Medsci 204 foundations block
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Drug Targets
Receptors
Ion channels
Transporters
Enzymes
some drugs act on DNA (anti cancer and a tip optic drugs)
4 steps of neuro transmission
Neurotransmitter synthesis
Neurotransmitter release
Action on Receptors
Inactivation
Two sites of action in choline synthesis
Choline transporter-transports choline into nerve terminal
ChAT- enzyme involved in synthesis of Ach
endogenous
natural- neurotransmitter/hormone
exogenous
synthetic- Drug/chemical
4 different receptor families
Ligand gated ion channels
G protein coupled receptors
Tyrosine kinase receptors
Nuclear/steroid hormone receptors
Ligand gated ion channels
Multi proteins subunit that conducts ions through the otherwise impermeable membrane in a highly selective manner when bound by a specific ligand
Examples of ligand gated ion channels
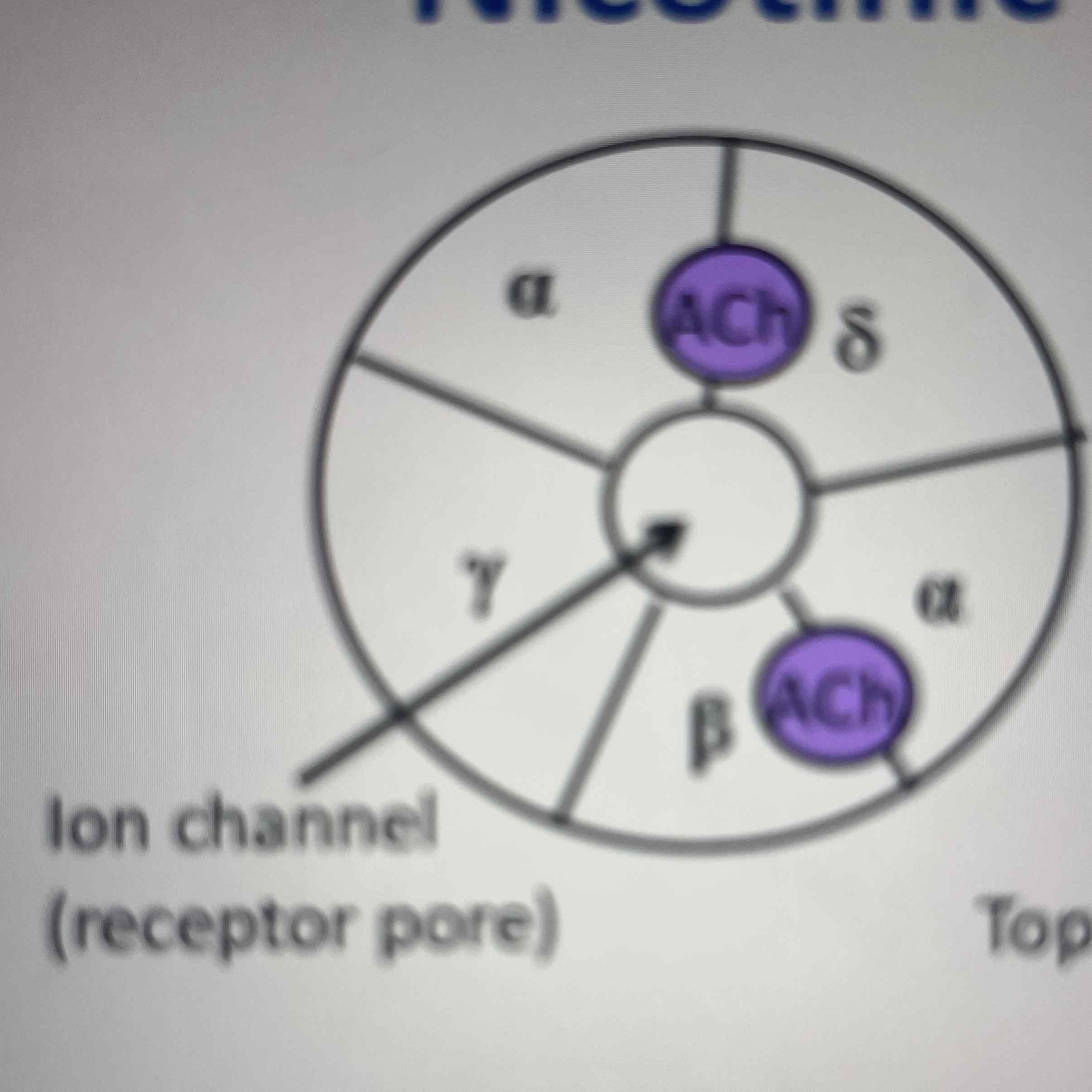
Nicotinic Acetylcholine receptors
Nicotinic Acetylcholine receptors
Ach binds to both sides of channel at the interfaces formed by the peptide loops between one of the 2 alpha subunits and its neighbour
Opening and closing of Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
transmembrane helices are sharply linked inwards forming a construction- when Ach binds confirmational change occurs opening the channel
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a drug target
Nicotine, pancuronium used as a muscle relaxant during anaesthesia
G protein coupled receptors
Monomer if proteins with 7 trans membrane domains coupled to g proteins
VEGFR
Essential for angiogenesis
Activation regulates- Endothelial cell survival, Endothelial cell proliferation, Endothelial cell migration, NO and prostaglandin release and increase vascular permeability
Drug specificity and selectivity
Drug specificity- acts only at the desired drug target
Drug selectivity- acting preferentially at a drug target (even the best drugs tend to only act selectivly)
Receptor Tyrosine kinase
Extracellular component that ligand binds to and intracellular part that functions as a kinase
Kinases
Enzymes that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to a substrate
Function of RTK
mediate the actions of growth factors, cytokines and certain hormones (eg.insulin)
what is the function of the kinases in RTK
the phosphate groups are transferred to tyrosine amino acid residues on intracellular target proteins
VEGFR
Essential for angiogenesis
