Plant biology unit 3
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Root function
Anchor plant in soil, absorb and conduct water and minerals, produces hormones, food storage
Where to find taproots
Dicots and gymnosperms
Taproot
Large main root developed directly from the radicle. Produces branch roots. Penetrates deep in the soil and spread out
Where to find fibrous roots
Seedless vascular plants, monocots
Fibrous roots
Radicle dies and numerous roots grow from lower part of stem. Adventitious roots, each one develops lateral roots. Shallower, more spreading
3 root zones
zone of cell division, zone of elongation, zone of maturation
Zone of cell division
apical meristem at root tip. Subdivided into protoderm, ground meristem, procambium
Root cap
Produced by root apical meristem, protects root, produces mucigel
Stele
Central cylinder of vascular and ground surrounded by cortex
Protostele
simplest type of stele
Pericycle
encircles stele, made of meristematic cells that give rise to lateral roots
Endodermis
regulates flow of materials between cortex and vascular tissues, surrounded on 4 of its 6 sides by casparian strips
Casparian strips
Specialized bands of suberin found in the endodermis of plant roots. They act as a barrier, preventing the movement of water and solutes between cells.
Aerial roots
Adventitious roots arise from stems, extra support
Buttress roots
flared roots that extend from tree trunks, stabilizes tree
Contractile roots
Shorten and pull plant deeper into soil
Suckers
Asexual reproduction, arise from underground roots, comes through soil
Pneumatophores
Air roots, provide oxygen for plants in swampy areas
Haustoria roots
parasitic roots, penetrates stems and roots of other plant to get nutrients
Endomychorrhizae
fungi penetrate plant roots, produces branching called arbuscules
Ectomychorrhizae
Network of fungi surrounds roots, produces mantle sheath
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
convert nitrogen into ammonium. Plants then take up fixed nitrogen, bacteria will infect roots, the roots form nodules for bacteria t0 live in which releases nitrates into soil
Zone of elongation
derivatives stop dividing and begin elongating
Zone of maturation
cells differentiate, roots hairs formed by epidermal cells
Guard cells
Specialized cells found in the epidermis of plant leaves that control the opening and closing of stomata.
Suberin
A waxy substance found in the cell walls of plants, especially in cork. It provides waterproofing and protection against pathogens and pests.
Corms
Resemble bulbs, made of stem tissue with papery leaves, stores food. Crocus
Rhizomes
Horizontal stems that grow below ground and have long-short internodes. Irises
