Monomers and Polymers
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Monomer: Think of monomers as individual beads. They are small, simple molecules that can join together. Monomers are made up of small, simple molecules like glucose (a sugar) or amino acids (the building blocks of proteins). Polymers are made by linking these monomers together in a chain. For example, proteins are polymers made of amino acid monomers, and starch is a polymer made of glucose monomers.. Polymer: Now imagine a necklace made by stringing those beads together. A polymer is a large molecule formed by linking many monomers together in a chain.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
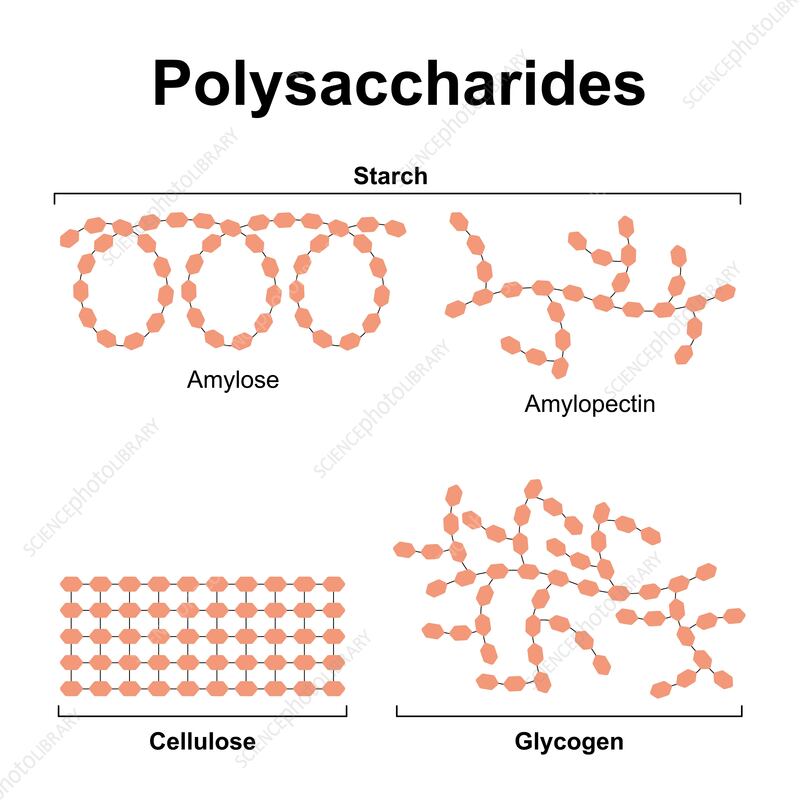
What role do monomers play in the formation of polysaccharides (large complex carbohydrates made up of many smaller sugar molecules (monomers) linked together)?
Monomers like glucose are the building blocks for polysaccharides (Polysaccharides are large, complex carbohydrates made up of many sugar molecules linked together.)
