Y2 - Principles of Marketing Semester 1 Key Terms
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
The Marketing Environment:
Marketing Environment: the actors and forces that effect management’s ability to build and maintain successful consumer relationships
encompasses internal and external factors impacting marketing activities.
6 Components of the Marketing Microenvironment:
Company as part of Marketing Microenvironment:
internal environment, HR hires correctly, finance concerned with budgeting, R&D innovates, operations and management
Suppliers and Intermediaries as part of Marketing Microenvironment:
Suppliers and Intermediaries:
Suppliers: provide raw materials and resources needed to create value, and thus share problems like delays
Intermediaries: assist promotion and distribution of products
Example: Retailers (Tesco), Logistics firms (DHL)
Competitors as part of Marketing Environment:
Competitors:
Marketers must gain strategic advantage by positioning offerings strongly.
Success = providing greater customer value than competitors
Example: Coca Cola and Pepsi, Apple and Samsung etc.
4 aspects of publics as part of Marketing Microenvironment:
Publics:
Any group that has a level of interest or impact on an organisation’s ability to achieve its objectives
Gedia: TV, newspapers, social media
Government: laws and regulations
Citizen-action: environmental groups, consumer advocates
Local: neighbourhood residents and community
Customers as a part of Marketing Microenvironment:
Customers:
To serve a target market and build profitable relationships
Consumer markets (individuals)
Business markets (organisations)
Government markets (public sector)
Costa’s suppliers, competitors and public:
Costa
Supplier:
Marks and Spencer’s
operate on a national scale supplying coffee to its stores
Coffee Nation
acquired by Costa in 2011 (now branded Costa Express)
Uses fresh ground coffee rather than powder
key commodities such as coffee and cocoa are sustainably sourced and third-party certified
Competitors: Starbucks, Pret a Manager
Publics:
Media - Costa Coffee has multiple social media accounts such as Facebook, Instagram and Youtube
Local - South Woodford residents, commuters, appealing to different age brackets
Marketing Macroenvironment:
Consists of larger societal forces that affect the microenvironment and shape opportunities, as well as pose threats. PESTLE
Political factor of Marketing Macroenvironment:
Political:
government reforms, political stability and impacts of policy
e.g. Brexit impacting trade flows, international relations
Economic factors of Marketing Macroenvironment:
Economic: impacts demand and supply, unemployment, inflation
boom - increased demand (vice versa)
Changes in interest rates and exchange rates impact business operations
e.g. freezing interest rates, spikes in inflation, supply shocks, financial crashes
Social cultural factors of Marketing Macroenvironment:
Socio-cultural forces:
forces that affect society values, perceptions and behaviours
changing demographics, increased demand for ethicality and responsible brands
growing interest in health, wellness and mindfulness
e.g. Strava, increased interest in gym, dieting, organisations
Technological factors of Marketing Macroenvironment:
Technological forces:
creates new products and causes creative destruction
e.g. Netflix streaming, OpenAI, Sora, social media apps
Legal factors of Marketing Macroenvironment:
lawsuits, copyright, patents, intangible goods and intellectual media
e.g. Burger King and Mcdonalds accused of false advertising, Tiktok sound copyrights
Environmental factors of Marketing Macroenvironment:
climate change, pollution, renewable resources, environmental degradation.
e.g. degradation of oil supplies, rise in wind, solar and tide energy, investment in nuclear energy in £10s of billions
Proactive vs reactive responses to the marketing environment:
Proactive responses:
taking action to shape environment, using strategy and innovation
e.g. fast food firms adapting during Covid to drive thru and delivery, superstores converting to delivery and digitalised shopping
Reactive responses:
views environment as uncontrollable, waiting for change and then adapting
e.g. Kodak not adapting to technological changes, reacting too late and thus bankruptcy (2012), companies may have thought Covid would pass and any long-term structural changes would be costly
Continuous Scanning of the Marketing Environment:
continuous monitoring of the marketing environment
Tools: trend forecasting, market research, competitive intelligence
Threats —> Opportunities.
