Biology P1 exam questions
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Which structure is found in plant cells but not animal cells?
Cell wall (1)
Which of these is a communicable disease?
Measles (1)
What is the main purpose of white blood cells?
To produce antibodies (1)
Describe how you would prepare a slide of an onion cell and observe it under a microscope. Include any safety precautions. (6)
Peel thin layer from inside of onion (1)
Place on slide and add iodine stain (1)
Use coverslip to avoid bubbles (1)
Place slide on stage and focus using low-power lens (1)
Switch to high-power lens to see detail (1)
Safety: avoid glass cuts / use stain safely (1)
Enzymes are biological catalysts.
a) What does “optimum temperature” mean for an enzyme? (2)
The temperature where enzyme activity is highest (1) because particles move faster and more collisions occur (1)
b) Describe what happens to an enzyme if the temperature is too high. (2)
Enzyme denatures at high temperature (1) – active site changes shape and substrate can’t bind (1)
Explain how the body defends itself against pathogens. Include physical and chemical barriers and how white blood cells respond. (6)
Skin acts as a barrier (1)
Mucus and stomach acid kill pathogens (1)
White blood cells engulf pathogens (1)
White blood cells produce antibodies (1)
Antitoxins neutralise toxins (1)
Memory cells create faster response next time (1)
Write the balanced symbol equation for photosynthesis. (2)
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ (2)
Describe one way to increase the rate of photosynthesis in a greenhouse. (2)
Increase temperature, CO₂, or light intensity (1); any correct example (1)
Explain why the rate of photosynthesis increases with temperature, up to a point. (2)
More collisions and enzyme activity increases (1); but too high denatures enzymes (1)
A student observes a slide of root hair cells.
a) Explain why root hair cells are specialised for absorption. (3)
Large surface area for absorption (1)
Thin membrane for short diffusion distance (1)
Contains many mitochondria for active transport (1)
b) Describe how to prepare and use a microscope slide to view the cells clearly. (3)
Use forceps to peel a thin layer of epidermis (1)
Add a drop of water/stain (e.g. iodine) and place coverslip (1)
Use light microscope; focus using low then high power objective (1)
You are investigating the effect of pH on amylase activity.
a) Describe a method to measure how pH affects the rate of starch breakdown. (4)
Add iodine to spotting tile (1)
Mix starch and amylase in test tube (1)
Add buffer of known pH (1)
At regular intervals, drop mixture into iodine and observe colour change (1)
b) Predict and explain the effect of adding acid to the reaction mixture. (2)
Acid lowers pH (1); enzyme denatures or activity slows due to pH being outside optimum (1)
Describe the function of the coronary arteries. (2)
Supply oxygenated blood to heart muscle (1); for respiration (1)
Explain how a blocked coronary artery can lead to a heart attack. (3)
Blockage reduces oxygen to cardiac muscle (1)
Cells cannot respire and die (1)
Heart muscle stops contracting properly (1)
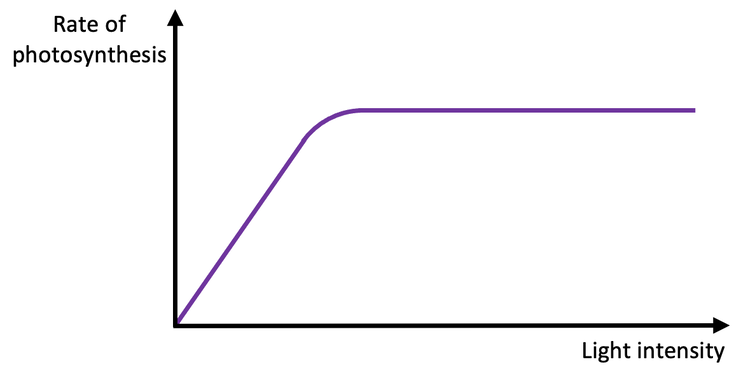
The graph below shows the rate of photosynthesis at different light intensities.
a) Describe the trend shown in the graph. (2)
Rate increases with light intensity then levels off (2)
b) Explain the trend using your knowledge of photosynthesis. (2)
More light = more energy for photosynthesis (1)
Enzymes work faster up to optimum (1)
c) Suggest a reason why the rate stops increasing at high light intensity. (2)
Another factor becomes limiting (CO₂ or temperature) (1)
Enzymes may be at max efficiency (1)