Chapter 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Tautomerism
Keto tautomer to enol tautomer goes through enolate.
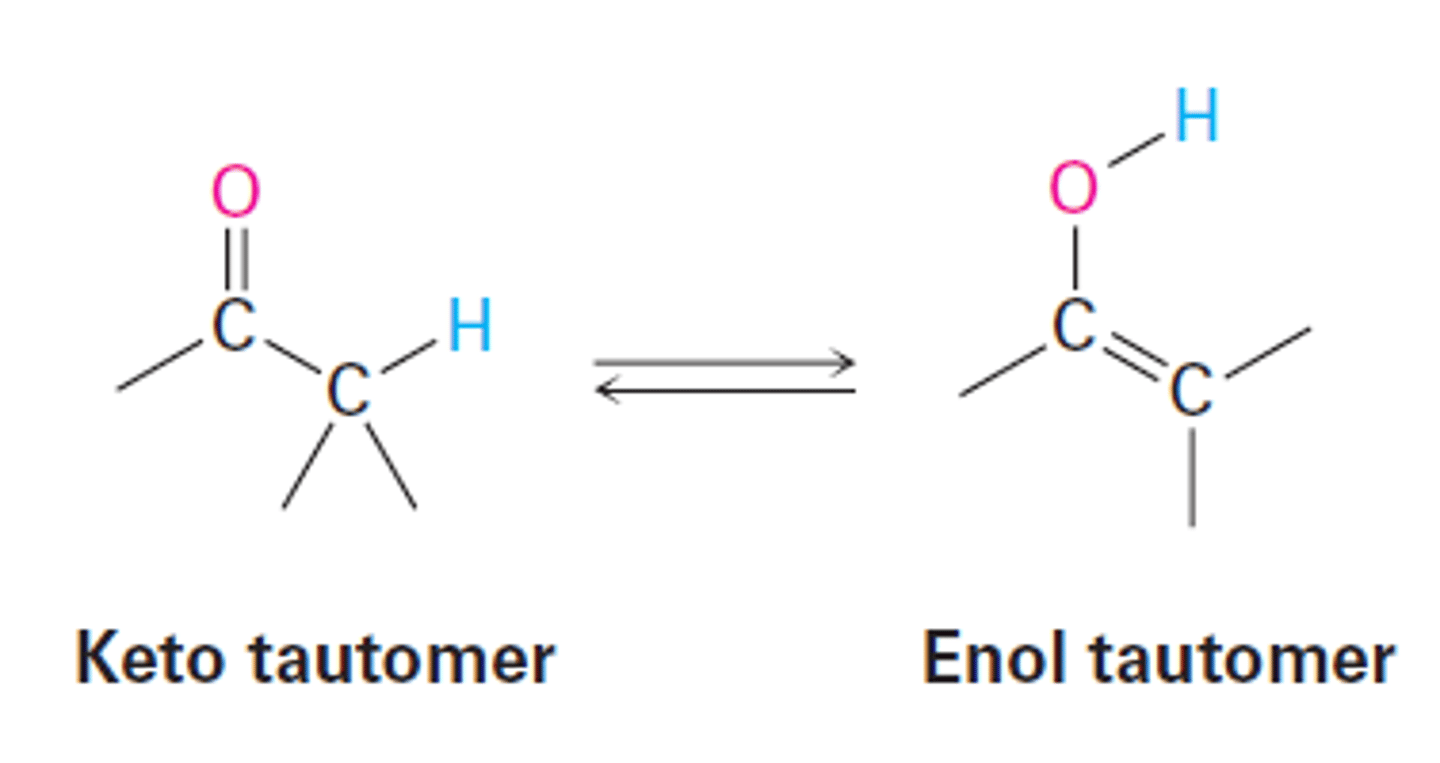
Tautomers are constitutional isomers; different compounds with different structures.
Resonance forms are different representations of a single compound based on the position of their π and lone pair electrons.
What is the difference between tautomers and resonance forms?
By both acids and bases
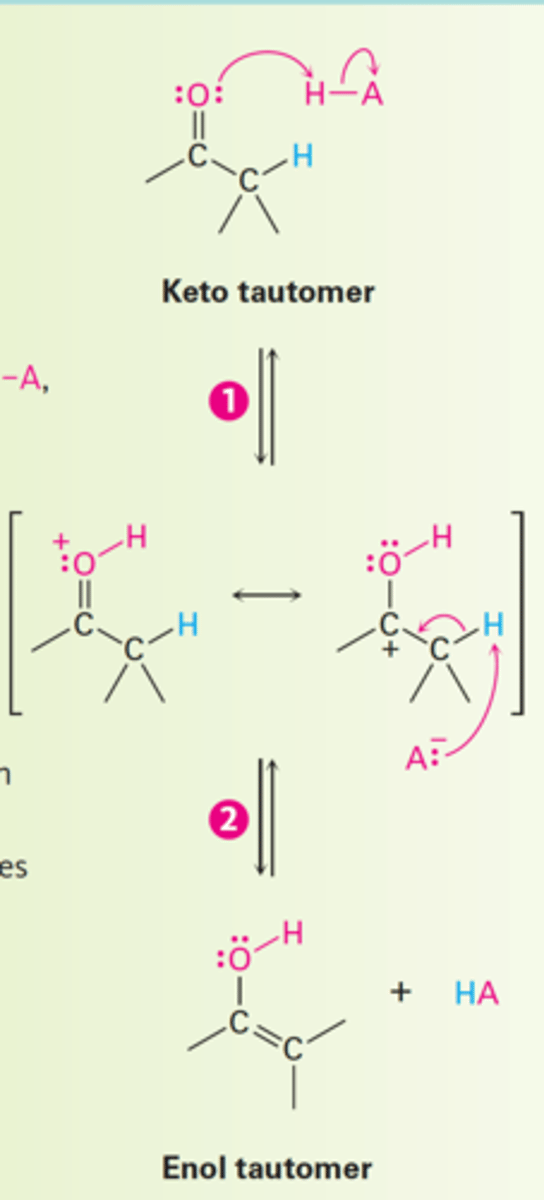
How is keto-enol tautomerism of carbonyl compounds catalyzed?
1. Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen atom by an acid.
2. Loss of H⁺ from the α position by reaction with a base gives the enol tautomer and regenerates the acid catalyst.
How does acid-catalyzed keto-enol tautomerism of carbonyl compounds occur?
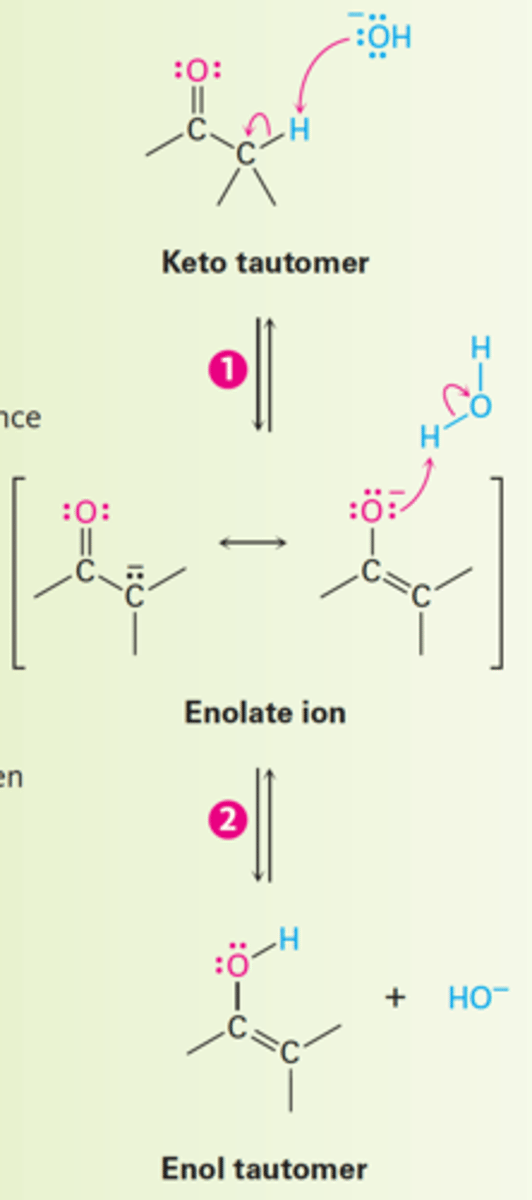
1. Deprotonation of the acidic α-hydrogen.
2. Protonation of the Enolate Ion (resonance-stabilized anion) on oxygen gives the enol tautomer and regenerates base catalyst.
How does base-catalyzed keto-enol tautomerism of carbonyl compounds occur?
α-hydrogens are of carbonyl compounds are the only acidic hydrogens.
Why are α-hydrogens the only hydrogens of carbonyl compounds that can be removed by a base in tautomerization?
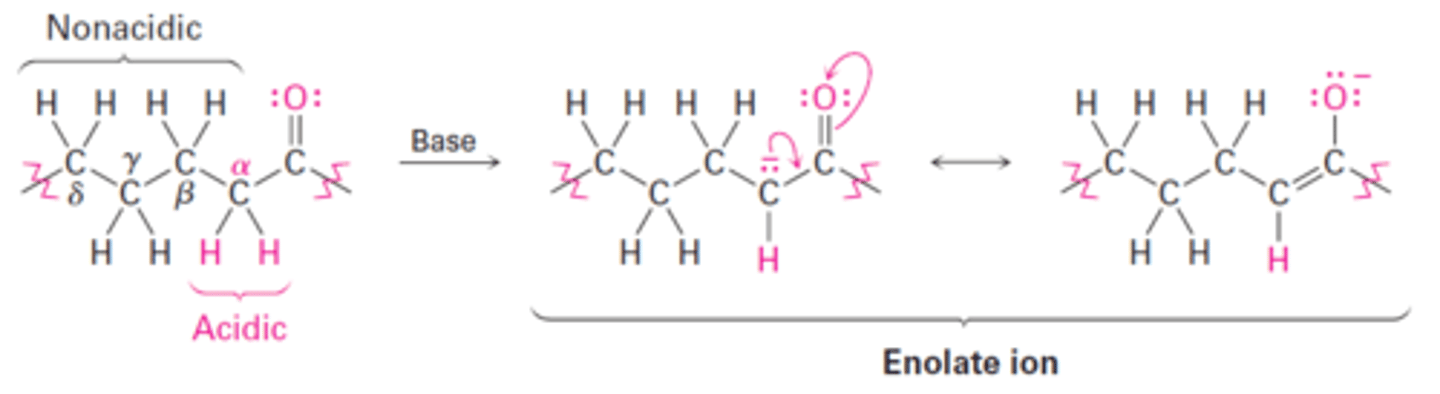
Hydrogens at β, γ, δ, etc. aren't acidic and can't be removed by base because the resulting anions can't be resonance-stabilized by the carbonyl group.
Why can't non-α-hydrogens be removed by a base in tautomerization?
