Chemistry - 1 Atomic Structure - 1.3 Separating Mixtures
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
Ratios (c vs m)
- Compounds have a fixed composition
- Mixtures have no fixed composition
Separation (c vs m)
- Compounds must be separated by chemical reactions
- Mixtures can be separated by physical means, using the properties of each separate substance
Chemical bonds (c vs m)
- Compounds contain different elements chemically bonded
- There are no chemical bonds between atoms of a different substance in a mixture
Filtration
A process used to separate an insoluble substance from a solvent - usually with filter paper and a funnel
Filtering sand [3]
- The sandy water is poured through filter paper
- The sand collected on the paper is rinsed to remove any remaining soluble solvents
- The sand is dried in a warm oven to evaporate off the water
Crystallisation
The formation of crystals by evaporating a solvent from a saturated solution
Crystallisation process [3]
- Heat an evaporating dish containing the saturated solution (either in a water bath or directly on the gauze and tripod)
- Stop heating at the point of crystallisation
- Leave the rest of the solvent to evaporate at room temp
Filtrate
liquid that has passed through a filter
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Distillation
A process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
Simple distillation
- Solution is heated over Bunsen burner
- A thermometer is placed so that we can record the gas's temperature
- the gas enters a condenser where it is cooled and again becomes liquid
- The liquid enters another glass
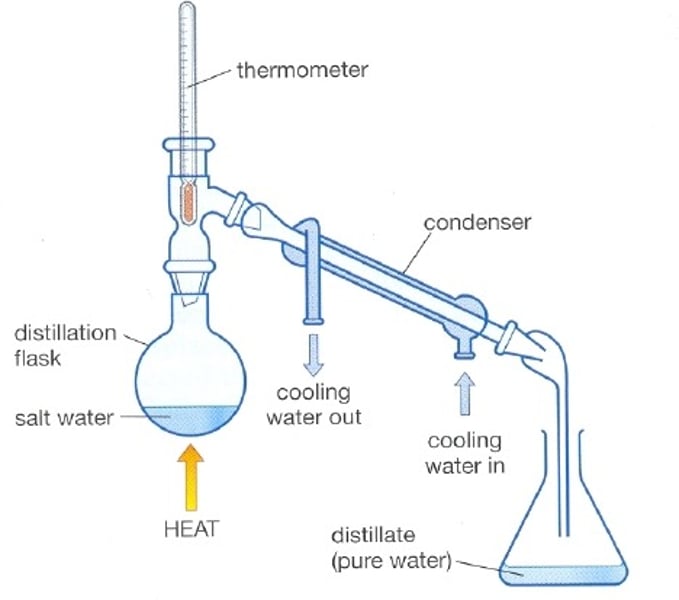
Condenser
A tube with an outer jacket that has water flowing through it, acting as a coolant to condense the vapours inside