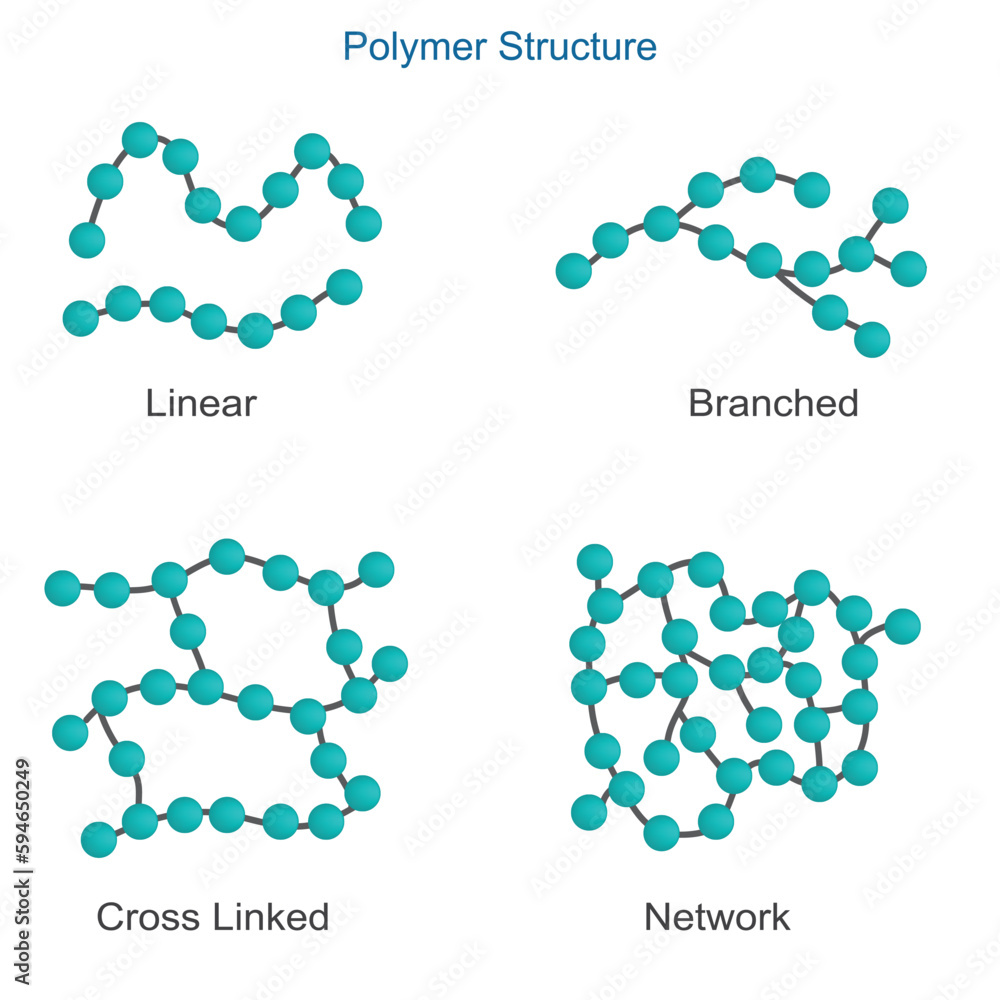
Cross-linked polymers have a network structure due to interconnected chains (a network-like structure with many connections (cross-links) between the polymer chains)
Examples include polyethylene, polypropylene, polyester