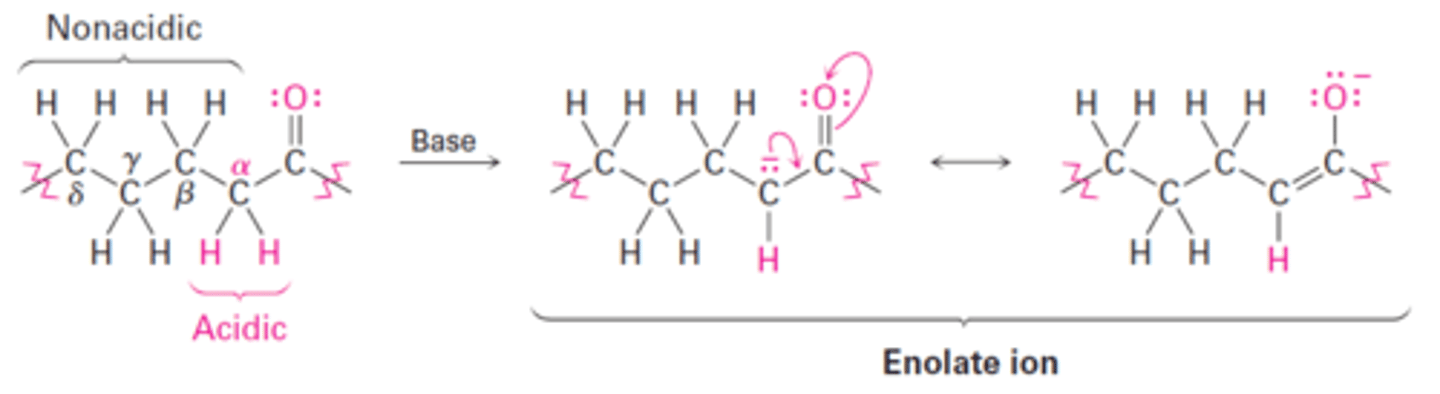
α-substitution reaction
Reaction that occurs at the position next to the carbonyl group—the a position—and involve the substitution of an a hydrogen atom by an electrophile (E) through either an enol or enolate ion intermediate.
Enolate ion
A resonance-stabilized anion resulting from the deprotonation of a carbon atom adjacent to a carbonyl functional group.
Basic conditions
Under what conditions is an enolate ion yielded during the enol formation?
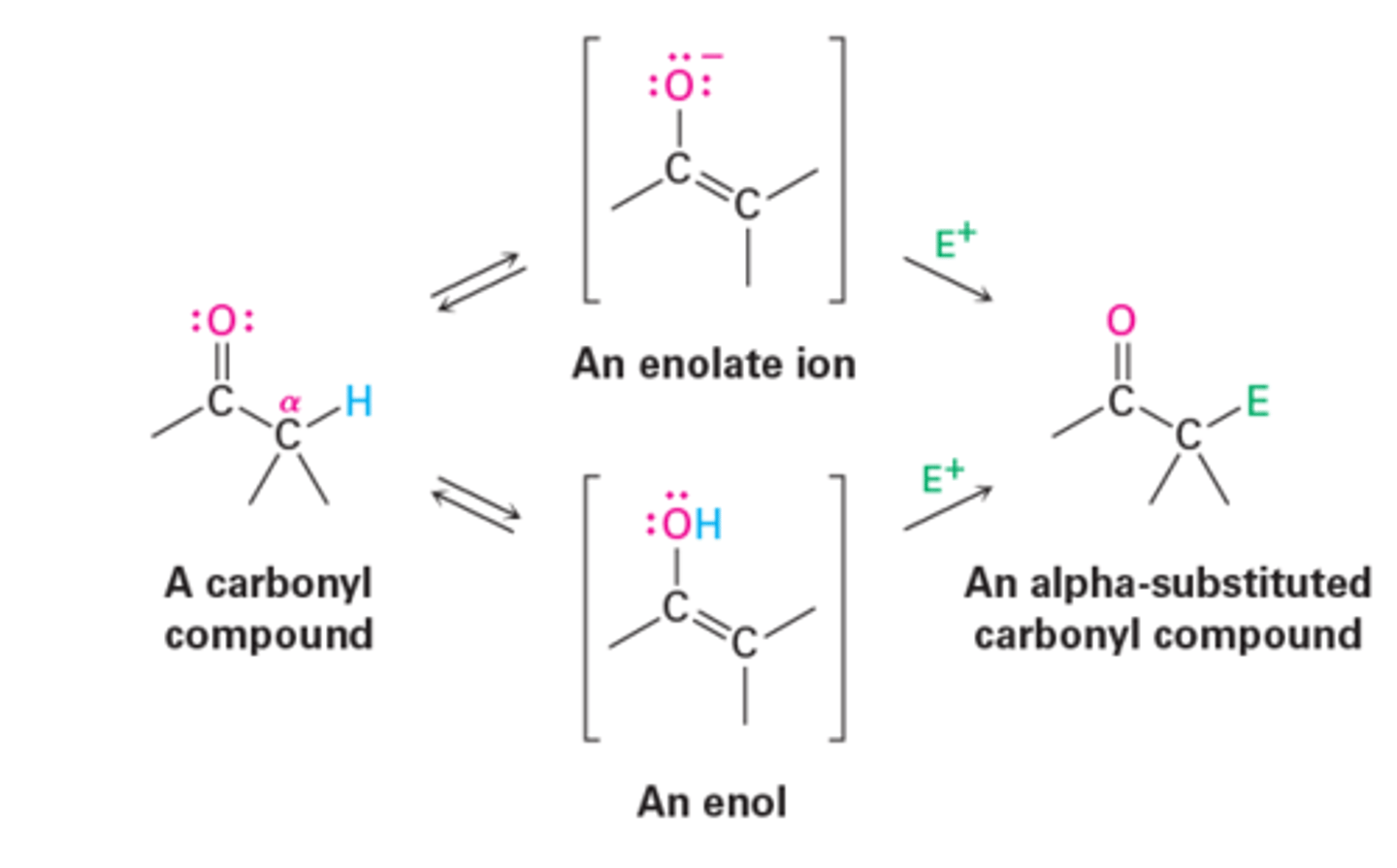
α-substitution reaction mechanism
1. Acid-catalyzed enol formation.
2. Electron pair from the enol oxygen attacks an electrophile.
- Forms a new bond and leaves a cation intermediate that is stabilized by resonance between two forms.
3. Loss of proton from oxygen yields the neutral product as a new C=O bond is formed.
1. Acid-catalyzed enol formation.
2. Electron pair from the enol oxygen attacks an electrophile.
- Forms a new bond and leaves a cation intermediate that is stabilized by resonance between two forms.
3. Loss of proton from oxygen yields the neutral product as a new C=O bond is formed.
α-substitution reaction mechanism
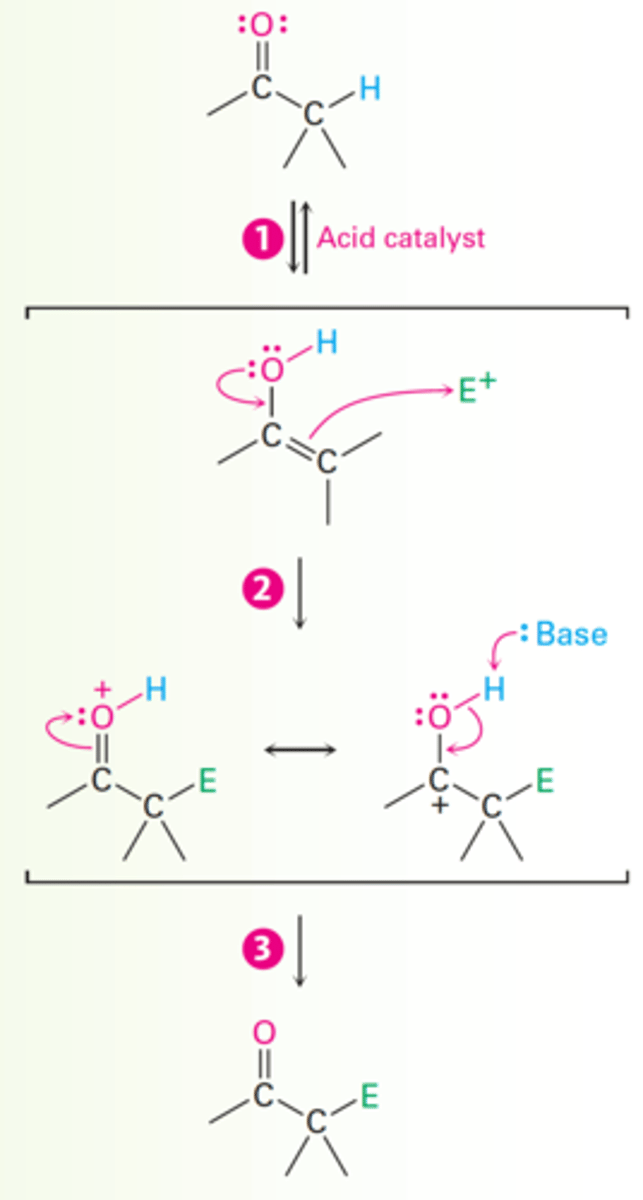
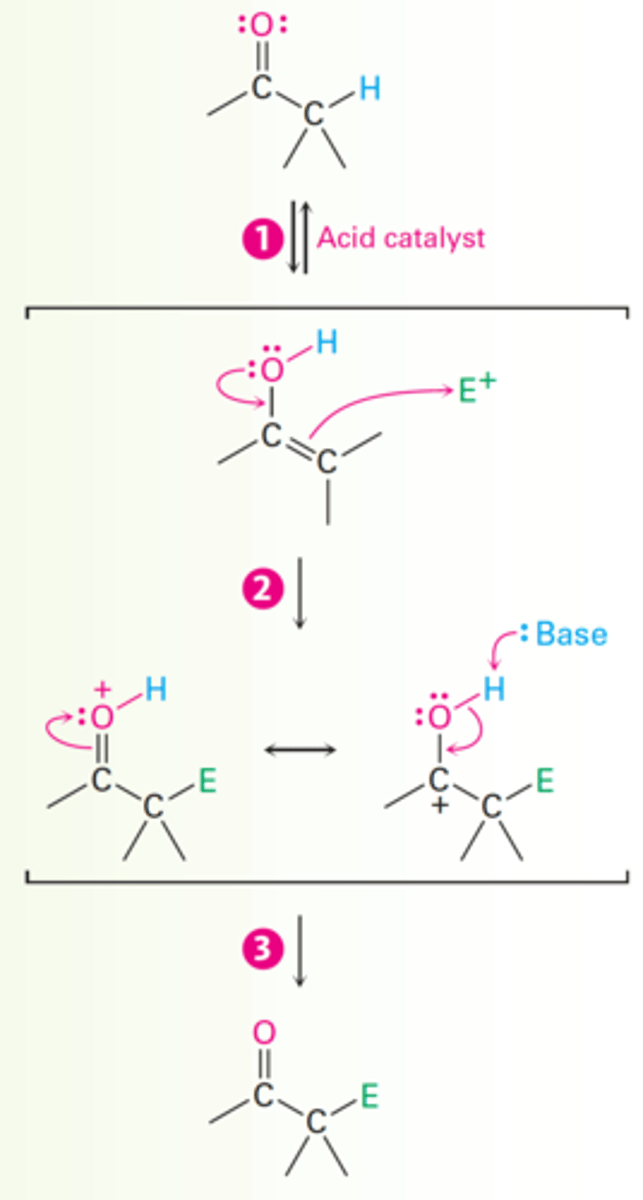
Acid-catalyzed Bromination of Acetone Mechanism
1. The carbonyl oxygen atom is protonated by acid catalyst (HBr).
2. Loss of an acidic proton from the alpha carbon takes place in the normal way to yield an enol intermediate.
3. An electron pair from the enol attacks bromine, giving an intermediate cation that is stabilized by resonance between two forms.
