M5 - Respiratory System
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
nasal cavity
Filters, warms, and moistens incoming air
Inside the nose
pharynx
Common air passage from nose/mouth to larynx
Behind the nasal and oral cavities (throat)
epiglottis
Prevents food and liquid from entering the airway during swallowing
Flap at the base of the tongue, above the larynx
larynx
produces sound, protects lower airway
Between the pharynx and trachea Keeps airway open
trachea
Conducts air to and from the
From larynx to bronchi lungs
lungs
Gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out)
Thoracic cavity, on either side of the heart
pleura
The pleura is a two-layered membrane surrounding the lungs, with one layer (parietal pleura) lining the chest wall and the other (visceral pleura) covering the lungs, creating a small space filled with lubricating fluid (pleural fluid) that allows the lungs to move smoothly during breathing. It's located within the chest cavity, separating the lungs from the thoracic wall
parietal pleura
Reduces friction during breathing
Lines the inner chest wall
visceral pleura
Reduces friction and allows lungs to move smoothly
Covers the surface of the lungs
bronchi
Conduct air into the lungs
Branches off the trachea into each lung
bronchioles
Regulate airflow to alveoli
Smaller branches within the lungs
alveoli
Site of gas exchange
End of bronchioles in the lungs
pulmonary capillaries
Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with alveoli
Surround alveoli
cilia
Move mucus and trapped particles out of the airway
Lining of nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi
cartilage
functions as a shock absorber, reduces friction between joints, and provides structural support for body parts like the nose and ears
A serous membrane (serosa)
is a thin, double-layered, lubricating membrane that lines closed body cavities and covers internal organs to reduce friction
What type of membrane lines the respiratory tract? What are the functions of this membrane?
Mucous membrane
Secretes mucus to trap dust, microbes, and debris
Moistens and warms inhaled air
Protects underlying tissues
Cilia move trapped particles upward toward the pharynx for removal
What is the function of the eustachian tubes?
Drain fluid from your middle ear
Equalize air pressure in your middle ear
Protect your middle ear
Explain the anatomical difference between the right and left lungs
Right lung
shorter, wider, and heavier
3 lobes (superior, middle, inferior)
2 fissures
Left lung
narrower, and lighter
2 lobes (superior, inferior),
1 fissure
has a cardiac notch to accommodate the heart.
The right lung lies over the liver, while the left provides space for the heart and the aorta.
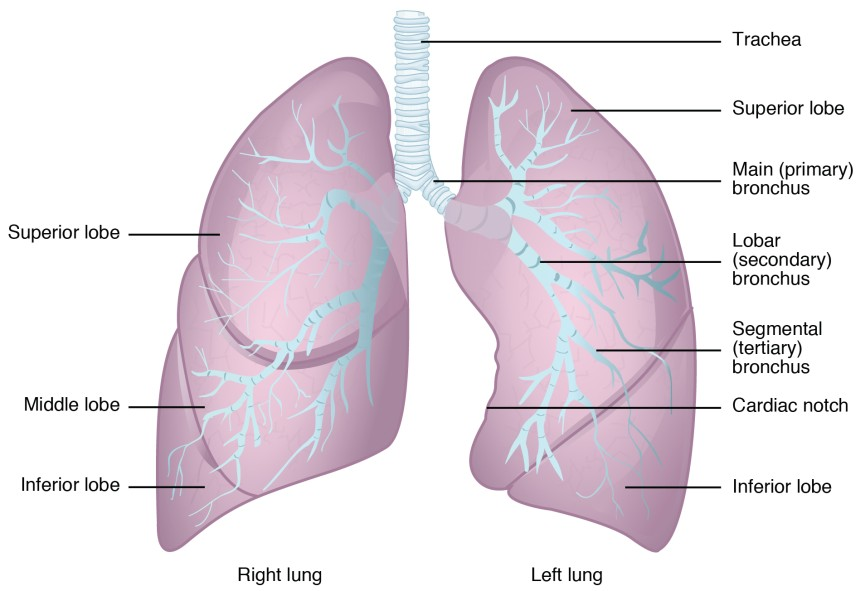
How are the lung surfaces protected from irritation due to breathing movements?
a double-layered membrane system containing a specialized, slippery lubricant. This mechanism ensures that the lungs can expand and contract smoothly against the chest wall without damage.
Inspiration and Expiration
Inspiration (inhalation):
Diaphragm contracts and moves downward
External intercostal muscles contract → ribs move up and out
Thoracic cavity volume increases
Intrapulmonary pressure decreases
Air moves into the lungs
Expiration (exhalation):
Diaphragm relaxes and moves upward
Intercostal muscles relax → ribs move down and in
Thoracic cavity volume decreases
Intrapulmonary pressure increases
Air moves out of the lungs
Recall the name of the serous membrane in the thoracic cavity.
pleura
Which layer of the serous membrane lines the thoracic cavity?