Customer behaviour:
Helps markets to:
Segment more effectively
Customer targeting + messaging
Brand positioning towards customers
Develop Marketing Mix
Customer behaviour: the study of how individuals, groups and organisations select, buy, use and dispose of g&s, ideas or experiences to satisfy needs and wants (Kotler & Keller, 2018
Stimulus response mdoel and selling:
Stimulus-response model
Inputs: Marketing (4P) and Environmental (PESTLE)
Buyer’s mind: Characteristics and decision process
Outputs: product, brand choice, purchase amount
Selling:
Business —> Customers g. groceries, Netflix; emotionally driven
Business —> Business g. computers, steel, resources; rational
Types of customers buying decisions (behaviour) :
Type of behaviour | Involvement | Brand Differences | Examples |
Complex | High | High | cars |
Dissonance-reducing | High | Low | carpets |
Habitual buying | Low | Low | salt |
Variety seeking | Low | High | biscuits |
5 stages of customer decision making process (name + def + example)
Problem recognition:
Buyer recognises need / problem
Triggered by
internal stimuli g. hunger
external stimuli g. adverts or social media
marketer’s role
Information search:
Buyer seeks information about solution, depending on involvement level
g. public sources, personal sources, commercial sources
Alternative Evaluation:
Evaluate choices of brand based on criteria
Marketer’s role: ensuring excellence in certain criteria
Purchase decision:
Formal purchase + choice
Disrupted by attitude of others + unexpected situations
Post-purchase behaviour:
Level of satisfaction
Cognitive dissonance
Marketing implications: customer service, reviews and expectations
Cultural influences on consumer behaviour:
Cultural
Power distance index: measures acceptance of unequal power distribution in society
Advertising in high ; community creation in low
Individualism vs Collectivism
Customer sneakers vs shared experiences
USA – just do it Nike vs Japan – family dining
Masculinity vs femininity
Masculine – performance; feminine – emotional appeals
Ambition via luxury car ads vs work-life balance campaigns
Uncertainty Avoidance Index: measures ambiguity risk
High – structure, low – flexibility / innovation
Nigeria money back offers vs Singapore tech ads
LT vs St orientation
China – promoting savings vs USA – instant gratification
Indulgence vs Restraint
Mexico – vibrant fun ads vs Russia - disciplined messaging
Social influences on consumer behaviour:
Reference groups and opinion leaders
Membership groups, aspirational groups, dissociative groups
Family, life cycle and changing roles and status
Personal and Psychological influences on consumer behaviour:
Personal:
Age and life cycle, occupation and economics
Lifestyle, frameworks, personality
Psychological:
Motivation (Maslow’s hierarchy), perception, beliefs and attitudes
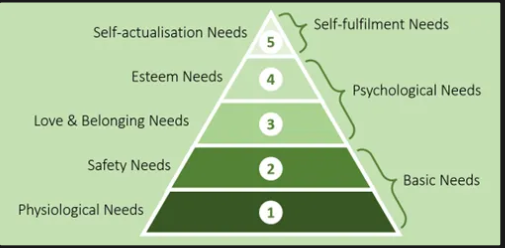
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs:
Examples:
5 - University degree
4 – luxury watch or premium car brand
3 – social media platform
2 – insurance, banking services
1 – necessities
Tech and value driven shifts of consumer behaviour:
What’s next? Technology-driven shifts:
hyper-personalisation:
recommendation engines, Open AI
Experience economy:
Shift from buying “things” to “memorable experiences”
Transformations, not just products g. Secret cinema
Value-driven shifts:
Sustainability and ethical consumption:
Transparency, sustainability
Subscription economy:
Ownership à access; growing beyond media into physical goodsg. clothing rentals
Health and wellbeing:
Physical and mental health, clean eating and wellness retreats
Digital marketing:
Actively promoting products and services using digital distribution channels as an alternative to traditional mediums
e.g. the internet, mobile apps, display advertising
Objectives of digital marketing:
Objectives:
reach and engage with audience
motivate audience action
maximise investment returns
Types of digital marketing (4):
Social media marketing
Search marketing
Email marketing
Display ads
Social media marketing and evaluation:
Utilising social networking sites as a marketing tool
Goal: product shareable content to help companies increase brand exposure and widen customer reach
Advantages:
Increased brand awareness, higher conversion rates, brand loyalty and authority
Disadvantages:
Negative feedback, time intensive, negative publicity
Search Marketing and evaluation + PPC:
Goal: visibility when customers seek solutions
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO):
Optimising website and content to rank higher in organic search results, long-term
Pay-per-click:
Digital marketing model in which advertisers pay publishers every time an ad link is clicked on,
The publisher can pays to place ads at top of search results, increasing L-T PPC and revenue.
