N Lecture 2 - Gross Human Neuroanatomy, Comparative Anatomy
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
The Brain
– large clump of 86 billion neurons
Responsible for complex behaviours, thought, perception and emotion
2 hemispheres
Ventricles
(Spaces between brain)
Cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Sewerage system of CNS
Blockages causes hydrocephalus (inflates ventricles, squashing brain)
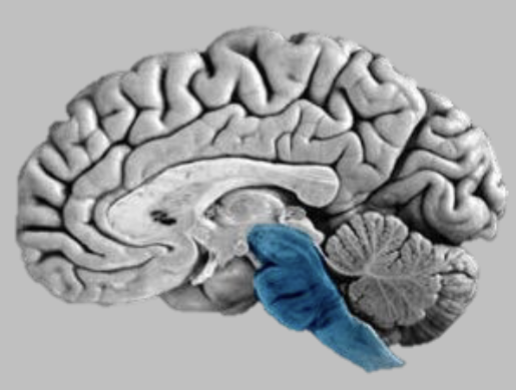
Major Subdivision of the Brain - Brainstem
Controls life supporting functions
Damage to brain stem causes loss of consciousness, coma, death - increased pressure inside the head can cause this
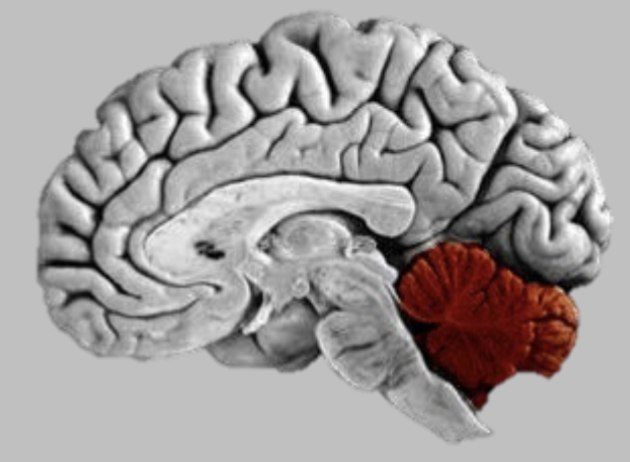
Major Subdivision of the Brain - Cerebellum (“Small Brain”)
Control of precision movements - fine accurate skills (include learned ones)
70% of neurons in brain in small brain for humans
Receiving visual input and other sensory input and learnt what muscles movements need to be sent out
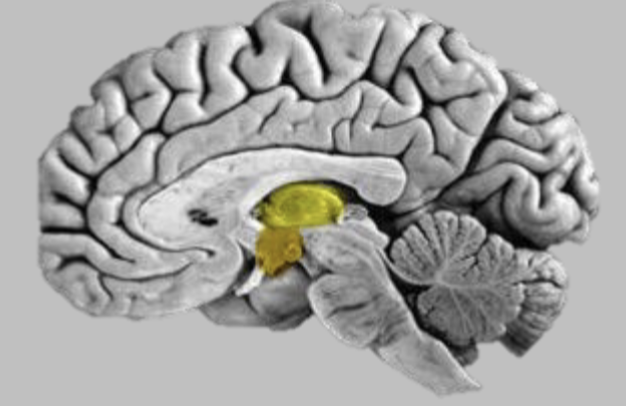
Major Subdivision of the Brain - Thalamus & Hypothalamus (Diencephalon)
Thalamus is sensory relay to cortex – auditory, visual etc
