US History: Imperialism & WWI
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
William Mckinley
The U.S president at the time of the SpAM war. Kept US out of the war for a little while but public outrage forced his hand.
Veleriano Weyler
Spanish general during SpAM war. Was a not very nice person. the “butcher of havana” since he was sent to just squash the rebellion. He would round cubans up and put them into copncentration camps. all out of a camp were consider hostiles.
Joseph Pulitzer
Man responsible for creating yellow journalism.
Jose Marti
Cuban poet exiled to NYC and returns to Cuba years later.
Becomes the head of the Cuban Revolution.
William Herst
Large influence on journalism and yellow journalism.
The Yellow Kid
From Hogan’s Alley comic strip
Publisjed in the New York World Newspaper and the New York Journal
Was used to convey yellow journalism
Balkans
A-H
Serbia
Romania
Bulgaria
Montenegro
Ottoman Turks
Albania
Many religions
Fought all of the time.
Serbia
The perpitrater of Franz Feridand’s Death. (allowe balck hand knwing full well what they will do) Allainced with Germany and part of the Balkins.
Paris
The capital of France and was the “center” (or at least what they wanted the center to be) of the attack for Germany, never got there,
Moscow
Capital of Russia, was the “war mind” of the Russain army.
London
Capital of England, was the “war mind” of the british army.
Nationalism
My country is better than yours.
Actul def: “identification with one's own nation and support for its interests, especially to the exclusion or detriment of the interests of other nations.”
Militarism
belief that government or people that a country should maintain a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend or promote national interests.
Alliance System
the Triple Entente was Briatian, France, and Russia (+ serbia on the side) while the Triple allaince system was Germany Asutraia -Hungary, and Italy.
The Allies
Britain, France, and Russia (countries that fought aganst Germany) Th U.S did lots of trade wiht them.
The Central Powers
Russia, Austria- Hunagry, and Germany.
Mobilization
“the action of a country or its government preparing and organizing troops for active service.”
Schlieffen Plan
The German plan of invasion where the german forces would all converge on the French capital, this did not go according to plan.
Trench Warfare
A defensive statagie taken up by al who were in the battle.
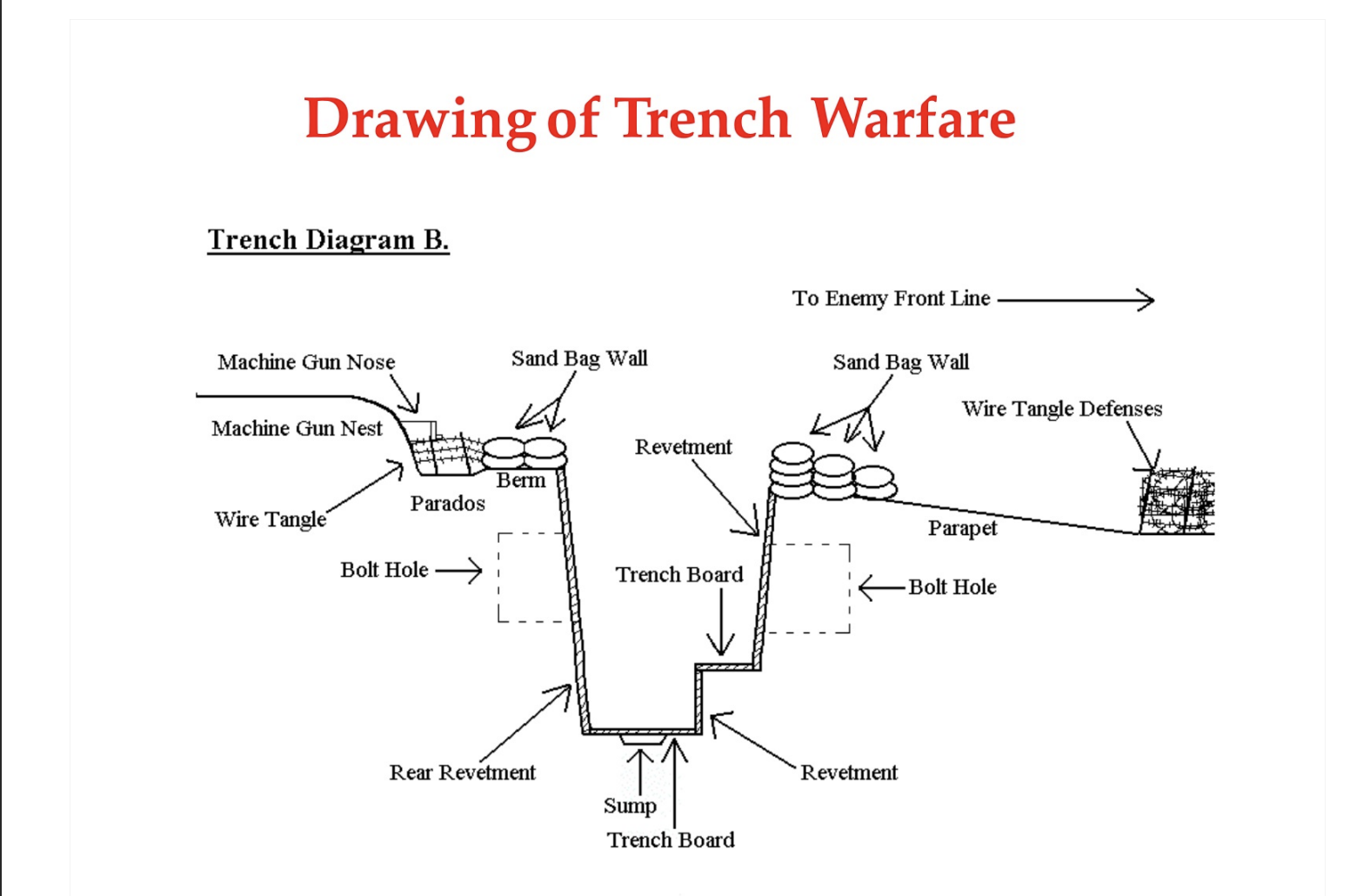
Western Front
Attack from germany though Beligum, this is where the fight with france took place.
Eastern Front
The front with Russia that soon disappeared after Russia backed out from the war.