4. Loss of the -OH proton then gives the alpha-halogenated product and generates more acid catalyst.
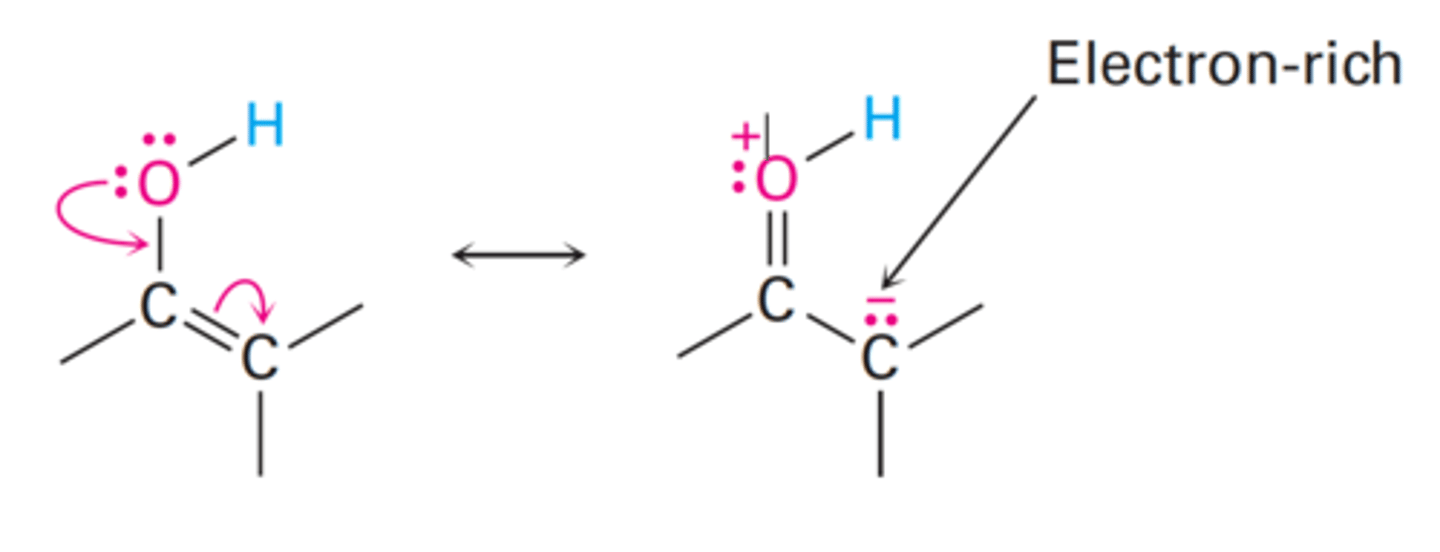
Enol Tautomer
The resonance form of a carbonyl that has a carbon-carbon double bond (ene) and an alcohol (-ol)
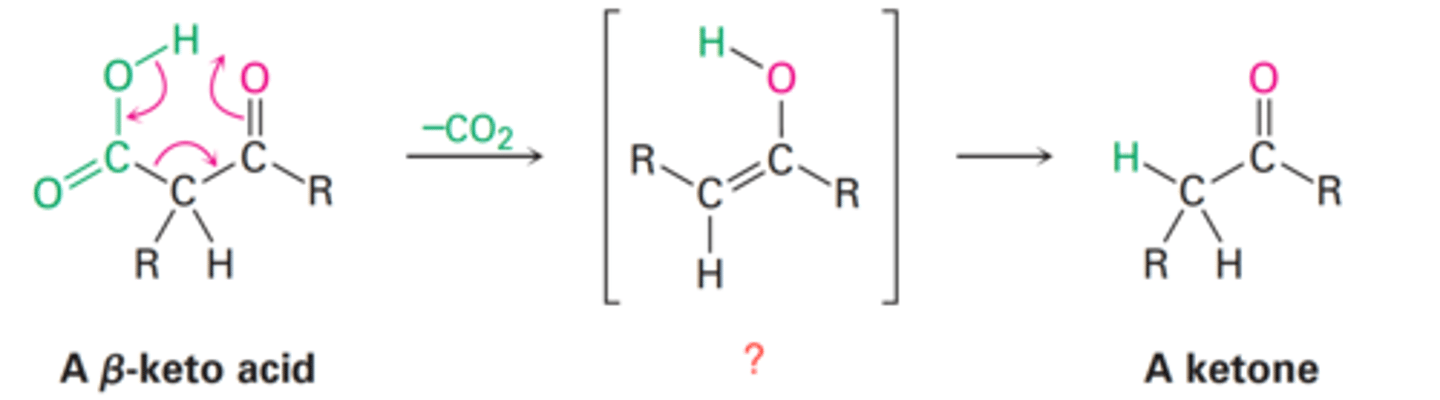
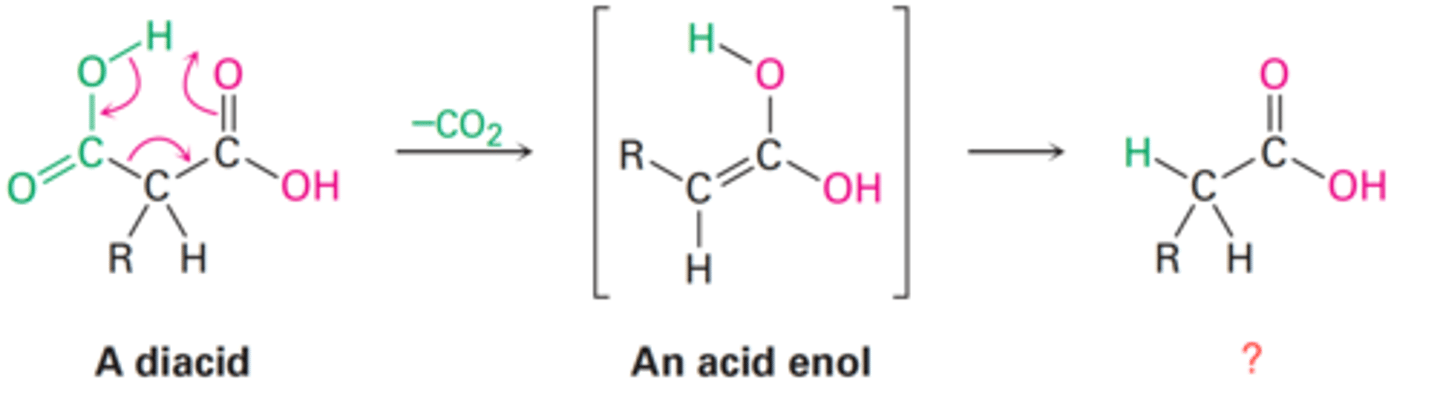
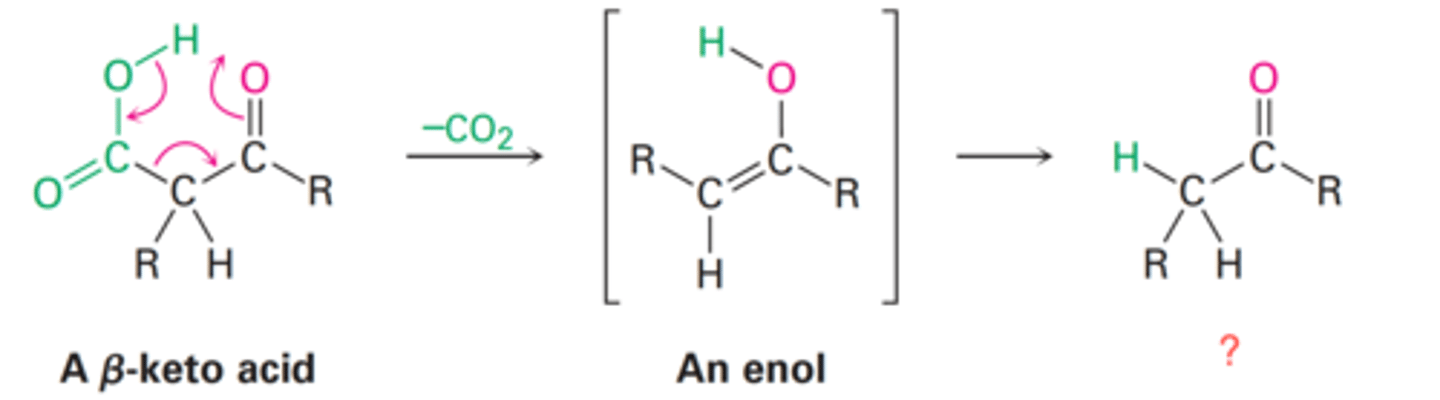
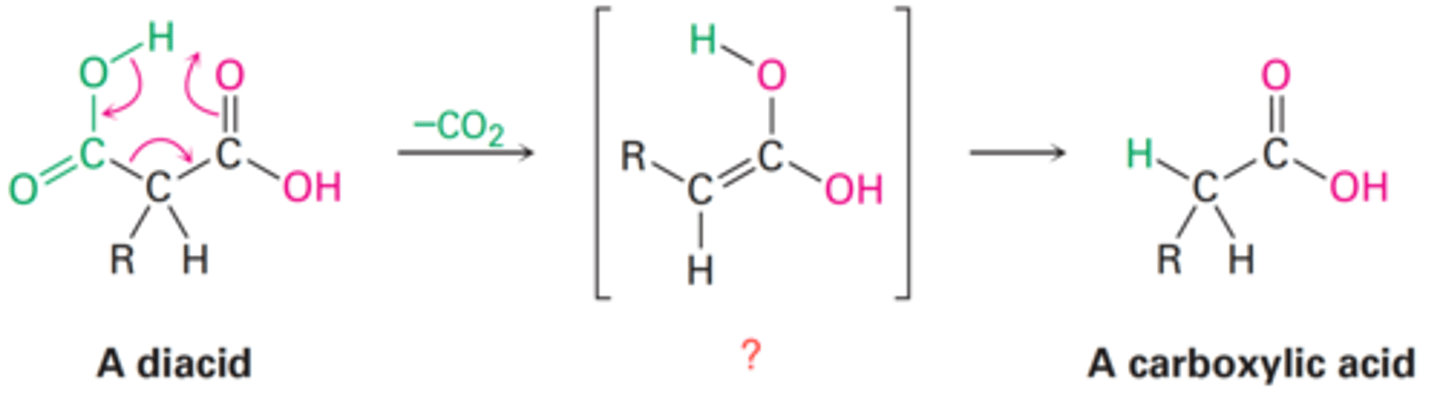
Decarboxylation
The complete loss of a carboxyl group as carbon dioxide CO₂
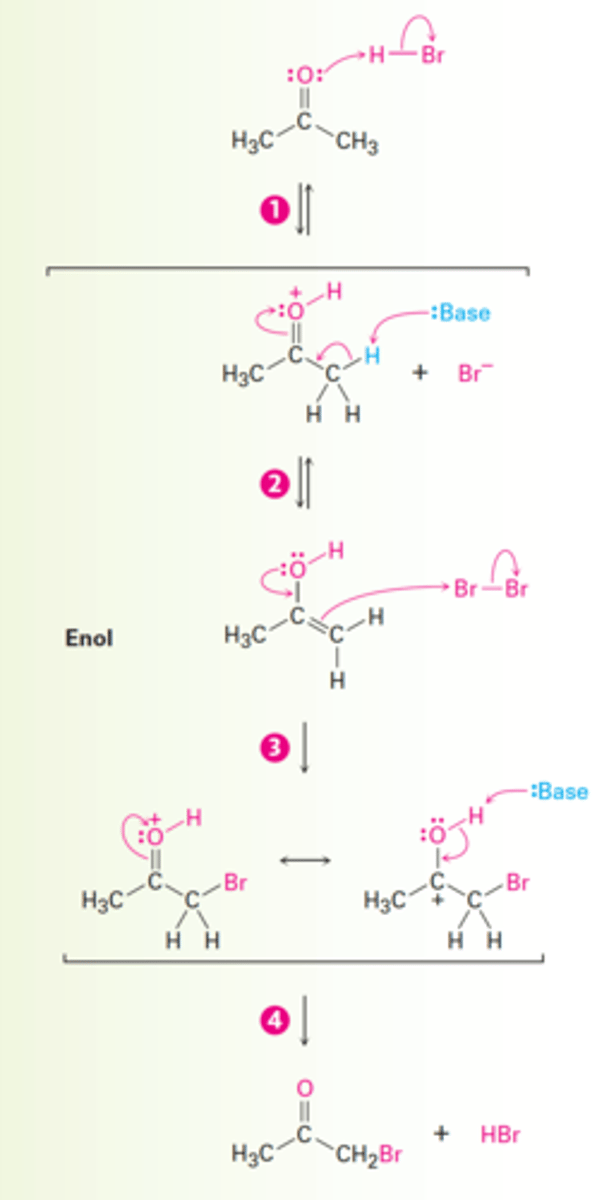
Aldehyde/Ketone Halogenation Reaction
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction
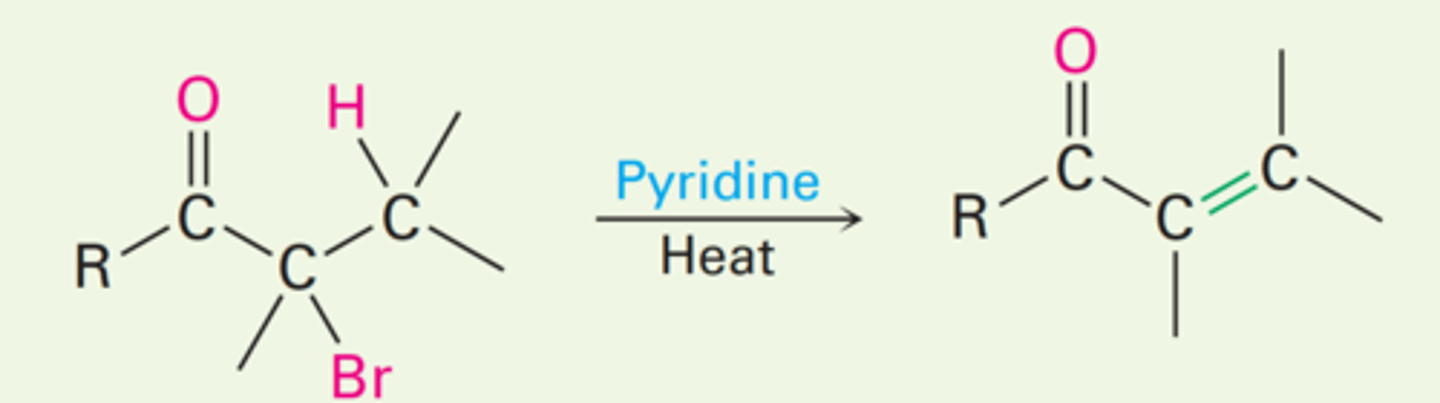
Dehydrobromination of α-bromo ketones
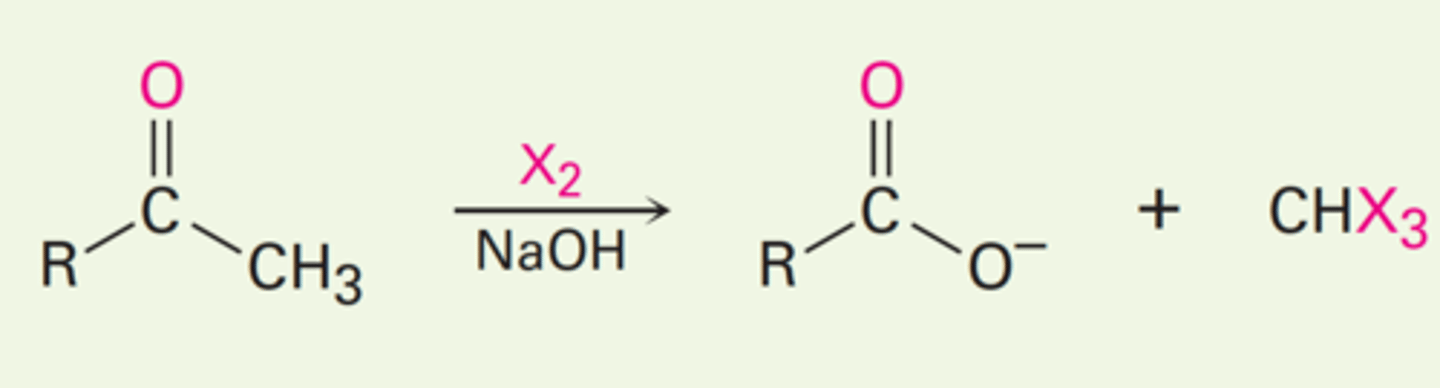
Haloform Reaction
- When a base is used with a methyl ketone, the alpha carbon will become completely halogenated.