e.g. Google Ads, Facebook Ads ; immediate but costly
Advantages:
fast results, demographic targeting, provides detailed data and allows for effective adjustment
Disadvantages:
costly, time-consuming, requires monitoring and optimisation, expertise requirement
Email Marketing and evaluation:
Email Marketing:
Sending emails to current and potential customers to increase brand awareness, driving engagement and sales
Successful, cost-effective and simple way to reach customers
e.g. welcome, newsletter, promotional, survey, retention
e.g. uber offers, Netflix promotional
Advantages:
brand awareness, generates web traffic, customer engagement, drive sales
Disadvantages:
spam / intrusive, time-consuming for results, technical issues
Display ads, types and evaluation:
Display Ads:
Ads placed on websites, networks or apps, typically image, text or video banner that relocate a user to a website or landing page
Placed mainly in corners or designated areas on webpages and platforms, showcased in the form of a banner
Types of Display Ads:
Banner:
Image-based rectangles or squares that link out to a website
Interstitial:
Full-screen ads that overlay screen e.g. text, video or input req.
Rich media:
Video, audio or interactive elements e.g. LEAPOMOTOR video above
Advantages:
building brand awareness, driving traffic, widespread deployment, measurable
Disadvantages:
Low conversion rates, intrusive, not in control of reputation
(think of Wreck it Ralph: Breaks the Internet with dodgy sites, display ads and search engines)
Digital Analytics:
Digital Analytics:
Analysing digital data from various sources to indicate user behaviour
Collecting and analysing quantitative and qualitative data, enhancing business operations to improve online experience
Tools: visitor numbers, popularity, duration, sales, referrals, Google Analytics
Reach Strategy of Digital Marketing:
Strategy | Objective | Goal | Key Channels | Key Performance Indicators |
Reach | Build awareness of your owned media properties | Drive traffic from external sites | SEO, PPC, Social Media | Impressions, Click-through rate, visitors |
Act Strategy of Digital Marketing:
Strategy | Objective | Goal | Key Channels | Key Performance Indicators |
Act | Persuade visitors to interact with your brand; lead generation | Encourage interaction and capture leads | content videos ,blogs, landing pages | Lead generation, downloads, duration |
Convert Strategy of Digital Marketing:
Strategy | Objective | Goal | Key Channels | Key Performance Indicators |
Convert | Convert leads into paying customers | Achieve sales | Follow ups, checkouts, retargeting ads | Sales, conversion rate, Average Order Value (£) |
Engage Strategy of Digital Marketing:
Strategy | Objective | Goal | Key Channels | Key Performance Indicators |
Engage | Build LT relationship and turn customers into advocates | Build customer loyalty and advocacy | Email marketing, excellent customer service, communities online | Customer Lifetime Values, Social media discussion, positive reviews, Repeat Purchase Rate |
What does the RACE strategy stand for?
Reach-Act-Convert-Engage Strategy
Ethical issues of Digital Marketing:
Ethical issues:
False advertising / Misleading information
Misuse of general and customer data
Advertising on Unethical sites
Manipulating search engine results
Persistent intrusiveness
Classification of key channels in terms of media types (OPE):
Classification of Key Channels:
Owned media:
Channels fully controlled, created and managed by the brand
company websites, profiles, email lists, apps
Paid Media:
Channels where a brand pays to promote content or reach an audience
PPC, Social media ads, display ads, influencer partnerships
Earned media:
Exposure gained through 3-P actions, not paid or controlled directly by the brand
Social media shares, press coverage, user generated content, organic search rankings from SEO
Marketing Communication:
Marketing Communication: How firms attempt to inform, persuade and remind consumers, directly or indirectly, about the product and brands they sell
voice of the brand —> establish dialogue and relationships
Integrated Marketing Communication Mix:
Integrated Marketing Communication Mix: Events, Advertising, Public relation, Digital, Direct, Sponsorship
Tools: advertising, selling, PR, sales promotion, direct marketing
Definition of advertising:
Any paid form of non-personal presentation or promotion of ideas, G&S by an identified sponsor
The role of advertising (AIARCEE):
Awareness
Information
Attitude
Reminder
Countering the competition
Expansion
Education
Explanation of each role of advertising (AIARCEE):
Awareness:
Awareness of brand, product, service, attracting target audience
A precondition to purchase and recall, ensuring knowledge and value
Information:
Informs the target audience, linking to awareness, highlights uses and features etc.