Activation regulates- Endothelial cell survival, Endothelial cell proliferation, Endothelial cell migration, NO and prostaglandin release and increase vascular permeability
activation of VEGFR2
Ach binds to both sides of channel at the interfaces formed by the peptide loops between one of the 2 alpha subunits and its neighbour
signal transduction pathway that drives proliferation
receptor activation leads to activation of PLCy which leads to PIP2 hydrolysing to DAG and IP3- DAG activated PKC which leads to activation of ERK which leads to increased gene transcription
Nuclear/steroid hormone receptors
Located intracellularly in the cytosol and nucleus
Functions to stimulate transcription of target genes
how do drugs bind to receptors
Van der Waals
Hydrogen binding
Ionic interactions
Covalent binding
Kd definition
The concentration of drug which occupies 50% of the existing receptor population
Bmax
Saturation- maximum occupancy of the receptors
higher affinity
lower the concentration at which it produces a given level of receptor occupancy
Agonist
Receptor is activated
Inverse agonist
Basal activity is decreased
Antagonist
Receptor is inhibited
EC50
effective concentration of a drug when you get 50% of max response
Emax
Maximum response that can occur with that agonist
Efficacy
the ability of a drug to bind to a receptor and cause a change in the receptors action
Potency
amount of drug required to produce a defined effect- measured by EC50
Opening and closing of Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
transmembrane helices are sharply linked inwards forming a construction- when Ach binds confirmational change occurs opening the channel
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a drug target
Nicotine, pancuronium used as a muscle relaxant during anaesthesia
G protein coupled receptors
Monomer if proteins with 7 trans membrane domains coupled to g proteins
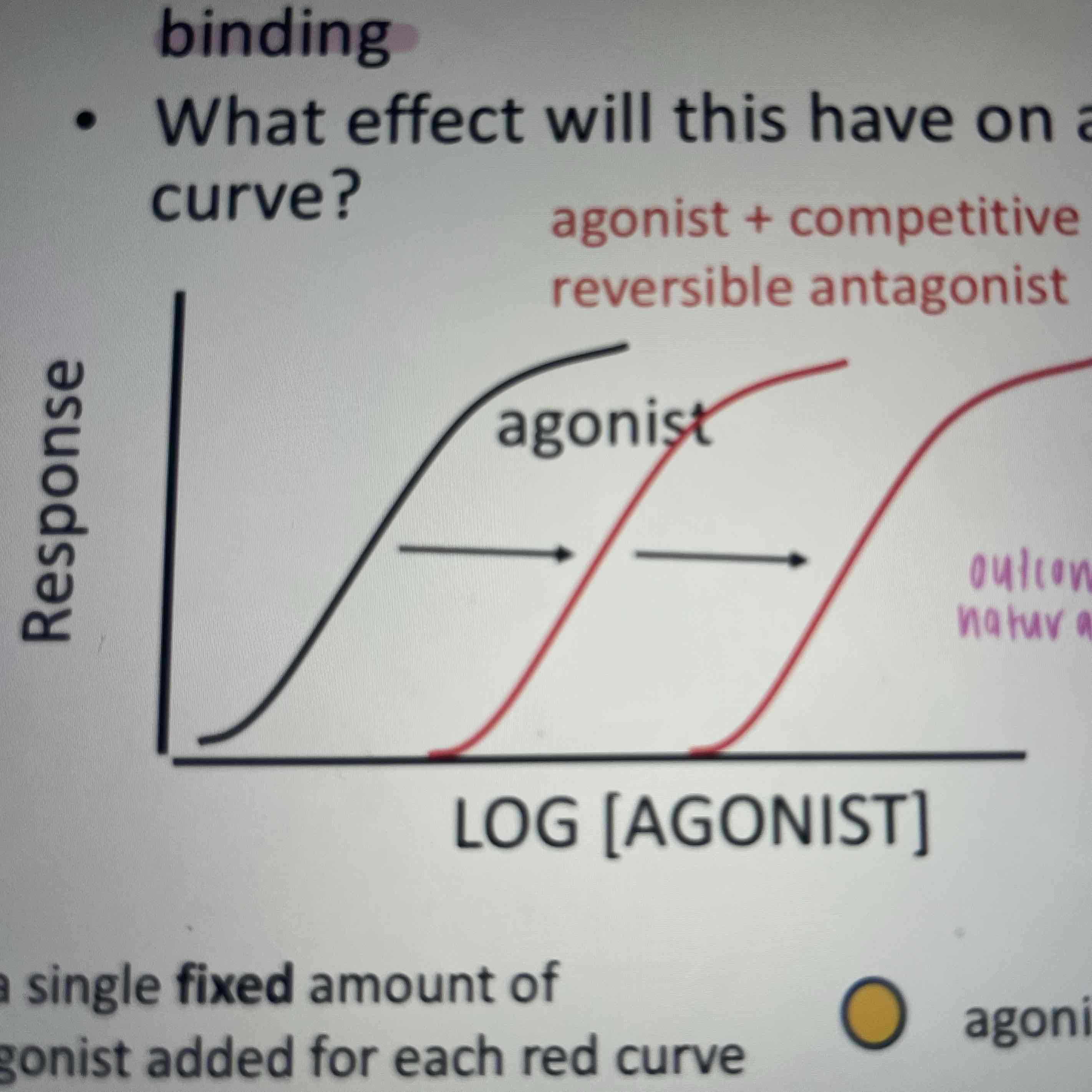
Reversible competitive antagonism
binds to a receptor in a reversible manner to compete with agonist binding
Irreversible antagonism
bind covalently to the receptor- reduces number of receptors available for the agonist- only way to overcome is to insert more receptors into the membrane

Allosteric modulators
Bind to allosteric site to modulate the binding of endogenous ligand and/or signalling properties at orthosteric site
Allosteric binding site
non-overlapping and spatially distinct site that is conformationaly linked to the orthosteric binding site
Positive allosteric modulators
Increasing ligand association rate and/or decreasing ligand dissociation rate
