Integumentary System
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Gland that secretes an oily substance
Sebaceous gland
Binds skin to underlying organisms
Subcutaneous Layer
Epidermal pigment ranging from yellow to brown to black
Melanin
An oily secretion that helps to waterproof your skin
Sebum
Tubelike part that contains the root of the hair
Hair follicle
General name of the entire superficial layer of skin
Epidermis
Inner layer of skin
Dermis
Become active at puberty, in the armpits
Apocrine sweat gland
Outermost layer of the epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Responds to elevated body temperature
Eccrine sweat gland
Causes hair to stand erect and goose bumps to appear
Arrector pili muscle
Hard protein of nails and hair
Keratin
What part of the hair is above the epidermis
Hair shaft
What part of the hair is below the epidermis
Hair root
True or False: Skin is a membrane
True
Functions of Body Membranes
Cover surfaces, line body cavities, form protective and lubricating sheets around organs
Function of skin
Protect the body, regulate body temperature, helps excrete waste through sweat
Two types of body membranes
Epithelial and Connective membranes
Membrane made of epithelial tissue AND underlying connective tissue
Epithelial Membrane
Because they contain multiple tissues, Epithelial membranes are technically simple ___
organs
Cutaneous Membrane
Skin
Epithelial membrane that lines all body cavities exposed to the exterior
Mucous Membranes
Cutaneous membranes are exposed to air, they are ___ ___
Dry Membranes
Name all locations of Mucous Membranes
Digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
Epithelial membrane that lines all body cavities NOT exposed to the exterior
Serous membrane
Layer of serous membrane that lines the wall of a cavity
Parietal Layer
Layer of serous membrane that lines the outside of an organ
Visceral Layer
Visceral and Parietal layers are separated by this to avoid friction