Essential for modification and customer purchasing decisions
Attitude:
Expected to create a favourable attitude towards brands, promotion is required
Increases sales and corrects negative attitude
Reminder:
A reminder objective is necessary if attitudes are positive
Repeated sales, highlights brand presence and outplays competition
Countering the Competition:
Creative advertising —> Superiority
Aggressive sales promotion
Expansion:
Caused by successful ads; local —> regional —> national —> international
Various techniques of promotion such as advertising
Education:
Some adverts educate product use, handling operations and brand advocacy
AIDA Advertising Model (a conversion theory):
AIDA Model (a conversion theory)
Cognitive stages a consumer passes through during their purchasing process, serving as a template for marketers to transition consumers from awareness to final action.
Attention - consumer becomes aware of your product via advertising
Interest - interest in benefits, attachment and uses
Desire - Favourable disposition is developed towards the product
Action - Consumer forms a purchase intention
Criticisms of the AIDA Model:
Little evidence of desire before action e.g. unsuccessful trials or competition arising
Focuses on converting non-buyers to buyers and neglects buyers who needed to be constantly persuaded
ATR Advertising Model:
ATR Model
Outlines stages a consumer goes through when encountering and adopting a new product or service; asserts the role of advertising to reinforce habitual behaviour
Attention - raise customer awareness of product or service presence
Trial - encourage testing among consumers
Reinforcement - Reinforce positive experience, build loyalty and encourage repeat purchases
Criticisms of the ATR Model:
Ignores complex factor e.g. multiple trials or exogenous influences
Customer loyalty is a long-term factor, extending beyond the reinforcement stage
Pre-requisites of advertising
Target audience
Message decisions
Media selection
Key Media Decisions of Advertising:
Key Media Decisions
Reach: exposure level during a certain time period
Frequency: how often will an individual in the TA be exposed
Impact: qualitative value through a given medium
An ad in vogue > has a greater impact for a fashion brand > ad in local paper
Types of line advertising (3):
Above-the-line
Below-the-line
Through-the-line
Above-the-line advertising:
Above-the-line: mass marketing methods that are mostly untargeted and aimed at brand establishment
everyone has access to the media receives the message and conversion rates and weakly weighted
Types of Above-the-line Advertising:
Television Advertising: traditionally most expensive, but creative and attention grabbing ; widespread
Radio advertising:
Live reads spoken by an on-air personality
Sponsorships of segments by businesses
Produce spots incorporating dialogue, music or effects
Print Advertising: any written form of communication used to inform, persuade or remind consumers of G&S
Outdoor advertising: billboards, visibility and 24-hour advertising
Below-the-line advertising:
Conversion rate focused, referring to specialised and direct promotion targeting a certain audience group
Direct messaging methods as part of Below-the-line advertising:
Sponsorship which is unconventional but non-media communication
Brand Activation Campaigns involving activities and creativity with audiences to create memorability e.g. Share a Coke or Have a —-, have a KitKat
In-store promotions - visual merch, pop ups, samples or displays
Through-the-line advertising:
Through-the-line: 360 degree advertising of ATL and BTL, aiming to enhance brand-building and increase conversion rates
360 marketing campaign: Targeted messaging across contact point, spanning all aspects of the brand’s marketing mix, intended to apply brand strategy
Ethical issues of advertising:
Advertising to children, teenagers and vulnerable people which may cause harm or unethical consequences e.g. rise in antisocial behaviour
Misleading advertising which leads to unsupported or incorrect purchases; different pricing levels on billboards compared to websites etc.
