INEL 15130 Inductance
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
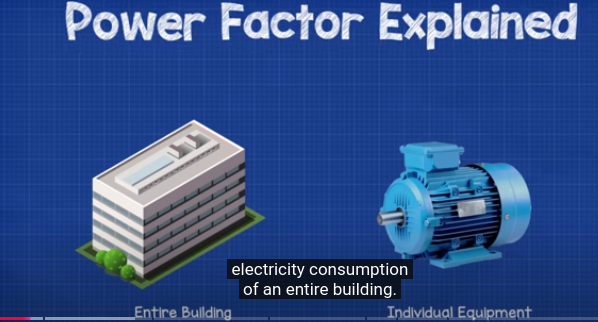
Power Factor
A unitless number used in AC circuits. It can be used to refer to a single piece of equipment such as an induction motor or through or through the energy consumption of an entire building.
Power Factor Formula
PF = True Power (kW) / Apparent Power (kVA)
Reactive Power Changes
Reactive power changes often happen when the power factor of a building falls below a certain level.
Perfect Power Factor: 1 (unlikely).
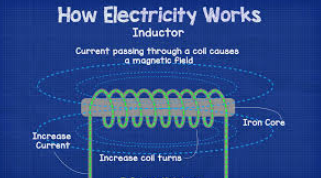
Inductance (L)
One of the primary types of loads in AC circuits. Some amount of inductance is present in all AC circuits because of the continually changing magnetic field. Measured in henrys.
When inductors are connected in series, the total inductance equals ______.
The sum of all inductances of all the inductors.
Induced Voltage
Voltage produced as a result of electromagnetic induction.
Reactance (x)
Opposition presented to AC current by inductance and capacitance.
Inductive Reactance (XL)
The property of an inductive coil that resists the change in AC through it and is similar to the opposition to DC in a resistance. Measured in ohms.
Inductors connected in parallel can be found using the ______ ______.
Reciprocal Formula.
Reactive Power (VARs)
Power that is reflected back to the grid. Can be calculated in the same way as watts except that inductive values are substituted for resistive values in formulas.
Quality of coil
Determined by amount of resistance compared with inductive Reactance. Inductors that have a higher ratio of Inductive Reactance to resistance are considered higher quality.
How many degrees are the current and voltage out of phase with each other in a pure RESITIVE circuit?
0* , they are in phase
How many degrees are the current and voltage out of phase with each other in a pure INDUCTIVE circuit?
90*