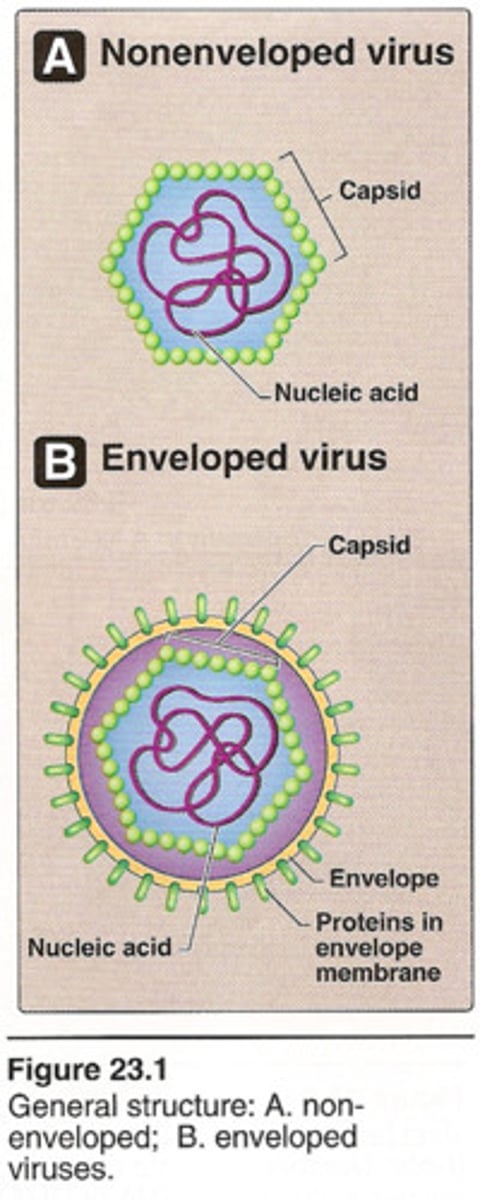
viral envelope
surrounding the viral nucleocapsid
made of lipids that come from the host cell's lips membrane during last stage or viral replication
can be studded with projects that help virus interact with target cell
mostly in animal cells
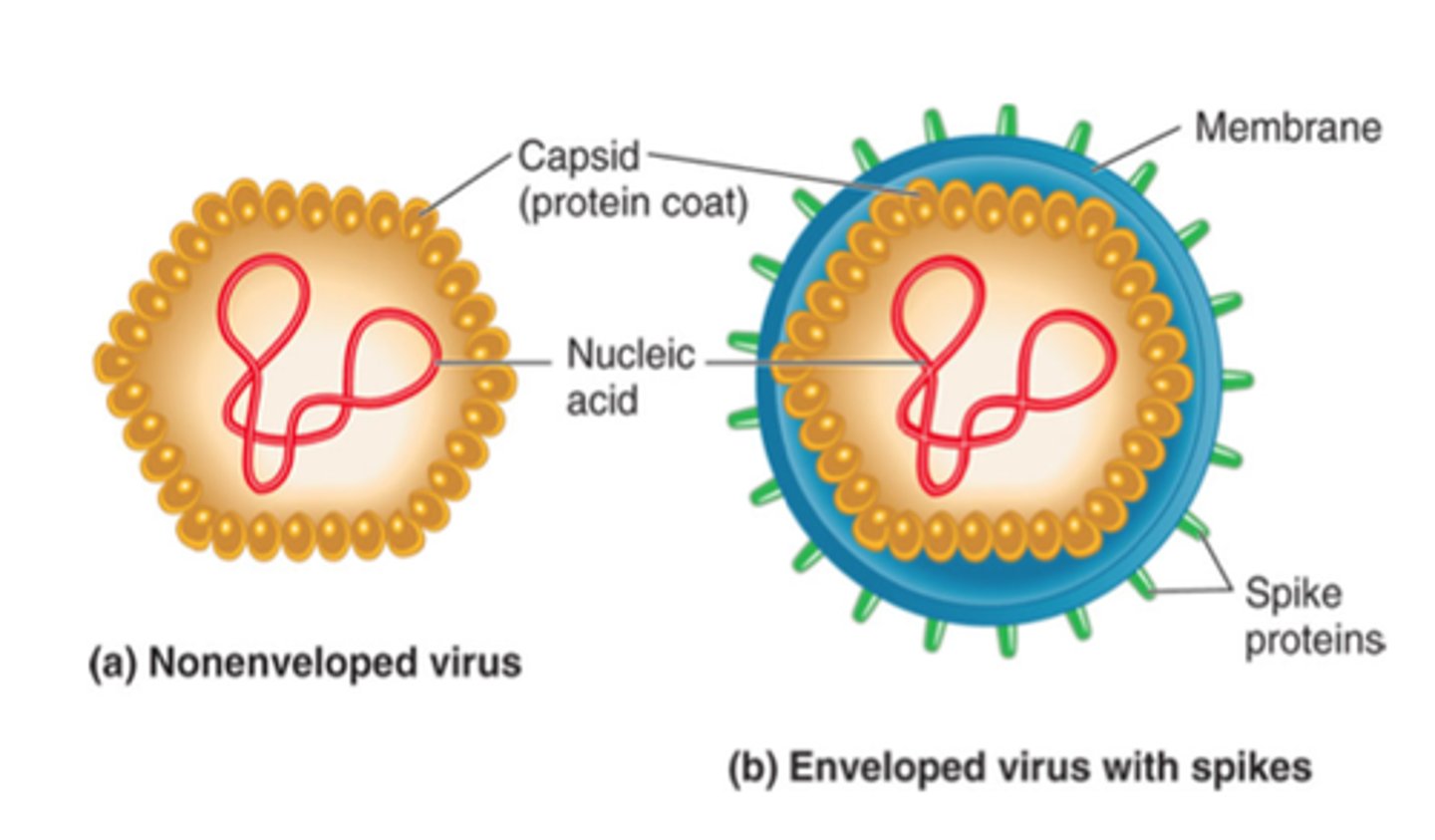
naked virus
virus that lacks viral envelope
virus + infection
