1.1 Atomic Structure ⚛️
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Chemistry Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Atom
simplest particle of an element that can exist on its own in stable environment
Ancient greek model
Atoms are tiny solid spheres which cannot be divided
JJ Thompson
Discovered electron and developed "plum-pudding" model
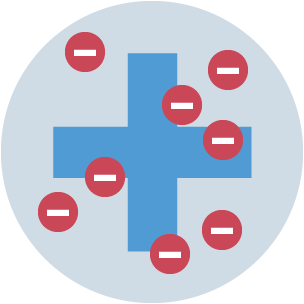
Plum pudding model
sphere of positive charge, with negatively charged electrons embedded in it
Rutherford
Carried out alpha particle scattering experiment and developed nuclear model
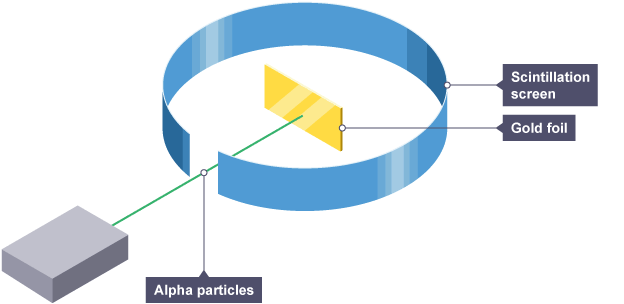
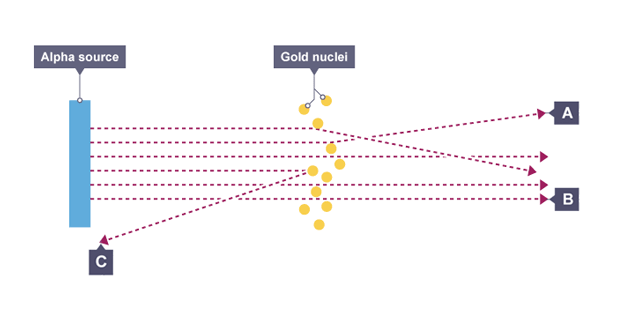
Alpha particle scattering experiment
directed beam of alpha particles at very thin gold foil suspended in a vacuum, tiny flash of light is emitted when it hits the screen
Observations from experiment
most alpha particles passed straight through foil but small number were deflected by large angles or straight back
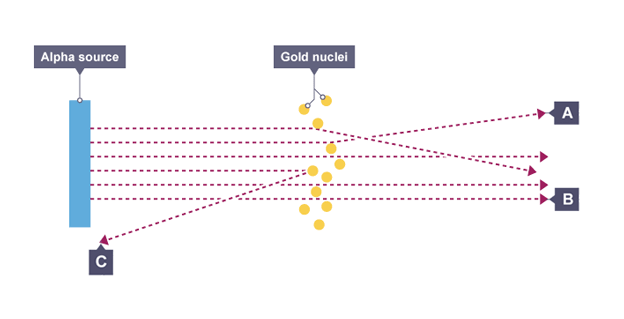
Conclusions from experiment
mass of atom is concentrated at the centre (nucleus) that had a positive charge
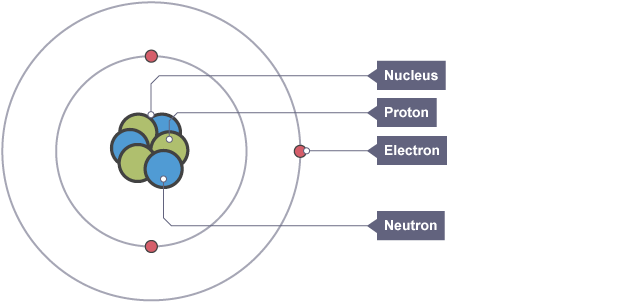
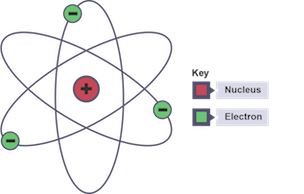
Nuclear model of the atom
atom is mostly empty space with positively charged centre containing most the mass and electrons orbiting
Niels Bohr
suggested electrons orbit nucleus at specific distances
James Chadwick
discovered the neutron leading to todays model
Why was the neutron hard to discover?
has no charge
Proton, charge and mass
positively charged particle found in the nucleus which defines the atom
+1, 1
Neutron, charge and mass
neutral particle found in the nucleus
0, 1
Electron, charge and mass
negatively charged particle found orbiting the nucleus in shells
-1, 1/1840
Why are atoms neutral?
same number of protons and electrons that cancel each other out
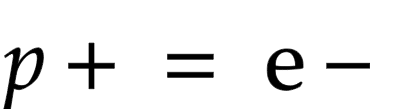
Atomic number (Z)
number of protons in (the nucleus of) an atom
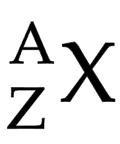
Mass number (A)
total number of protons and neutrons in (the nucleus of) an atom
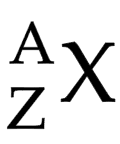
How to calculate neutrons
mass number - atomic number
Average atomic radius
0.1 nm (1 × 10-10 m)
Average radius of an atomic nucleus
10,000 times smaller than an atom (1 x 10-14 m)
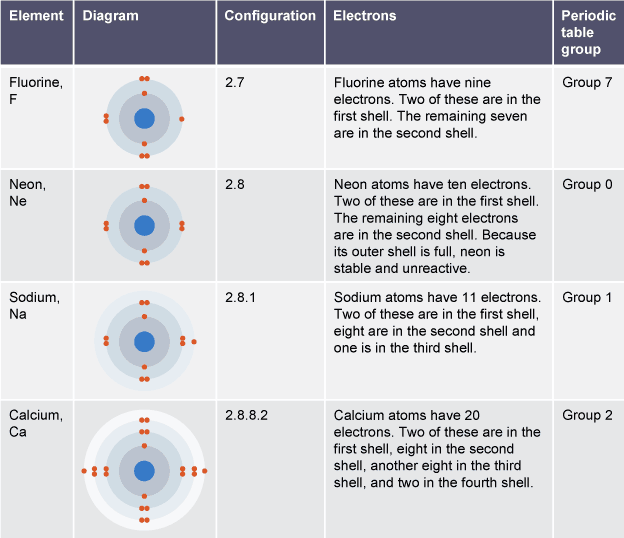
Shells can hold
2, 8, 8, 2
Number of shells =
Period on the periodic table
What are valence electrons?
Outer shell electrons which are involved in reactions
Number of valence electrons =
Group number on periodic table
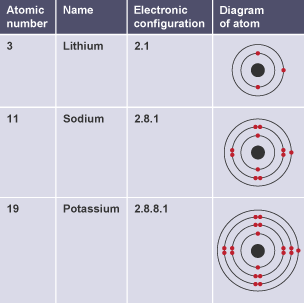
Drawing electronic configuration
nucleus in middle, drawing circle around for each shell and pairs of electrons inside
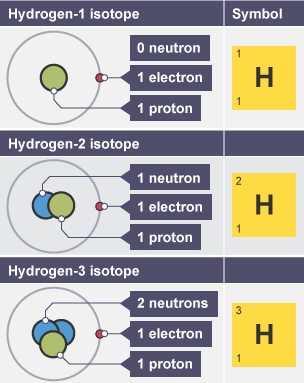
Isotopes
atoms of same element with same number protons but different number of neutrons
Relative atomic mass formula
isotope * abundance/ total percentage abundance

Why we use relative atomic mass
to accurately represent average mass of all isotopes in typical sample