Gateway of sensory info coming into brain and allows it to participate in selective attention
You can control what sensory input you are paying attention to – can regulate it
Hypothalamus is involved in hormonal regulation and motivational control (feeding and sex)
Connected to pituitary
Self releases a lot of hormones
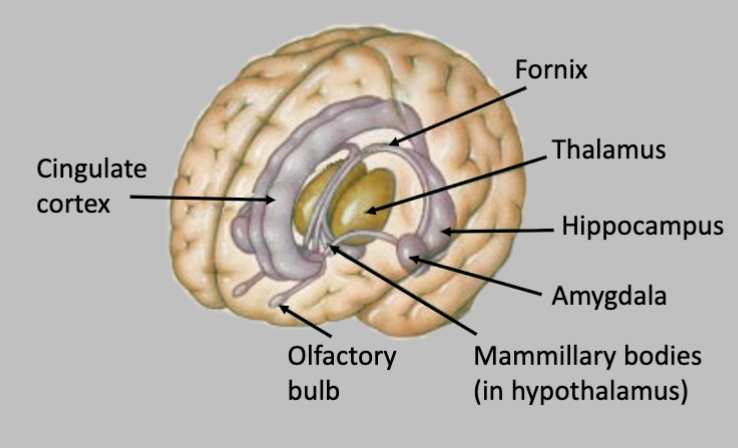
Major Subdivision of the Brain - Limbic System
Control of emotion and memory
Fornix
Thalamus
Hippocampus
Amydgala
Mammillary bodies
Olfactory bulb
Cingulate Cortex
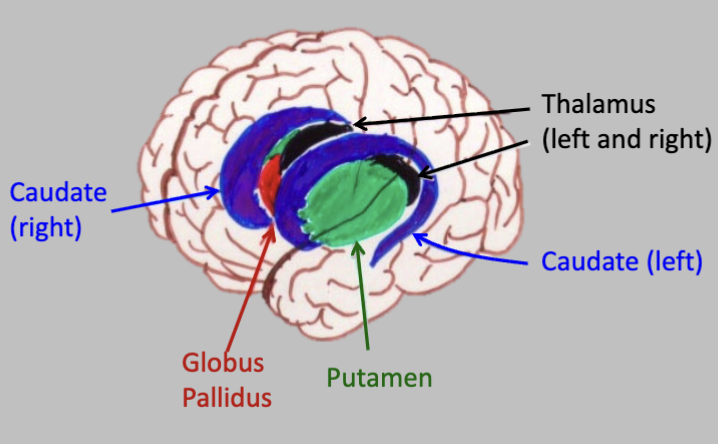
Major Subdivision of the Brain - Basal Ganglia
Action and thought
Thalamus (left and right)
Caudate (left and right)
Putamen
Globus Pallidus
Parkinsons and Huntingtons affect the basal ganglia
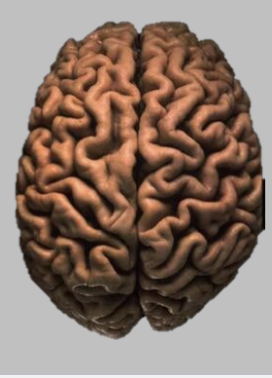
Major Subdivision of the Brain - Neocortex
Convoluted sheet on top of the brain
4 lobes of neocortex
Frontal Lobes
Parietal Lobes
Temporal Lobes
Occipital Lobes
Neocortex — Frontal Lobes (Red)
Planning & executive functions (inhibitions, self control – inhibition, ability to plan for the future, memory)
Primary motor cortex - neurons send axons to spinal cord to send signals to muscles to move – one of main output centre in brain - voluntary movements
