Amino Acids, Protein Structure, and Function: Comprehensive Review for Biology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Amino Acids
makeproteins
Structure of Amino acids (4)
1. α amino group 2. α carboxyl group 3. α carbon 4. side chain R group
Chiral
4 different groups attached to α carbon
Stereoisomers
2 different amino acid forms L R handedness
L vs. D amino acids
Left vs Right
Peptide bonds
How amino acids are linked together to form proteins
Side chain
Structure on the amino acid that determines the identity/properties of the amino acid
Nonpolar/hydrophobic amino acids
Glycine (Gly), Alanine (Ala), Valine (Val), Leucine (Leu), Isoleucine (lie), Methionine (Met), Proline (Pro), Phenylalanine (pue), Tryptophan (Trp)
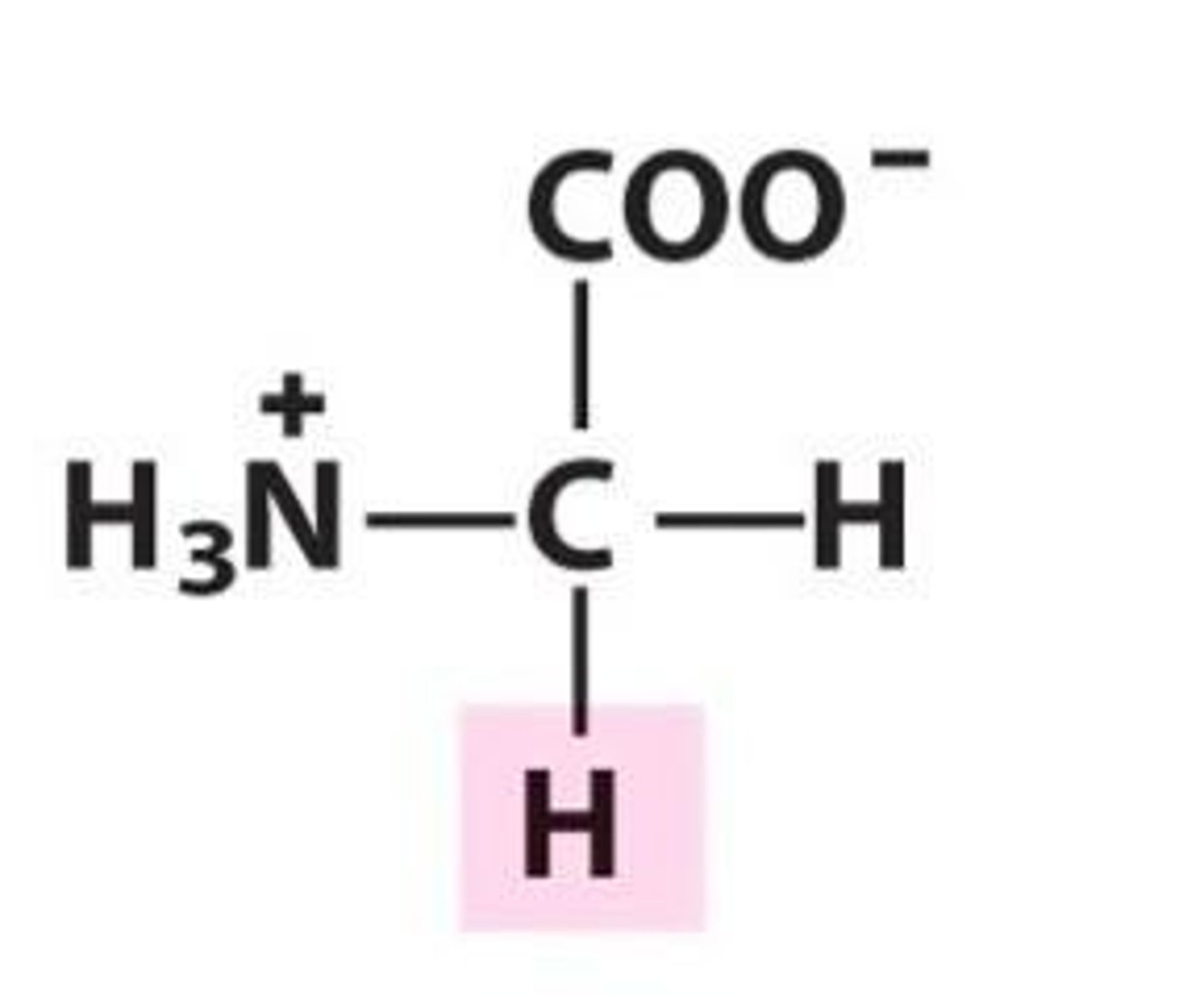
Polar, uncharged amino acids