Allosteric modulation ceiling effect
Allosteric modulators can influence the orthosteric binding site to a maximum after which altering the does will not create a greater effect
Advantages of Allosteric modulators
Ceiling effect
Increased selectivity
Maintenance of spatial and temporal signalling by endogenous ligand
Drugs that act on enzymes and transporters mainly inhibit
True
Two key mechanisms of enzymatic degradation
Enzymatic degradation
Transport back into presynaptic terminal
Inhibitors of acetylcholine esterase
Irreversible- eg.nerve gas
forms stable phosphorous bonds with AChE leading to a build up of ACh at synapses
Reversible-
binds breifly to increase duration of ACh at synapse
Serotonin transporter
involved in sleep, appetite, memory, sexual behavior, neuroendocrine function and mood
Synthesised from tryptofan and packed into vesicles which are released into synapses following an action potential
Reputable determines the extent and duration of receptor activation
Two things needed for carrying out the assay
Means of detecting ligand
Sample containing target of interest
Basic procedure of an assay
Incubate labelled compound with tissue/cell
Seperate bouncy ligand from free
Measure signal
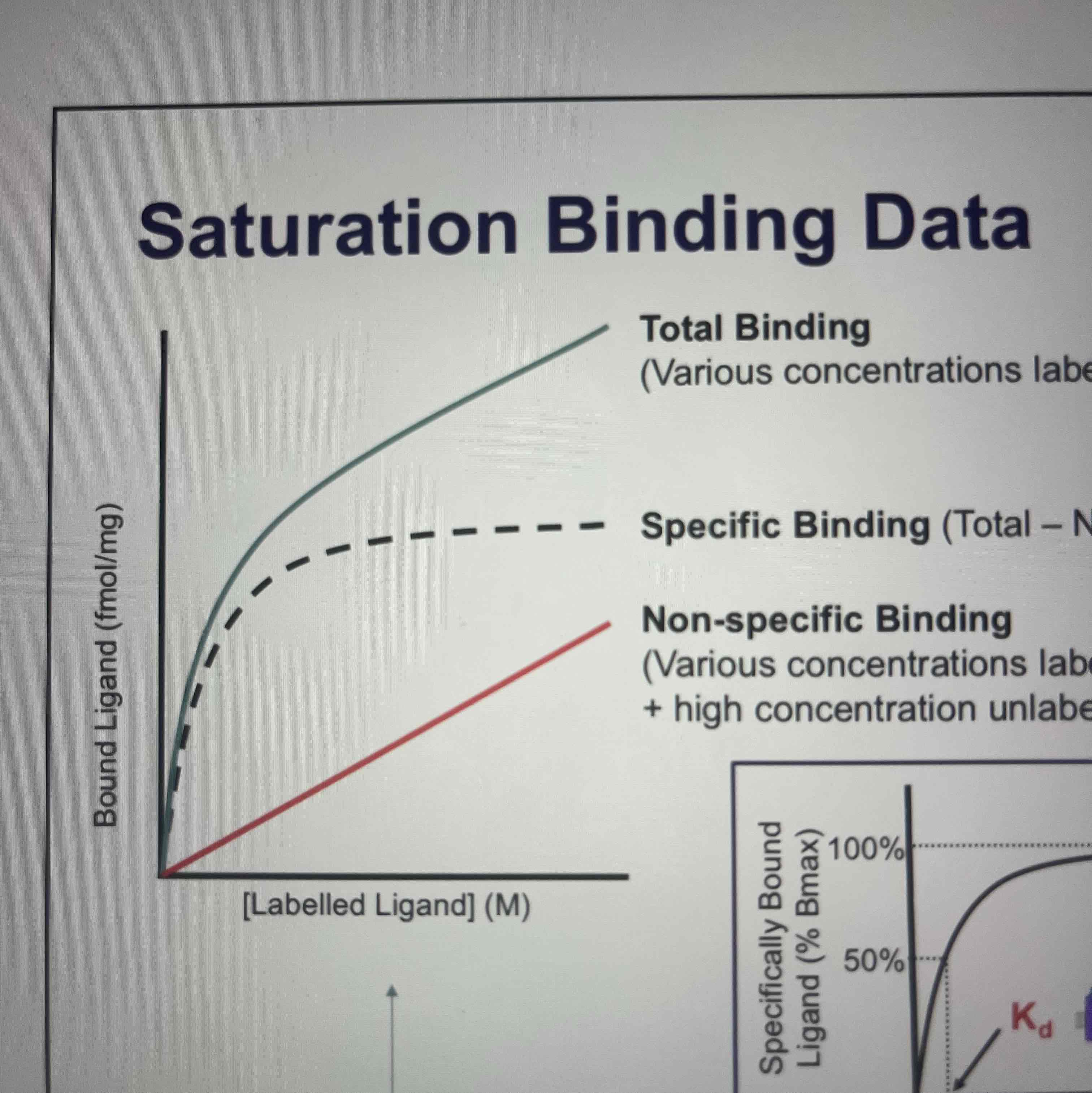
Saturation binding
Gives information about labelled ligand
Non-specific binding
most compounds bind to sites in sample other than receptor of interest- eg. binding to lipid components or free ligand not completely washed away
How to determine receptor binding when non-specific binding occurs
Incubate labelled logan with high concentration of an equivalent non-labelled ligand that binds to receptor of interest and have no effect on non-specific binding
Total binding- non-specific binding= specific binding
Ki
dissociation constant of the inhibitor of labelled ligand
Unlabelled ligand affinity
adme
absorption
distribution
metabolism
excretion
Major organs involved in ADME
Gastrointestinal tract
Liver
Kidney
Lungs
Physiochemical properties that influence ADME
Solubility
Lipophilicity
Ionisation
Mechanisms of membrane transport
Passive diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport
Endocytosis
Filtration
Passive diffusion
Most common mechanism for drug absorption
Driven by concentration gradient
Non-selective
Which molecules travel by passive diffusion
lipophilic, uncharged, and small molecules pass easily
eg. aspirin
When is competitive binding used
When interested in an unlabelled compound
Competition binding procedure