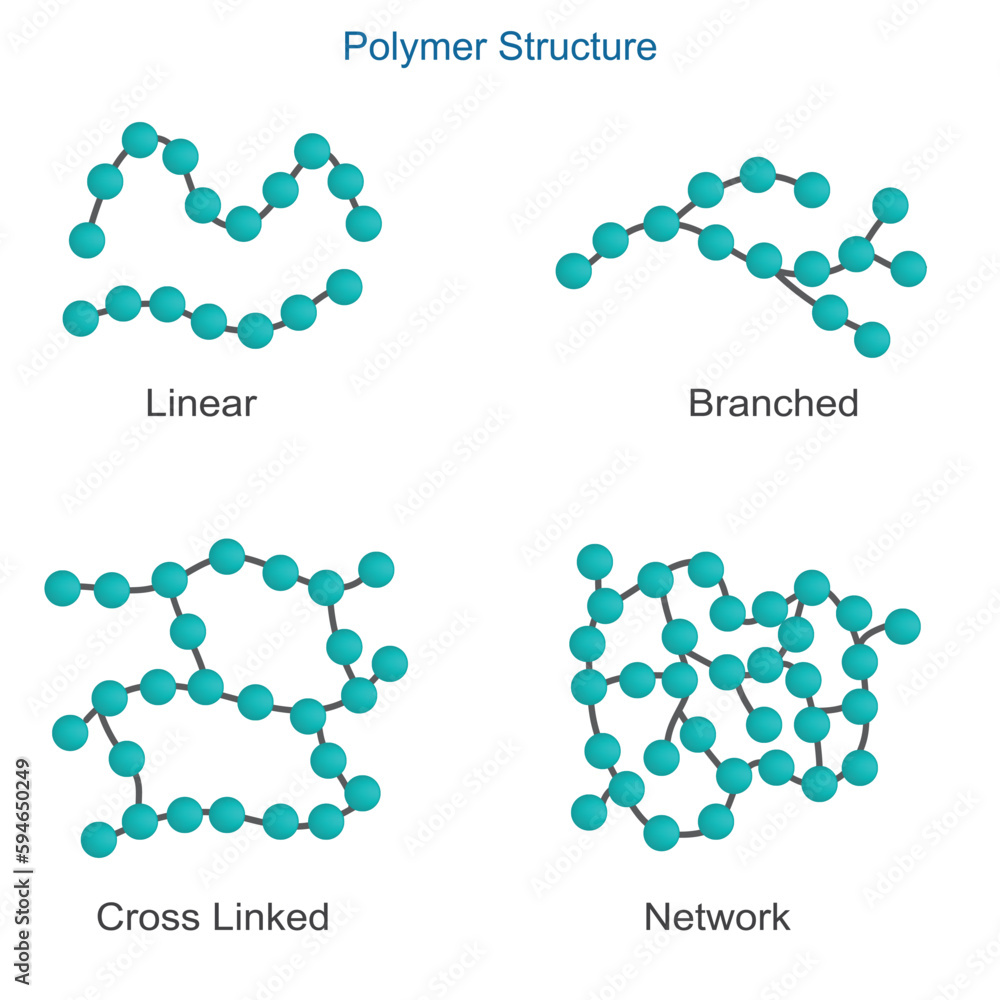
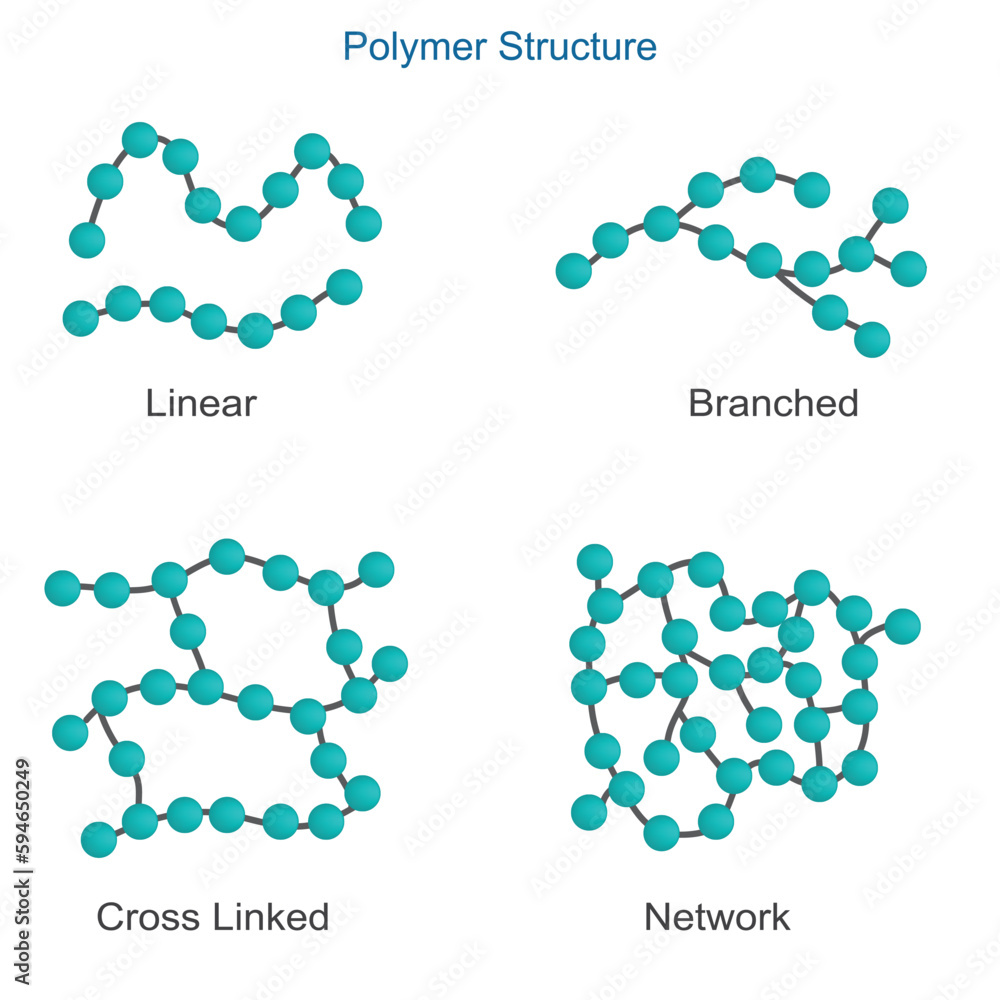
What type of monomers typically undergo addition polymerization (monomer molecules react together to form a polymer without the loss of any small molecules)?
