Software Engineering FInal Review
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Design
Creative process of transforming process into solution
Cohesion
Degree to which elements inside a module belong together
Does good design have high or low cohesion?
High cohesion
Divide and Conquer
Solve complex problem by breaking it down into smaller pieces
Coupling
Degree of interdependence between modules/ strength of the relationship between modules
Encapsulations
Bundling of Data with the methods that operate on that data in one module
Information Hiding
Make the Information inside a module invisible to the modules clients
Separation of Concerns
Separate a program into distant modules such that each module addresses a separate concern.
Correctness formula
{P}A{Q}
{P} Hoare triple
Preconditions
A Hoare triple
Method or program
{Q} Hoare triple
Post Condition
Option of Preconditions Design (Design by contract)
Assumed precondition
-Demanding Design: assign the responsibility to clients
-Clients Check for conditions before calling method
-Software to software communication: trusted clients
Option of Preconditions design (Defensive Programming)
Validated Precondition
-Tolerant Design
-Software to human or software-to-outside-world: Untrusted client modules or external environments
- VERY important for safety/security-critical software
DBC: Assumed Precondition Principle
(aka Non-Redundancy Principle)
The body of a method should not test for its precondition
◦ The precondition is an assumed benefit for the
supplier
IF call(client) does not satisfy the preconditions, the method(Suplier) is not bound by postcondition
DB: pre/postcondition violation rules
Precondition violation: A bug in the client
Postcondition violation: a bug in the supllier
DBC: Precondition Availability
Rule
Every client in a position to call the method
will also be in a position to check for its
precond
◦ The precondition must not use private methods
hidden from the client
Rule of Contract Change
A safe change to a method may replace the existing preconditions by an equal or weaker one and the existing postconditions by an equal or stronger one
- existing client will not be affected
Postconditions
Postconditions often focus on the change s
A complete specification should also consider what remains unchanged

Solid Arrow Closed Triangle
Inheritance
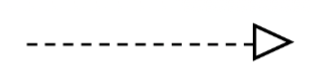
Dotted Arrow Closed Triangle
Implementation/realization
Solid Arrow Open Triangle
Association
Dotted Arrow Open Triangle
Dependency
Solid Arrow Hollow Diamond
Aggregation
Solid Arrow Solid Diamond
Composition
Inheritance
Generalization relationship
◦ Super-classes vs sub-classes (base vs derived)
Abstract date types
Abstraction the process or result of Generalization by reducing the information content of a concept or an observable phenomenon
Represent the essential features
Function Categories
Creator function
Query function
peek , pop
OCP(Open Close Principle)
Software Modules should be open for extension but closed for modification
What is refactoring?
A change made to the internal structure of c software to make it easier to understand and cheaper to modify
Module View vs type view
Module view → implementation focused
Type view→ behavior focused
Purpose of Coding Activities
Add or modify functionality
Fix bugs(remove defect)
Refactor
Code tuning
Code Smells
Code smells are not bugs
◦ They do not always indicate a problem
◦ They do indicate something that we should have
a closer look at
Server
the class/object to which the client has direct access
Delegate
the end object that contains the functionality needed by the client
What is quality assurance?
A set of activities that monitor and assess the software development methods and process to ensure proper quality of the software
The earlier in the process a defect is discovered and corrected, the cheaper the correction
Validation ensures that
the software meets the needs of the customers
the right product is being built to fulfill its purpose
“Are we building the right thing“
Verification ensures that
The software complies with the existing
requirements, specifications, or regulations.
e.g., it does not crash, meets the
requirements, handles failures gracefully,...
“Are we building it right“
Inspection team: four members
Moderator
A member of the team for the current workflow
A member of the team for the next workflow
A member of the SQA group
Static Code Analysis
Analysis of code or binary without actually executing(running) it
Black Box Testing
Testing without knowledge of internal working
White Box test
Testing with knowledge of internal working/ code
Gray Box testing
Combination of white and black box
Use information about the requirements (or
interfaces) and the code (e.g., structures)
Incorrect/Inaccurate Statements
Testing is the process of demonstrating that
errors are not present.
The purpose of testing is to show a program
performs its intended functions correctly.
Testing is the process of establishing
confidence that a program does what is
supposed to do.
Code coverage
Showing what test case can uncover and the faults in the code
Subsumption relationship