not alive on their own, must infect host cell to survive, and then uses machinery of host cell to reproduce
1. virus gets genes inside cell
2. viral genes copied many times
3. new viral genes come together and assemble into whole new viruses
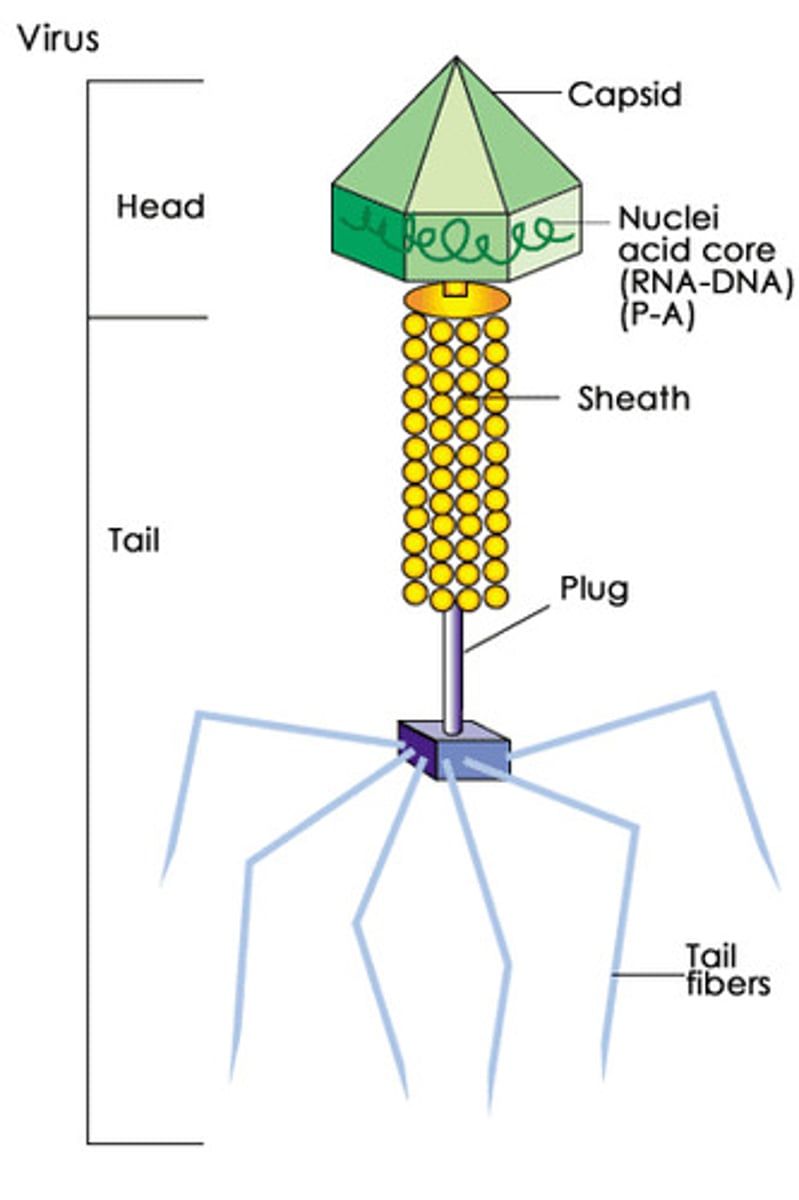
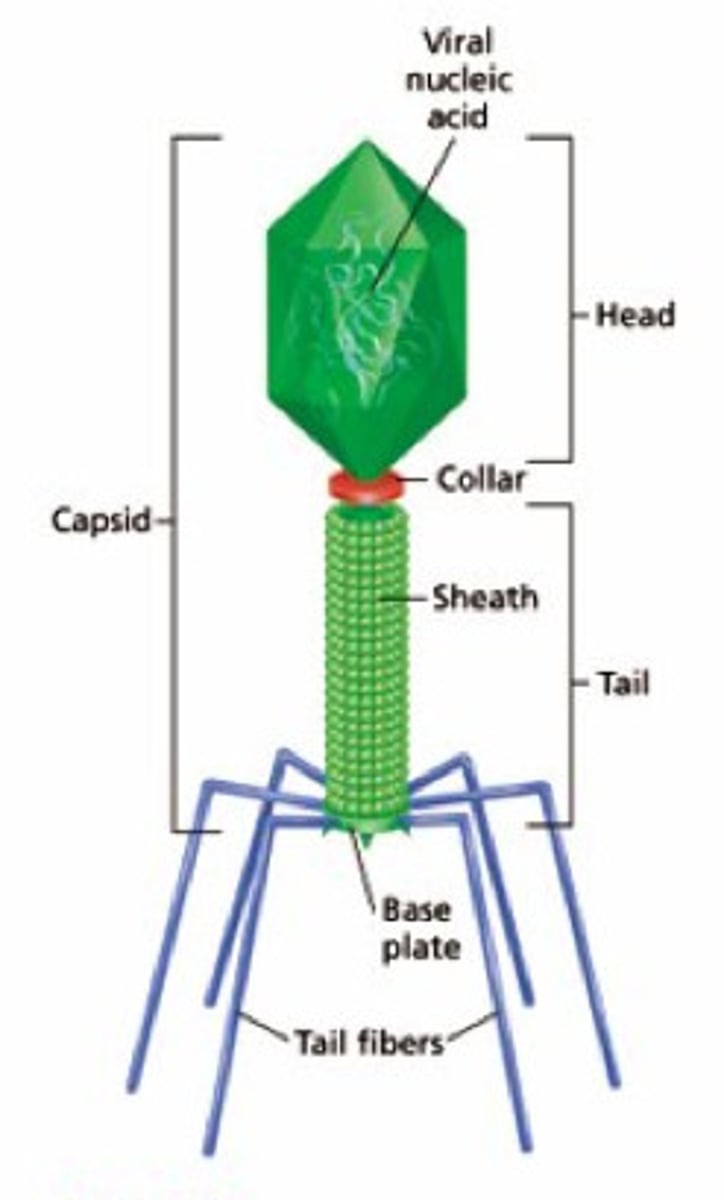
bacteriophages
viruses that infect bacteria; genome composed of DNA; most complicated viral structure
^icosahedral head attached to a tail with filaments