Stolons
Horiztonal stems grow above ground and have long internodes
Tubers
swollen fleshy underground stem, stores food
Bulbs
Large buds surrounded by fleshy leaves with a small stem at lower end, stores food. Onions, tulips
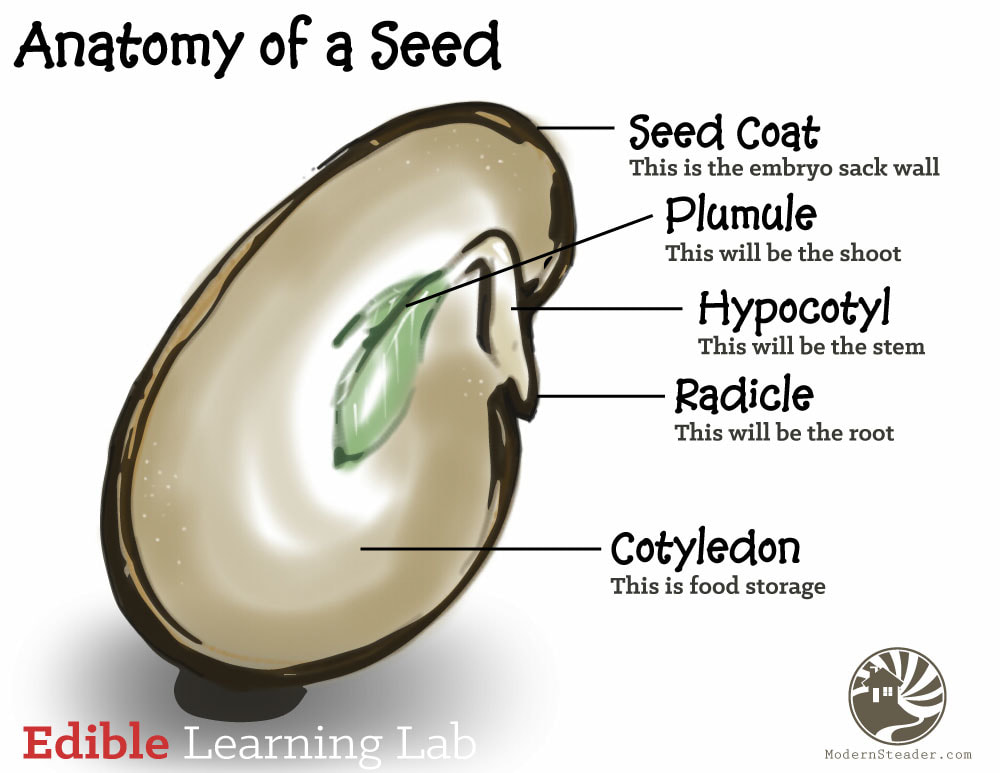
Cotyledons
Seed leaves, stores good for germinating seed
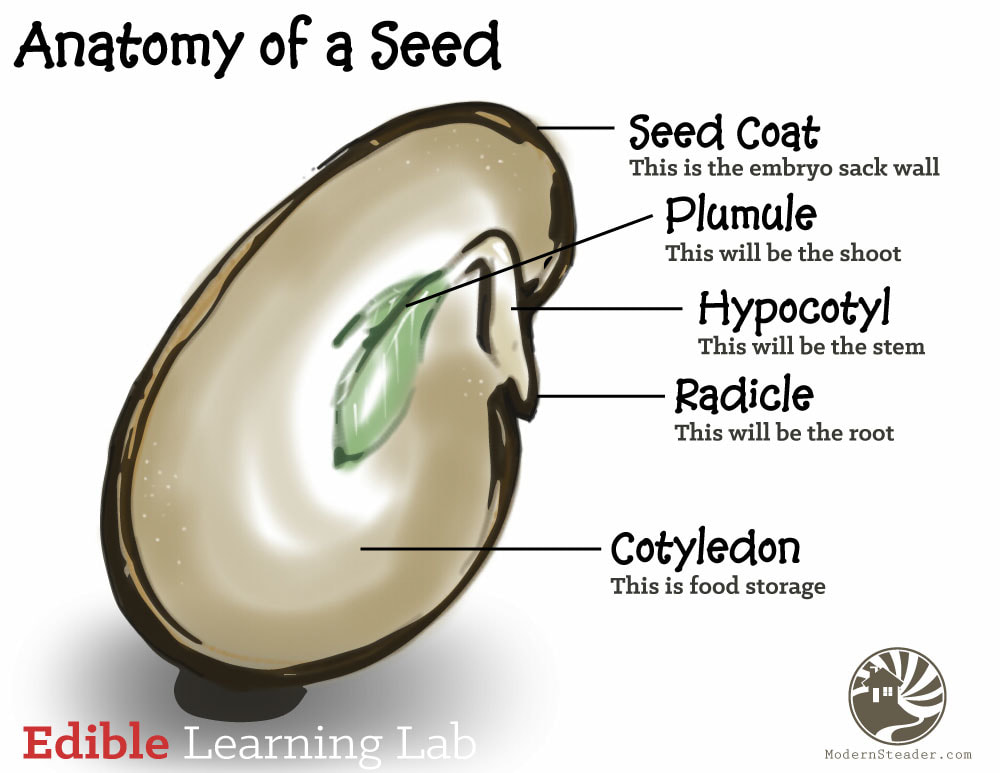
Radicle
embryonic root
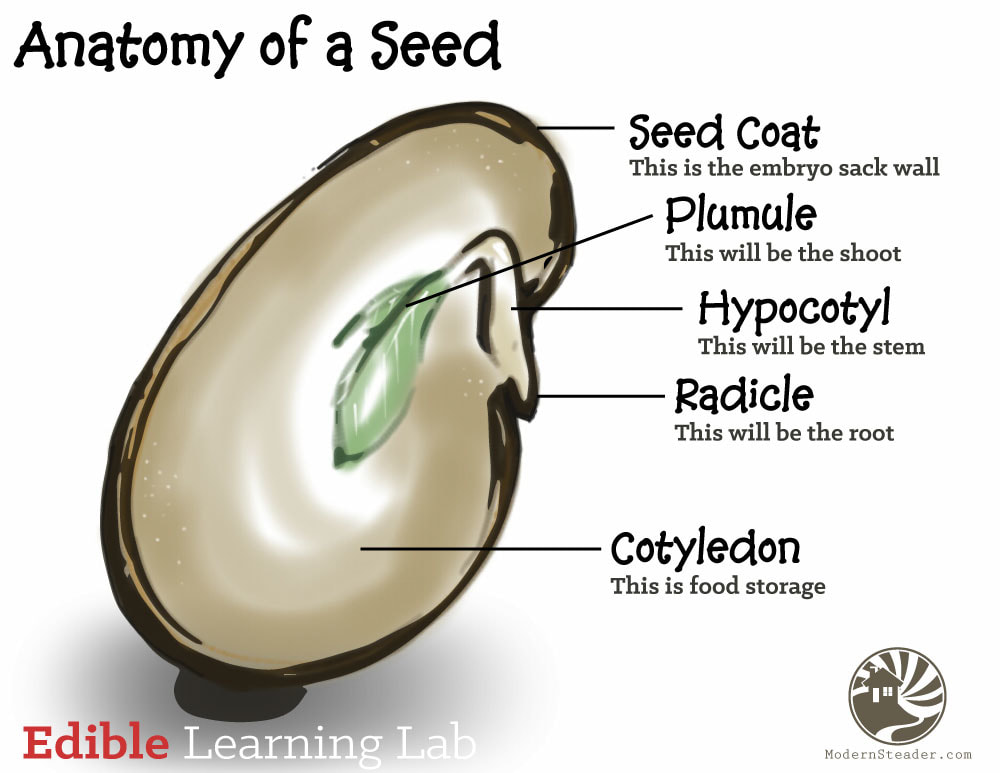
Plumule
embryonic shoot, generates epicotyl
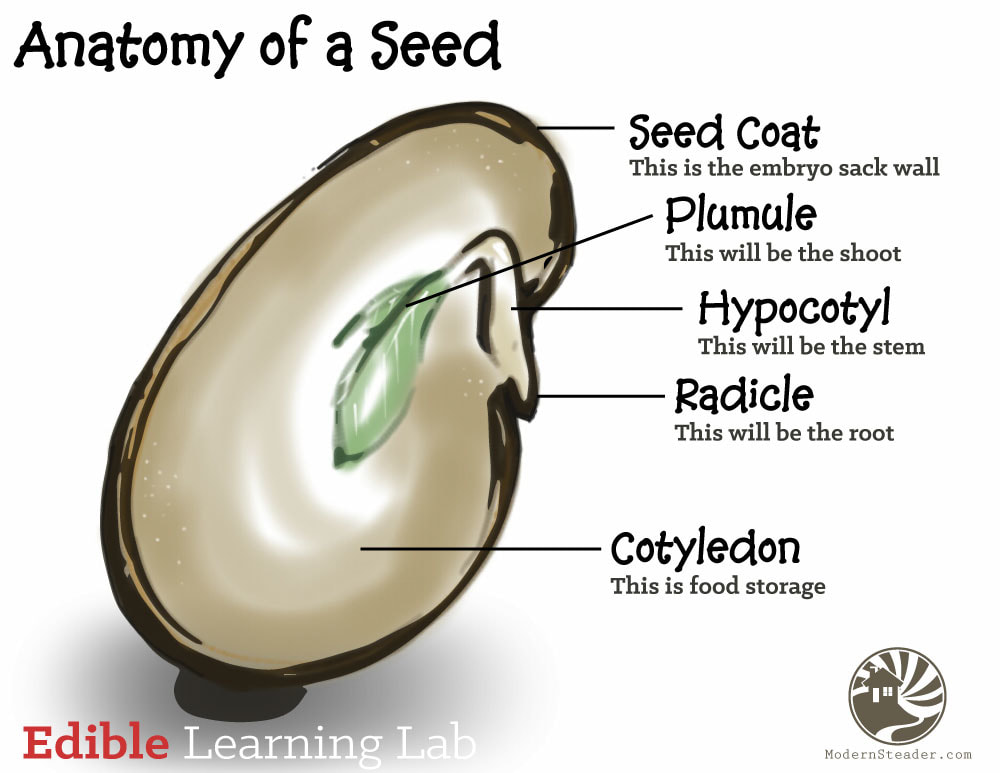
Hypocotyl
portion of the embryonic stem under the cotyledon and above radicle
Endosperm
Food storage tissue surrounding the embryo, breaks down to nourish embryo
Testa
seed coat
Leaf epidermis
Single layer of non photosynthetic cells derived from protoderm. Prevents water loss, abrasions, entry of diseases. Regulates gas exchange through stomates. Transpiration pulls water and minerals up roots and cools the leaf
Netted venation
Branching networks, most dicots and ferns
Parallel venation
long lines, most monocots and gymnosperms
Thorns
Sharp, pointed, and protective structures found on the stems or branches of certain plants. Thorns deter animals from feeding on the plant, acting as a defense mechanism.
Bracts
Modified leaves found at the base of a flower or flower cluster. They are often brightly colored and attract pollinators.
