Intro Operative [Resin-Based Composite]
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Composite
A solid that contains two or more different component materials or phases when considered at greater than an atomic scale.
Strength and elasticity are significantly changed in comparison with a homogenous material consisting of one component alone
Terminology
Resin-based composite (RBC)
Dental comosite
Polymer matrix composite
Particulate-reinforced polymer matrix composite
What are resin-based composites used for
Direct restoration of anterior and posterior teeth
Dental sealants
Luting of indirect restorations
Cementation of orthodontic appliances
Resin blocks for indirect composite restorations using CAD-CAM technology
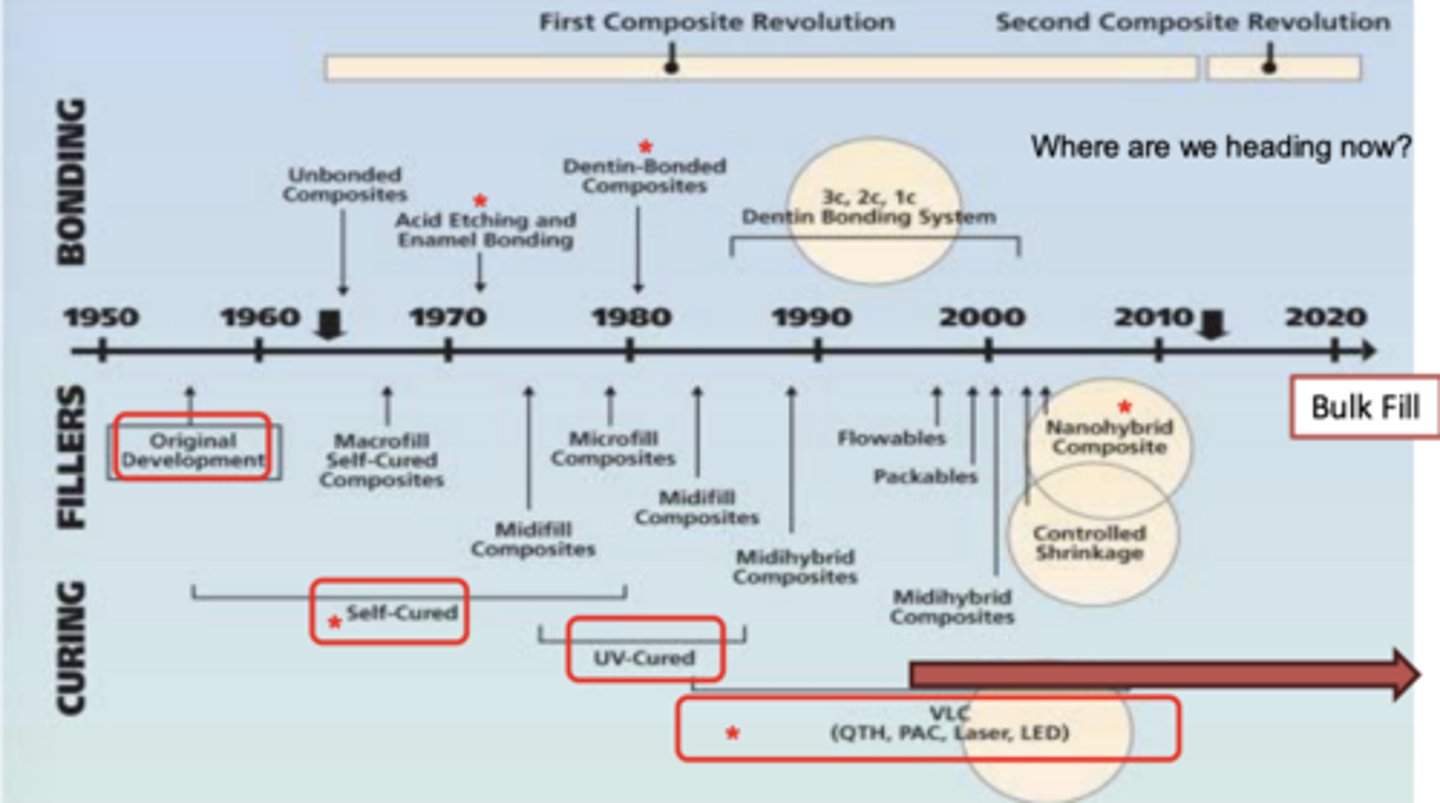
Original development of resin was
around the 60s
Before that used acrylic
Summary of the evolution of dental composite over more than 60 years IMAGE
Basic compositions of RBC
1. Resin matrix
2. Filler particles
3. Coupling agent
4. Initiator and inhibitors
5. Pigments
6. Others (antibacterial etc)
