Aseptic Technique and Sterile Compounding Vocab
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Anteroom
Room adjacent to the ‘clean room’ used for donning PPE and wiping down supplies to be used in the Compounding area.
Aseptic Technique
Procedures used to eliminate the possibility of drug contamination with microbes/particles.
Beyond-Use-Date(BUD)
Defined by USP <797> as the date/time after which a compounded sterile preparation(CSP) should not be administered, stored, or transported. It is determined from the date of Compounding.
Biological Safety Cabinet(BSC)
Vertical flow hood used for making hazardous sterile preparations in the clean room.
Compounding Aseptic Containment Isolator(CACI)
ISO Class 5 Compounding area used to prepare hazardous drugs.
Clean Room
A contained and controlled environment in the pharmacy that has a low level of pollutants(dust, airborne microbes, aerosol particles, chemical vapors). It is used for preparing sterile medication products.
Compounded Sterile Preparations(CSP)
Preparations prepared in a sterile environment using non-sterile ingredients or devices that must be sterilized before administration.
Critical Site
Any surface/area exposed to first air, which is exposed/at risk of contact(ex. vial tops, open ampules, needle hubs, injection ports)
Gauges
The size of needle openings.
First Air
Air leaving a HEPA filter in a unidirectional air stream.
Hazardous Drug
Any drug proven to have dangerous effects during animal or human testing.
Hazardous Waste
Any waste that meets the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act(RCRA) criteria of ignitability, corrosiveness, reactivity, or toxicity.
Healthcare-Associated Infection(HAI)
Any infection a patient acquires during the course of receiving treatment for other conditions in a healthcare setting.
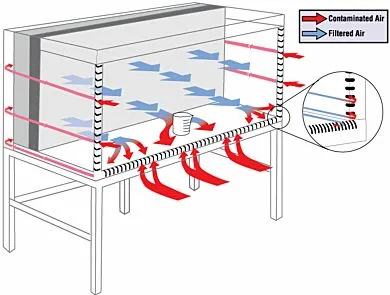
Horizontal Laminar Flow Hood
Environment for the preparation of compounded sterile preparations in which air from the back of the hood moves forward across the hood and into the room.
Hyperalimentation
Parenteral Nutrition for individuals who cannot eat solids or liquids.
Infection Control
Policies and procedures put in place to minimize the risk of spreading infections in hospitals or other healthcare facilities.
Laminar Airflow Hood
An environment for the preparation of sterile products.
Parenteral Medications.
Medications that bypass the digestive system but are intended for systemic action. The term parenteral is most often used to describe injected medications.
Peripheral Parenteral
Injection of a medication into veins on the periphery of the body instead of into a central vein or an artery.
Peripheral Parenteral Nutrition(PPN)
IV nutrition administered through veins on the periphery of the body
Precipitate
To separate from solution or suspension; a solid that emerges from a liquid solution.
Primary Engineering Control(PEC)
A device/zone that provides a Class environment for sterile compounding(ex. hoods)
Reconstituted
A substance that has had a diluent added to a powder.
Standard Operating Procedures(SOPs)
Written guidelines and criteria that list specific steps for various competencies.
Standard Precautions/Universal Precautions
A set of standards that reduces the possibility of contamination and the risk for transmission of infectious disease; these standards are used throughout a health care facility, including for medication preparation.
Sterile Preparation
A preparation that contains no living organisms.
Total Parenteral Nutrition(TPN)
Large volume IV nutrition administered through a central vein, which allows for a higher concentration.
USP <797>
A section of the USP that contains a set of enforceable sterile compounding standards; describes the guidelines, procedures, and compliance requirements for compounding sterile preparations and sets the standards for settings that host the compounding of sterile preparations.
USP <800>
‘A new general chapter created to identify the requirements for receipt, storage, mixing, preparing, compounding, dispensing, and administration of hazardous drugs to protect the patient, healthcare personnel, and environment.’
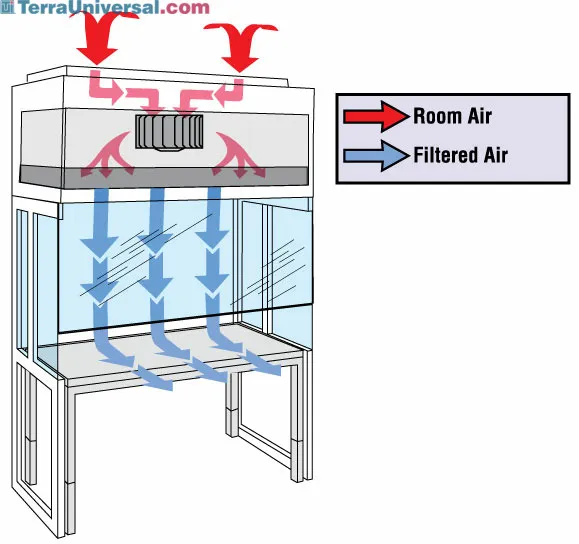
Vertical Laminar Flow Hood
An environment meant for the preparation of chemotherapeutic and other hazardous agents in which air from the roof of the hood moves downward(over the agent) and is captured in a vent on the floor of the hood.