- This trihalo product reacts further with the base
1. Malonic ester synthesis
2. Acetoacetic ester synthesis
3. Direct alkylation of ketones
4. Direct alkylation of esters
5. Direct alkylation of nitriles
Alkylation reactions of Enolates ions
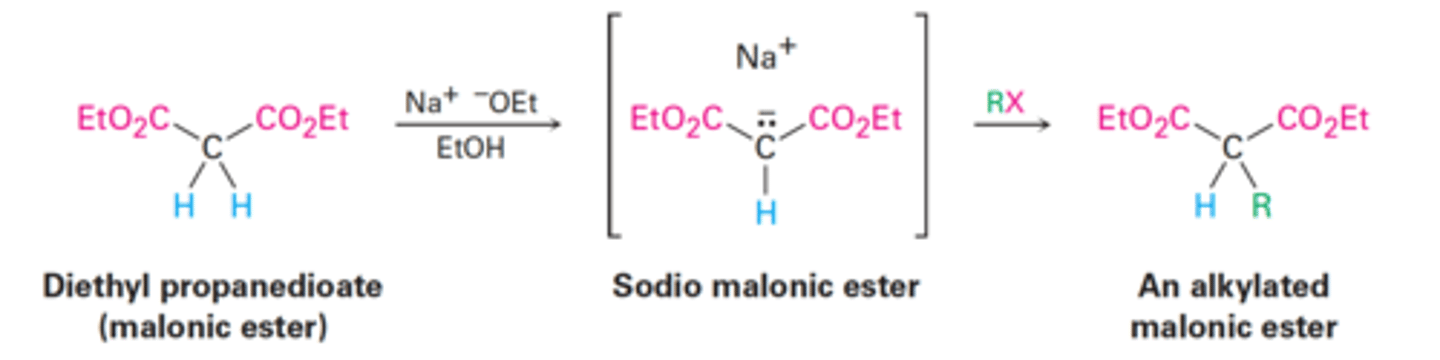
Malonic ester synthesis
Converts an alkyl halide into a carboxylic acid with the addition of two carbon atoms.
RX → RCH₂CO₂H
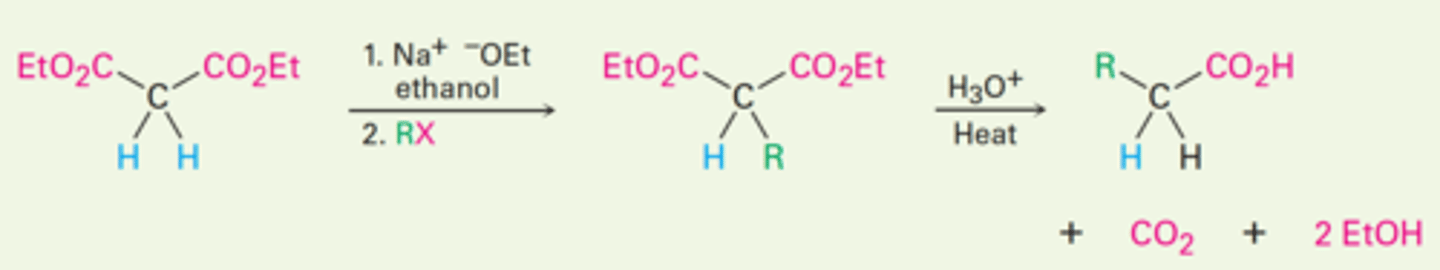
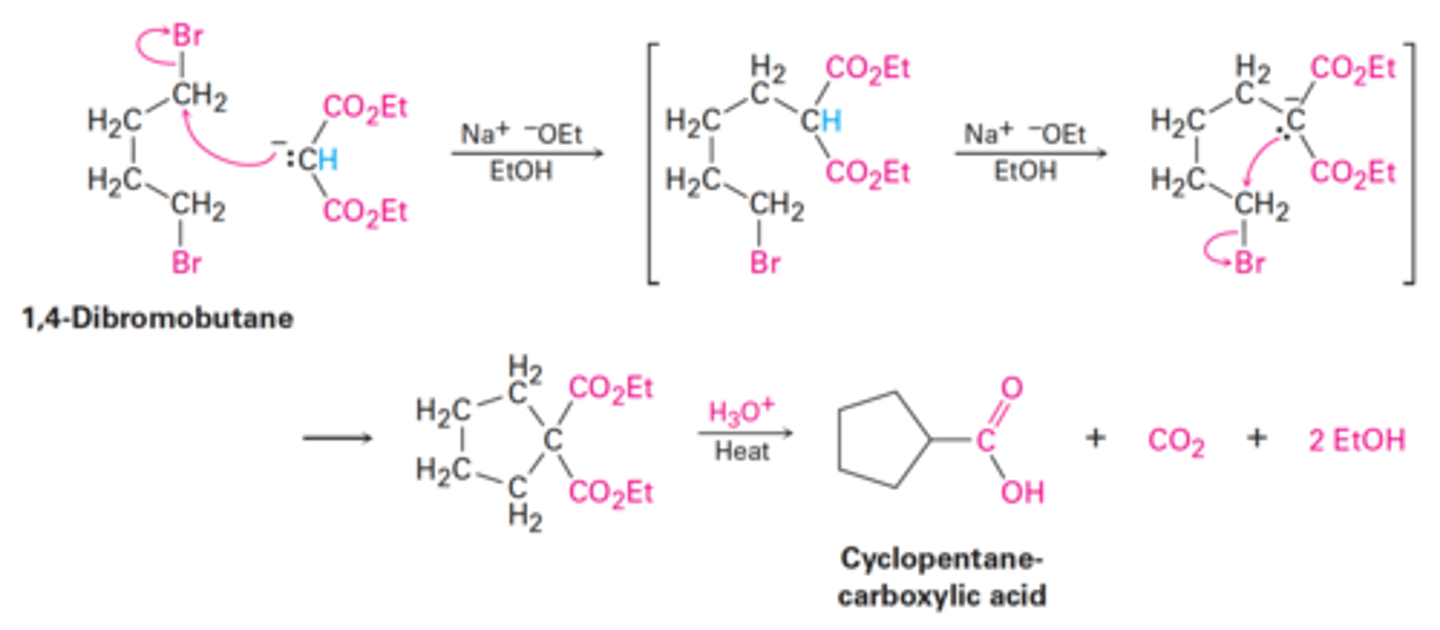
Malonic ester synthesis using diethyl malonate in the presence of two equivalents of sodium ethoxide base (Na⁺ ⁻OEt) to treat an alkane.
The second alkylation step occurs intramolecularly to yield a cyclic product.
Hydrolysis and decarboxylation then gives the cycloalkanecarboxylic acid.
How can cycloalkanecarboxylic acids be prepared?