who created the first resin composite and Bis-GMA
R. L. Bowen
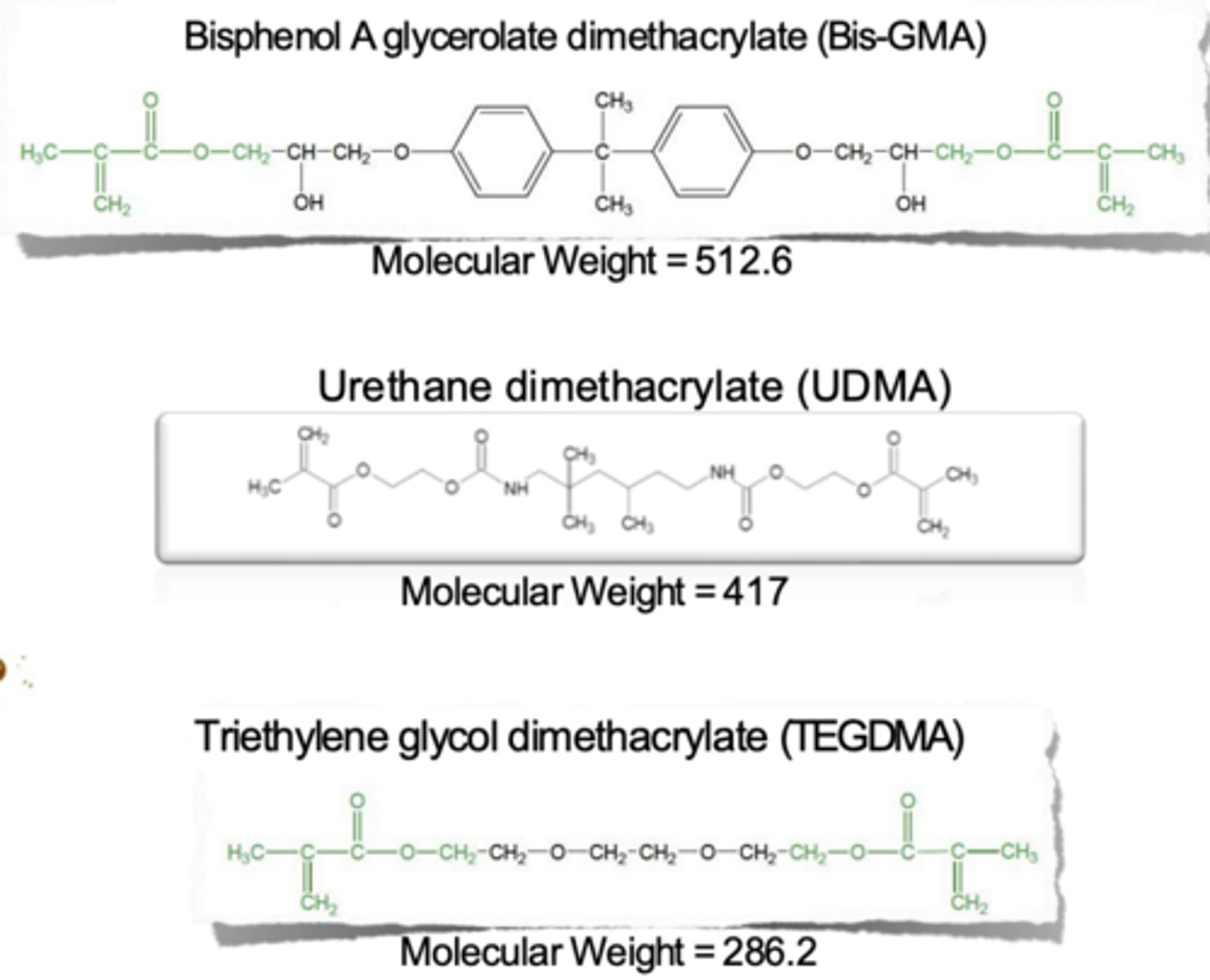
Resin matrix monomers
Bis GMA
UDMA
TEGDMA
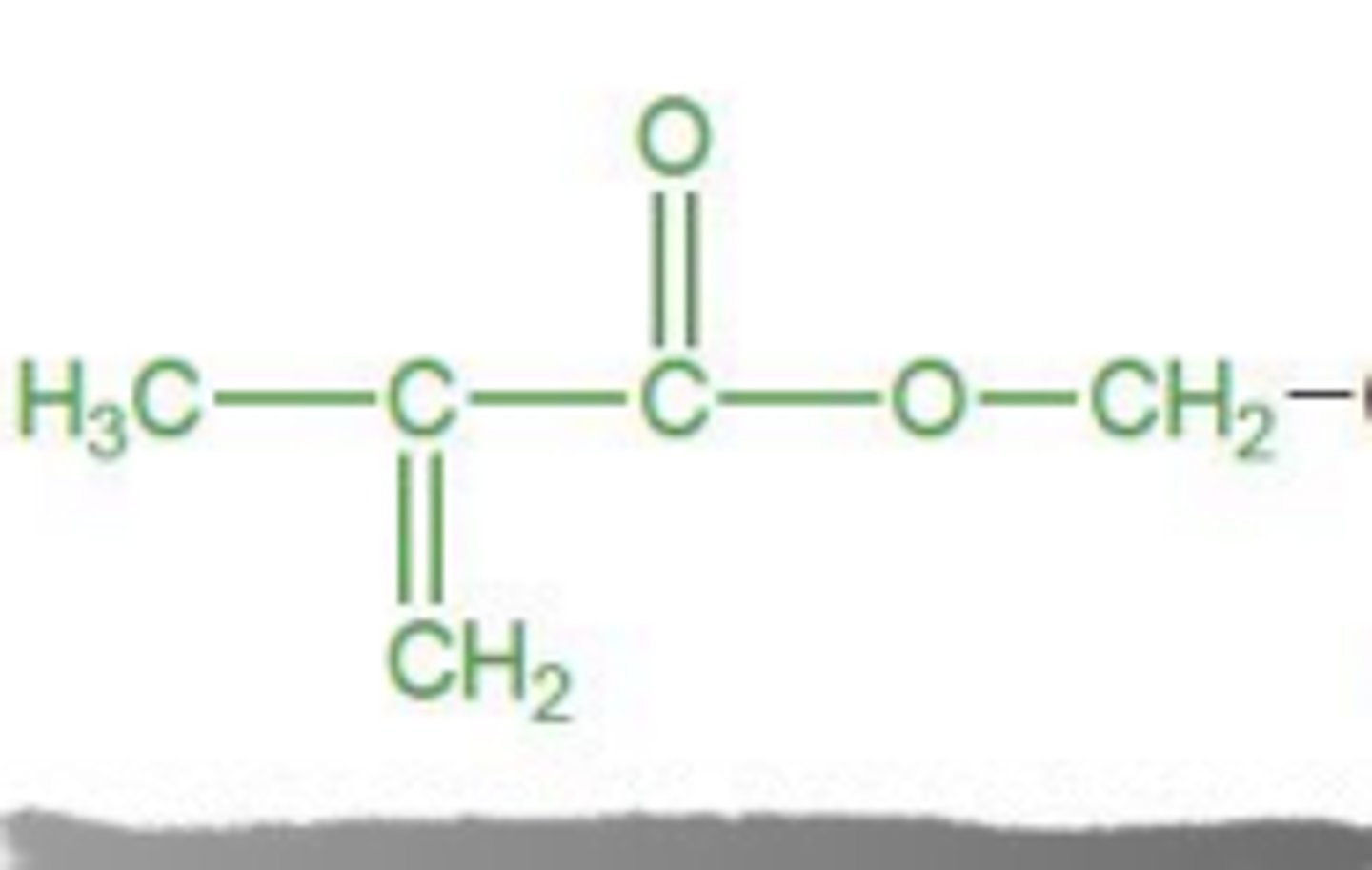
Main component of the monomers
Methacrylate
React with each others
The molecular weight of the 3 monomers tells us what
larger MW mixed with smaller MW helps dilute the mixture
High MW are to big and stiff that you can't add much fillers
Add a lower MW with the higher MW makes it all more fluid and fillers will mix together better
Fillers are __ -__% by volume
30-70%
Filler particles types
- Finely ground quartz or glass sol-gel ceramic
- Microfine silica
- Silica nanoparticles
Functions of filler particles
Reinforcement of the resin matrix
Reduction of polymerization shrinkage
Reduction of the thermal expansion/contraction
Decrease water sorption
Impart radiopacity
Control workability/viscosity
What is Phoenix's body weight
188
The more fillers we have will proportionally reduce
the amount of organic matrix
More filler = better
Coupling agent- silane
Provides the bonding between the inorganic filler particles and the organic resin matrix