Advertising and its influence on societal values
Offensive or stereotypical adverts such as racist stereotypes
Constant exposure may damage privacy or deter customers from a purchase
Brand definition:
Brand: A name, term, design, symbol or any feature that identifies one seller’s G or S as distinct from those of other sellers (AMA) ; intangible appearance
not just physical features but also feelings towards a company or product
Brand: built in the consumer mind, emotional connection, unique, abstract, irreplicable
"Your brand is what other people say about you when you're not in the room.” - Jeff Bezos
Product definition:
Product: An item which is ready for sale in the market
tangible features, replicable and factory produced
6/7 types of brands:
Product - e.g. Apple
Service - e.g. BA / Barclays
Place - London Eye
Person - Cristiano Ronaldo, Lewis Hamilton
Idea - save the planet, Nike Just Do It
Organisation / Institution - Loughborough University, NHS
Branding definition:
Branding: The process by which companies differentiate or distinguish their product offering from the competition (Baines and Fill, 2014)
Creating a valuable image of a product
Branding adds value to base value
Symbolises luxury and social status —> spending habits
Impact on Consumers - simplifies choice, reduces risk and increased self-expression
Impact on Firm - price premium, customer loyalty, power and leverage, financial asset
Brand equity definition:
Brand equity: A term that represents the value of a company’s brand based on recognition
Recognition / willing to pay more = more brand equity —> direct impact on sales volume
Consumers gravitate to products with reputation
e.g. Apple, premium price consumers are willing to pay for an iPhone, built on innovation, creativity and design
Model: Identity + Meaning + Response + Relationships (Keller, 2013)
Negative brand equity:
Volkswagen - recalled 11M diesel cards due to flawed emissions tests —> ~£10bn losses
How to build a brand:
Brand Elements
Brand Positioning
Brand Personality
Brand Elements (Identity):
Brand Elements (Identity)
Likeable, memorable and meaningful
Name e.g. Google
Logo e.g. Nike Swoosh
Colour e.g. Cadbury Purple
Slogan e.g. “Just Do It”
Jingle e.g. McDonald’s “ba-da-ba-ba-ba”
Character e.g. Aleksandr the Meerkat
Brand Positioning:
Act of designing your brand’s image to occupy a clear and desirable place in the mind of target consumers
Brand Personality and characteristics:
Brand Personality
If the brand walked into the room, what would they be like?
Key way to differentiate brands
Characteristics:
sincerity - caring and honest e.g. Dove
excitement - daring and imaginative e.g. Red Bull
competence - reliable and efficient e.g. Amazon
sophistication - charming and classy e.g. Rolex
Key issues of Branding:
How do we measure brand equity
How do we position the brand effectively?
The role of AI in modern branding
Geographic and cultural boundaries
Ethical issues of branding
“Anxiety”
Segmentation:
Segmentation: Dividing a large, heterogeneous market into smaller, more homogenous groups
Segments have similar needs, characteristics and behaviours who are likely to respond similarly to a given marketing strategy
Allows for target selection, opportunities, differentiation and tailoring mix.
Criteria and bases of Segmentation:
Criteria: measurable, accessible, substantial, actionable
Bases: demographic, geographic, psychographic, behavioural
Case study: Nike and Gender segmentation
historically male oriented —> actively pursuing women’s segment
Designing sports bras, footwear and apparel for women
Campaigns focus on female empowerment and diverse pursuits
Targeting definition and steps:
Definition: Process of evaluating the various market segments of a company has identified and selecting which ones to focus on
Choose segments that offer highest potential for growth, profitability and alignment with the company’s objectives
Steps: Size and growth potential —> Profitability —> Accessibility —> Alignment with company resources / goals
4 Targeting Marketing Strategies:
Undifferentiated (Mass) Marketing
Differentiated (Segmented) Marketing
Concentrated (Niche) Marketing
Micromarketing (Individual):
Undifferentiated (Mass) Marketing:
Concept: one product, one message
Best for: commodities
Risk: rise of segmented markets reduces effectiveness
Example: popular fast food chains, e.g. KFC, Coca-Cola too
Differentiated (Segmented) Marketing
Concept: Targeting several segments, designing separate offers for each
Advantage: Higher total market coverage, reduced risk, diversification
Challenge: High cost e.g. production, R&D
Example: Toyota Corolla, Prius and Land Crusiers, varying in budget, reliability and efficiency
Concentrated (Niche) Marketing
Concept: Focusing on single niches to achieve large shares in a small pond
Advantage: Specialisation, strong brand authority
Challenge: high-risk, dependence
Example: Rolls-Royce, targeting ultra high net-worth.
