Social Perception and Managing Diversity
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Social Perception
The process we use to process social information -- information related to interactions with others, motives for behavior, etc.
Person Perception
influenced by 3 components
- characteristics of perceiver
- characteristics of target
- characteristics of situation
Model of Social Information Processing
1. Selective Attention / Awareness
2. Encoding and Simplification
3. Storage and Retention
4. Retrieval and Response
Selective Attention / Awareness
relates to environmental stimuli/information; retaining of salient/meaningful information (Cocktail Party Effect: we selectively pay attention while filtering out background noise)
Encoding and Simplification
interpretation and categorization
-schemas
-scripts
-categories
-stereotypes
(ex: chunking to remember phone numbers)
Storage and Retention
Memory
-semantic
-episodic
-people
Semantic memory
memory of data, facts, concepts, general knowledge of the world)
Episodic memory
memory of events
Person memory
memory of people or groups of people
Retrieval and Response
relates to judgments and decisions
Implicit cognition (aka implicit bias)
represents any thoughts or beliefs that are automatically activated from memory without our conscious awareness
Stereotype
a generalized belief about a group of people
Stereotype Formation
1. Categorize
2. Inferences
3. Expectations
4. Maintenance
Causal Attribution
suspected or inferred causes of behavior
Fundamental Attribution Bias (FA Error)
tendency to make internal attributions rather than external (ex: if a friend is late, we tend to assume that they didn't keep track of time rather than traffic problems)
Self-Serving Bias
the tendency for people to take personal credit for success but blame failure on external factors (ex: if I aced a test it's because I studied, if I fail a test it's because the test was too hard)
Halo Error
when one favorable characteristic of someone makes you see them as good in other unrelated areas
Pitchfork Error (aka Horns Error)
one unfavorable characteristic of someone makes you see them as bad in other unrelated areas
Leniency Error
too lenient on people
Severity Error
too tough on people
Central Tendency Error
tendency to assume that everyone is average
Recency Effect
when presented with a string of things, it's easiest to remember the most recent one
Primacy Effect
when presented with a string of things, it's easiest to remember the first one
Stereotyping
creating an oversimplified image of a particular group of people, usually by assuming that all members of the group are alike (ex: Asian woman: "I turn now good luck everybody else")
Projection
projecting values of yourself onto another because of a shared characteristic (ex: "I'm Asian and smart so since they are Asian they must also be smart")
Contrast Effect
thinking someone is extraordinary because the previous one is a lot worse
"Similar to Me" Effect
tendency to favor someone just because they are similar to you
Attribution Theory
to determine whether someone's behavior/result is as a result of external factors or internal ones; 3 dimensions
- Consensus
- Distinctiveness
- Consistency
Consensus
compares an individual's behavior with that of his or her peers (ex: I scored a 90 on the exam, the class average is 89 -> consensus is high)
Distinctiveness
compares a person's behavior on one task with their behavior on other tasks (ex: I scored a 90 on my Accounting exam but failed all my other exams -> high distinctiveness)
Consistency
compares an individual's behavior on a task with their behavior at different times (ex: I scored a 90 on my first Accounting exam and also aced the next two Accounting exams -> high consistency)
Attribution made to external causes (task difficulty, environmental factors, etc.)
- High consensus
- High distinctiveness
- Low consistency
Attribution made to internal causes (personal ability, characteristics, hard work, etc.)
