Mathematics of Finance: Interest, Annuities, and Investment Strategies
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Interest
amount paid in exchange for borrowing or using another person's or organization's money.
Principal
initial amount borrowed or deposited.
Annual rate of interest (r)
interest rate expressed in decimal.
Time (t)
number of years the amount is deposited or borrowed.
Number of times interest is compounded (n)
number of times the interest is compounded per year.
Simple Interest
interest paid on the original principal only.
Ordinary Interest
type of interest wherein the interest is computed based on the assumption that the year contains 360 days and each month has 30 days.
Exact Interest
type of interest where interest is computed based on the assumption that the year has 365 days.
Annuity
regular equal deposits/payments made at equal intervals.
Ordinary Annuity
annuity paid at the end of each term.
Annuity Due
annuity paid at the beginning of the term.
Future Value
value of an asset or cash at a specified date in the future that is equivalent in value to a specified today.
Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity
formula to calculate the present value based on future payments.
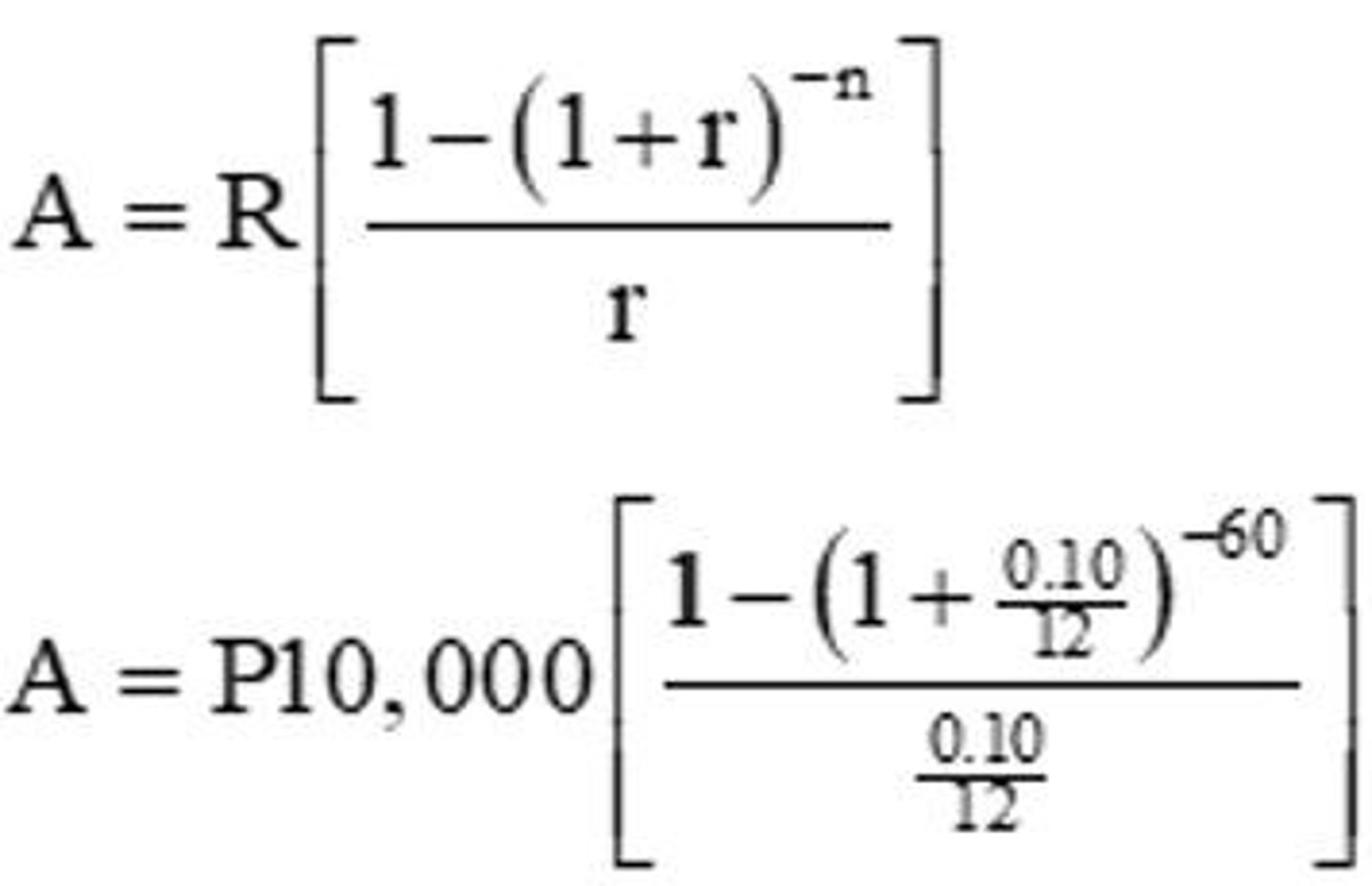
Compound Interest
calculated on the principal amount and also on the accumulated interest of previous periods.
