Time of Flight Diffraction
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Sound can be defined as…
Propagation of particle displacement through a medium. Sound waves are vibrations of the particles of solids, liquids or gasses.
The human ear can only detect frequencies from roughly…
16 cycles per second (16Hz) to 20,000 cycles per second (20 KHz)
Four modes of sound propagation
Compression (Longitudinal), Transverse (Shear Wave), Surface Wave (Rayleigh) and Lamb Wave (Plate).
Shear Waves can only exist in…
Solids.
Surface Wave can only affect the surface layer of the solid to a depth of?
About one wavelength.
The rate at which sound waves propagate through a material are affected by two things:
Material properties (elasticity and density) and Mode of vibration * Compression, Shear, etc.)
Shear waves are roughly _____ of Longitudinal waves.
Half the speed
Surface waves also have their own velocity, which is generally taken to be approximately ____ of the shear wave velocity.
90%
Distance traveled by the sound wave during one cycle of vibration is called the…
Wavelength.
In general, if the maximum dimension of a reflecting surface is equal to or greater than _____ ___ ________, the reflection will be detectabel.
Half a wavelength.
Wavelength formula.
Lambda = Velocity / Frequency
In Lambda = V/F, which is directly proportional and which is indirectly proportional?
Numerators are Directly proportional, Denominators are Indirectly proportional.
Reflection , refraction and Mode Conversion occur when?
Beam incidence is at an angle to the surface boundary.
Acoustic impedance.
The measure of resistance a medium offers to the propagation of sound waves, defined as the product of density and sound velocity in the medium.
Acoustic impedance formula.
Z = p (density) x V (Velocity)
Reflection calculation.
= (Z1-Z2 / Z1+Z2)² x 100%
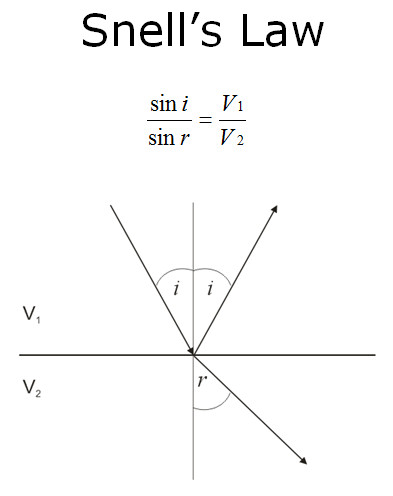
Refraction occurs because…
The difference in velocity on either side of the interface.
Snells law.
First critical angle.
The critical angle at which the longitudinal wave is refracted to 90° in the part.
Second critical angle.
The critical angle at which the transverse wave (shear wave) is refracted to 90° in the part. This shear wave will mode convert to a Surface (Rayleigh) wave.
Sound beams attenuate due to:
Absorption, scatter, interface effects (near field) and beam spread.
Near field (Fresnal Zone)
The parallel section of the sound path after leaving the transducer where the interaction of various wave fronts traveling in opposite directions causes phase changes and intensity fluctuations.
Beam Spread.
Beam divergence. Intensity drops to a quarter of the original intensity at double the distance from the probe.
Dead zone.
The part of the time base occupied by the initial pulse when using a single crystal contact probe (doesn’t occur with a dual element).
Near field formula.
NF= (D² x F) / (4 x V)
Large reflectors.
Diameter of reflector exceeds the sound beam cross section at the testing range.
Gain of amplification can be expressed as:
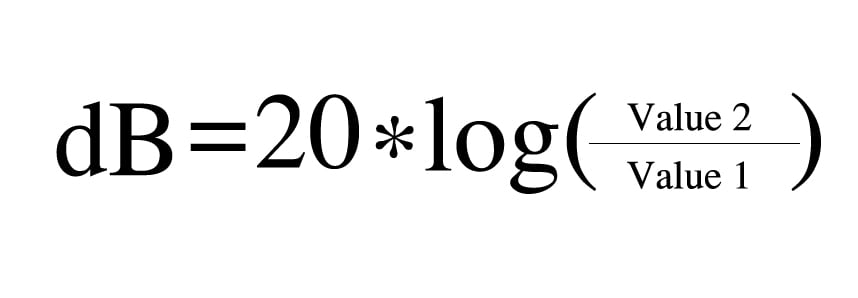
dB difference ratio.