- Low consensus
- Low distinctiveness
- High consistency
Diversity
the multitude of individual differences and similarities that exist among people; isn't automatically an advantage or disadvantage because without inclusion, it can possibly drive differences
Inclusion
the extent to which the diversity of members are brought together in a meaningful way to increase success; recognizes differences but primary focus is bring those differences together
Four Layers of Diversity
- Personality
- Internal dimensions
- External dimensions
- Organizational dimensions

Internal dimensions
surface level characteristics; quickly obvious to outsiders (ex: age, race, gender)
External dimensions
deep level characteristics; takes time to emerge through attitudes, values, etc. (ex: religion, income)
Organizational dimensions
characteristics relating to an organizational setting (ex: seniority, management status, work location)
Affirmative Action
artificial interventions that allow companies to correct imbalances, address diversity problems; can be seen as more of an "enforcement" to diversity, can be divisive and not necessarily beneficial
Managing diversity
focuses on changing organizational systems, culture, etc. to drive an inclusive work environment
3 Strategies for managing diversity
1. Educational: help people develop for success in a diverse workplace
2. Enforcement: accountability mechanism to change the system
3. Exposure: expose people to others with different backgrounds
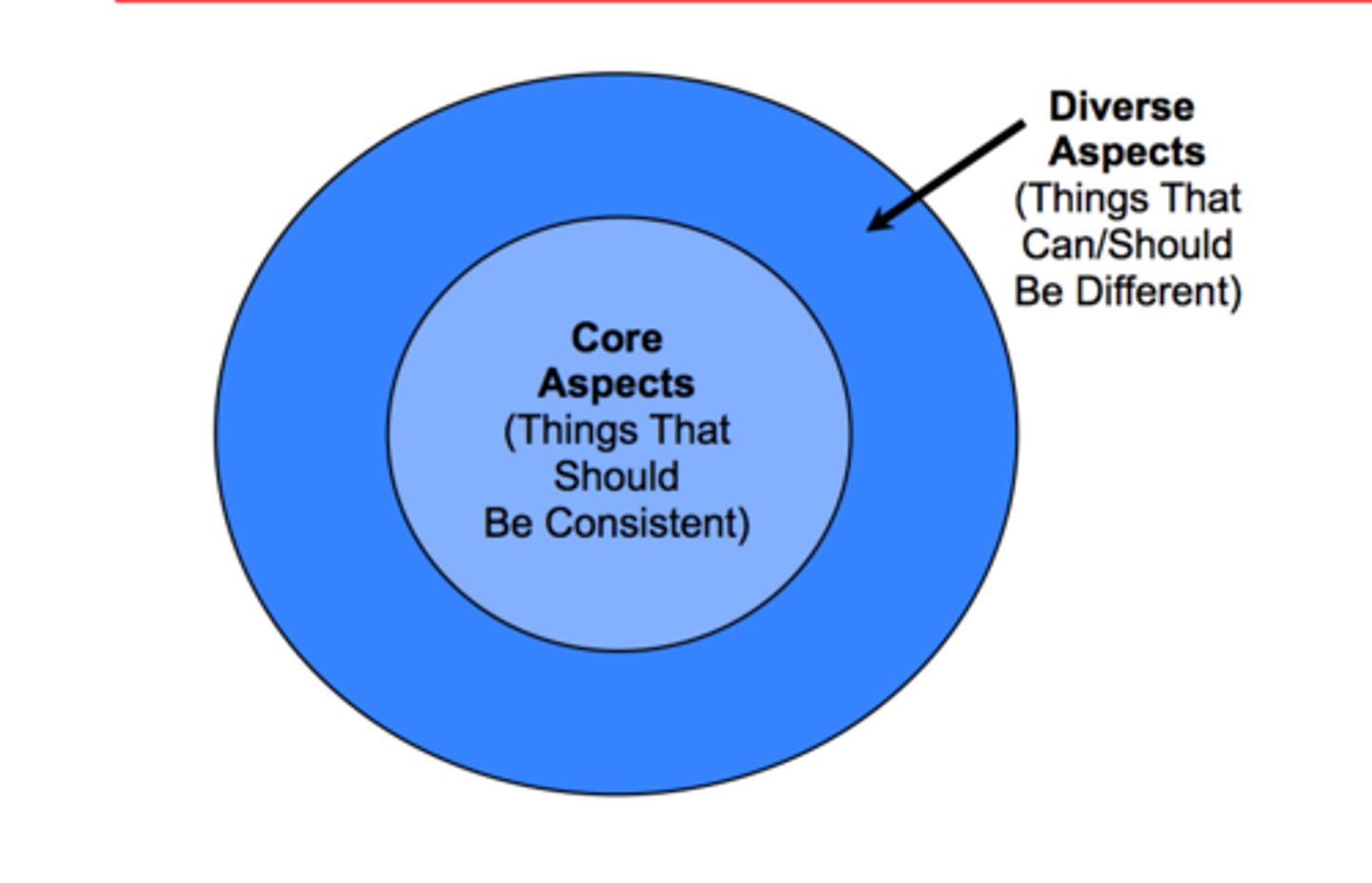
Simple Model of Diversity in Organizations
Core Aspects: things that should be consistent
Diverse Aspects: things that can/should be different
(ex: military -> more core, less diversity)