Sex Estimation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
biological sex
influenced by:
chromosomes
genetics
hormones
gender
a social category based on cultural norms (also culturally specific); an aspect of one’s personal and social identity
sexual dimorphism
phenotypic differences between males and females of the same species; dramatic in some species
adults
Biological anthropologists only estimate sex in what age group?
90-100%
How accurate is sex estimation with the entire skeleton present?
90-95%
How accurate is sex estimation with only the bones of pelvis present?
80-90%
How accurate is sex estimation with only the skull present?
female pubic bone
broader
wider pubic bone (squared off rather than V-shaped)
wider subpubic angle
male pubic bone
narrower
V-shaped
narrower subpubic angle
up to 96%
How accurate is sex estimation when using the following?
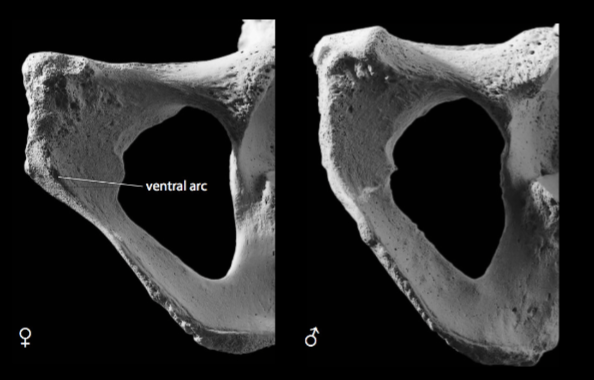
ventral arc
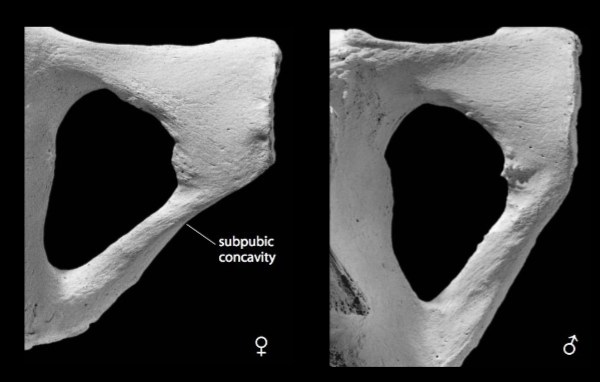
subpubic concavity
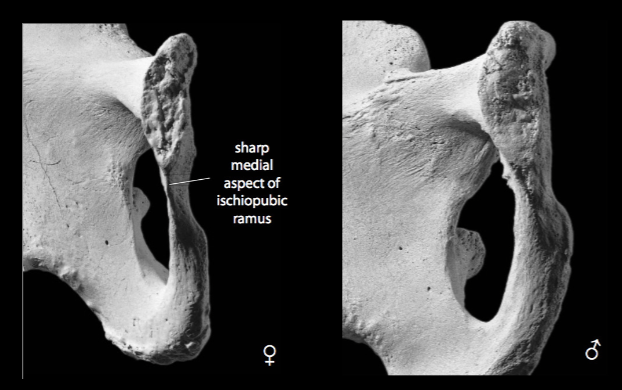
ischiopubic ramus
ventral arc
present in females, absent in males
subpubic concavity
present in females, absent in males
ischiopubic ramus
narrow and sharp in females, broad and dull in males
sciatic notch
wider and larger in females
preauricular sulcus
variable groove, more often present in females
nuchal crest
pronounced and rough in males, smoother and slender in females
mastoid process
larger in males than in females
supraorbital margin
broader and thicker in males, thinner and sharper in females
supraorbital ridge
pronounced and rounded in males, smooth and flat in females
mental eminence
larger and squarer in males, smaller and pointed in females
up to 90%
How accurate is sex estimation when using sectioning points (univariate)?
up to 94%
How accurate is sex estimation when using discriminant functions (multivariate)?