Pharmaceutics EXAM 1 - TOPIC 1 ONLY (not on final exam)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Division by zero or infinity is…
undefined.
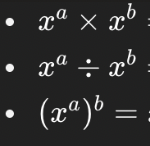
Solve these
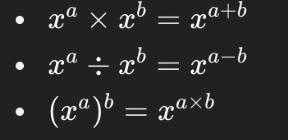

Solve this


Solve this

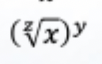
Solve this:
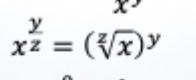
What is greater? -1 or -3?
-1 is greater than -3
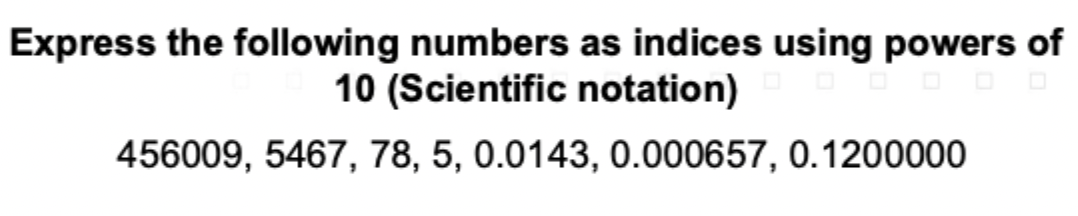
Solve this


Solve this
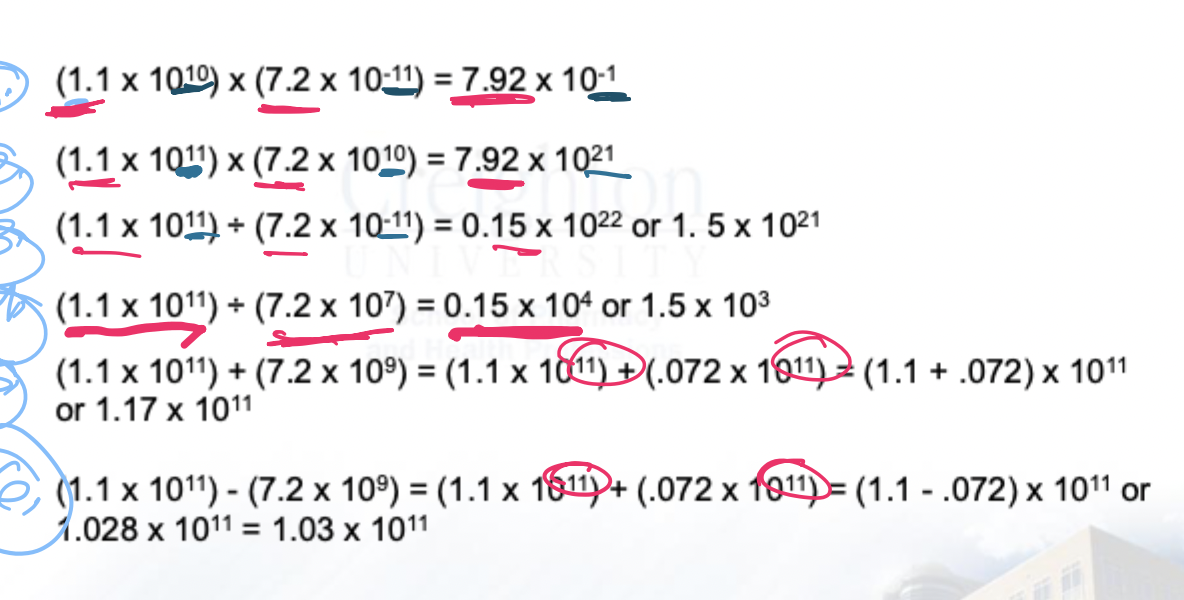
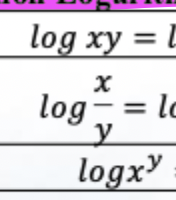
solve this
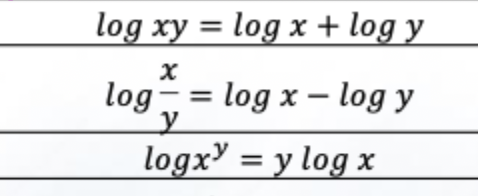
Solve this
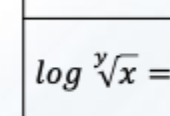
Solve this
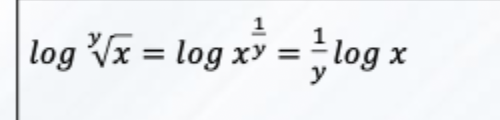
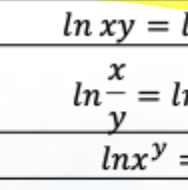
Solve this
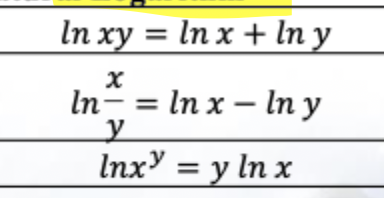
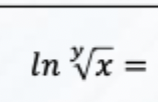
Solve this
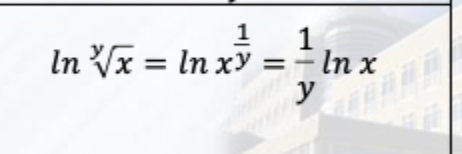
Show me
a. common log
b. natural log
a. Log (base 10)
b. Natural Log (ln)
a. What type of log does pharmacy use?
a. In pharmacy, natural phenomena (drug distribution, elimination) follow natural log, so both log types are needed.
Use logs to simplify multiplication/division of very large or small numbers
Exact numbers:
Counted values (e.g., 110 students).
no sig figs needed
Inexact numbers:
Measurements (e.g., 52 ± 1 mL in a beaker).
use significant figures
Example: Beaker 52 mL (2 sig figs), cylinder 36.5 mL (3 sig figs), buret 20.38 mL (4 sig figs)
Rule of thumb when reading measurements?
Rule of Thumb: Read 0.1 of the smallest division.
Last digit = estimated (guess)→ determines precision.
The more the precise the tool, the more….
more sig figs
Accuracy means:
How close is your measured result to the true or correct value
What is USP?
United States Pharmacopeia: "rulebook" for quality in pharmacy.
we compare measurements to an official standard from the USP
USP error for
a. purity testing
b. compounding
a. error must be less than ±0.1%
b. the allowed error is ±5%
Find by calculating the percent error. If it is less than 5%, we're good. If more than a percent error, we bad!

Precision
If you repeat your measurement many times, do you get the same or very similar results each time?
It’s about consistency, not correctness.
USP Requirements for Precision
To prove your precision in the lab:
Measure 10 samples (like 10 capsules).
Find the average weight of those 10.
Then calculate how far each value is from the average (this is called standard deviation, or SD).
Multiply the SD by 3.
→ If 3 × SD is less than 0.001, your precision is acceptable under USP rules.
Why precision important?
If your measurements aren’t precise, a drug might contain too little (won’t work) or too much (might cause side effects).
This is especially serious for drugs that are very strong or have a narrow safe range (called a narrow therapeutic window).
For those, you need very precise balances that can detect even tiny changes in weight.
What are “Balances” in Pharmacy?
Balances = Scales that measure tiny amounts of medicine.
In pharmacy, you need scales that can measure very small weights—even in micrograms (mg) or smaller!
What Does “Resolution” Mean?
Resolution = the smallest amount the scale can detect or measure.
The smaller the number, the more sensitive and precise the scale is
The smaller the resolution number….
the more sensitive, precision and safety
What re the types of balances?