- forms an interfacial bridge that strongly binds the fillers to the resin matrix
- It enhances the mechanical properties of the resin composite and minimizes the loss of the filler from resin matrix during clinical wear
TA:
- bridging material
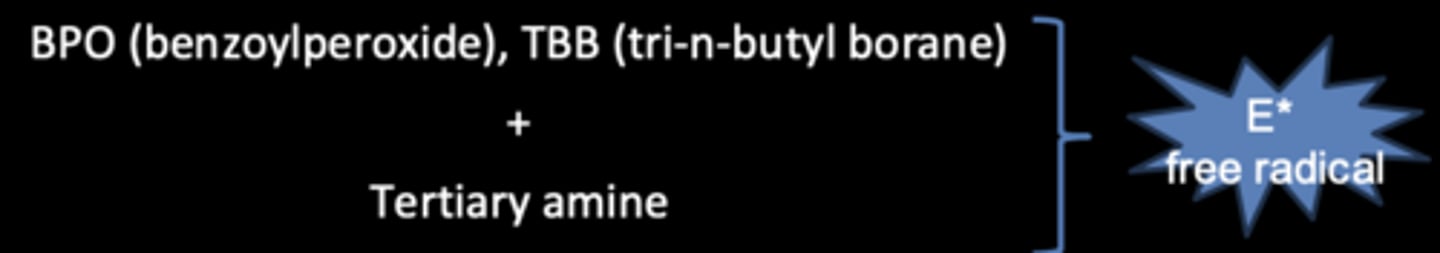
Initiators: Chemically activated resin composites
Polymerization begins when the two components are mixed
Initiators: Light cured resin composites
Photo-initiators
- absorb electromagnetic energy

Inhibitors
Prevent spontaneous polymerization
ex: Hydroquinone
Increases:
- shelf-life
- Workin time
Resin polymerization
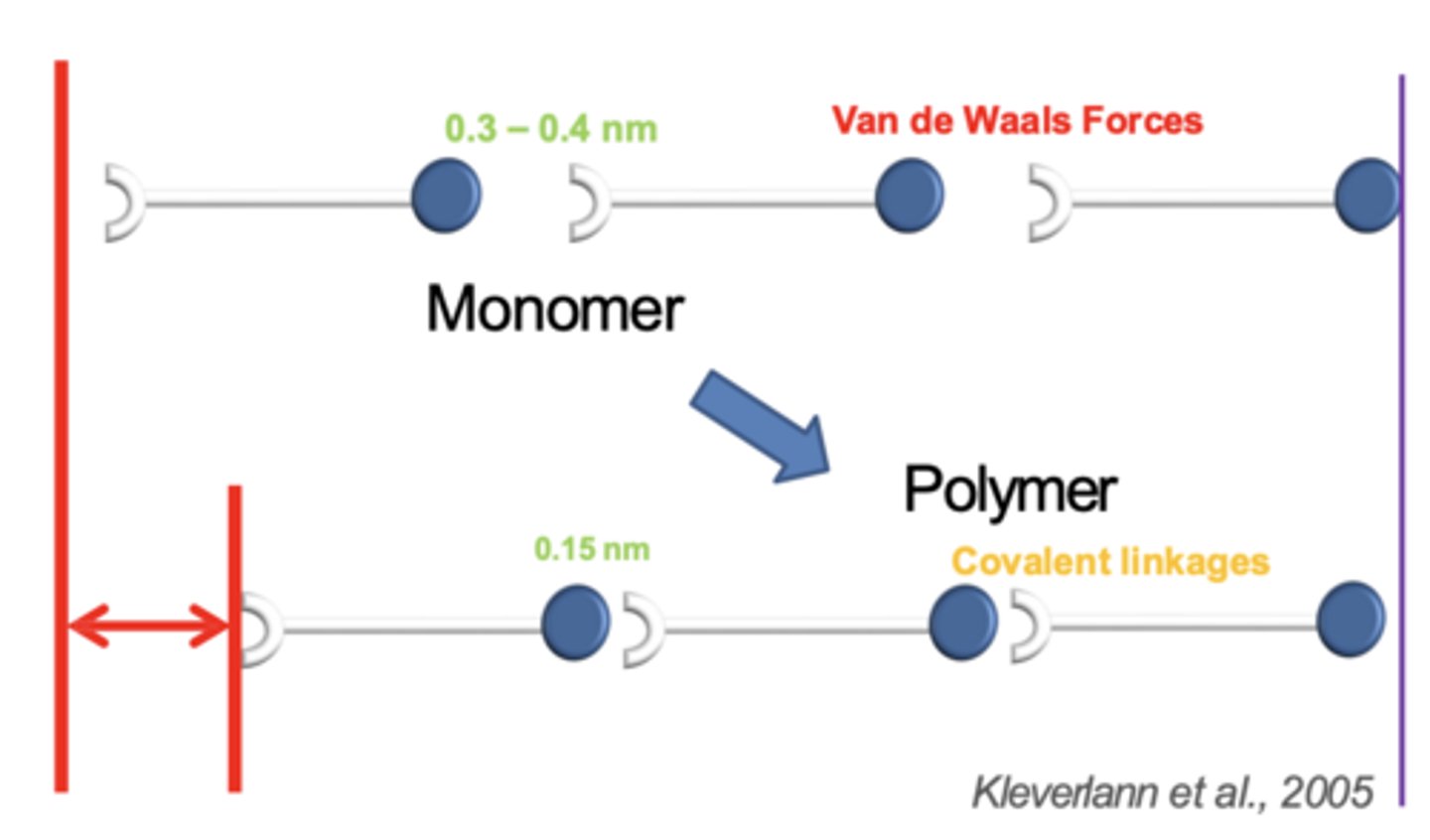
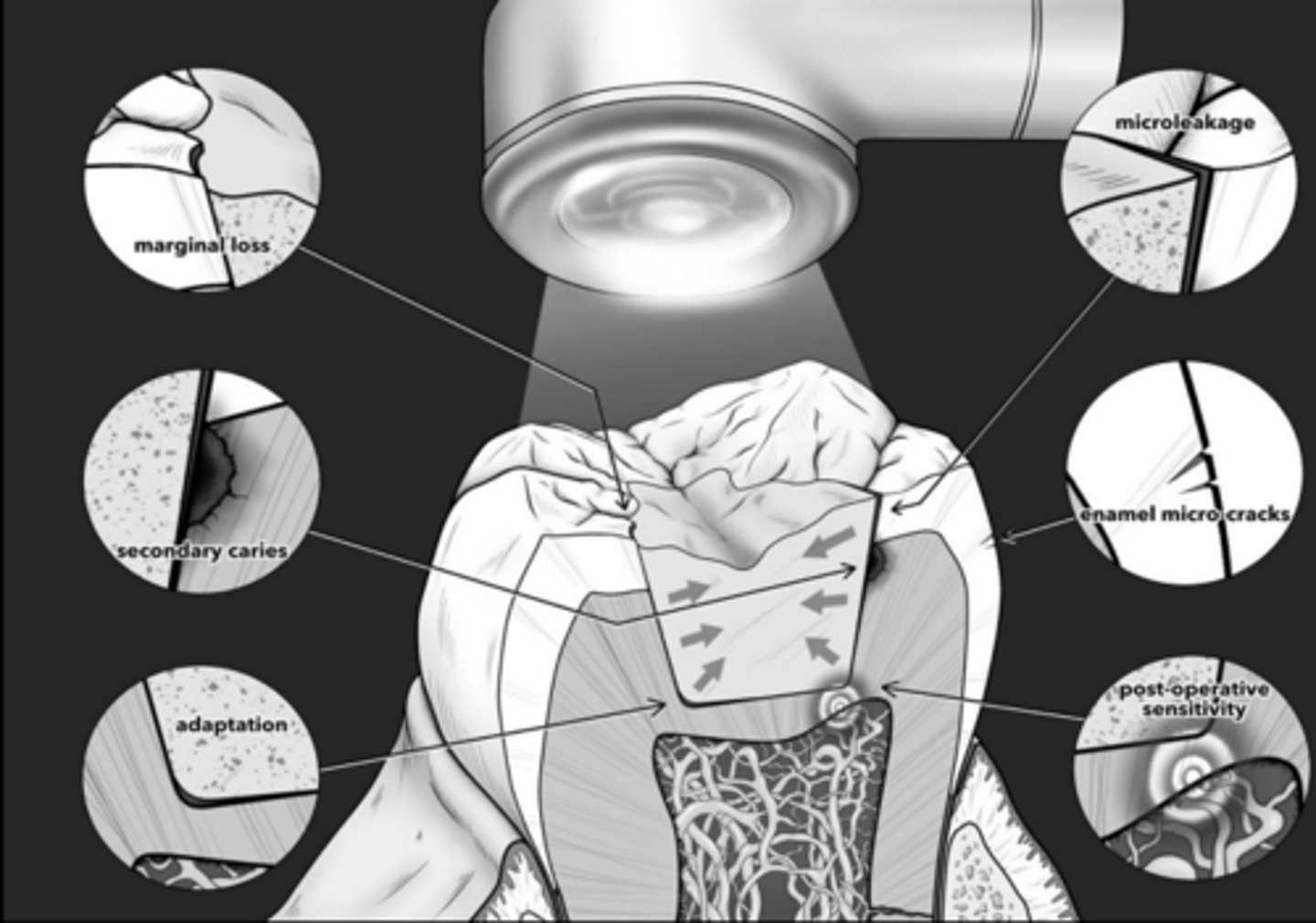
Polymerization shrinkage: Clinical implications
Creation of internal stress
Cusp deformation
Marginal gaps
Enamel cracks
- marginal leakage
- postoperative sensitivity
- secondary caries
Optical characteristics
Multiple shades and transclucency of both enamel and dentin
Dentin like: opaque, dentin, body, etc
Enamel-like: Enamel, body etc