Monomers like ethylene and propylene typically undergo addition polymerization.
Natural polymers are essential for life processes. (Such as DNA, proteins, cellulose…)
Natural polymers include DNA, proteins, and cellulose
The term 'polymer' comes from the Greek words 'poly’, meaning many, and 'meros,' meaning part.
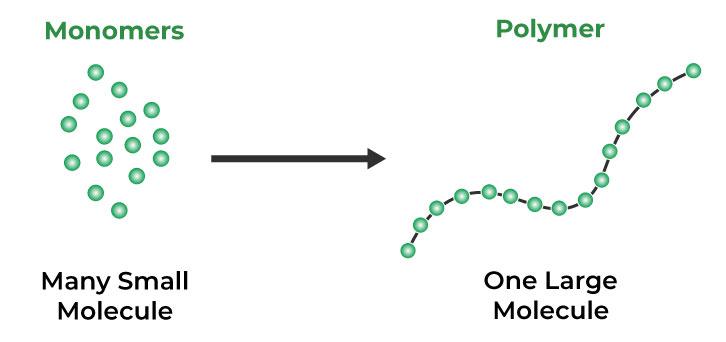
Polymers are large, complex molecules composed of repeating units of monomers linked by covalent bonds.
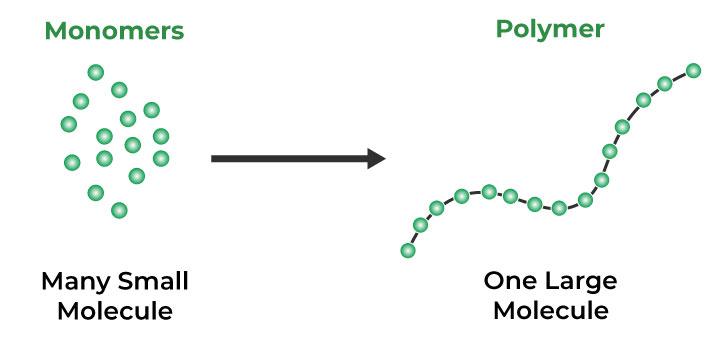
Monomers are crucial for the synthesis of vital macromolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides.
Amino acids have an amine group (amine group is part of a molecule that has a nitrogen (N) atom attached to one or more hydrogen (H) atoms) and a carboxyl group (carboxyl group is part of a molecule that has a carbon atom (C) bonded to an oxygen atom (O) with a double bond).
Common monomers include glucose, amino acids, and nucleotides.
The term 'monomer' is derived from the Greek words 'mono’, meaning single, and 'meros,' meaning part.
Monomers are small, basic molecular units that can join together to form larger structures called polymers.
The monomers of carbohydrates are what?
Monosaccharides, these are simple sugar molecules, and the most common example is glucose.