Serine (S), Threonine (Tur), Asparagine (Asn), Glutamine (Gln), Tyrosine (Tyr)
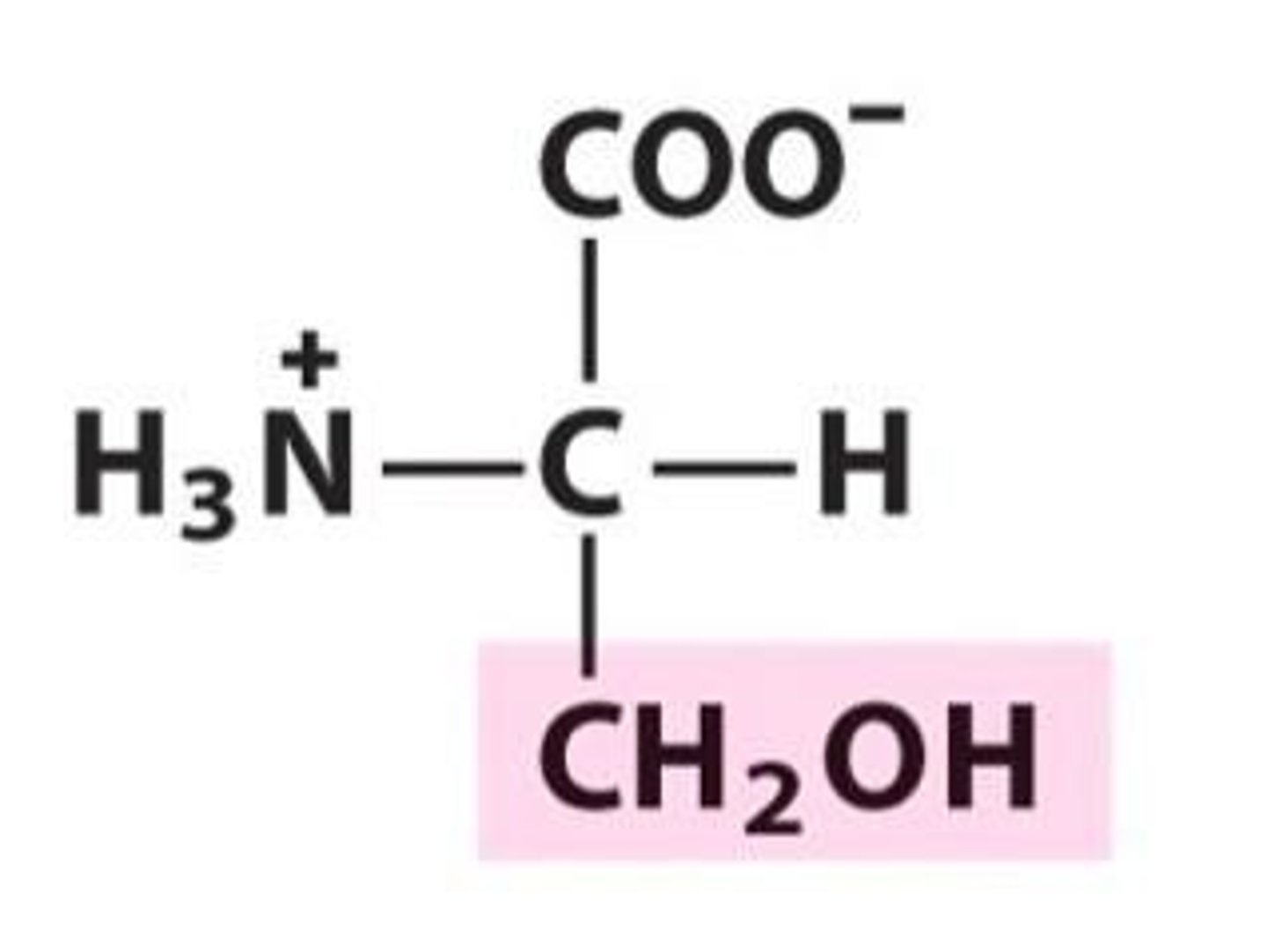
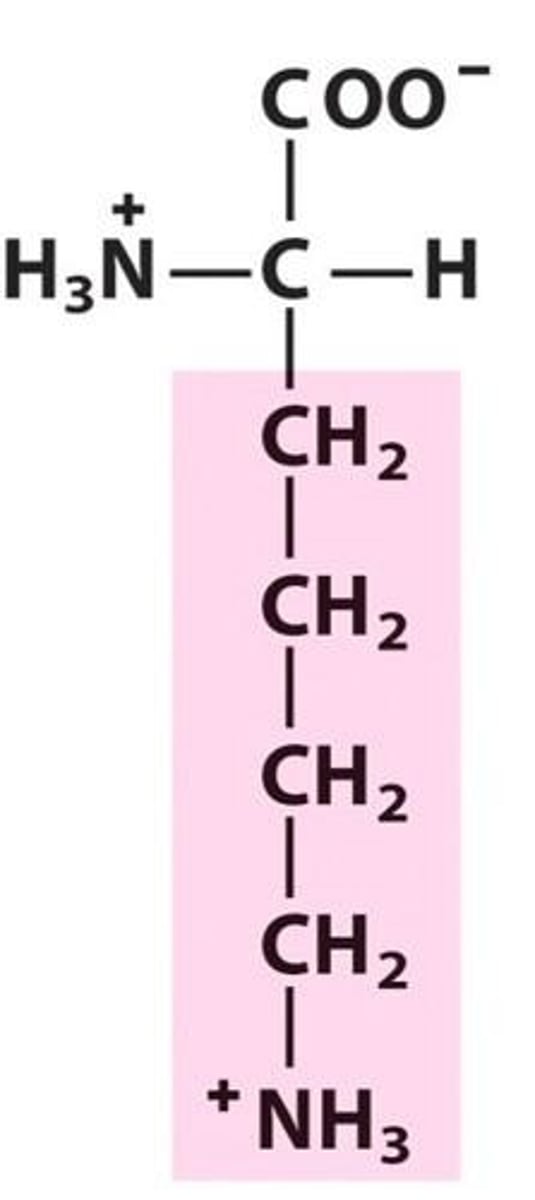
Basic amino acids
Lysine (Lys), Arginine (Arg), Histidine (His)
Acidic amino acids
Aspartic Acid (Asp), Glutamic Acid (Glu)
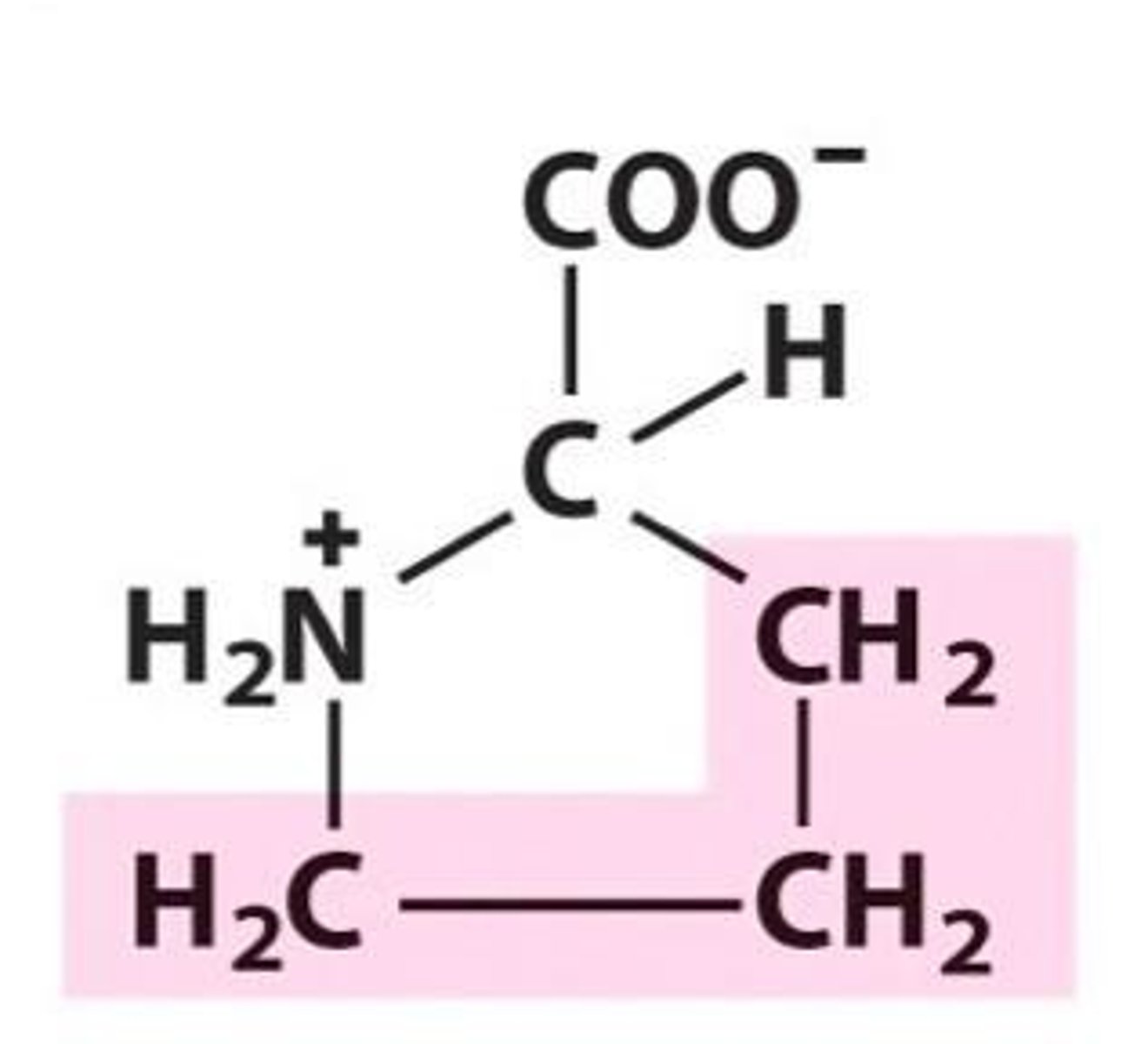
Aliphatic
It has no aromatic ring
Diprotic
Amino acids are diprotic, has 2 pKa's in 2 buffer regions at different pH levels