Translucent-like shades: incisal translucent
- Intermediate opacity usually used for posterior restorations (single shade)
- Multiple shades used for anterior restorations

Classification of Resin-based composites
1. Filler particle size and distribution
2. Clinical usage (flowable, universal, bulk fill)
3. Polymerization reaction (light-cured; self cured; dual cured)
Classification: Filler particle size
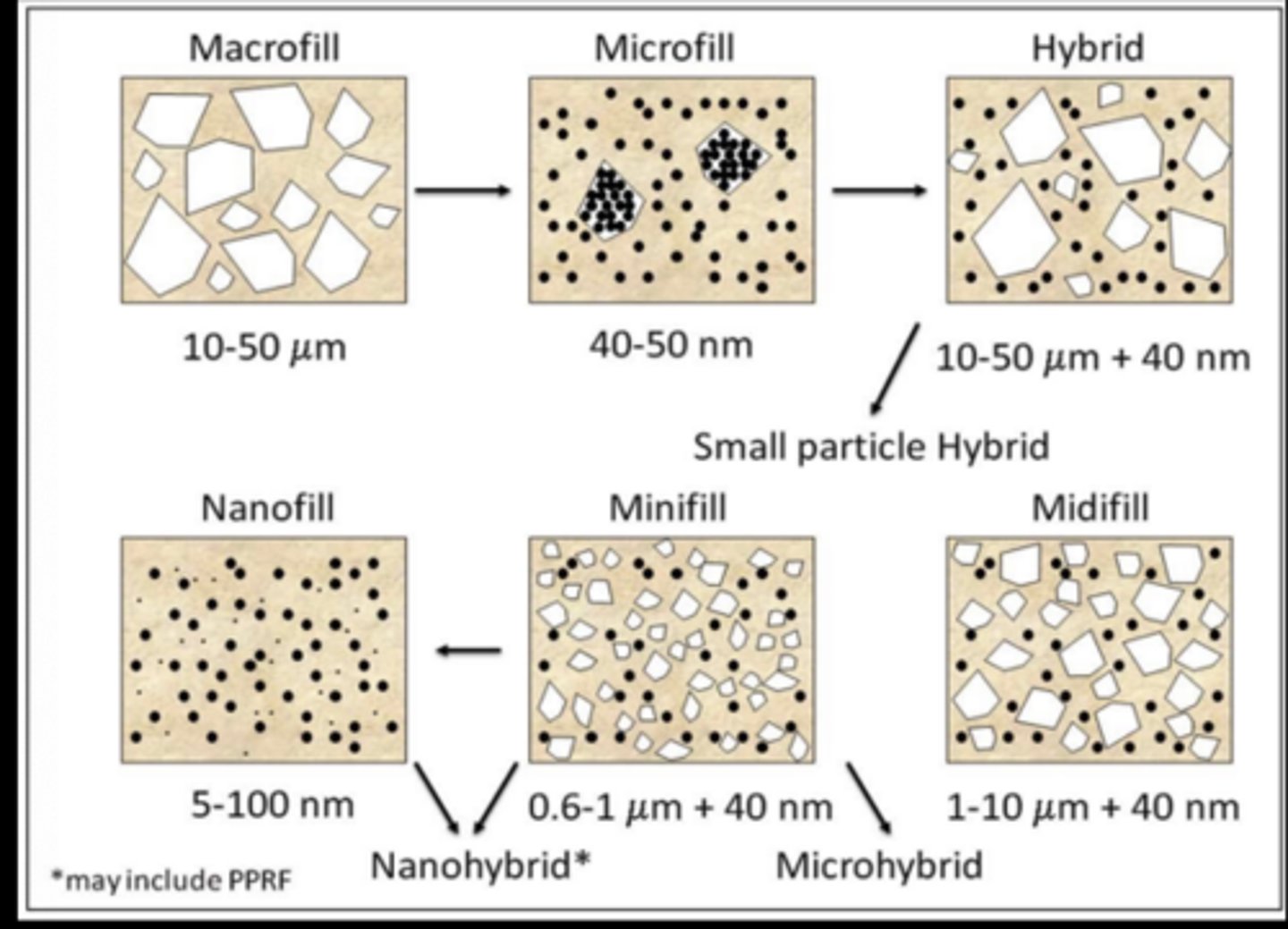
Microfil
40-50 nanometer sized fillers, pre-polymerizated filled resin particle mixed with the monmers
Polished to the highest luster and smoothest surface
Not as strong as other RB- low stress bearing and esthetic areas
Mini/midfill or microhybrid
Less than 1 micrometer sized fillers
Intermediate filler loading between microfills and hybrids (high strength and good resistance)
Used for anterior and posterior restorations
Nanofilled and nanohybrid
< 100 nanometer sized filled or conventional fillers with added nanometer particles
High strength esthetics and polishability
Classification- clinical application and viscosity: Packable
Packable (high viscosity)