Future Value of an Annuity Due
formula to calculate the future value of an annuity paid at the beginning of each term.
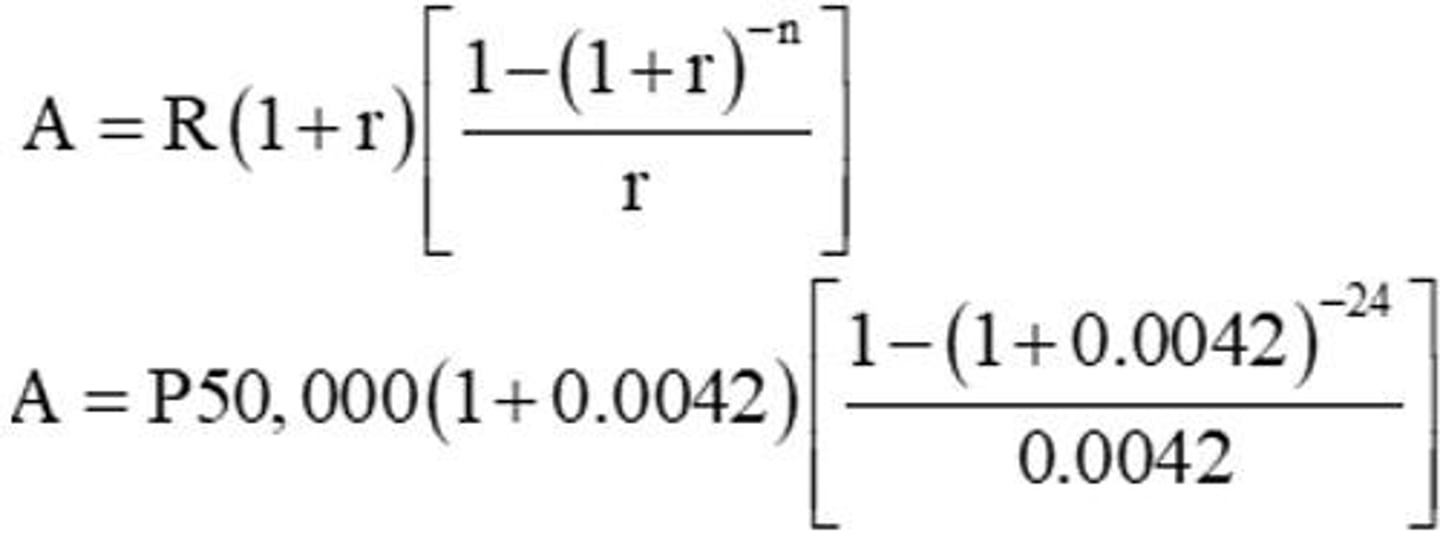
Present Value of an Annuity Due
formula to calculate the present value of an annuity paid at the beginning of each term.