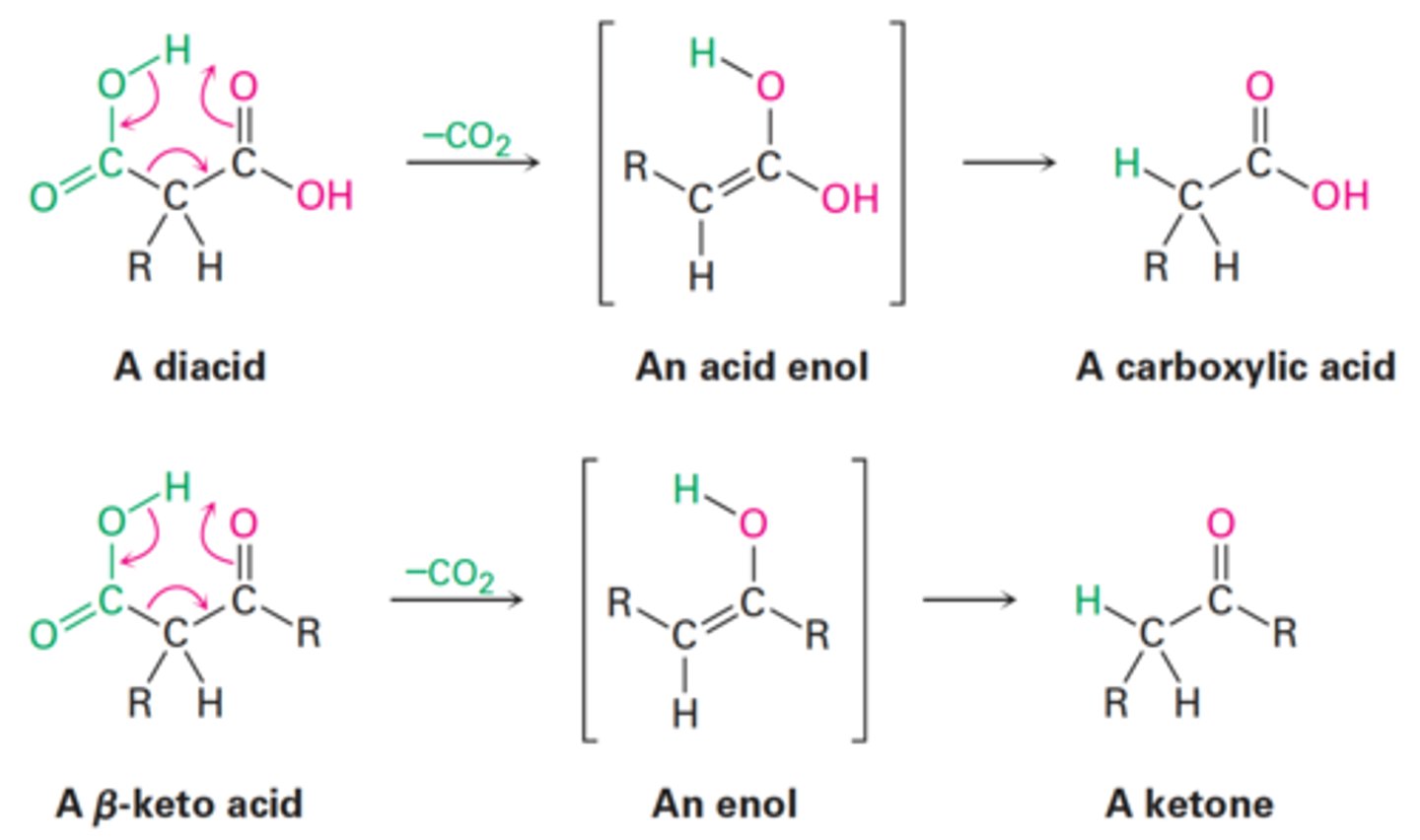
Decarboxylation of β-keto acids and diacid
What is the most critical step of malonic ester synthesis?
Acetoacetic Ester synthesis
Converts an alkyl halide into a methyl ketone with the addition of three carbon atoms.
RX → RCH₂COCH₃
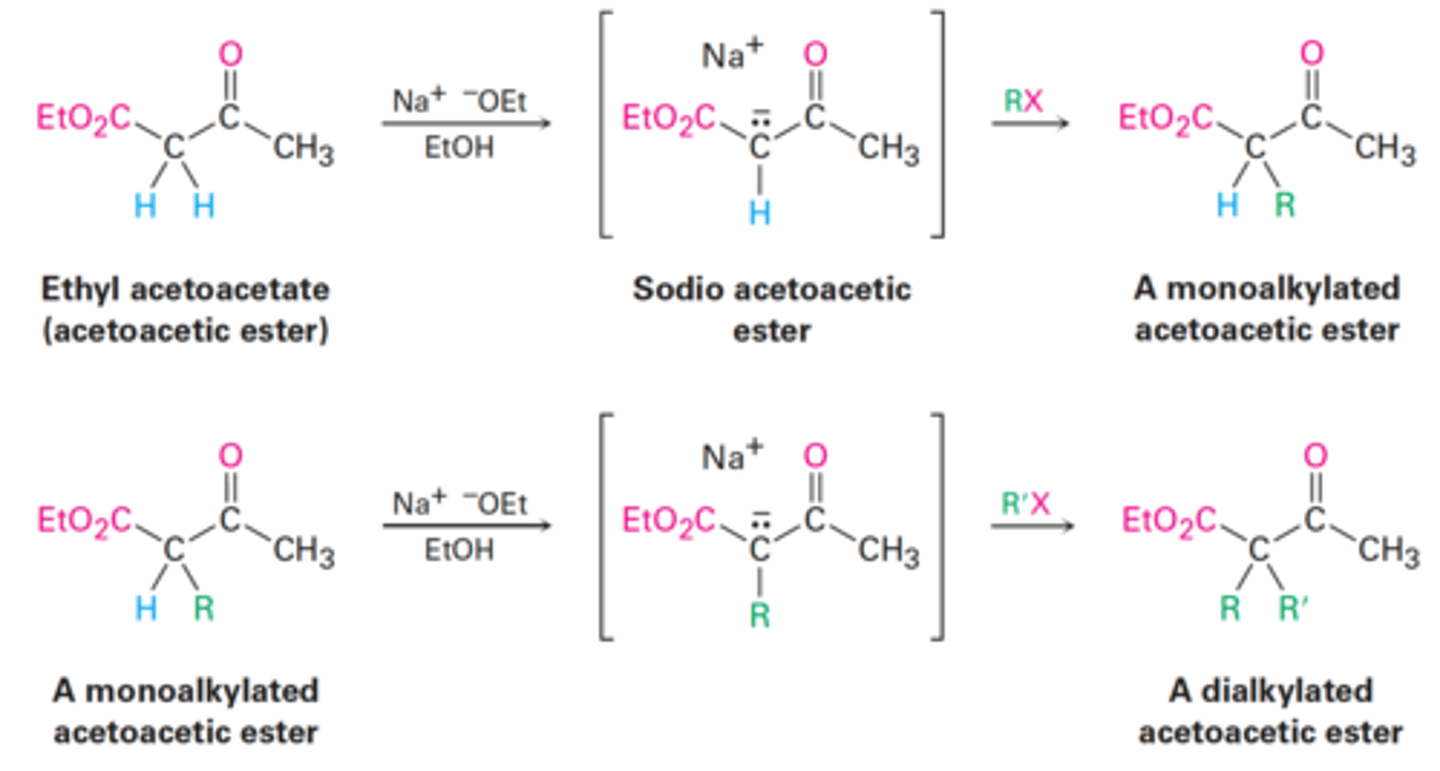
Acetoacetic esters have two acidic α-hydrogens
Why is it possible for acetoacetic ester to undergo a second alkylation step?
Direct alkylation of ketones
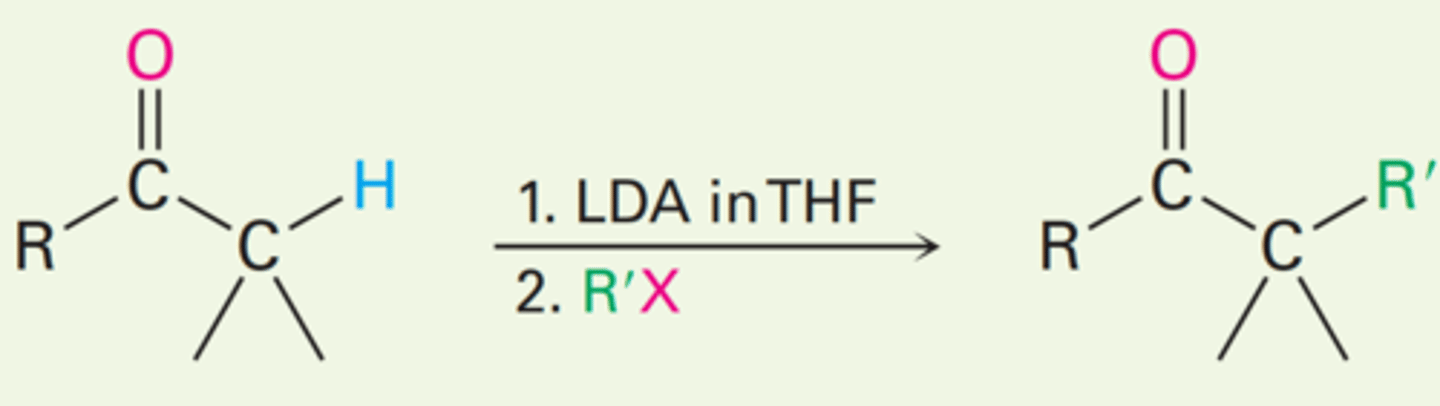
Direct alkylation of esters
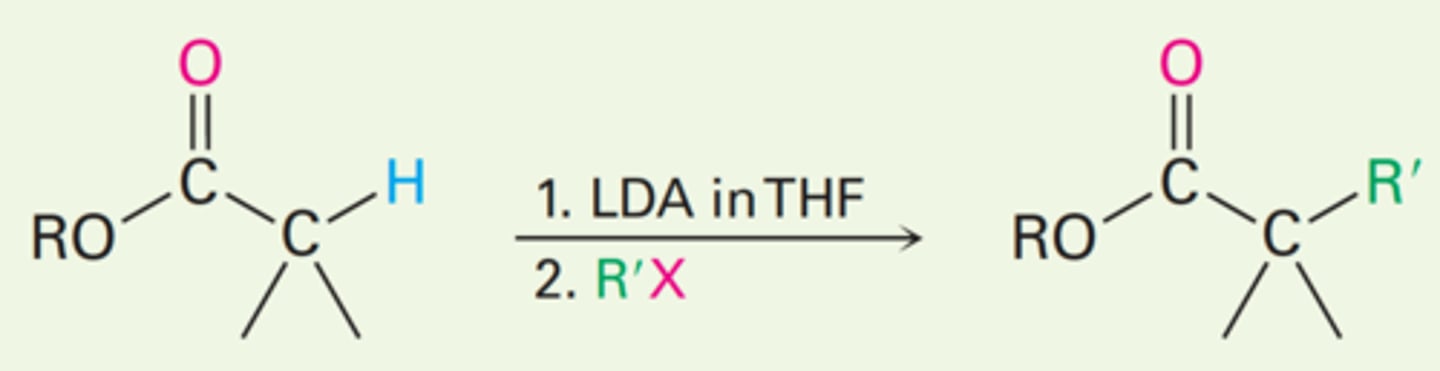
Direct alkylation of nitriles
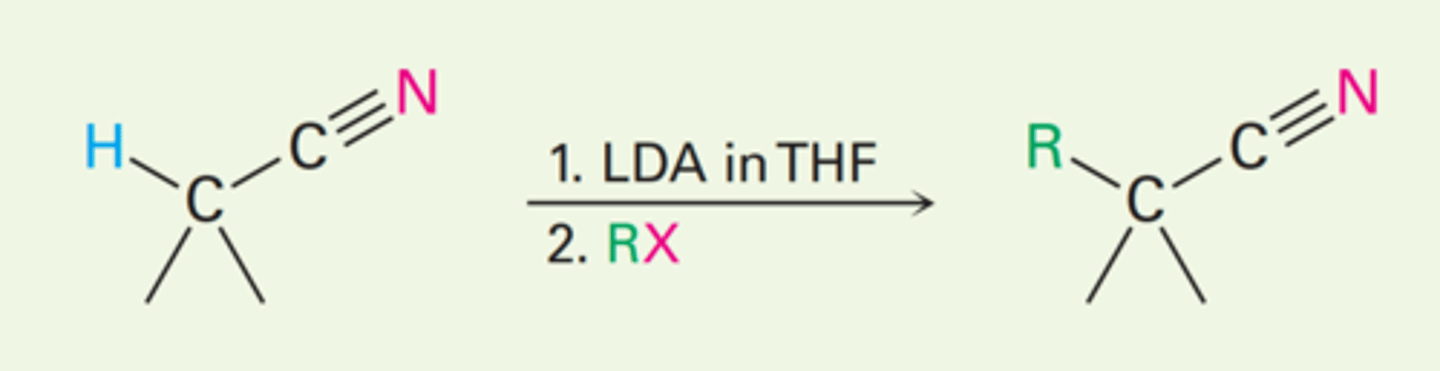
1. LDA, THF
2. CH₃I
What reagents are used to in this reaction?