Lateral meristems
Type of meristem responsible for the growth in girth of plants. Found in the cambium layer. Produces secondary tissues such as secondary xylem and phloem.
2 types of lateral meristems
Vascular cambium and cork cambium
Where are lateral meristems?
Woody plants
What do lateral meristems produce?
Secondary growth
Wood vs bark
Bark is thinner, wood is secondary xylem
Lenticels
Small openings in the bark of woody plants that allow for gas exchange between the internal tissues and the external environment.
Vascular cambium
secondary xylem and phloem
Cork cambium
produces periderm, does not expand in diameter, new cambium forms within old cork cambium
Inflorescence
A compact cluster of flowers on a plant stem, often surrounded by modified leaves.
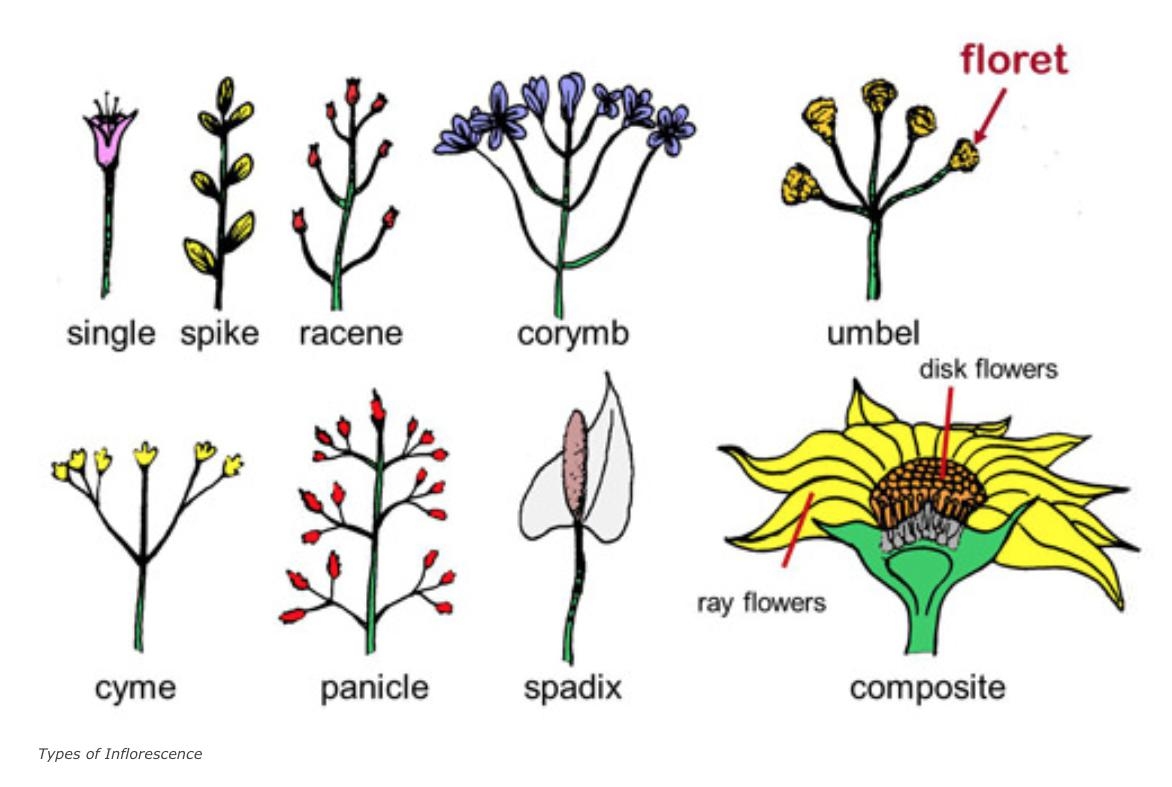
Examples of modified leaves
thorns, tendrils, bracts
Examples of modified roots
Aerial roots, buttress roots
Example of modified stems
Rhizomes, stolons, tubers, bulbs
Pericycle
Outermost layer of the vascular cylinder in plants, located just inside the endodermis. It gives rise to lateral roots and secondary growth.
Stem anatomy
leaves attach at internodes, nodes, dormant axillary buds
Lignin
A complex polymer found in plant cell walls that provides structural support and rigidity. It is the second most abundant organic compound on Earth, after cellulose. Lignin is responsible for the woody texture of plants and is highly resistant to degradation, making it difficult to break down in industrial processes.
Mucigel
Substance secreted by root cells that lubricates and protects the root surface. It helps plants absorb water and nutrients efficiently.