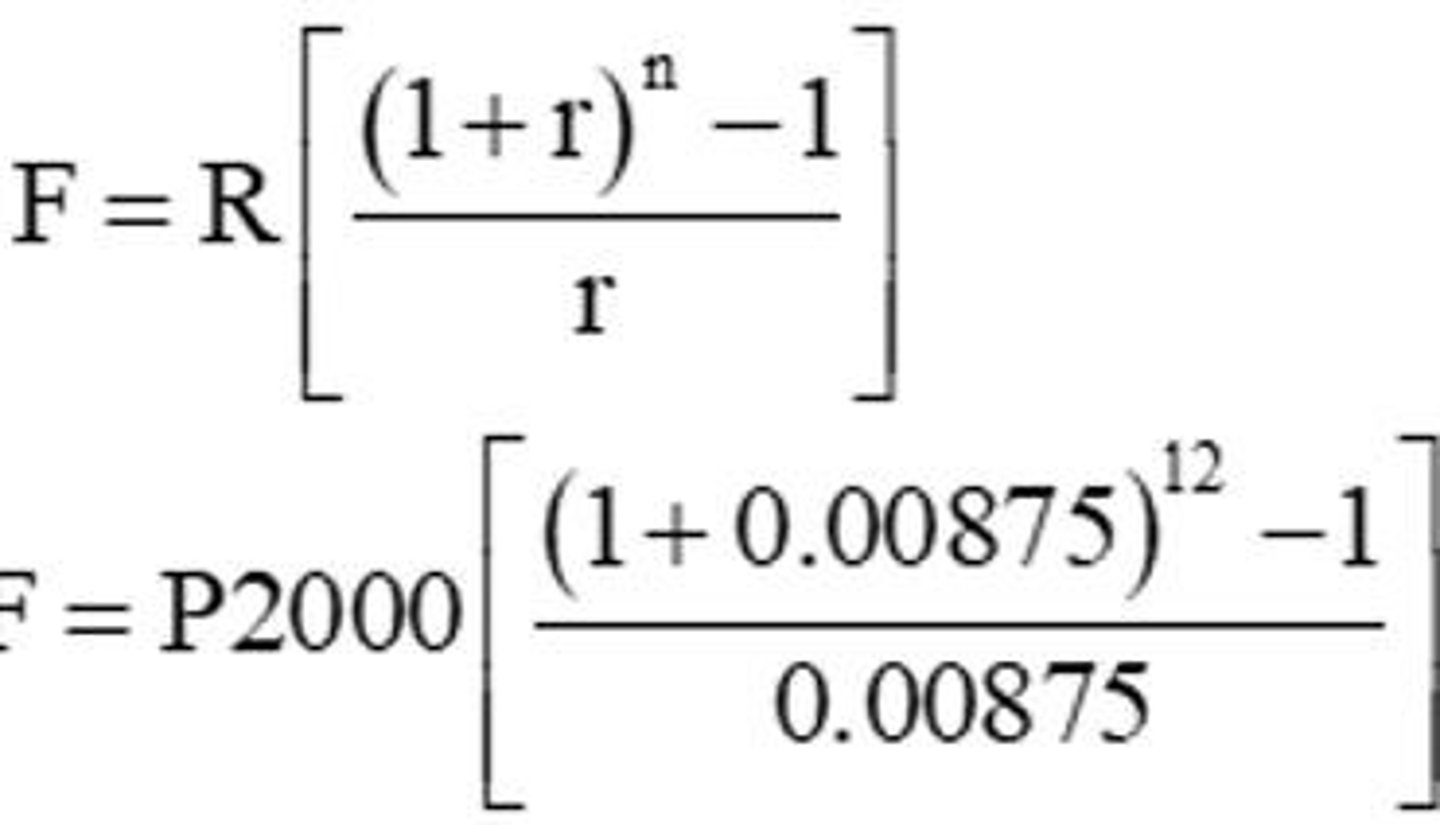
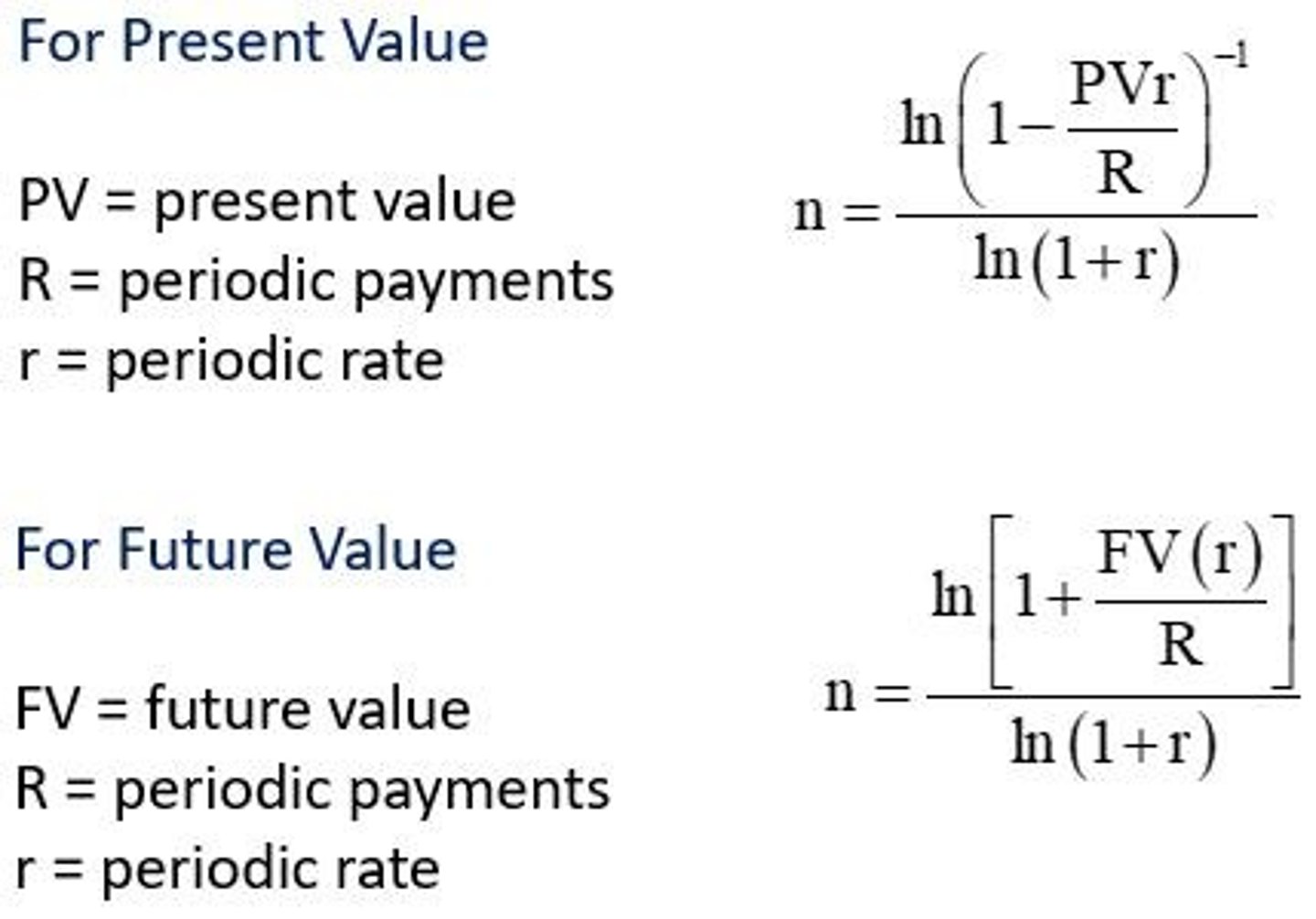
Periodic Payment (R)
amount of each periodic payment in an annuity.
Interest Rate per Period (r)
interest rate applicable for each period or payment.
Number of Periods (n)
number of periods or payments in an annuity.
Savings Calculation Problem
example of calculating future savings based on regular deposits and interest.
Investment Problem
example of calculating future value based on an initial investment and interest.
Loan Payment Problem
example of calculating the full payment for a loan based on periodic payments.