- Posterior teeth
- difficult adaptation
- rarely used
- Idea that packing composites would be similar to dental amalgam (Not really)
Classification- clinical application and viscosity: Flowable
Flowable (low viscosity)
- Easily adapt to the preparation
- Inferior mechanical properties
- Not to be used in load bearing area
- Better results with newer formulation
Classification- clinical application and viscosity: Conventional
Conventional (regular viscosity)
- Universal composites
- nanofilled, nanohybrids and microhybrids
- higher resistance, low wear, can be used in load bearing areas
- Polymerization shrinkage (stress)
Classification- clinical application and viscosity: Bulk-fill
Bulk-fill (conventional or low-viscosity
- Posterior restorations
- Reduced stress from polymerization shrinkage
- Deeper curing depth
- Conventional: Higher resistance, low wear, can be used in load bearing areas
- Low viscosity: not recommended in areas of high wear or loading stresses
Classification- Polymerization reaction: Type 1
Polymer-based restorative materials claimed by the mainufacturer as suitable for restorations involving occlusal
Classification- Polymerization reaction: Type 2
All other polymer-based restorative material, and luting materials
Classification- Polymerization reaction: Class 1
Materials whose setting is initiated by mixing an initiator and activator (self-curing materials)
Classification- Polymerization reaction: Class 2
Materials whose setting is initiated by the application of energy from an external source, such as blue light or heat
Group 1: materials whose use requires the energy to be applied intra-orally;
Group 2: materials whose use requires the energy to be applied extra-orally; these materials will be luted into place.
Classification- Polymerization reaction: Class 3
cured by the application of external energy and also have a self-curing mechanism present ("dual cure" materials)
Desirable physical and mechanical properties
Linear coefficient of thermal expansion (better when similar to the tooth's)
Water sorption (organic phase: increase filler- decrease water sorption)