Micromarketing (Individual):
Micromarketing (Individual):
Concept: Tailoring products and programs to specific locations or individuals
e.g. Nike By You (customing shoes)
Positioning Strategies (5):
Strategies:
Attribute positioning:
based on specific product feature
e.g. Dyson’s bagless, high-suction technology
Benefit positioning:
based on value the customer receives
e.g. Uber’s position on speed and convenience
Application positioning:
Associating the product with a specific usage
e.g. Red bull position —> drink for energy and performance needs
Competitor positioning:
positioning directly against a competitor
e.g. Avis vs Hertz: “We’re not #1, so we try harder”
Price / Quality Positioning:
More for more: premium ; same for less —> Value proposition
Chanel —> Walmart
The S-T-P Model of Marketing:
The S-T-P Model
Divide: GDPB factors determine sectors
Choose: Measurable, Accessible, Substantial, Actionable segments
Define: Create a strong, unique position in consumer’s mind, guided by positioning
Sustainable Marketing:
Sustainable Marketing: Socially and environmentally responsible marketing that meeds the present needs of consumers and business whilst preserving the ability of future generations to meet their needs - Kotler and Armstrong
Sustainability of Marketing on the Macroenvironment:
Social: Increased consumer awareness, social justice movement
Environmental: Climate change, resource scarcity, pollution
Legal: new regulations, taxes, ESG
key drivers of sustainable marketing:
Conscious consumers, seeking brands that algin with their SEEP values
Triple Bottom Line: bearable, equitable and viable between people, profit and planet
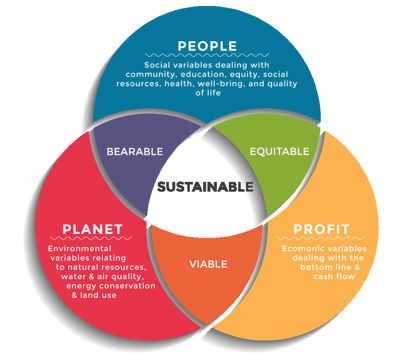
Triple Bottom Line: bearable, equitable and viable between people, profit and planet
People: Social responsibility and impact on key stakeholders / employees
fe.g. air labour practices, safe work environment, well-being
Planet: ecological footprint, sustainability of companies
e.g. reducing GGE, waste, resource conservation, renewable and ethical
Profit: broader economic impact a business has on society
e.g. job creation, tax payments, innovation, LT economic viability / prosperity
Corporate Social Responsibility
Primary framework for how organisations manage their responsibilities, with profits and impacts on society, integrating social and ethical concerns into operations and interactions
Carroll’s Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility:
Level 1: Economic Responsibilities - Be profitable
primary responsibility of profitability, providing rewards to owners, fair payment and fair pricing to consumers
Level 2: Legal Responsibilities - Obey the law
Society requires businesses to follow the laws e.g. employment law, product safety
Level 3: Ethical Responsibilities - be ethical
What is fair, just and right e.g. liveable minimum wage to overseas workers
Level 4: Philanthropic Responsibilities - be a good corporate citizen
Actively contributing resources to the community to improve QoL e.g. donations, volunteering
A company is not truly responsible if it is philanthropic but unethical and illegal
Creating shared value definition:
Creating Shared Value: Addressing societal needs and challenges through the business itself via a business model
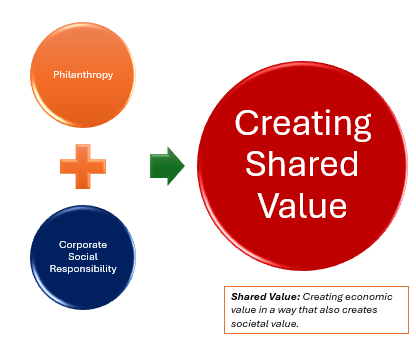
Approaches to transition from Corporate Social Responsibility to Creating Shared Value:
Green Marketing
Ethical Marketing
Circular Economy
Cause-related Marketing
Approach to Sustainable CSV: Green Marketing
Marketing products and services based on environmental benefits, not just green promotion and must integrate the marketing mix.