=Antilog (dB/20) gives ratio. Then divide 80 by your ratio to get FSH%
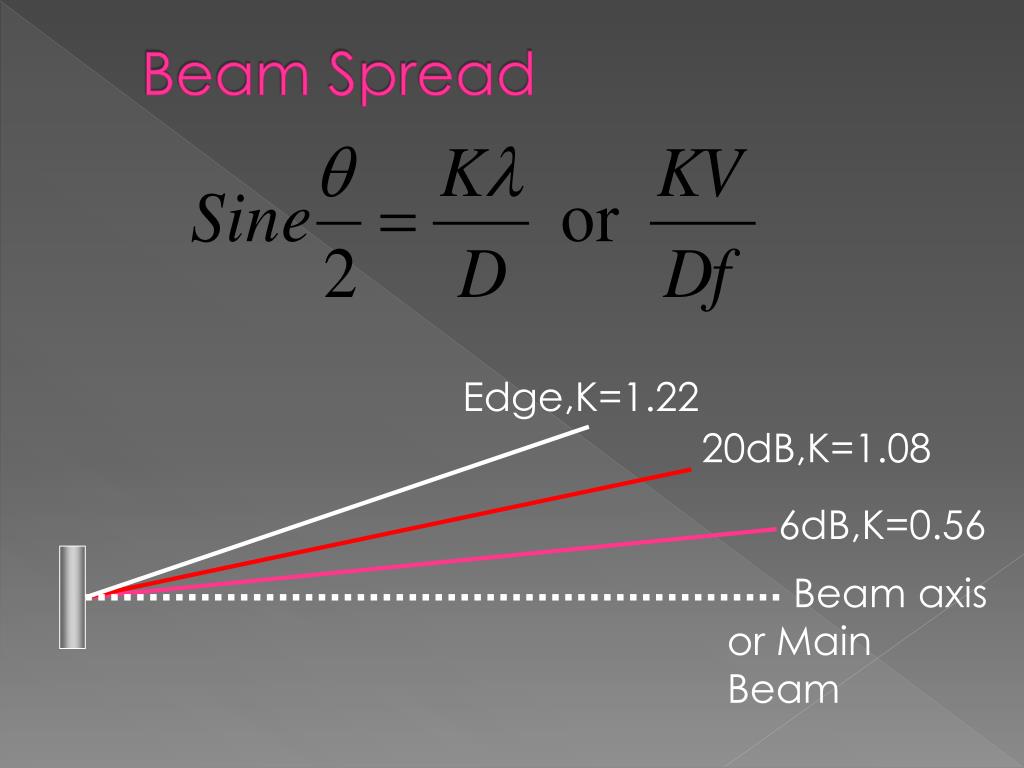
Three theoretical beam divergence edges:
Absolute = 1.22
20 dB edge = 1.08
6 dB edge = 0.56
Beam divergence formula for half-angle beam spread.
Main factor in resolution.
Frequency bandwidth.
Temporal resolution.
Ability to separate two flaws in time.
Spatial resolution.
Ability to separate two flaws within the beam.
Piezoelectricity comes from the Greek words for…
Pressure and Electricity
Most crystals created today are made from?
Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) because of its greater efficiency, higher Z number and relatively higher operating temperatures.
Advantages and limitations of Quartz
Advantage: Electric and thermal stability, insoluble in most liquids
Disadvantage: Low conversion efficiency
Advantages and limitations of Lithium Sulfate
Advantage: Easily damped, excellent receiver.
Disadvantage: Very fragile, max temp. of 165°F, soluble in water
Advantages and limitations of Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT)
Advantage: High conversion efficiency, mechanical strength, moderate temperature range, best all around for industrial use. Disadvantage: High acoustic impedance.
Advantages and limitations of Barium Titanate
Advantage: Mechanical strength, good generator.
Disadvantage: Efficiency changes with temperature.
Advantages and limitations of Lead Metaniobate
Advantage: Low mechanical damping, high tolerance to temperature.
Disadvantage: High dielectric capacitance.
To produce an effective piezoelectric disc, the material must be…
Polarized
X and Y cut crystals.
X-cut: Most common; longitudinal.
Y-cut: Generates shear waves.
To improve resolution, we need to ensure the pulse length is as ________ as possible.
Short
Pulse length math:
Number of cycles in the pulse multiplied by the wavelength.
A low voltage pulse produces better _______, while a higher voltage produces ___________.
Resolution, penetrating power.
Amplitude is affected by (8 things):
Attenuation, surface finish, shape of reflector, orientation of reflector,, material properties of reflector, acoustic beam profile, couplant, size of reflector in direction of measurement.
Huygen’s principle.
Each point of the object acts as a new source of spherical waves.
TOFD sizing accuracy.
± 1mm (0.039”)
TOFD crack growth monitoring capability:
±0.3 mm (0.01”)
Depending on the nature of the defect, length sizing on the order of _________ are achievable.
1-2 mm (0.04”-0.08”)
Dynamic range definition.
Ratio of the amplitude of the largest signal to the smallest signal which an ultrasonic instrument can display.
What controls the time increment between data capture points?
Digitization or Sampling rate.
Time taken to complete 1 wavelength is termed?
A period.
Delay (Hold time) must be ½ the time period for the dominant frequency to create….
Constructive interference (waves in phase).
Typical averaging for TOFD,
Value of eight (may need to increase to 16, 32, etc.).
When using TOFD to estimate flaw size (height), the smallest resolvable flaw is a function of the…
PCS, Probe frequency, and damping quality as well as the depth of the flaw below the surface.
Distance formula.
2*√(s²+d²)
s=half the PCS
d=depth
Time calculation.
t= (2*√(s²+d²)) ÷ v
Lateral wave formula.
LW= (PCS/v) + 2 * (Probe delay)
Non-parallel scan is also known as a…
D-Scan
Parallel scan is also known as a…
B-Scan
Precision means the accuracy with which the time of arrival of a signal can be made. The best that can be achieved is _____ of a wavelength.
0.1, in practice this cannot be achieved.
Beam spread formula.
(K*V) ÷ (F*D)
K is a constant.
General “rule of thumb” minimum amount of cycles which should fit between the lateral wave and the back wall signals.
20 cycles
thickness / (velocity*frequency)
PCS determinations.
Material thickness, number of scans, consideration of beam angle and area of scrutiny required.
PCS calculation
(4/3)d * tan angle
Focus at a point of interest calculation
PCS=2D*tan angle
D = depth of interest
How can the lateral wave dead zone be reduced?