Balance Type | Smallest Amount It Can Detect (Resolution) |
Top Pan Balance | 0.001 grams = 1 mg (most common) |
Analytical Balance | 0.1 mg or 0.01 mg (for tiny/potent drugs) |
Semi-Micro Balance | 0.001 or 0.002 mg |
Micro Balance | 0.0001 mg (for tiny/potent drugs) |
The last digit in a measurement is always the one that’s
estimated or uncertain.
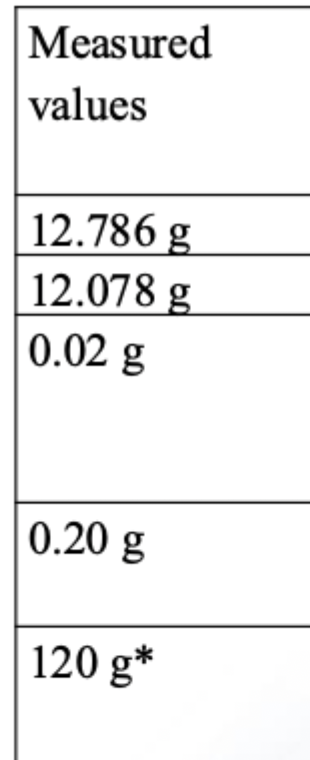
How many sig fig?
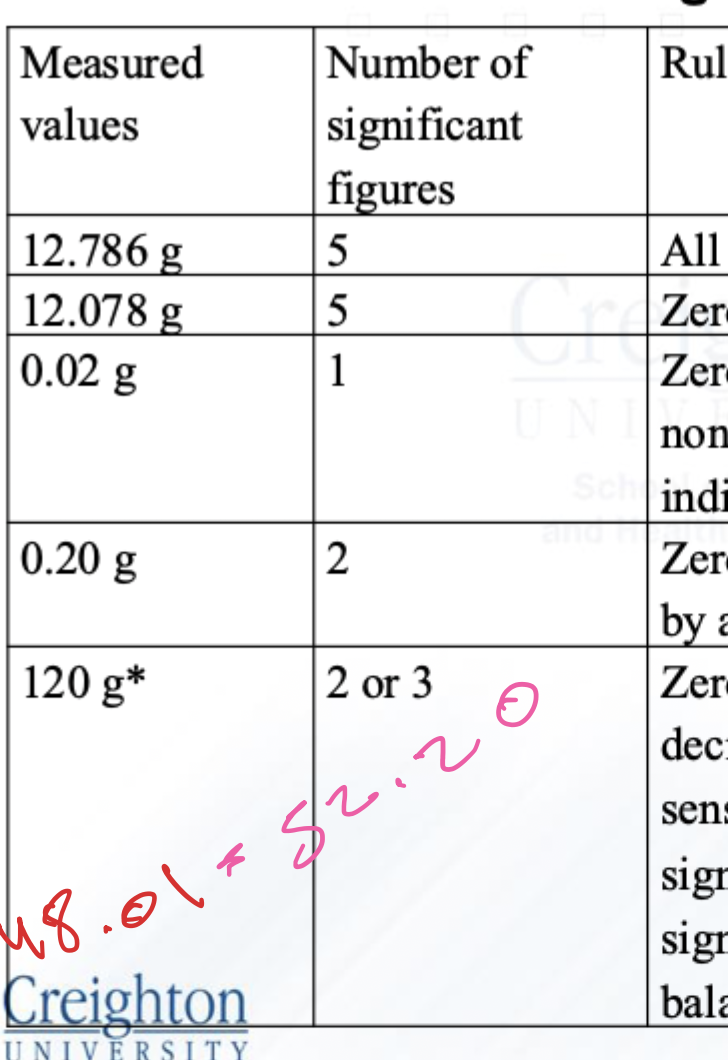
Why 120 has 2 or 3 sig fig?
Because it depends on what kind of scale was used to measure it.
Now he explains two types of scales:
1⃣ If the scale has a sensitivity of 10 grams:
That means the scale can’t tell the difference between 120, 121, or 122.