4Ps:
Product: design, less packaging, recycled materials e.g. Ecover
Place: sustainable distribution: shorter supply chains, CN shipping
Price: premium, reflecting higher costs or higher perceived value e.g. Organic food
Promotion: communicating eco-benefits transparently
e.g. Patagonia, sustainable mission, gold standard of authentic green marketing,
“We’re in the business to save our home planet”, 1% for the planet
Approach to Sustainable CSV: Ethical Marketing
Application of moral standards and principles to marketing decisions and behaviour
Without —> leads to simple tactics or greenwashing
Principles: transparency and substantiated, fairness and reduce exploitation, respect for privacy and data, consumer well being
Conflict between economic and ethical responsibilities:
Profit vs Principle Dilemma
Economic responsibility of Profit (Carroll’s Pyramid
Ethical Responsibility (Principle)
Short vs Long term sacrifices
Approach to Sustainable CSV: Circular Marketing
Challenge traditional economic model by recovering maximum value from resources, practicing repairing, repurposing and recycling existing products and materials
Approach to Sustainable CSV: Cause-related Marketing
Approach 4: Cause-Related Marketing
linking a product to a donation of cause, collaboration profit and non-profit organisations to promote non-profit cause for common benefit e.g. Pampers and UNICEF: 1 pack = 1 vaccine
Benefits: differentiates the brand and builds emotional connection
Can be seen as exploitative, customer cynicism
Greenwashing definition and example:
Deceptively promoting an organisation products, policies or aims as environmentally friendly when they are not, aimed to mislead consumers
Vague claims e.g. “all-natural”
Hidden trade offs: eco-friendly product made in polluting factories
Irrelevant claims: CFC-free (banned for decades)
Violates ethical and legal responsibility, erodes consumer trust and harms authentic brands
Example: Volkswagen (2015 “Dieselgate”)
VW marketed its diesel cars as “clean diesel” and environmentally friendly.
Cars were fitted with software that cheated emissions test, making pollution levels appear far lower than they actually were.
Product:
Product: Anything that can be offered to a market for attention, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need (Kotler and Armstrong)
Levels of Product with examples:
Level of product:
Core Customer Value: fundamental benefit or problem solved
Actual Product: tangible features, design and brand name
Augmented Product: additional services and benefits
Ford Example: CCV: transportation; AP = Ford Focus Car; AP = warranty, financing
Smartphone example: CCV: connection, info and entertainment; AP: handset, brand, camera; AP: warranty, storage, support, App Store ecosystem
4 characteristics of services (VIIP):
Characteristics of Services:
Intangibility: Services cannot be touched or owned, distinguished from tangible products
Inseparability: services are produced and consumed simultaneously, linked to their provides
Variability: service quality can change based on provider and situation
Perishability: Once performed, services cannot be repeated
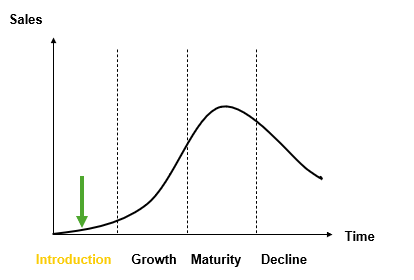
4 stages of Product Life Cycle (IGMD):
Introduction:
Slow sales, high costs (R&D, Marketing)
Building awareness, low penetration or high skim pricing, innovation. establish quality
Growth:
rapid acceptance, rising profits, competition
quality and pricing maintenance, increased demand, new channels,
Maturity:
Sales peak, market is saturated, optimal position, defending market share
Product enhancement and differentiation, lower pricing due to competition, intensive distribution
Decline:
Sales and profits fall caused by tech shifts and changing tastes
Options: maintain quality with potential additions, reduce costs or discontinue product
Usefulness of the PLC:
Usefulness
Diagnostic > predictive
Could assist with product planning and management
Strategies for PPPP must evolve overtime
Escape via Innovation
Innovation definition:
Innovation: Turning an invention into a commercial success that creates value
Invention: MP3 file —> Innovation: Monzo / Revolut: innovated the banking model with app-first, fee-free experience