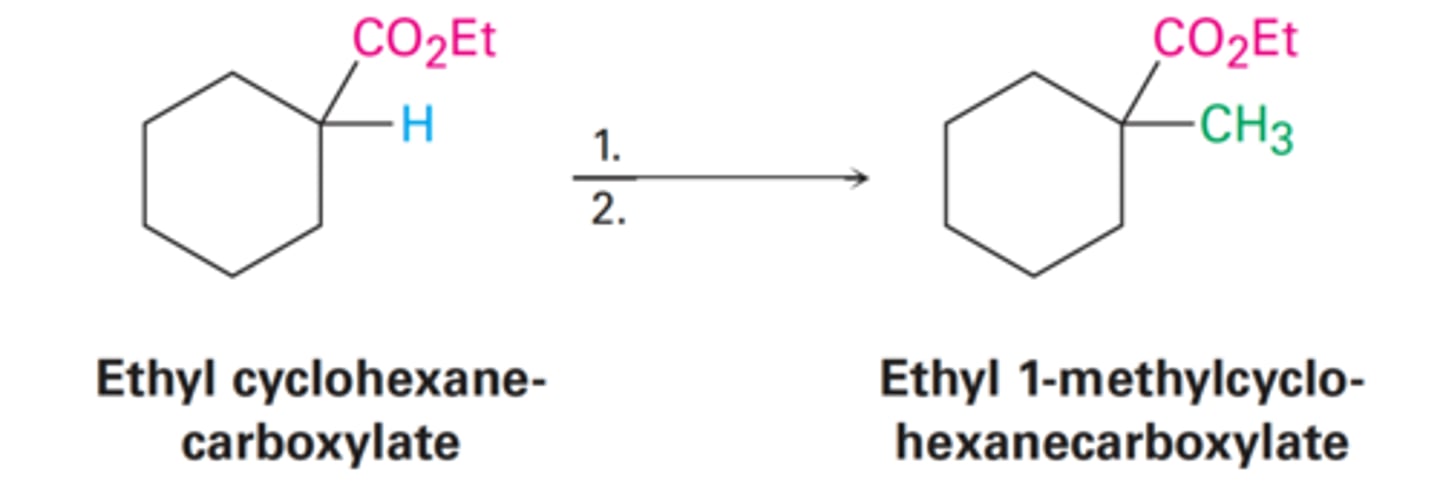
Ethyl 1-methylcyclohexane-carboxylate
- CH₃ replaces the H
What is the yielded product from Ethyl cyclohexane-carboxylate
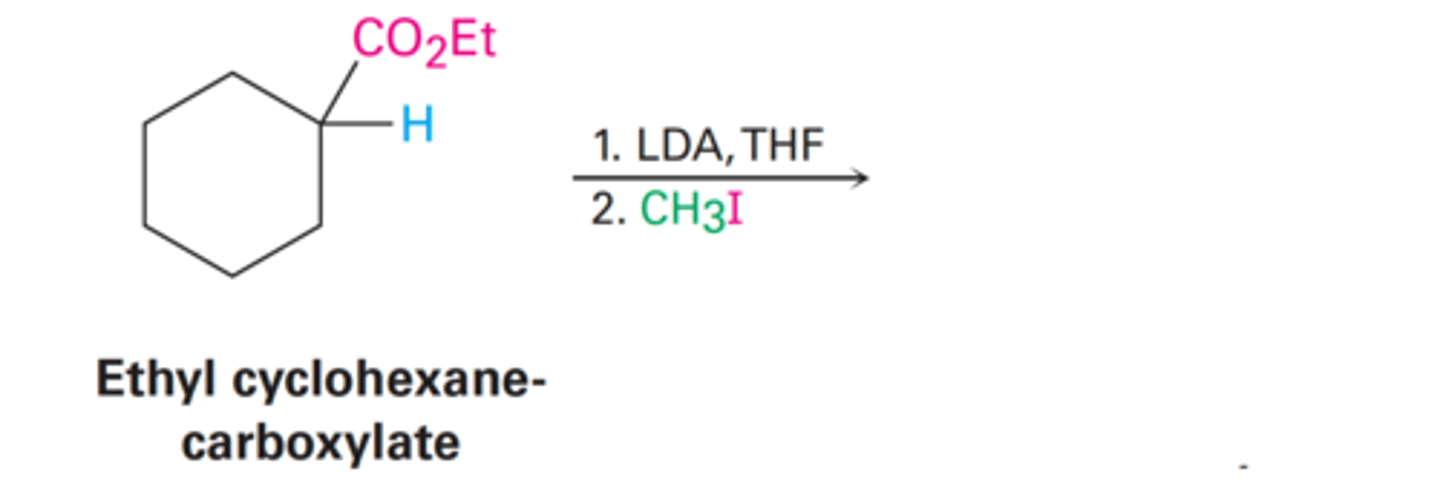
LDA
What reagent is used for alkylation of ketones, esters, and nitriles?
True. Each carbonyl compound can be directly alkylated by LDA.
True or False:
Many carbonyl compounds, including ketones, esters, and nitriles, can be directly alkylated by treatment with LDA and an alkyl halide.
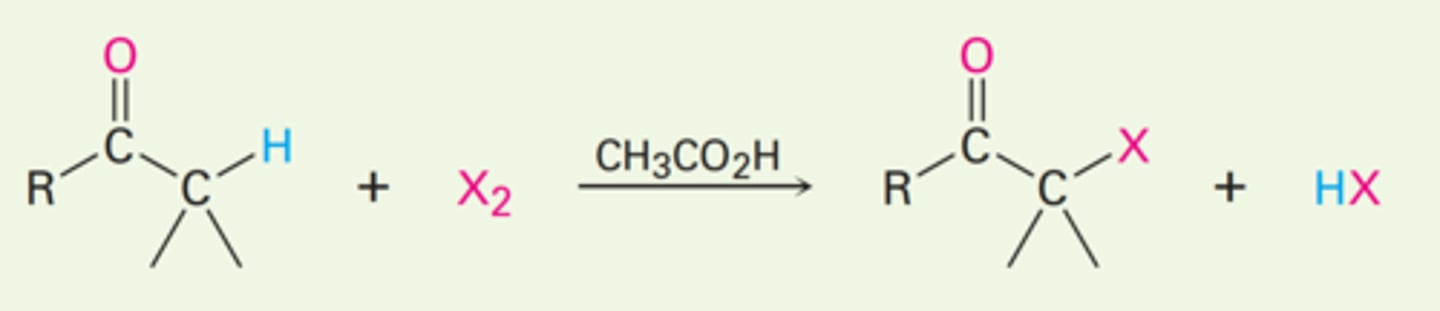
Br₂ | CH₃CO₂H (Acetic Acid)
What reagent and solvent is used in an α-halogenation reaction with ketones and aldehydes
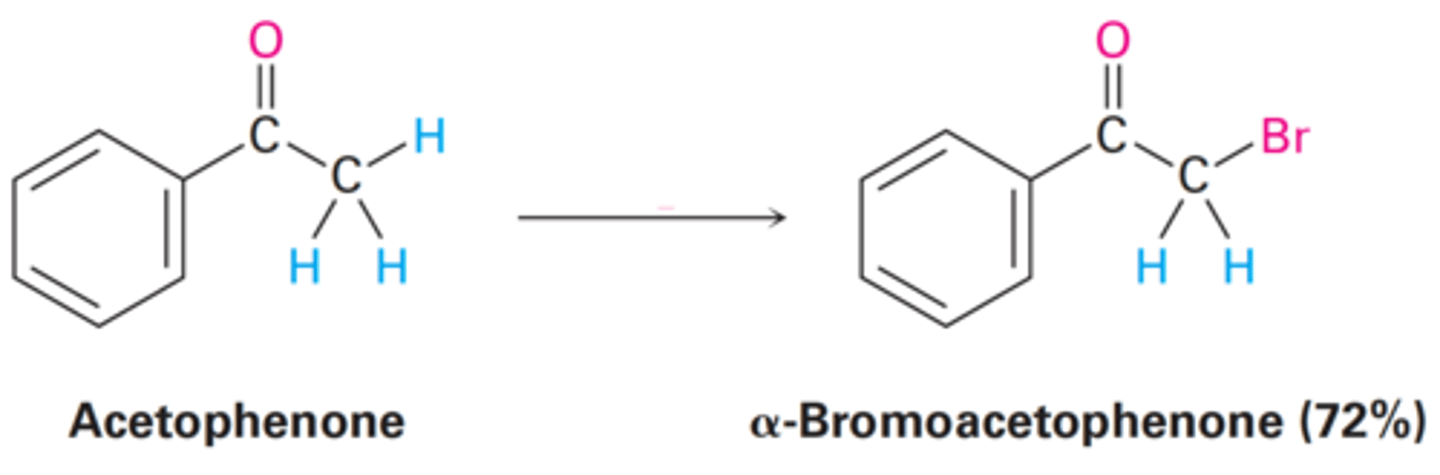
They can be dehydrobrominated by base treatment to yield α,β-unsaturated ketones by an E2 elimination pathway.
Why are α-bromo ketones useful in the lab?
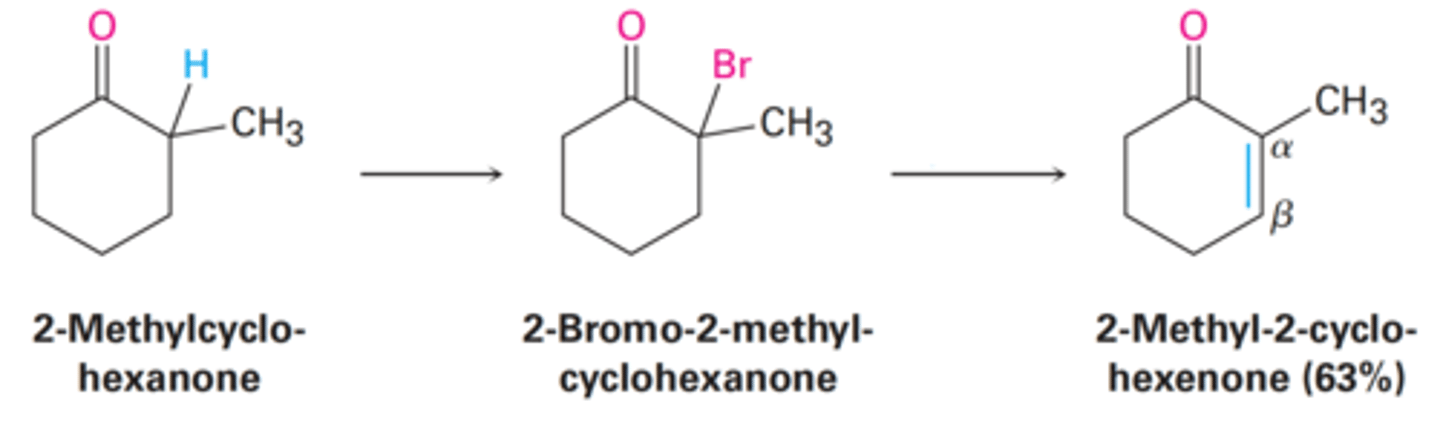
1. Br₂ | Acetic Acid
2. Pyridine | Heat
What reagents and solvents will be used to yield an α,β-unsaturated ketone in an E2 reaction pathway?