Wear (filler size, shape and content, position in the dental arch, occlusion)
Modulus of elasticity (stiffness): increase filler - increase stiffness
Color stability (hydrolysis- marginal discoloration)
Physical and mechanical properties: Linear coefficient of thermal expansion
Increase in volume due to atomic vibration promoted by increased temperature in a solid
Clinical relevance: In the mouth, a composite restoration will undergo temperature changes between 4°C and 60°C
Better when similar to the tooth's
Physical and mechanical properties: Water sorption/swelling
Differential volume/weight of the material after immersion in water or another fluid
Influenced by the type of monomers (more hydrophilic monomers will absorb more water) and the amount of fillers
Clinical significance:
- Color, stability, volume stability, weakening of the polymeric structure
Physical and mechanical properties: Water resistance
Surface or volumetric loss of material due to wear
Clinical significance: margin deficiencies, volumetric loss of material, loss of surface gloss
Physical and mechanical properties: Fracture resistance
Maximum force that a body can resist when tested under compressive or tensile loads
Physical and mechanical properties: Fracture toughness
Measure of materials resistance to the propagation of a crack from a preexisting flaw of known size and infinite sharpness
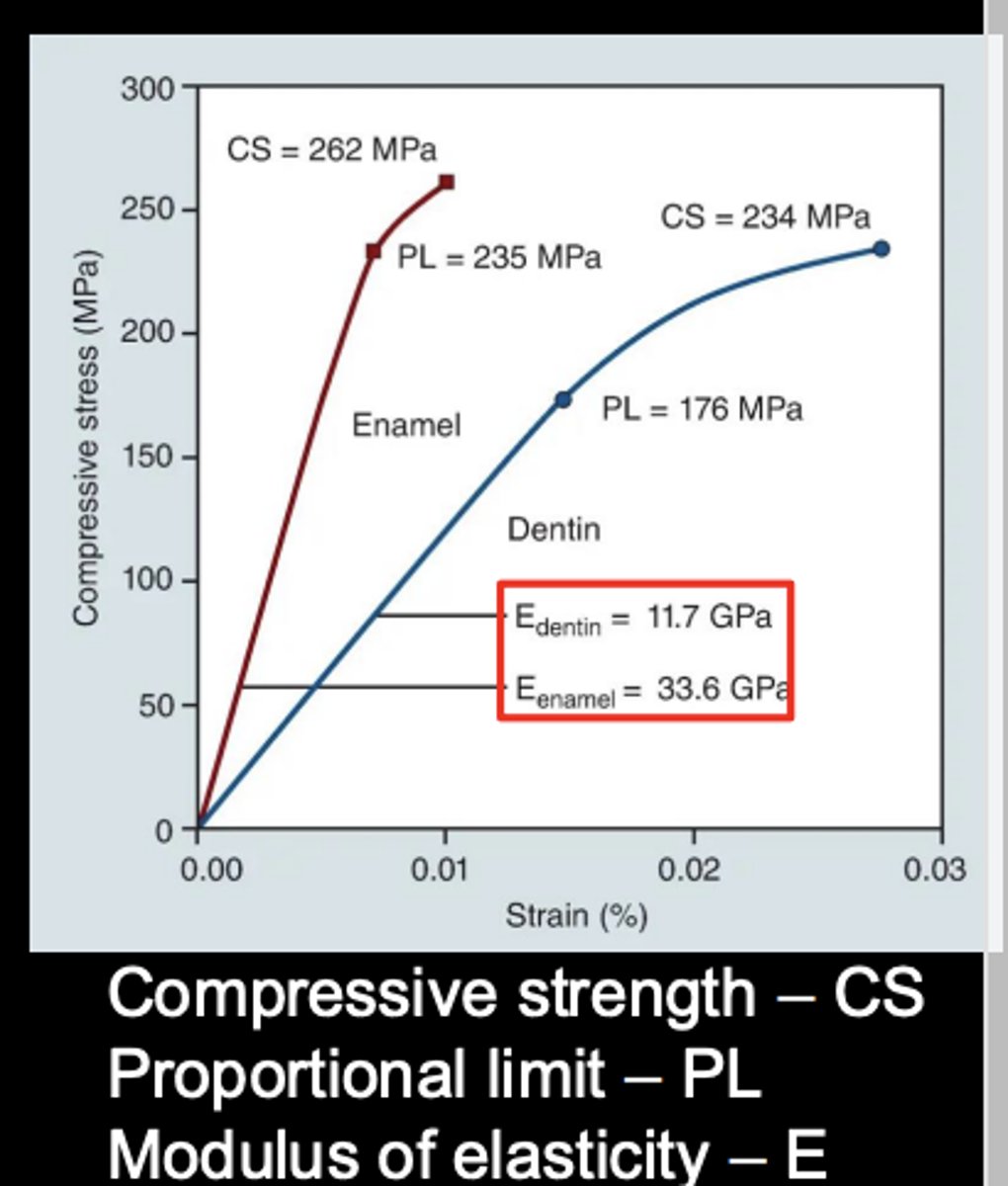
Physical and mechanical properties: Modulus of elasticity and stiffness
The elastic modulus will determine the stiffness of a material
Measured by slope of the elastic region of a stress strain graph
Resin composites are suitable for replacing dentin- similar modulus of elasticity
Higher filler concentration - higher elastic modulus
Resin monomer composition and properties

Road to improvement
Improved sealing and toughness
Bacterial colonization and biofilm formation- antibacterial surface (less secondary caries)
Material degradation resistance- current materials can be degraded by certain salivary and bacterial enzymes
Self repairing materials- crack repair
Multifunctional and stimuli-responsive materials- beneficial pulp response, self adaptation/ repair when unde stress