Havana
less than a week later after the De Lome letter the Havana harbor blows up killing 266 American sailors.
Reports say it was a bomb or torpedo and the consensus during the time that the spanish did it (in reality they probably didn't)
Manila
Capital of Panama
Guantanamo Bay
The bay and naval station of the US in Cuba. US still has it and it has a lot of dark history.
Teller Amendment
The US had no intentions to permanently take over or dominate Cuba except to restore peace and order.
The US promised to leave the island as soon as the war was over.
Platt Amendment
Treaty made between US and Cuba to protect its independence from foreign invasion.
Treaty of Paris of 1898
Offical end of war with Spain.
US got….
Cuba (was granted independence afterwards)
Puerto Rico
Philippines
Guam
Spain got…
20 mil from US
Emilio Aguinaldo
Theodore Roosevelt
Sec of Navy
Gov of NY
Rough Rider
Pre of US (1901-1909)
Progressive
John Hay
American secirtary of state who negotated the treaty with Panama to build the Canal.
Suez Canal
In Egypt
Built between 1859-69
Connects the Med. Sea to Red sea & Indian Ocean
Designed and built by the French under Ferdinand de Lesseps
Tanks
These giant machines were supposed to end trench warfare but were very unreliable, slow, easy to destroy, and too few to actually do anything.
1st Battle of the Marne
The battle when germans went around france and to get it from the otherside.
No-Man’s Land
The space between the front line trenches. There was no life there and no shelter. Lots pf men sent over the top of trenches died there. Less than 1% survived.
Lusitania
A large British passanger ship that was sunk by a german submarine after the Germans said they would stop. U.S. tourists were on said boat.
Zimmerman Note
German note to Mexico, “hey mexico, help us with the war and then we will help you get claifornia and texas back” and mexico was like, “germany are you stupid?”
Selective Service Act
Where all 18+ men are required to register for the draft.
Franz Ferdinand
The crown prince of Austrai-Hungary that was mudreded by Black Hand, caused the start of WWI.
Black Hand
A Terrosrist organization in Serbia that was responsible for the murder of Franz-Furdiand.
Gavrilo Princip
One of the members of the Black hand and shot France Ferdidand.
Manfred von Richthofen
The Red Baron
The “Red Baron”
Captan Manfred Von Richthofen was the “red Baron”. This german pilot was one of the most renowned and deadly aierl and dogfight pilots. He was shot down by british soliders and was given a full military funeral to honor his amazing skills and devotion to his country.