Serous Fluid
Location of Visceral Pericardia
Part of serous membrane touching the HEART
Location of Parietal Pericardia
Part of serous membrane on the cavity side of the HEART
Location of Visceral Pleurae
Part of serous membrane touching the LUNGS
Location of Parietal Pleurae
Part of serous membrane on the cavity side of the LUNGS
Location of Visceral Peritoneum
Part of serous membrane surrounding abdominal organs
Location of Parietal Peritoneum
Part of serous membrane facing the abdominal cavity
Fibrous capsules surrounding joints
Connective Tissue Membranes
Type of tissue in Synovial Membranes
Loose areolar connective tissue
What is the lubricating fluid in synovial membranes?
Synovial fluid
Parts of the integumentary system
Skin, sweat and oil glands, hair, and nails (does not include internal membranes)
Two places of the body with 5 layers of epidermis
Heels and palms
Toughening of the skin
Keratinization
Second layer of of epidermis, only present in palms and heels
Stratum Lucidum
Bottom layer of epidermis, site of cell division
Stratum Basale
List the layers of epidermis in order
Corneum, Lucidum, Granulosum, Spinosum, Basale
Produces melanin, found in stratum basale
Melanocytes
Cells that alert and activate immune system
Epidermal Dendritic cells
At junction of epidermis and dermis, act as touch receptors
Merkel Cells
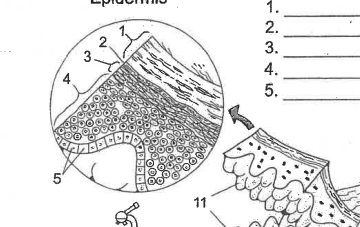
Name area 1
Stratum Corneum
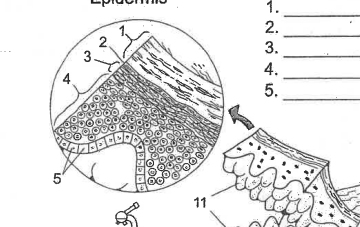
Name area 2
Stratum Lucidum
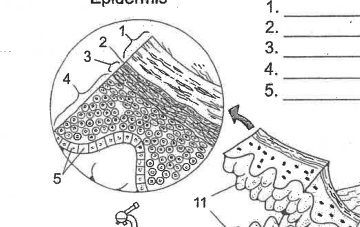
Name area 3
Stratum granulosum
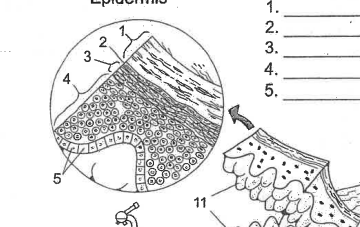
Name area 4
Stratum spinosum
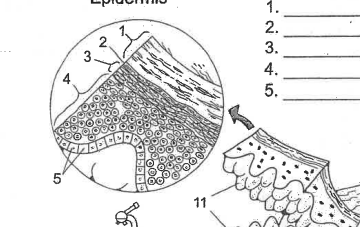
Name area 5
Stratum Basale
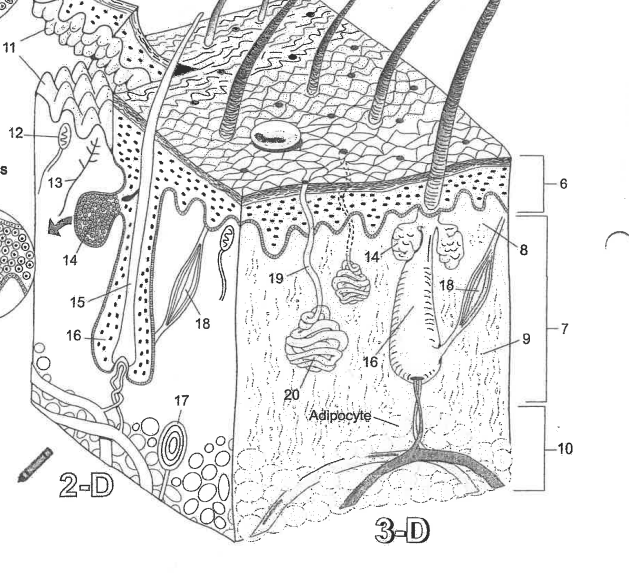
Name region 6
Epidermis
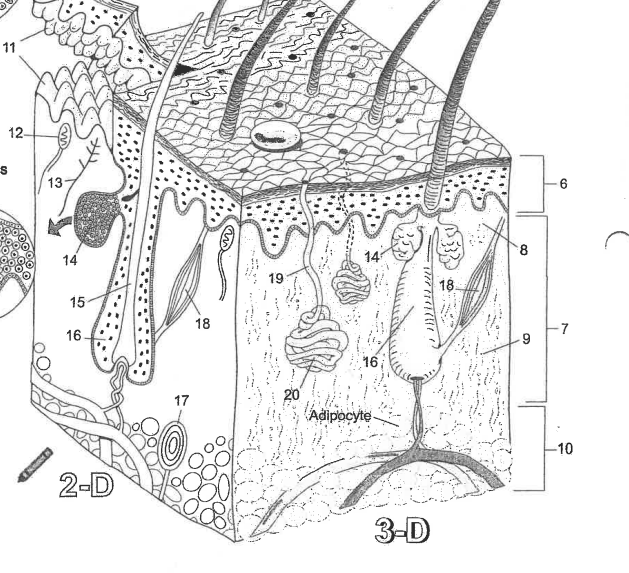
Name region 7
Dermis
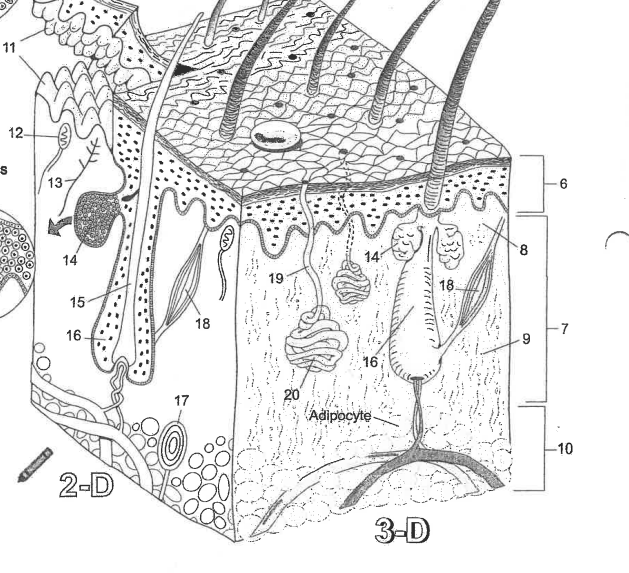
Name region 8
Papillary layer
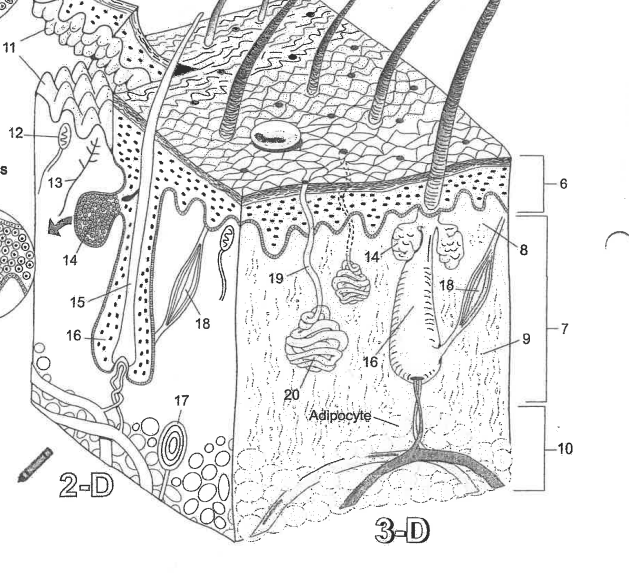
Name region 9