labelled applied at approximate kd concentration
unlabelled ligand applied at range of concentration in presence of labelled ligand
Facilitated diffusion
Passive diffusion of drugs through transmembrane proteins
Requires recognition by carrier or channel protein
Rate is faster and can saturate
which molecules travel by facilitated diffusion
Sugars and amino acids eg. glucose through Glucose transporter
active transport
uses cellular energy to transport drugs across the membrane
requires recognition by membrane transporters
active transport allows
accumulate compounds essential for growth
remove waste products
be protected against toxins
where are active drug transporters highly expressed
liver, kidney, Blood brain barrier, gut epithelium
ATP binding cassette
present in GI tract and kidney
act to efflux from cell
wide range of substrates
Endocytosis
Drug is taken up by vesicles
energu dependant
types of drugs that travel through endocytosis
mainly for drugs with mw>1000Da
eg. hormones cytokines growth factors antibodies such as monoclonal antibodies immunoglobines
2 types of endocytosis
Pinocytosis
Receptor mediated endocytosis
most drugs pass through cells to cross biological barriers except
Blood capillaries- contain remedy rations that allow rapid interchange between blood and interstitial fluid
Glomerular capillaries- extremely porous allowing passage of all plasma constituents excoet macromolecules
some cells in the liver also contain fenestrations
enteral and paraental
enteral- gastric eg. oral, sublingual, buffaloes, rectal
paraental- around - avoid first pass metabolism eg. intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, transdermal, respiratory tract, topical
define drug absorption
transfer of drug from administration site to the systemic circulation
Rate definition
how rapidly the drug gets from the site of administration to the systemic circulation
Extent definition
how much of the administered dose enters the systemic circulation
with an oral dose what happens to the drug
some metabolised in gut wall
some delivered to liver via portal vein
some removed by hepatic first pass metabolism
some pumped back by efflux transporters to be expelled by gut
some arrives in systemic circulation
advantages of IV
very rapid
precise control
can be administered as a bolus infusion or both
no absorption involved
good for drugs with high irritation
disadvantages of IV
requires hospitalisation
careful preparation of injected material requires
most hazardous- no recall