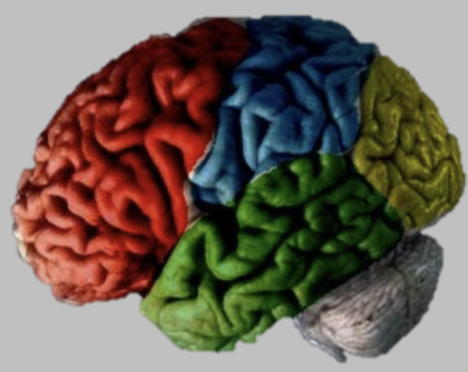
Neocortex — Parietal Lobes (Blue)
Perception and understanding of space around us – represents space for action
Somatosensory cortex - when neurons are stimulated/activated you will feel touch

Neocortex — Temporal Lobes (Green)
Memory and language
Has the hippocampus
Primary auditory cortex - auditory information arrives from the thalamus here
Taste and smell

Neocortex — Occipital Lobes (Yellow)
Vision - recognise things, people, understand how the vision experience is organised

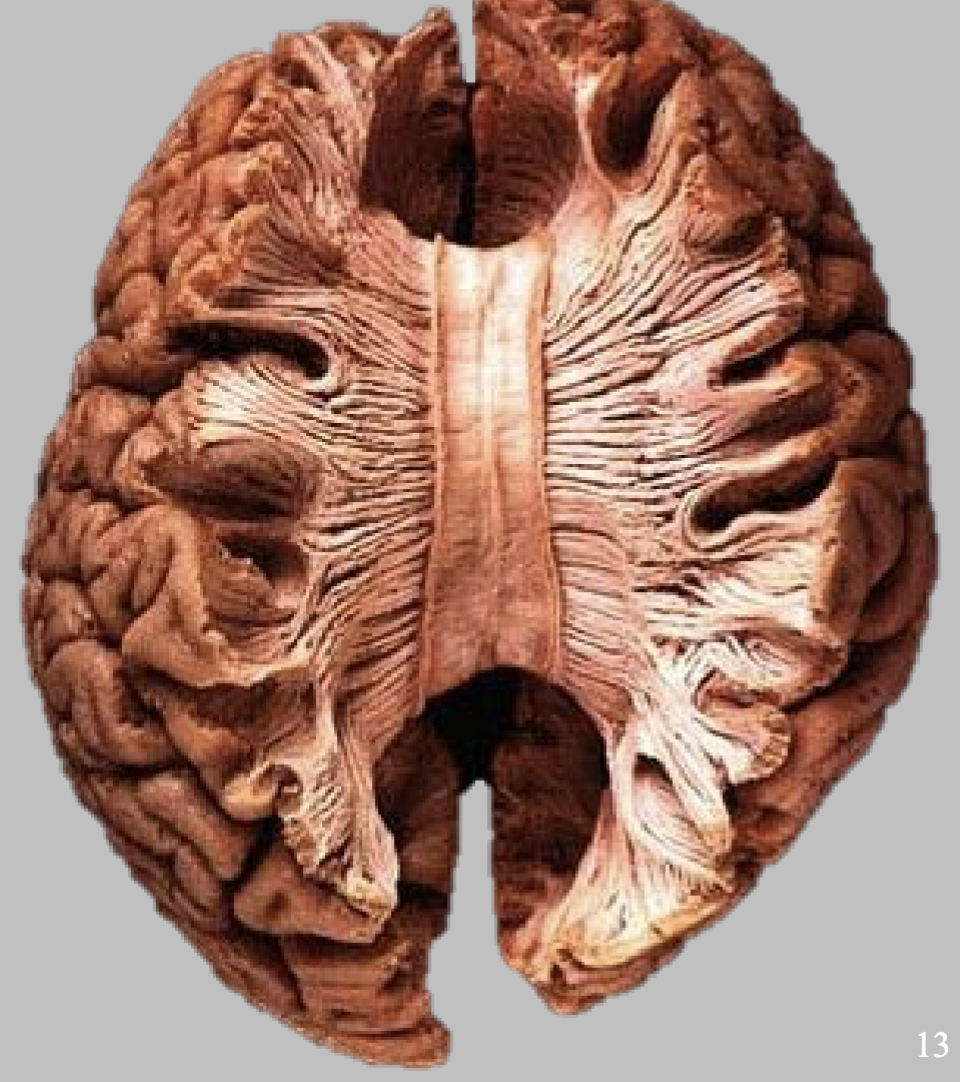
Corpus Callosum
Connecting 2 hemispheres
Comparative Neuroanatomy
Nervous system almost a defining feature of animals
Roundworm - 302 neurons
Starfish - 500 neurons
Jellyfish - 5,000 to 10,000 neurons
Nervous system has more complex organisation in insects
Clusters of neurons (ganglia) forming cord or “brain”
Some specialisation of neurons (e.g. motor vs sensory)
Vertebrates have separation between PNS and CNS
Among vertebrates – large diff in relative size of diff regions of brain – reflecting complexity of behaviour
Large increase in size of forebrain across vertebrates
Appearance & enlargement of neocortex in mammals