Reticular layer
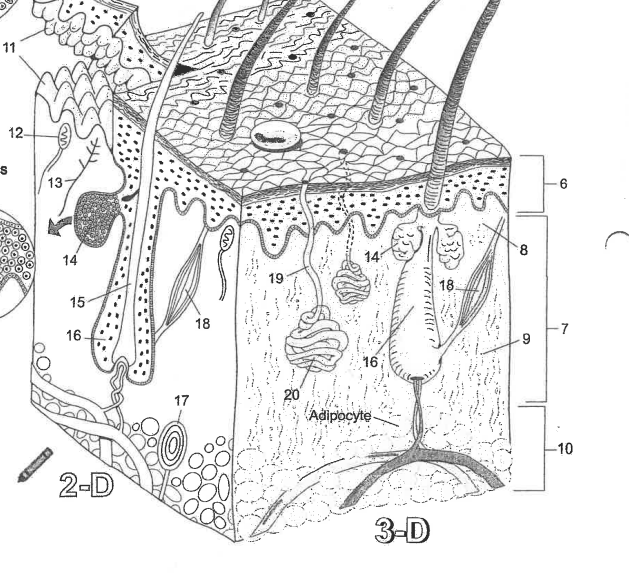
Name region 10
Hypodermis
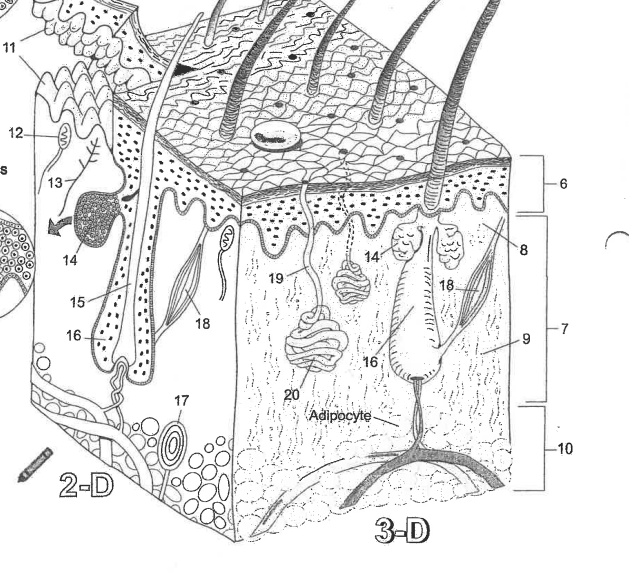
Name essential structure 11
Dermal Papillae
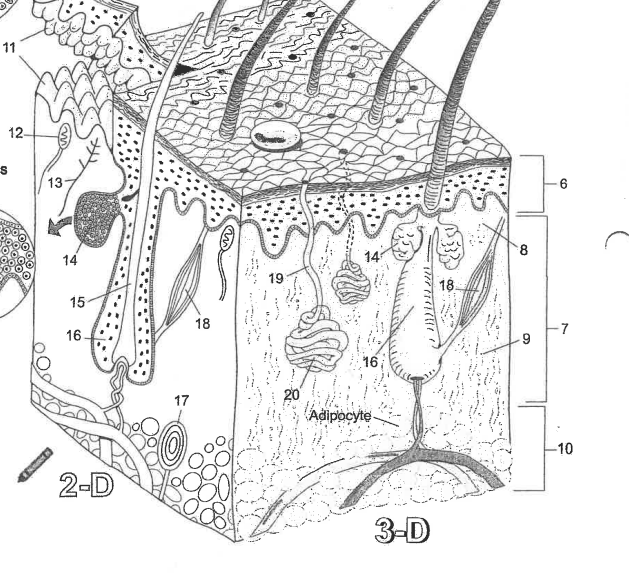
Name essential structure 12
Merkle cell
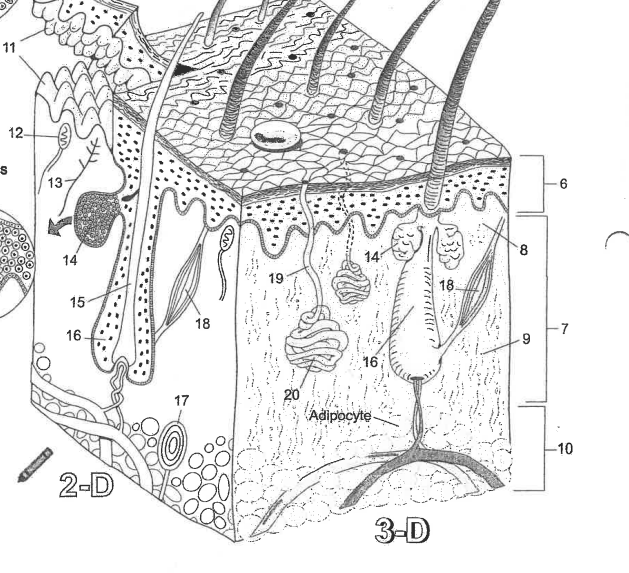
Name essential structure 13
Sensory nerve fiber
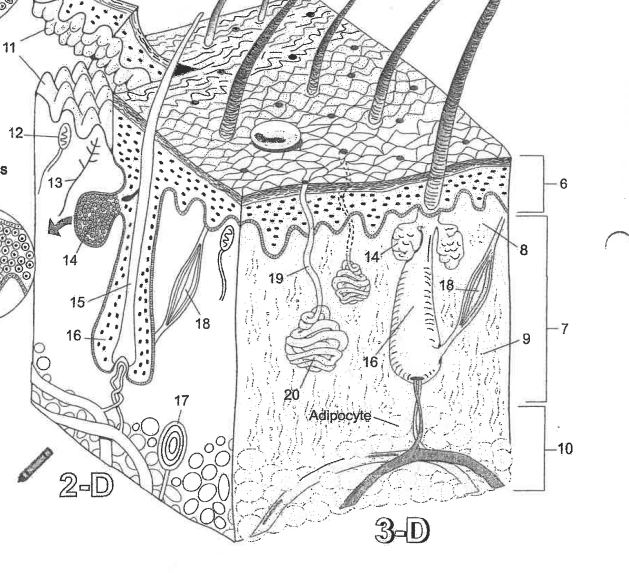
Name essential structure 14
Sebaceous gland
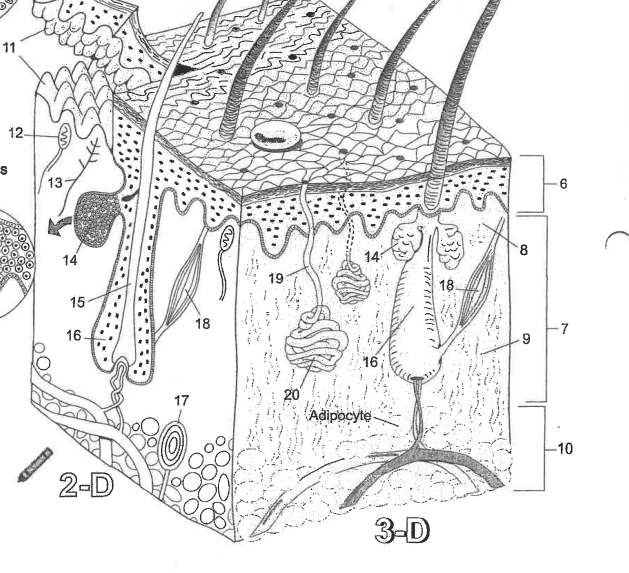
Name essential structure 15
Hair shaft
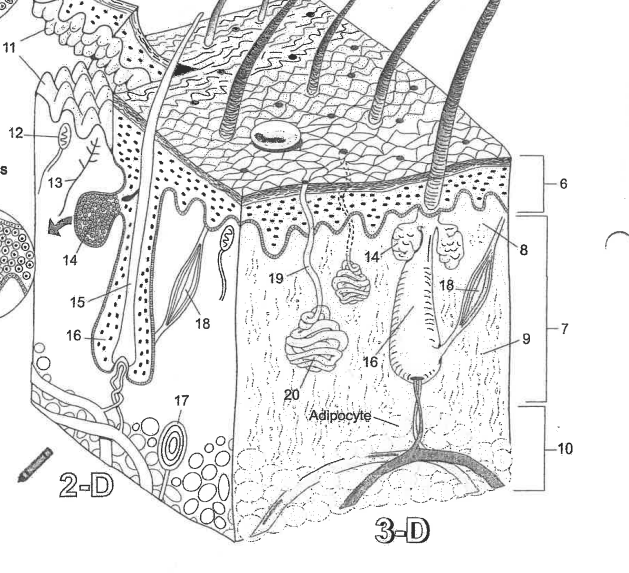
Name essential structure 16
Hair follicle
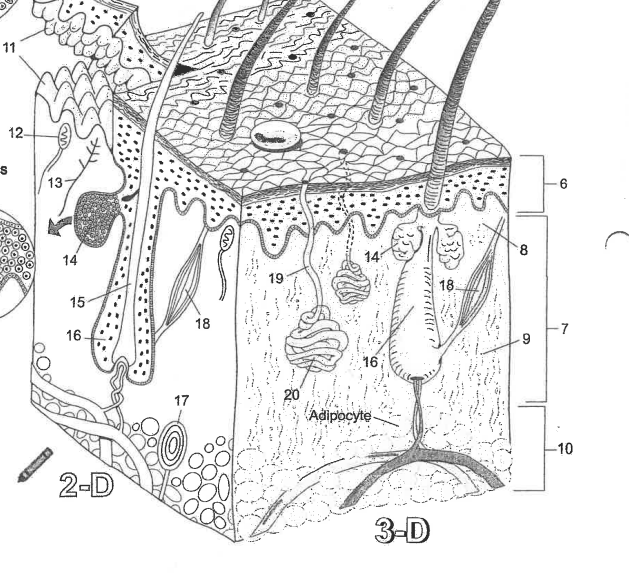
Name essential structure 17
Lamellar corpuscle
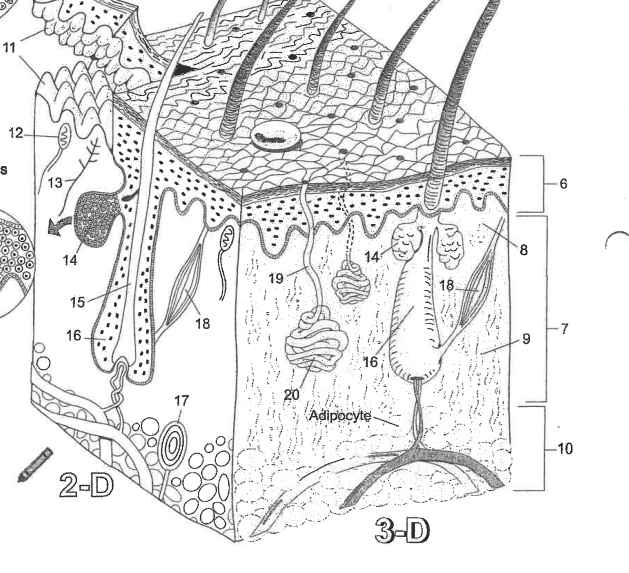
Name essential structure 18
Arector Pili muscle
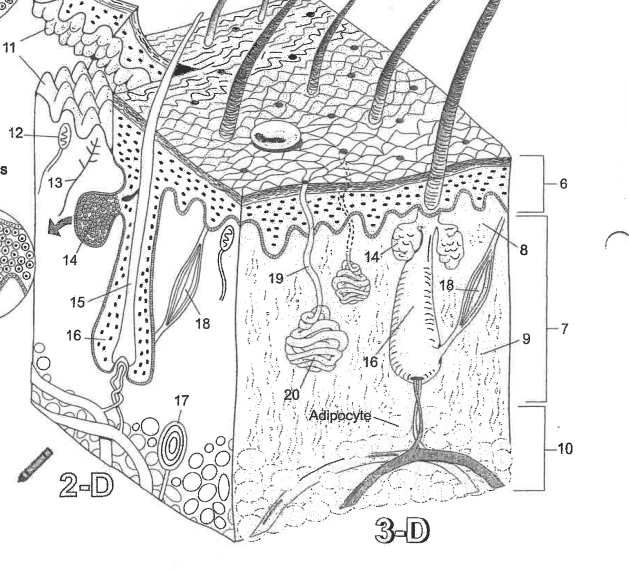
Name essential structure 19
Pore/Duct
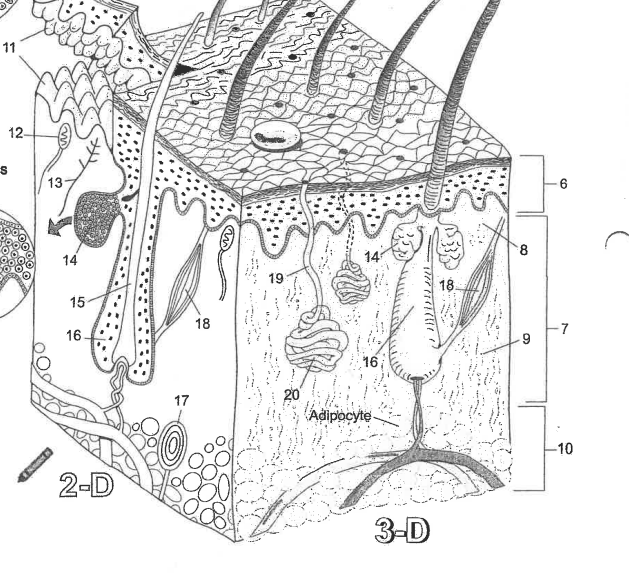
Name essential structure 20
Eccrine sweat gland
Types of fibers found throughout the dermis
Collagen and elastin
Found throughout the dermis, find and keep out microbes that want to enter deeper into the body
Phagocytes
Deep pressure sensors found in dermis
Lamellar Corpuscles
Layer under dermis, not technically part of the skin, made of adipose tissue
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous)
Orange-yellow pigment (from carrots, leafy vegetables)
Carotene
Pigment in red blood cells
Hemoglobin
Tissue damage/death due to heat, electricity, ultraviolet light, or chemicals
Burns
Superficial burn (no blisters)
1st degree burn
Partial thickness burn (blistering)
Second degree
Full thickness burns (regeneration not possible skin grafts needed)
Third degree burns
Burn with deep tissue involvement (bone, muscle, tendons)
Fourth degree
Name the seven protective functions of the skin
Insulate/Cushion internal organs, Guard acidic damage, Limit heat damage, Gaurd UV damage, Protect against water loss, Protect against infection, Synthesize vitamin D