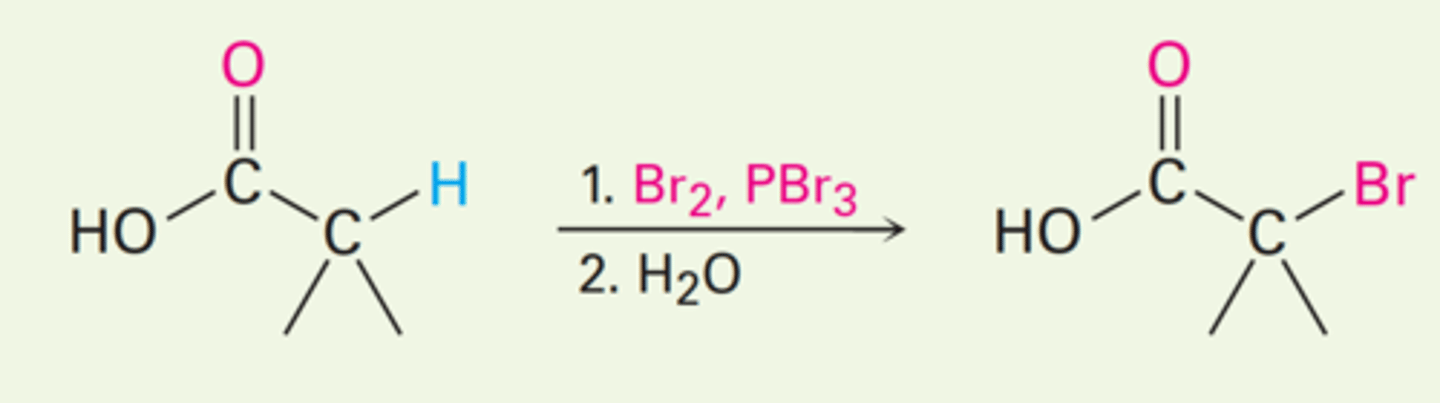
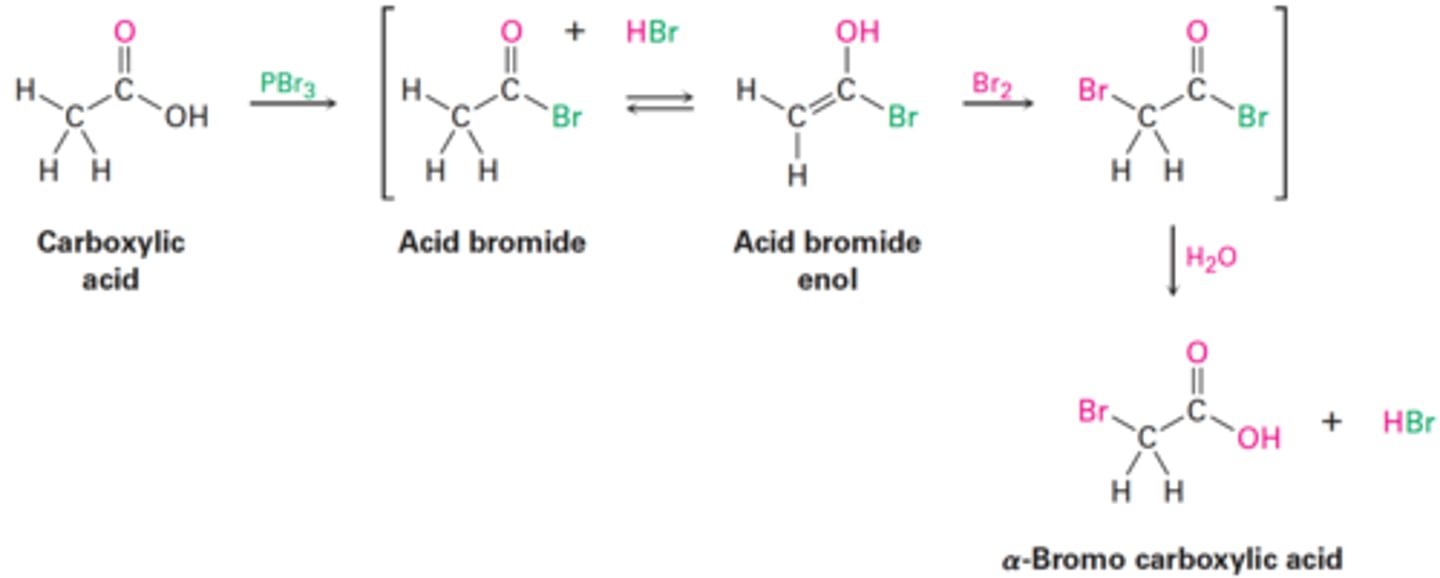
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction Stages
1. Reaction of the carboxylic acid with PBr₃ to form an acid bromide + HBr.
2. HBr catalyzes Enolization of the acid bromide, and the resultant enol reacts with Br₂ in an α-bromo acid bromide.
3. Addition of water hydrolyzes the acid bromide in a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction and yields the α-bromo carboxylic acid product.
1. PBr₃, Br₂
2. H₂O
What are the reagents and solvents used in a Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction?
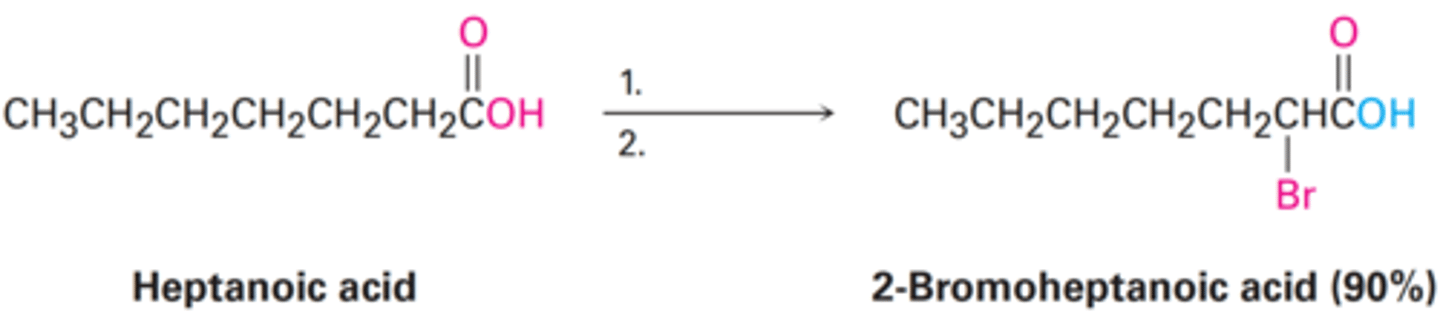
LDA | THF
What is the strong base and solvent used as a reagent to make Enolates ions?
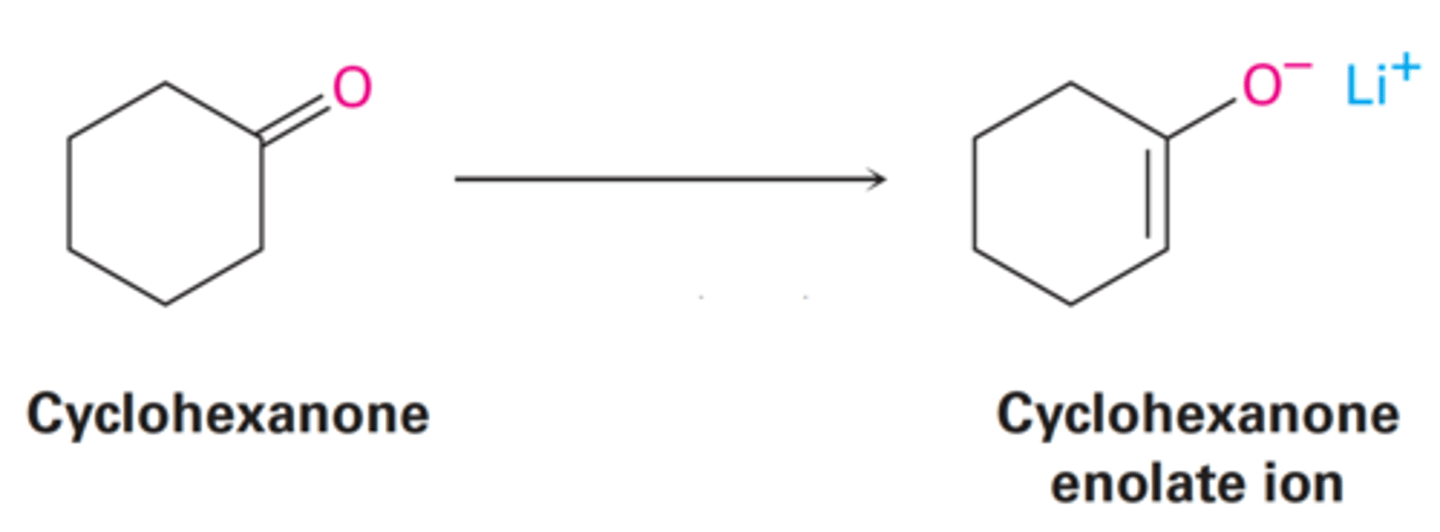
By sharing the negative charge of the two neighboring carbonyl oxygens.
How are enolate ions derived from β-dicarbonyl compounds?
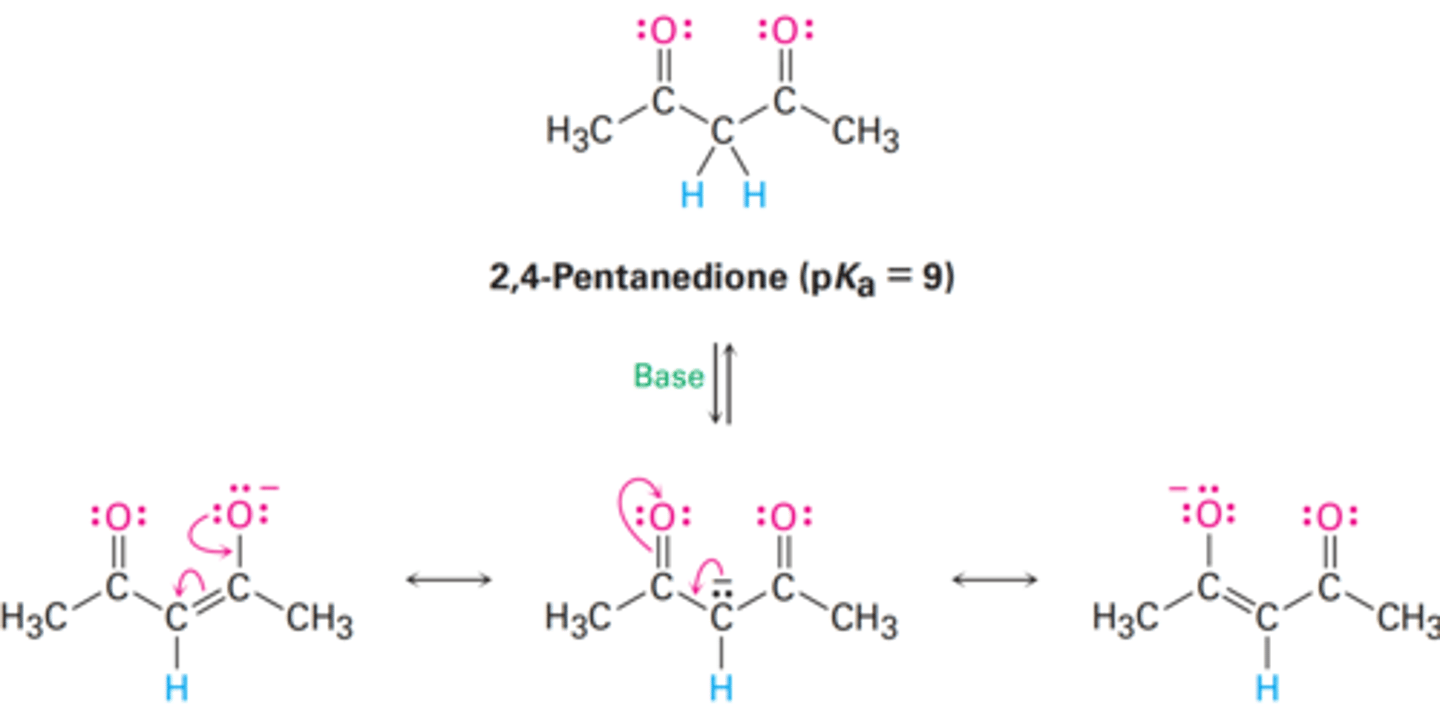
a > c > b
Rank the compounds in order of increasing acidity.