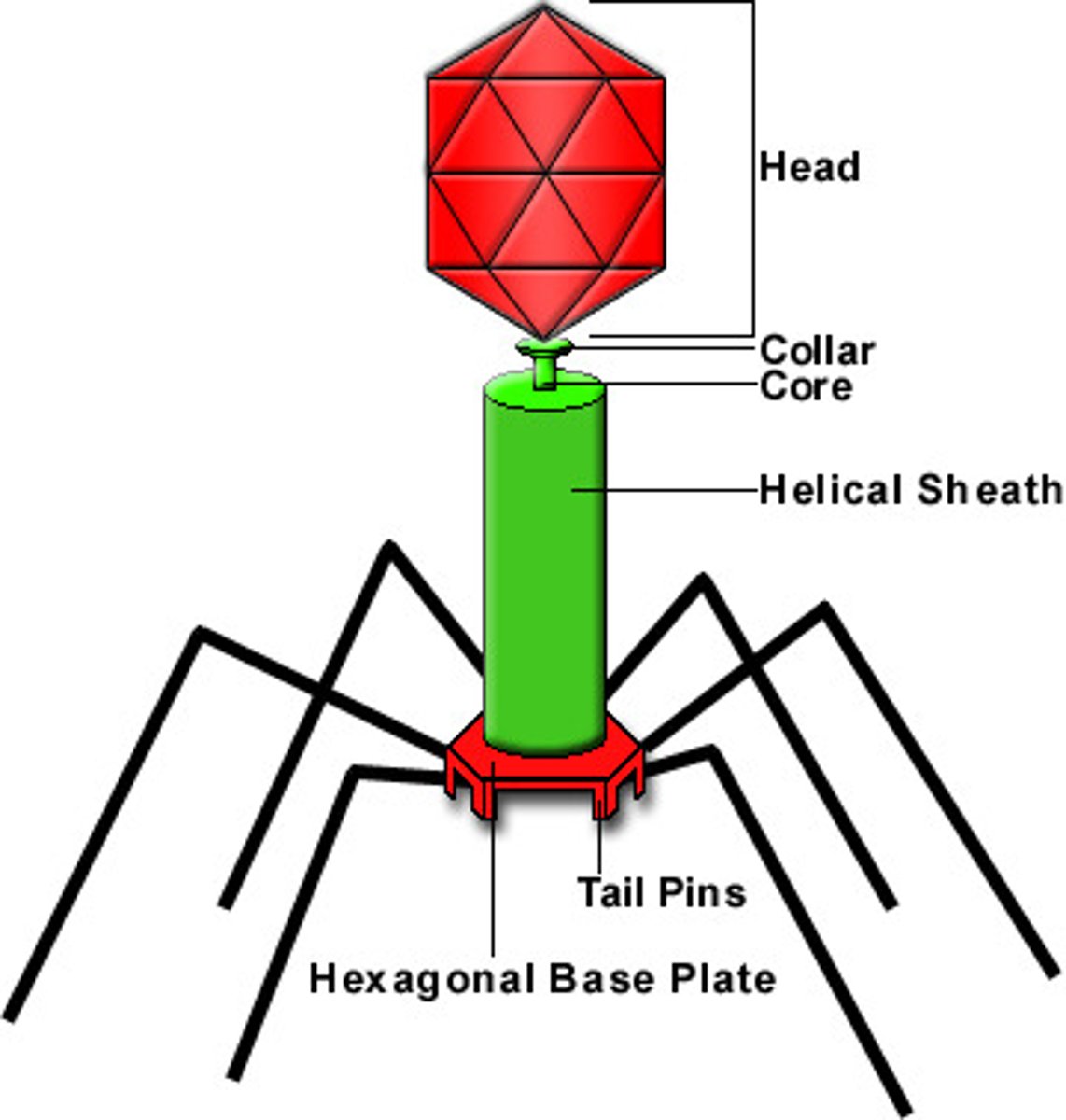
virophages
viruses that infect other viruses
DNA viruses
can have single-stranded or double-stranded DNA molecules within nucleocapsid
double-stranded --> can be used directly for transcription+translation
single-stranded --> needs to form a double-stranded DNA intermediate before it can be used
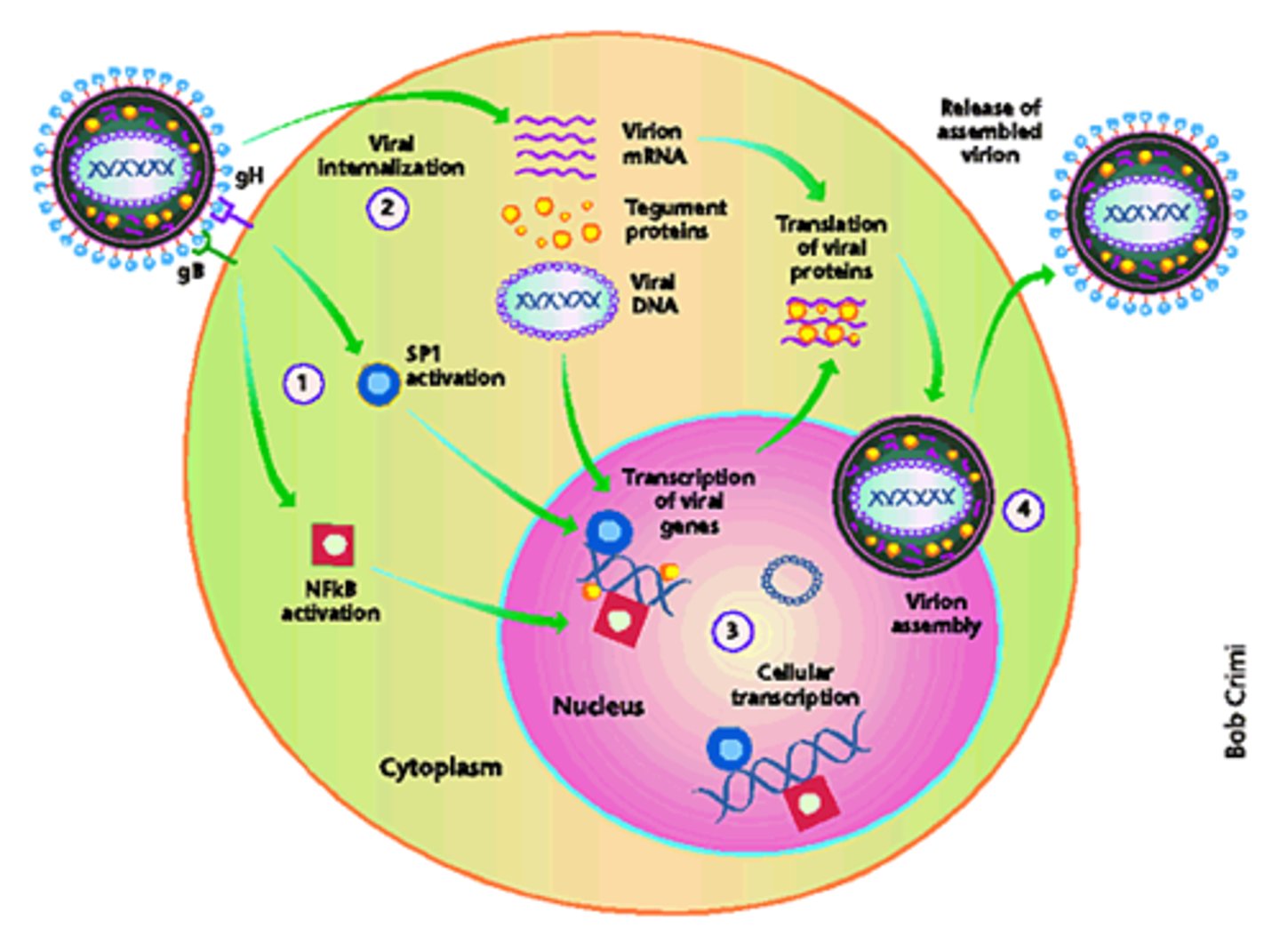
RNA viruses