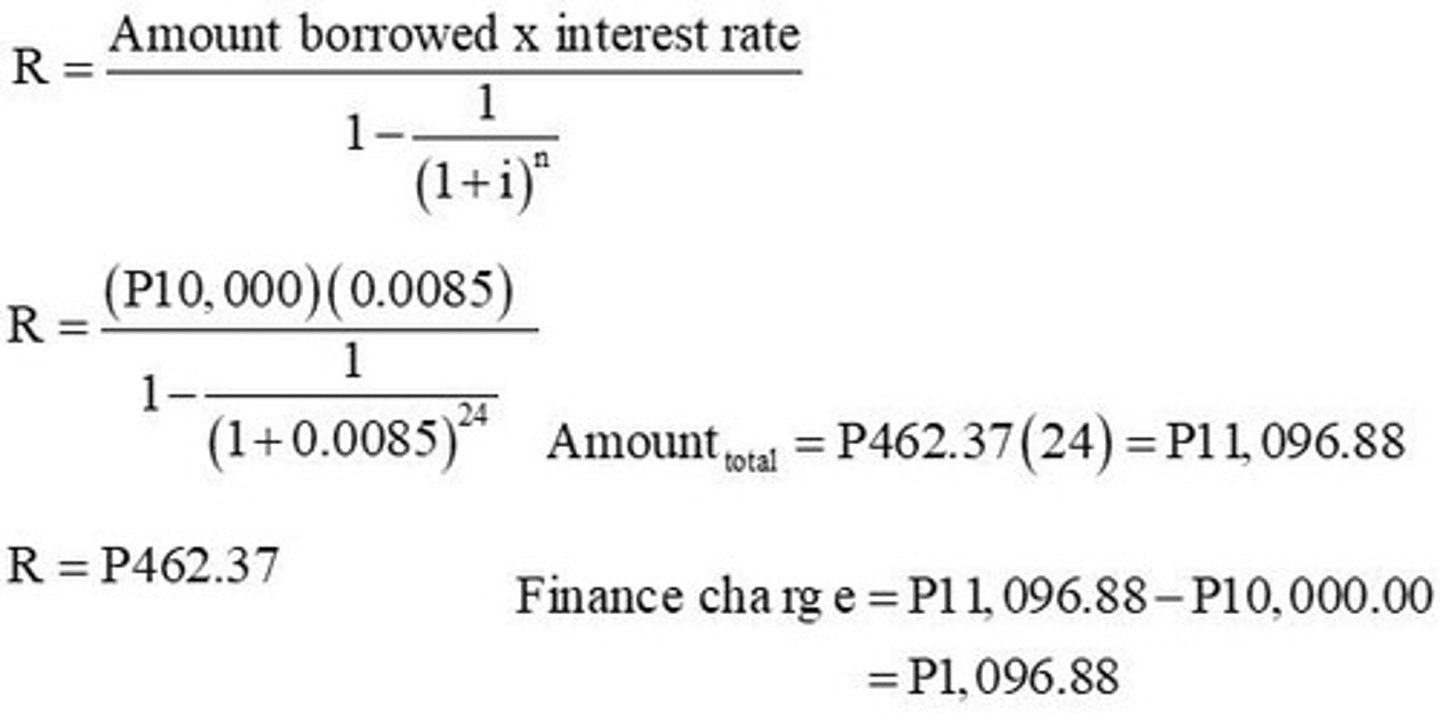
Education Savings Problem
example of calculating how much to deposit for future education expenses.
Consumer Loan
A loan given to consumers to finance specific types of expenditures.
Deferred Annuity
An annuity in which the first payment is not made at the beginning nor end of the payment interval, but at a later date.
Mortgages
Loans used by consumers to finance the purchase of a house.
Credit Cards
A piece of plastic or metal issued by a bank or financial services that allows cardholders to borrow funds for purchases.
Auto Loans
Loans used by consumers to finance the purchase of a vehicle.
Student Loans
Loans used by consumers to finance education.
Personal Loans
Loans used by consumers for personal purposes.
Installment Buying
A system for paying goods, products, or services in fixed amounts at specified intervals, usually monthly.
Deferment Period
Length of time from the present to the beginning of the first payment interval.
Cash Price
Actual amount of money to be exchanged for the item or product.
Amount to be Financed
Difference between cash price and down payment.
Finance Charge
Amount paid for the use of credit or the extension of existing credit.
Total Installment Price
Total amount a buyer pays for an item over time.
Equity
Value of the shares issued by a company.
Share
A unit of ownership of a corporation's profits and assets.
Investment
An item (asset) acquired with the goal of generating income or appreciation.
Certificate
Document issued to stockholder that contains details like corporation's name, owner's name, number of shares owned, certificate number, and par value.
Dividend
Payment made by the corporation to the shareholder when profit is realized or has surplus.
Common Stock
Represents a share of company's assets and profit.
Fixed Income
Investment security that pays a fixed return over time.
Risk and Return
Two sides of the same coin in investing.
Quantifying Ownership
Ownership can be quantified by dividing the number of shares owned by the number of shares issued.