So if the real weight was 121, the scale would still show 120.
In this case, the last digit (the 0) isn't reliable.
So we only count 1 and 2 → That gives 2 significant figures.
2⃣ If the scale has a sensitivity of 1 gram:
Now, the scale can show 119, 120, 121, etc.
That means the “0” was actually measured, not just a guess.
So all three digits — 1, 2, and 0 — are meaningful.
That gives 3 significant figures.
What is mode?
most frequent value.
What is mean?
average
What is USP rule for Chlorpromazine Suppositories and Ciprofloxacin Tablets?
not less than (NLT) 90.0% and not more than (NMT) 110.0% of the labeled amount.
so 110.5% would work but 89.9% will not work
if a quantity in USP monographs is mentioned as 110.0 %, 110.1, or 110.2 %
could be acceptable, but certainly 110.6% would not be acceptable because the
error involved is 6% which is >5%. On p. 20, read why 89.9% is not acceptable if
requirement is not less than 90.0 %

The best drugs depends on…
the clinical situation
What is median?
The median is the middle number when you line up all values in order.
If there's an even number of values, it’s the average of the two middle numbers.
What is standard deviation?
(SD) tells you how far each number is from the mean/average
A low SD means most scores are close to the average.
A high SD means scores are more spread out.
How do you compare theoretical and measured values?
Make a graph (like a scatter plot)
Then, you add a "trend line" to see the pattern in your data
Straight lines in graphs (like Dose vs. Response) help predict…
how changes in dose affect outcomes.
Who makes trend line?
excel
What are the Excel trendline values?
r (correlation coefficient): Shows how well the points fit on a line.
r ranges from -1 to +1:
+1 = perfect fit
0 = no fit
-1 = complete negative correlation
we want r ≥ 0.95 for clinical use (
r² (coefficient of determination): Tells you how much change in Y is due to X.
r² close to 1 = strong relationship.
What is a trendline equation?
y = mx + c
y = mx + c
a. m mean?
b. c mean?
a. m = slop
b. c = constant
What is a unit
Number with a measurement
Dimension
What kind of thing it is
Fundamental Dimensions
Length
Mass
Time
density formula?
mass / volume
volume = mL, cm3, or m3.
mass = g, kg
CGS units: g/cm3 or g/mL
SI units: kg/m3
Symbol: ρ (rho)
You should note that: 1 m3 = 1,000,000 cm3. Also, 1 mL = 1 cm3
specific gravity formula
density of substance/density of water
no units (it’s a ratio)
equal to one if the same as water
used in machines like TPN
relate between density and specific gravity
Numerical values of both density and specific gravity in cgs system would be same.
a. cm3 = mL
b. m3 = cm3
a. 1 cm3 = 1mL
b. 1 m3 = 10^6 cm3
Force equation
mass x acceleration
Weight equation
mass x acceleration due to gravity (g-a) or (g+a)
W = m(g ± a)
Weight = 1 g of mass x 981 g cm/sec2 or 981 dyne
weight does not change
Gravitational Acceleration = 9.81 g cm/sec2 or 981 dyne (Given in formula sheet)
Weight is force or mass
FORCE
What is the Pressure equation?
Pressure = Force/Area
Pressure = dynes/cm²
There is one more unit (add later)
What is Work Formula?
Work = Force x Distance
1 erg or Joules = 1 dyne x 1 cm
What all have the same units?
Work, heat and energy – all three have the same unit.
1 Joule (J) = 10^7 ergs and 1 calorie = 4.184 Joules (given in formula sheet)
What is Energy?
ability to do work
unites same work (Joules or ergs)
Heat
unit is calorie or kilocalorie.
How are heat and energy related?
heat and energy can be interconverted
1 calorie = 4.184 Joules (given in formula sheet)
Review all case studies in OneNote section called W1:Topic 1: Intro: Terminology, Basic Mathematical Skills and Calculations