Palisade mesophyll
elongated thick layer lined up under upper epidermis
Spongy mesophyll
loosely organized layer that has space for diffusion for CO2 to travel from stomata to other parts of a leaf
Abscission zones
Specialized regions in plants where leaves, flowers, or fruits detach from the plant. They contain cells that weaken and break down the connection between the plant and the organ, allowing for its separation. triggered by environment
Rays
divide to produce parenchyma cells for storage
Fruit anatomy
Pericarp: exocarp, mesocarp, endocarp
Seed
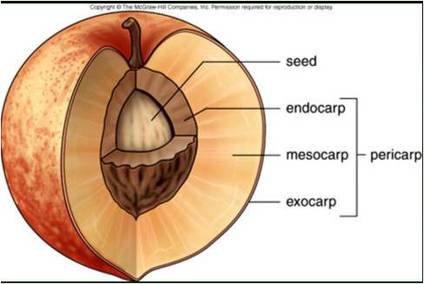
Fruit
protect embryo from drying out, promote seed distribution, consists of one or more mature ovaries
Quiescent center
A region of undifferentiated cells located in the root meristem of plants. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the stem cell population and is responsible for the regeneration of damaged tissues.
Adventitious roots
Roots that develop from non-root tissues, such as stems or leaves. They help plants anchor in soil, absorb water and nutrients, and provide additional support. Adventitious roots are commonly found in plants like ivy, corn, and mangroves.
Intercalary meristems
Sphionostele
most seedless vascular plants. Continuous cylinder that surrounds a core of pith
Eustele
most gymnosperms and dicots. Forms vascular bundles of xylem and phloem. Vascular bundles arranged in a circle around the pith
2 models of shoot apical meristem
Zone model and cell layer model
Zone model
shoot apical meristem has 3 regions.
Central mother cell zone: divides and makes cells of peripheral and pith zones
Peripheral zone: divides to make leaf primordia and cells for protoderm, procambium, and ground meristem
Pith zone: Divides to make cells for ground meristem
Cell Layer Model
initials of shoot apical meristem form several cell layers. Outer layers are tunica, creates protoderm. Inner layer is corpus, created procambium and ground meristem
Periderm
produced by cork cambium, produces cork
Hardwood vs sapwood
Hardwood: Many fibers, burns longer, harder to damage, denser, dicot trees
Sapwood: Less fibers, burns fast, softer, less dense, conifers
Reaction wood vs tension wood
Reaction wood: Irregular growth pattern due to wind or gravity
Tension wood: Response to bending
Monocot vascular bundles
scattered throughout ground tissue
Dicot vascular bundles
arranged in a ring
Growth rings
Forms from vascular cambium annually
Meiosis vs mitosis
Mitosis: independent homologous chromosome, identical daughter cells
Meiosis: homologous chromosomes pair forming bivalents until anaphase 1, chromosome number reduces, daughter cells are haploid, daughter cells have new assortment of parental chromosomes
Meiosis 1
S phase
Prophase 1
Metaphase 1
Anaphase 1
Telophase 1
Cytokinesis
Meiosis S phase
chromosomes replicated
Prophase 1
homologous chromosomes form pairs, a tetrad of 4 chromatids
Metaphase 1
Tetrads move onto metaphase plate
Anaphase 1
phase when overall chromosome numbers is halved for each of the 2 new daughter cells
Telophase 1
Cell returns to pre-meiotic state
Meiosis II
similar to mitosis, begins with haploid cells, ends with 4 haploid nuclei. Daughter cells become spores
Haploid
Has 1 set of chromosomes
Diploid
Has 2 set of chromosomes
Asexual reproduction
Involves 1 parent, mitosis
Produces genetically identical offspring (clones), rapid and effective allowing spread of an organism, no diversity
Sexual reproduction
Forms new individual by combining 2 haploid cells (gametes), takes a lot of energy but gives genetic advantage
Alternation of generations
the two adult forms alternate in producing each other
Sporophyte
consists of diploid cells
Gametophyte
consists of haploid cells
Gametes
sperm and egg
Double fertilization
the fusion of the egg and sperm and the simultaneous fusion of a second sperm and two polar nuclei that ultimately results in the formation of the endosperm (the food-storage tissue) of the seed.
Gymnosperm pollination
different cones on same plant participate in pollination
Angiosperm pollination
different parts of same flower participate in pollination if perfect flower
Imperfect flower pollination
Monoecious: Male and female flowers on same plant pollinate
Dioecious: Male or female flowers on different plants pollinate
Complete flower
contains sepals, petals, stamens, carpels
Incomplete flower
missing 1 or more parts