Periodic Payments
Payments made at regular intervals over a specified time period.
Interest Rate
The percentage of a loan charged as interest to the borrower.
Present Value
Current worth of a future sum of money given a specified rate of return.
Preferred stock
Entitles holders to a fixed dividend before any payment is distributed to other shareholders.
Bonds
Long-term debt instruments that promise a fixed income in the form of interest.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Value of a company's assets that are cash or can be converted into cash immediately.
Bank Accounts
A type of account held at a financial institution that allows deposits and withdrawals.
Money Market Accounts
A type of savings account that typically offers higher interest rates and allows limited check writing.
Stock
Type of security that signifies ownership or share in a corporation.
Mutual Fund
An investment where investors pool their resources together to invest in some diversified assets.
Equity Fund (Stock Fund)
Fund invested in the stocks of corporations listed in the PSE, with the highest possibility of growth but also high risk.
Bond Fund
Investment on some fixed-income securities.
Balanced Fund
A mixture of both equity and bond fund.
Money Market Fund
Similar to bond fund but of shorter term.
Government Bonds
Issued by governments to fund programs, meet payrolls, and pay bills.
Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
Debt instruments that allow the public to lend their money to the state.
Fixed Rate Treasury Notes (FXTNs)
Debt instruments with a level interest rate over its entire term.
Retail Treasury Bonds (RTB)
Offers investors the opportunity to invest smaller amounts with maturity of 3 to 5 years.
Corporate bonds
Issued by businesses to help them pay expenses, typically with higher interest rates due to higher risk.
Amortization
Paying off debt or loan over time in equal installments.
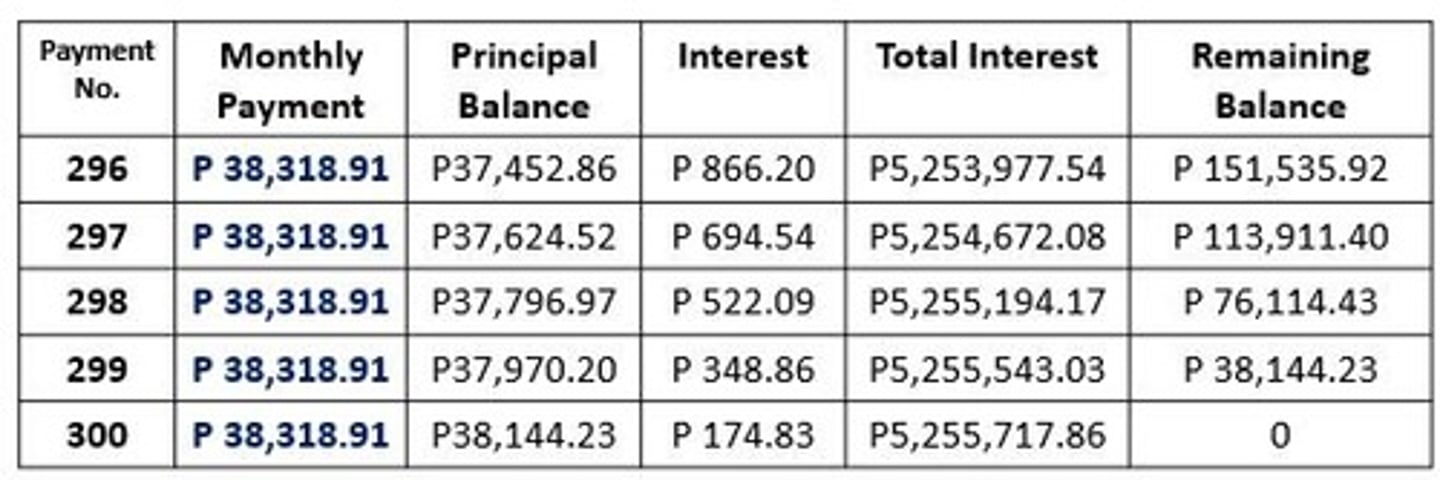
Amortization schedule
A table which shows the specific periodic payments - the principal, interest, and balance at the end of each period.
APR
Annual Percentage Rate, the annual rate charged for borrowing or earned through an investment.
DIR
Daily Interest Rate, calculated as the annual interest rate divided by the number of days in a year.
Home Ownership
Owning a house.