oral advantages
safest
most convenient
economic
oral disadvantages
slow
unpredictable in regard to
rate
extent
reproducibility
absorption sites in GI tract
oral mucosa- limited absorption
stomach - absorption site for weak acids and neutral drugs
small intestine - major site of drug absorption
large intestine - little absorption
drug characteristics effecting absorption of oral drugs
dosage form
dissolution rate
water and lipid solubility
ionisation
chemical stability
liability for metabolism
patient characteristics effecting absorption of oral drugs
gastric emptying rate
intestinal mobility
drug-food interactions in the gut
distribution
transfer of drug from the blood circulation to the various tissues in the body
exception to capillary permeability
brain capillaries have no pores and an additional later of glial cells- only lipid soluble drugs diffuse across brain capillaries into the brain unless they undergo active transport
what does rate of distribution depend on
relative blood flow
plasma protein binding
bound drug will remain in circulation
pharmacologically inactive, protected from metabolism and excretion and binding is reversible and rapid
binding to tissue proteins may also influence where drugs collect
elimination
metabolism + excretion
metabolism
biotransformation of drugs
often terminates activity but can also increase, cause no change and produce toxic or carcinogenic metabolites
possible sites of drug metabolism
Liver
intestinal wall
GI tract
plasma
lungs
what are the different metabolism reactions
oxidation
reduction
hydrolysis
conjunction
CYP450
most important oxidative enzymes
5 features of CYP oxidation
substrate binding
oxygen binding
oxygen splitting
inserting oxygen into substrate
release of the metabolite
factors influencing drug metabolism
organ function, diseases, other drugs, diet, cigarettes. alcohol. age, sex , pregnancy
excretion
process by which drugs are removed from the body
organs for drug excretion
kidney expelled in the urine
biliary excretion- into the bile out into faeces
faecal excretion of non-absorbed drug
tears, respiration, sweat, milk, saliva
the kidneys
regulate volume and composition of body fluids
conserve essential compounds and remove waste products
specialised transport systems
removes water soluble drugs and metabolites
lipophilic drugs and metabolites usually retained
factors that influence renal drug excretion
Age. pregnancy, disease, other medications
pharmacokinetics
is the study of the concentration time profile of a drug in the body