Module 9 - Business Continuity
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
BC
the process of preparing for and recovering from system outages to keep operations running smoothly
Ensure continuous access to data and services
Use proactive/reactive measures
Automation to reduce downtime and manual effort
Main goal is to maximize availability of apps and info
Ex: if a natural disaster caused a power outage, a good BC plan ensures power kicks in or shifts operations to another data center to keep services running
Information Availability
the ability of an IT infrastructure to function according to business requirements and customer expectations, during its specified time of operation.
IA can be defined in terms of:
accessibility, reliability, and timelines
accessibility
information should be accessible to the right user when required
reliability
information should be reliable and correct in all aspects. I tis the same as what was stored and there is no alteration or corruption to the information
Timelines
defines the time window during which information must be accessible
Causes of information Unavailability
Application failure
Data center outage
Refreshing IT infrastructure
Infrastructure Component Failure
Data Loss
planned outages
such as installation and upgrades, facility constructions
unplanned outages
such as human error or natural disaster
impact of information unavailability
lost productivity, lost revenue, financial performance, other expenses, and damaged reputation
MTBF
mean time between failure
average time for a system to perform its normal operations until another failure
total uptime/number of failures
MTTR
average time is takes to repair a failed component
total downtime/number of failures
IA formula
IA = MTBF / (MTBF + MTTR) or IA = Uptime / (Uptime + Downtime)
RPO
Recovery Point Objective
point in time to which data must be recovered
RTO
Recovery Time Objective
Time within which systems and applications must be recovered
units of RPO and RTO
both are counted in units of time
usually the lower the RTO and RPO
the higher is the cost of a BC solution
Disaster Recovery
involved a set of policies for restoring IT infrastructure
the fundamental principle of DR
maintain a secondary data center or site called a DR site which should be located in a different geographical region
BC Technology Solutions
implementing FT mechanisms
deploying data protection solutions
automatic failover mechanisms
architecting resilient modern applications
Fault Tolerance
the ability of an IT system to continue working in the event of a failure
Key Requirements for FT
fault isolation and eliminating SPOF
Fault Isolation
contains the scope of a fault so that the other areas of a system are not impacted by the fault.
Single Point of Failure
refers to any individual or aspect of an infrastructure whose failure can make the entire system or service unavailable
How to eliminate SPOF
implement redundancy at component level: compute network storage
implement multiple availability zones
Network FT Mechanisms
link aggregation
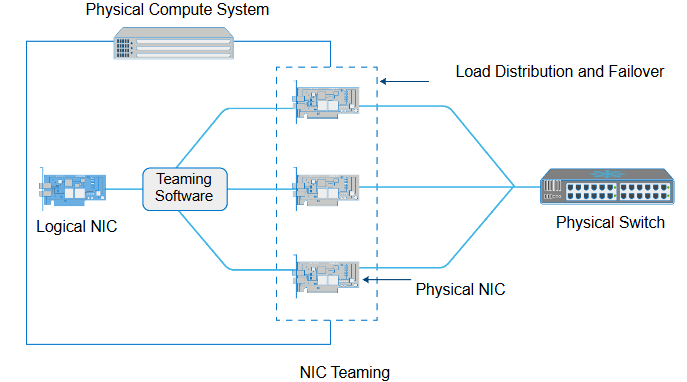
NIC teaming
Multipathing
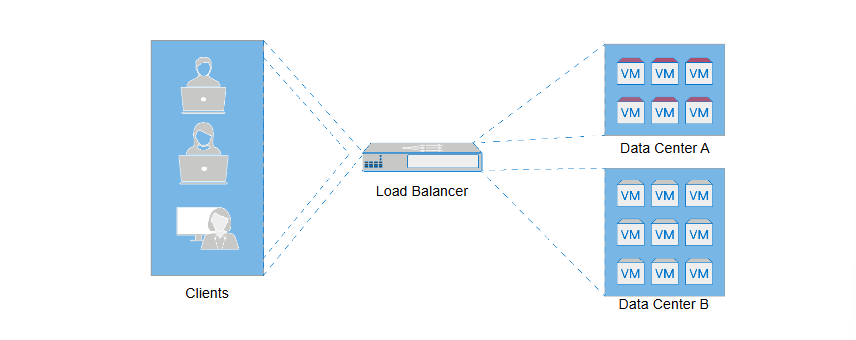
Elastic Load Balancing
link aggregation
combines link between 2 switches/nodes to enable network traffic failover
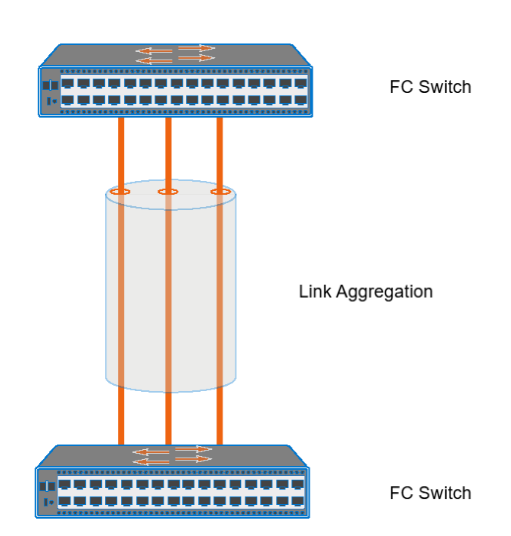
NIC teaming:
groups NIC so that they appear as a single logical NIC to the operating system or hypervisor
Multipathing
enabling a compute system to use multiple paths for transferring data to a LUN
Elastic Load Balancing
detecting the unhealthy VM instances and automatically redirects the I/Os to other healthy VM instances.
Storage Fault Tolerance Mechanisms
RAID
Erasure coding
Dynamic Disk Sparing
Cache protection
Erasure coding
provide space optimal data redundancy to prevent data loss against multiple disk drive failures
Set of n disk divided into m disk to hold data and k disks to hold coding infos

Dynamic Disk Sparing:
hot spare
Cache protection
- mirroring
Erasure Coding
Provides space-optimal data redundancy to protect data loss against multiple drive failure
Cache Protection - Mirroring
Each write to cache is held in two different memory locations on two independent memory cards. • If a cache failure occurs, the write data will still be safe in the mirrored location and can be committed to the storage drive
FT at Site-Level - Availability Zones
Availability zone is a location with its own set of resources and isolated from other zones
Dell EMC PowerPath
a family of software products that ensures consistent application availability and performance across I/O paths on physical and virtual platforms. • PowerPath provides automated path management and tools that enable you to satisfy aggressive service-level agreements without investing in additional infrastructure