The Flying Circus
The name of a flight groupo that the red baron was in. This was a German pakc. they wiuld fight in a pack in dogfights.
Vladimir Lenin
The Bolshevik leader who overthrew the Russian government and removed Russia from the war
Bolcheviks
This was the ruling or prodomanemt class in Russia before the war but during the war the communist uprising made this group less then 15%. These people were in support of the Czar.
Kaiser Willhelm
The emperor of Germany during WWI
Czar Nicholas
The Czar (emperor) who abdicated during the Russian revolts in WWI
Edith Cavell
British Nurse who went to Belgium to help injured soliders. she would heal them and then try and send them to there home countries, regardless of where they are from. This was found ouyt by German soliders and they gave her a trail and executed her in 5 minites. Her story was fuel to the fire for the US joining the battle.
Philippe Bunau-Varilla
HE was the guy that conviced US to take over the Canal project.
Panama Canal
The canal in Panama connects the Atlantic and Pacific without having to go around South America.
Was attempted by Ferdinand De Lesseps but failed due to many issues (Malaria, snakes, etc.)
It was finished by Teddy Roosevelt about 10 years after.
During this time, there was the Panamanian revolution.
Panamanian Revolution
The French back up on the offer of the canal and now the U.S tries to take cover but Columbia is not to happy about this.
The U.S. presses the Panamanians to revolt, causing them to claim there sovereignty
The U.S. Builds canal and gives them a list of requirements that Panama must follow due to the U.S help.
This includes Guantanamo Bay.
Enrique DeLome
The ambassador From Spain during SpAm war.
He wrote a letter back to a friend in cuba and it was intercepted and opened.
the Letter was found to have insults to the American peoples regarding there actions on the spAM war.
He quickly resigns after giving an a apolgy.
The DeLome Letter
2/9/1898: Letter from Spanish Ambassador-> Spain, intercepted by US
Insults McKinley (weak for favor of the crowd)=outrage in US
Roosevelt Corollary
After Spanish defeat, the US declared that it would attack central and south america if they had funny business.
Hay-Banau-Varilla Treaty
The treaty which gave America the rights to the Panama canal.
Woodrow Wilson
President of Princeton
Gov of NJ
Pres of US (1913)
Was kinda a bad guy
Vittorio Orlando
Italian guy at the treaty of Versailles.
Victor Berger
Congressman who was opposed to war
Congress refused him multiple times for his reelection and was evenutly convicted under the espionage act for refusing war.
Eugene Debs
Was an anarchist and thought that US should not join war. Was yeeted into prison yet again
Jeannette Rankin
First women elected to the US congress (before women had aright to vote) and pacifist who voted against both word wars.
Espionage Act of 1917
Prohibit interference with military operations or recruitments
to prevent insubordination in the military
to prevent the support of US enemies during war
The sedation Act was simular. (no profane, disloyal, abusive, scurrilous langue)
Armistice
“an agreement made by opposing sides in a war to stop fighting for a certain time; a truce.” This was the day the war ended. This has now turened to veterans day in the US.
Treaty of Versailles
Meeting where leaders of US, France, Britian, and Itlay met up to make Germany pay after WWI.
Henry Cabot Lodge
American senator from MA. He opposed the treaty of vercie and didn’t want it to be ratified. He was the reason it was never ratified.
Self-determination
Where smaller countries or offshoots of larger countries may decided to be independent and separate themselves from the large country. For example Ukraine from Russia.
Sussex Pledge
The pledge the Germans made to stop submarine warfare and shooting of passnager ships.
Great White fleet
1890s: Under Sec.Of the Navy, Theodore Roosevelt, US begins to build modern navy
Made a whole bunch a big white boats
What is Imperialism?
The idea that (your) country is better
What does a country need to engage in it?
Military (especially a navy), ports, people, and lots of money.
Why was the US interested in Imperialism at the end of the 19th century/early 20th century?
Monroe Potrone: 1823
Manifest Destiny
And an Abudnece of goods
Monroe Potrone: 1823
No new European colonies in the western hemisphere (this was said by the U.S, but we didn’t have the military to back it up)
But lucky enough, the British navy wanted this too and enforced it for us :)
Manifest destiny impact on Imperialism
This was American Progress and the U.S said “shouldn’t it be everywhere?”