Isoelectric point (pI)
pH when net charge is 0
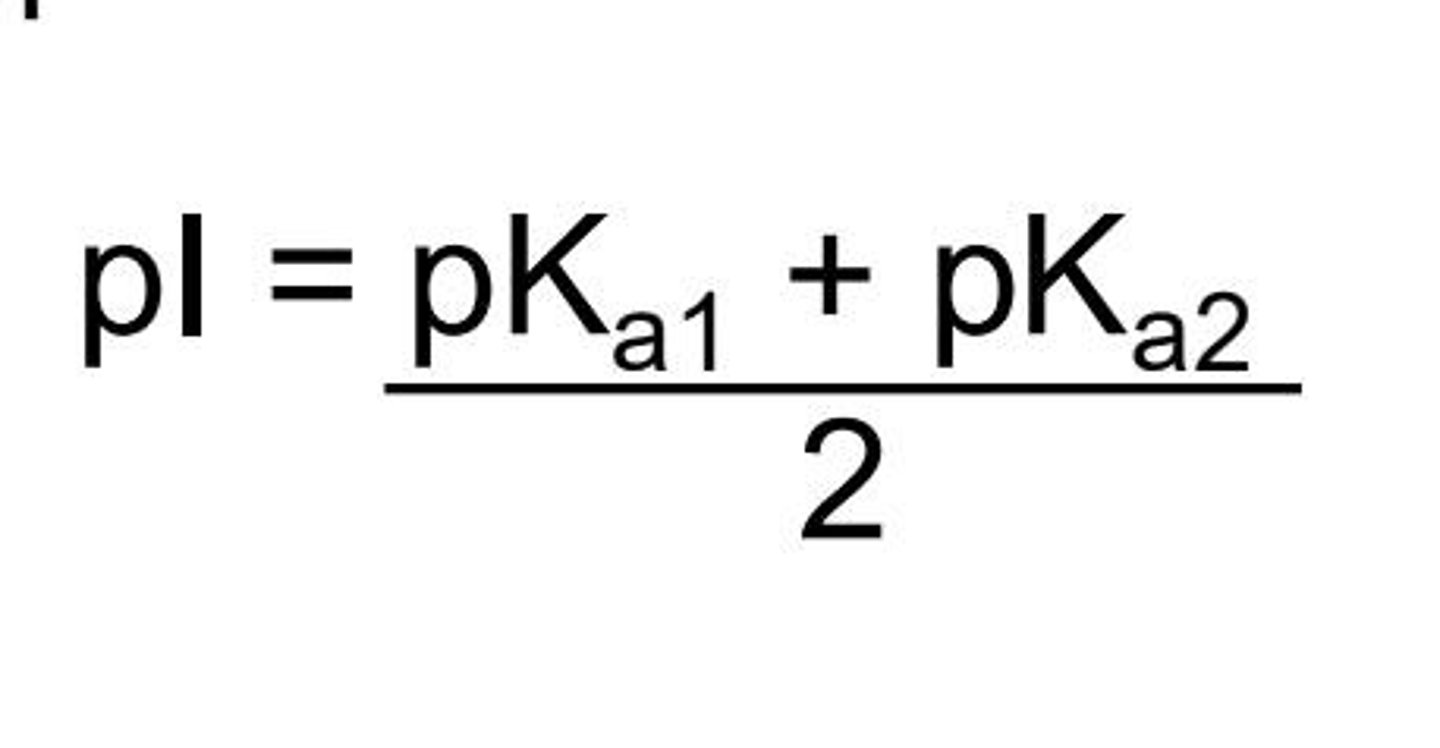
pI of Leu
6
pI of Met
5
Peptide bond
Covalent bond between the a-carboxly group and α-amino group of different amino acids
What is lost when a peptide bond forms?
H2O
Peptides vs polypeptide chain
peptides are links of serval amino acids and polypeptide chains are links of >100 amino acids, making proteins
N-terminal vs C terminal
1st amino acid vs Last amino acid
Function in proteins
Determined by Structure: SEQUENCE -> STRUCTURE -> FUNCTION
Effect of mutation from Glu to Val
Affects primary structure
Why is sickle cell more common near the equator?
Mutation against malaria
Psi vs Phi bond
C-C vs C-N
Bond stabilizing the turn of the alpha Helix
H bond
Primary structure of a protein
Determines the 3D structure of the protein