can have either single-stranded or double-stranded RNA molecules within nucleocapsid
need to encode RNA polymerase for replication because host cells do not have enzyme that can make RNA from RNA template
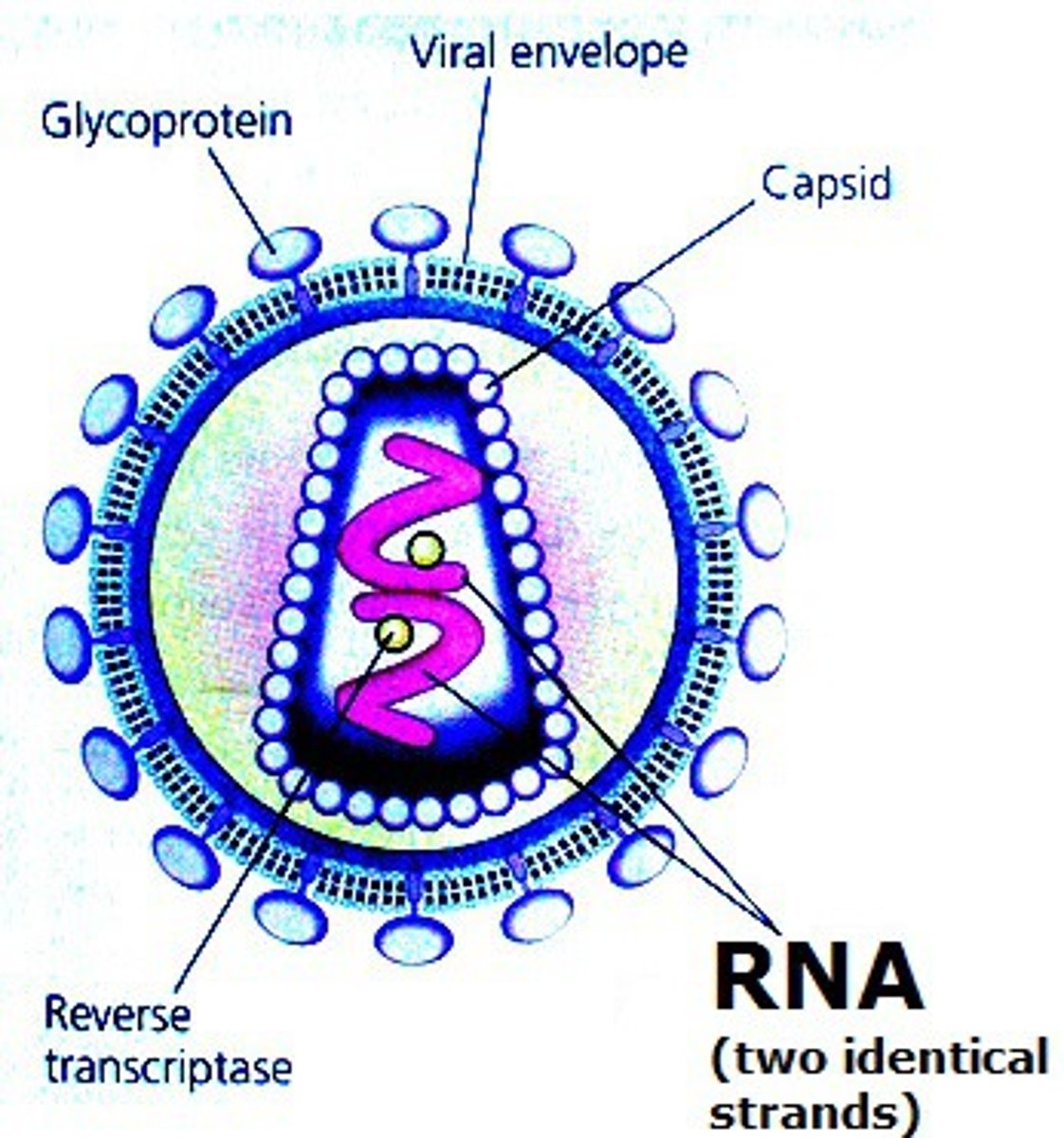
retroviruses
exist as ssRNA that has a to first be made into DNA, which can then be used for transcription and as template to make the genomic copy
carries the reverse transcriptase enzyme with them in capsid
bacteria
single-celled prokaryotic organisms
bacteria making food
some can make food from sunlight (they give off oxygen), others can absorb food from the material they live on or in
aerobic bacteria
can survive in oxygenated environment
anaerobic bacteria
does not require oxygen for survival
facultative anaerobes
bacteria that grow either in the presence or absence of oxygen
yes oxygen --> use it during respiration
no oxygen --> use other pathways for metabolism
bacterial diseases
caused by pathogenic bacteria
cocci
spherical bacteria shape
bacilli
rod-shaped (bacteria)

spirillum
spiral or helical bacteria shape

filamentous
complex bacteria shape
gram positive bacteria
thick peptidoglycan cell wall
retain crystal violet stain
gram negative bacteria
thin inner peptidoglycan wall + outer wall
do not retain crystal violet stain and appear red