Overabundance of good impact on Imperialism
The U.S has so many goods but no where to trade them too… so we need to spread America so we have more to trade!
The U.S market was saturated due to so many goods
Pressure was put on gov to make new connections and markets.
Alfred Mahan
Naval Officer
Taught at Naval War collage in Newport, RI, & at the Naval Academy in Annapolis, MD
Convinced US leaders (like TR) that we had the power to be the world leader and need to use it.
Jingosim
Name for some one with extreme nationalism (to a problematic point)
How was the SpAm War an example of imperialism?
What is yellow journalism?
Published information that was highly emanational, speculative, sensationalized, and therefore often not true.
Used by New York World Newspaper and the New York Journal mostly.
What were the significant events/incidents/occurrences that lead to the US decision to go to war with Spain?
German Submarine warfare: Lusitania!
Edith Cavell
Belgium destruction
etc.
What were the significant battles in the war (what type of power decided the war in the US’s favor?)
battle of the marne
SCheiifer plan
etc.
How did US goals change from the beginning of the conflict to the end? (hint: think Teller Amendment and Platt Amendments, and think what the US wound up with at the end of the war compared to what it originally went to war over)
In the beginning, they wanted to be neutral, but it became very hard as time progressed, and they eventually sided with the Allies.
Things like the sinking of the Lusitania, British propaganda, and Germany’s impact on Belgium contributed to this.
How was the building of the canal an example of imperialism?
It was a new invention or a forward thinking of engineerging to modernize and connect the world.
Who first tried to build a canal across the Isthmus of Panama?
French Man named Ferdinand de Lesseps
Why did the first canal across Panama not succeed?
Because they were trying to make a sea-level canal when Panama is very mountainous with uneven ground and environments + the mass amounts of dangers (Mudslides, snakes, diseases, etc.)
Why were Teddy Roosevelt and the US gov’t so interested in the canal?
Roosevelt was very interested in the Canal due to its emenec power over where/when/how products and information is shipped. It was also a gave them an extremely powerful military base we still hold on to today.
What was the ‘man-made’ obstacle to the US building the canal?
Columbia!
How did TR ‘overcome’ this obstacle?
By making hints/being the straw that breaks the camels back for the Panama revolution which made Panama sovereign and be able to have relations with the U.S.
What was the long-term significance of the canal for US foreign policy?
The U.S got lots of benefits at first
They controlled the Canal for a little while
And got a pretty snazzy navy base still in their possession today.
Alliance system: dominos
When Serbia was in trouble they went to Russia, which called on, France, which called on England and then Italy and so on. Dominoooooooooooooooooos
Russian Mobilization
Stalemate
“a situation in which further action or progress by opposing or competing parties seems impossible.” this is what Trench warfare was.
Artillery: creeping barrage
Artillery bombs would fall along a pre-determined line and then slowly “creep” forward toward tqord the enemy trench. Troops hide behind the explosion as a defesnive while attacking.
Poison Gas
First used by German but was not utilized well. This opened the flood gates for gas warfare. (the Germans did not pay attention to wind direction so they often poison themselves)
Aircraft: Dogfights & Reconnaissance
First used for reconnaissance but radios weren’t a thing so it was difficult. They were then sed for arial fights and minimal bombings.
Why’d the US wait so long to get involved?
It wanted to stay neutral and Widrow Wilsion wanted to get reelected and by keeping them out of war, it allowed him to be “the man who kept us lut of war” and then he put us in the war…..
Propaganda in WWI
All info the US got was british propaganda; propaganda was a big thing.
How did the war end in WWI?
Germany was pushed back to its borders and finally surrendered. Germans pwed ALOT of money so they just printed it, but it made their economy tank. They also had to admit that they were the ones who started it…
Who won, who lost WWI?
“The allies” won and Germany lost.
Why did they loose and why did they win in WWI?
The german’s king was sent of into exile after the germans forged there last attack on France and became spent soon after. they failed in this attempt and were pushed back to their borders and then signed a peace treaty.
Who were the ‘big’ representatives in the Versailles Peace Conference? Where were they from?
Lyoyd George (britian) Georges Clemenceau (France)
Wilson’s 14 points (know the main ones)?
end Secret Treaties
Freedom of the Seas
Disarmament
Free trade (no tariffs)
Border Adjustments (self-determination)
League of nations (To settle disputes between countries)