The parietal pleura
What is unique about the pressure in this space?
The pressure in the pleural cavity is negative (sub-atmospheric).
This negative pressure keeps the lungs expanded and adhered to the chest wall and prevents lung collapse during normal breathing.
What is the space between the two layers of the serous membrane called?
pleural cavity (pleural space)
Which layer of the serous membrane covers the lung tissue?
visceral pleura
What muscles perform the function of normal breathing?
External intercostal muscles: are primary muscles of inspiration that elevate the ribs and sternum, increasing the thoracic cavity's volume and decreasing internal pressure to pull air into the lungs
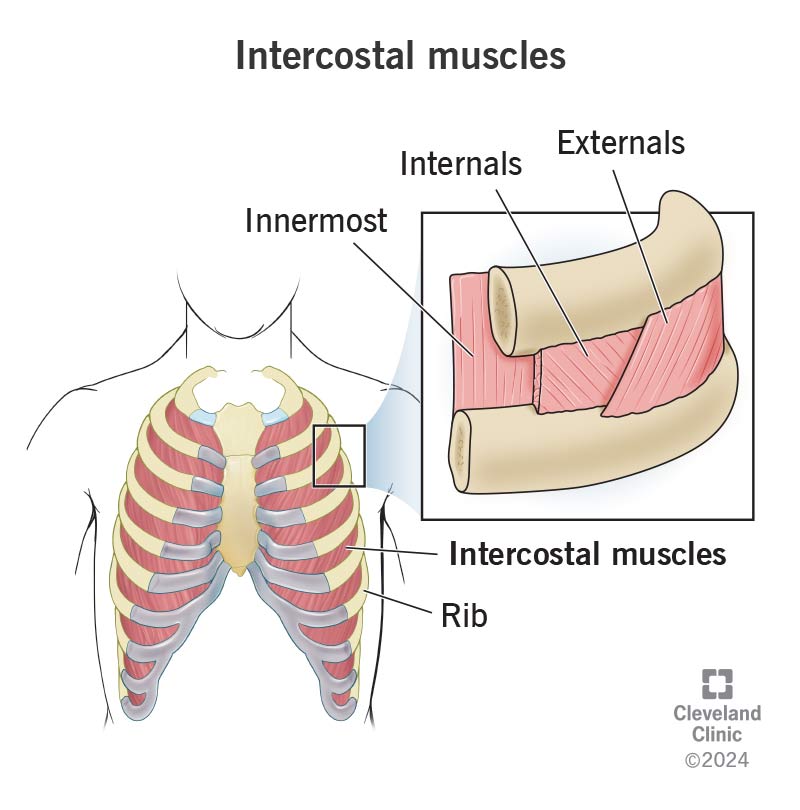
The muscle that divides the thoracic and abdominal cavities also has a role in breathing. What is the name of this muscle and how does it assist in breathing?
Diaphragm: is the primary, dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs that enables breathing by contracting and flattening to expand the chest cavity, drawing air in (inhalation)
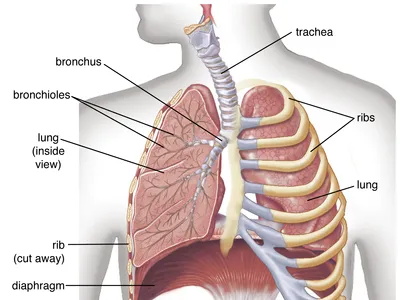
Organs in Thoracic Cavity
heart, lungs, thymus, trachea, and esophagus
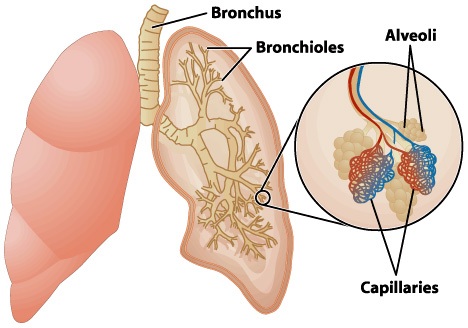
Alveoli
are tiny, balloon-shaped air sacs at the end of the bronchioles in the lungs, acting as the primary site for gas exchange between the respiratory and circulatory systems
Arterial blood
is bright red, oxygen-rich blood pumped from the heart under high pressure to supply organs
Venous blood
is dark red, deoxygenated blood returning to the heart under low pressure
arterial blood gases
are a crucial blood test measuring oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in blood from an artery, assessing lung function, oxygenation, ventilation, and the body's acid-base balance (acidosis/alkalosis).