1. Stable solution of pure enolate ions are easily prepared from most carbonyl compounds by reaction with a strong base.
2. Enolate ions are more reactive than enols and undergo many reactions that enols don't.
- Enolate ions are negatively charged, making them better nucleophiles.
Why are enolate ions more useful than Enols?
Yields an enol derivative (1) when reaction takes place on the oxygen of the electrophile.
What do enolate ions yield when reaction takes place on the oxygen of the electrophile?
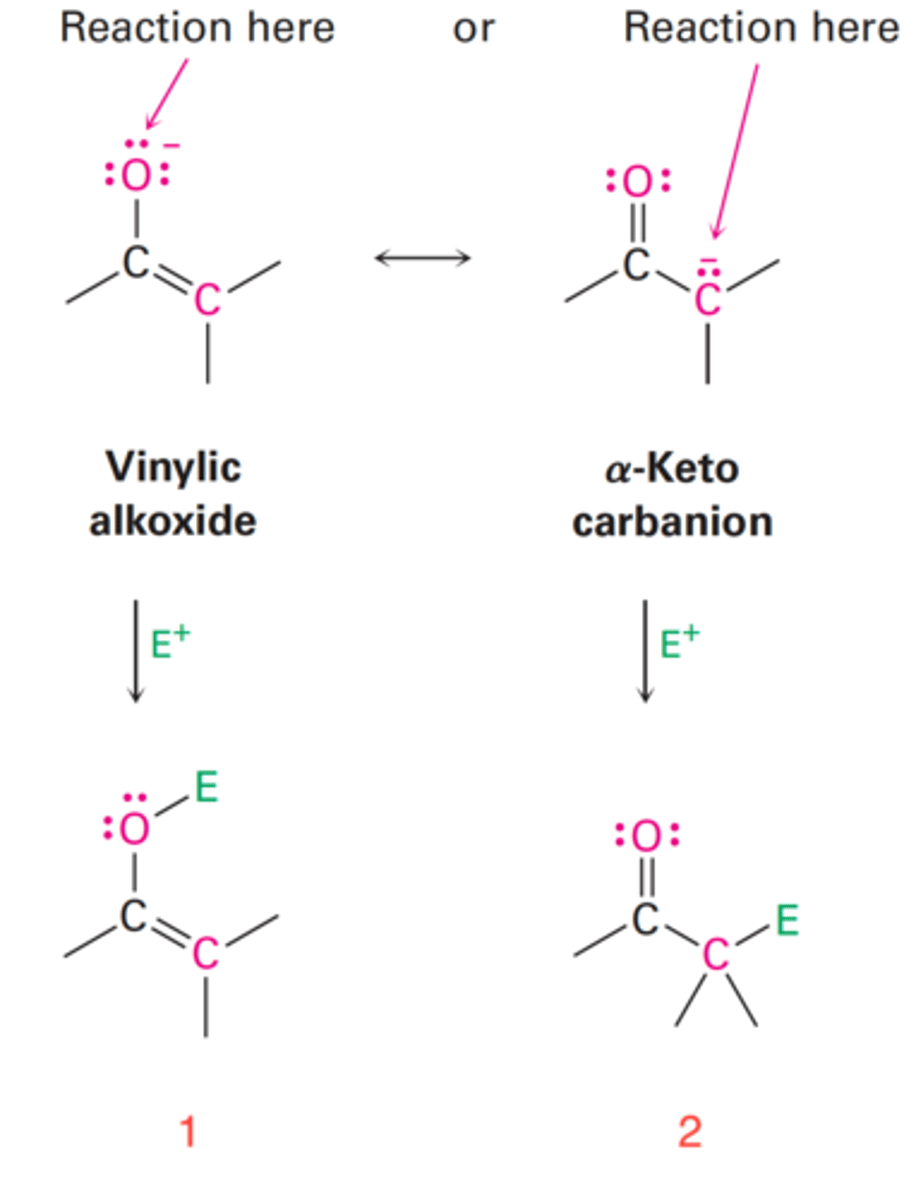
Yields an α-substituted carbonyl compound (2) when reaction takes place on the oxygen of the electrophile.
What do enolate ions yield when reaction takes place on the carbon of the electrophile?
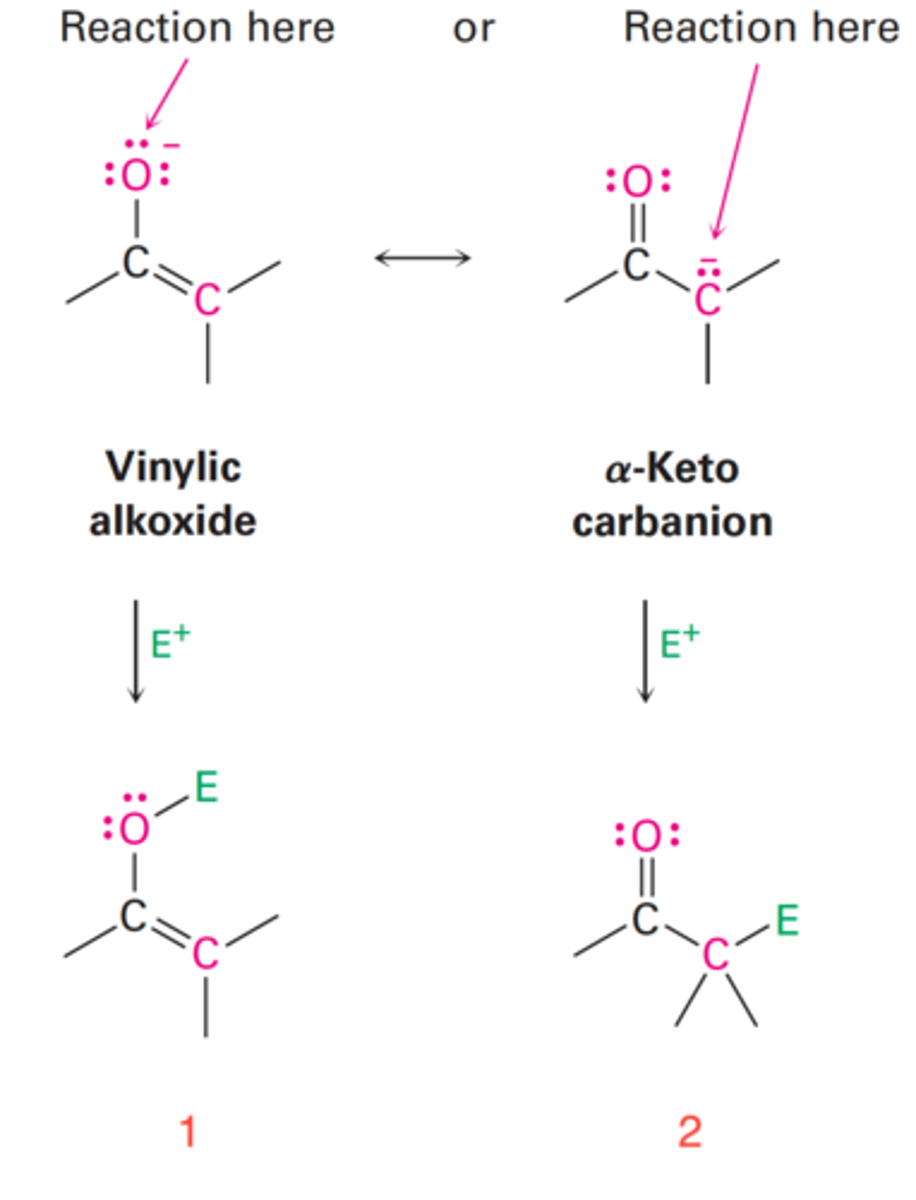
In acid-catalyzed reaction, the proton attacks at the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group and regenerated by base.
In base-promoted reaction, the base attacks at the carbon of the carbonyl group and it can't be regenerated.
Why is a full equivalent of base required for halogenation?
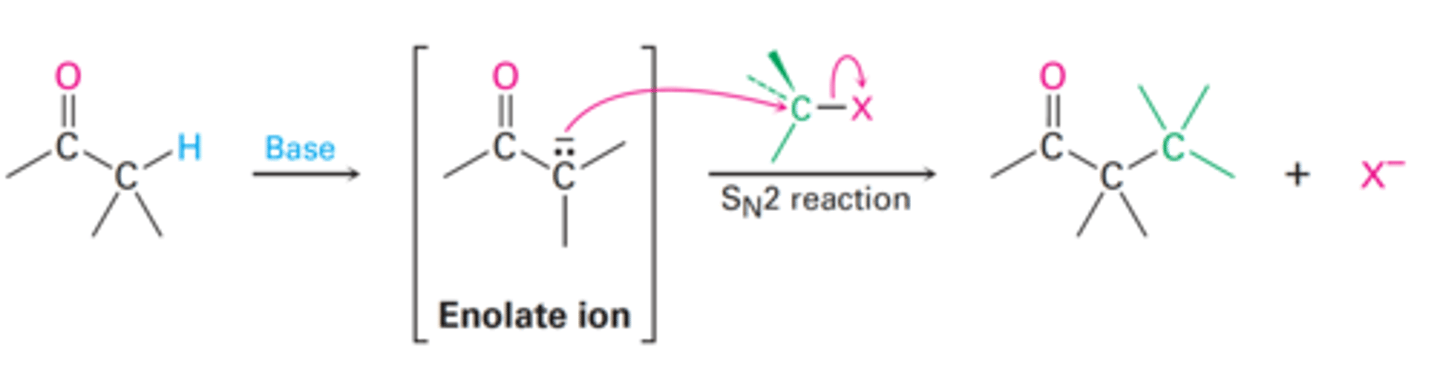
Alkylation by treatment with an alkyl halide or tosylate.
How can enolate ions form new C-C bonds?
Occurs when the nucleophilic enolate ion reacts with the electrophilic alkyl halide in a SN2 reaction and displaces the leaving group.
How does alkylation of enolate ions occur?
Their α-hydrogens are flanked by two carbonyl groups.
Why are malonic esters relatively acidic?
Cyclic mechanism and involving heat and the initial formation of an enol.
How does decarboxylation occur?
Carboxylic acid
What is the final product of a diacid following decarboxylation?
Ketone
What is the final product of an α-keto acid following decarboxylation?
Acid enol
What is the intermediate of a diacid following decarboxylation?
Enol
What is the intermediate of an α-keto acid following decarboxylation?