Managerial Accounting Ch.1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: (management responsibilities) Operational Planning
Focuses on short- term action. dealing with day-today operations (1 year)
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: (management responsibilities) Strategic Planning
Developing long-term strategies to achieve company goals (3 years)
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: (management responsibilities) Directing
Running the day to day operations of a company
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: (management responsibilities) Controlling
Monitoring the day to day operations and keeping the company on track
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: Managerial accounting
Focuses on internal user, managers & employees
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: Purposes of managerial accounting
Give info to management so they can plan better for operations within their company
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: Focus & time dimension of the info of managerial accoutning
Managers need relevant info and focus on the future (proving the business in the future)
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: Rules & restrictions in managerial accounting
Does not need to follow GAAP n=and less restrictions
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: scope of info in managerial acc.
Managers need detailed reports on parts of the company on a daily or weekly basis, broken down into diff departments, territories and products
Why is Managerial Accounting Important: behavioral in managerial accounting
Concern about how reports will affect employee behavior
How are costs classified: Business are classify as a?
Service company, merchandise company or manufacturing company.
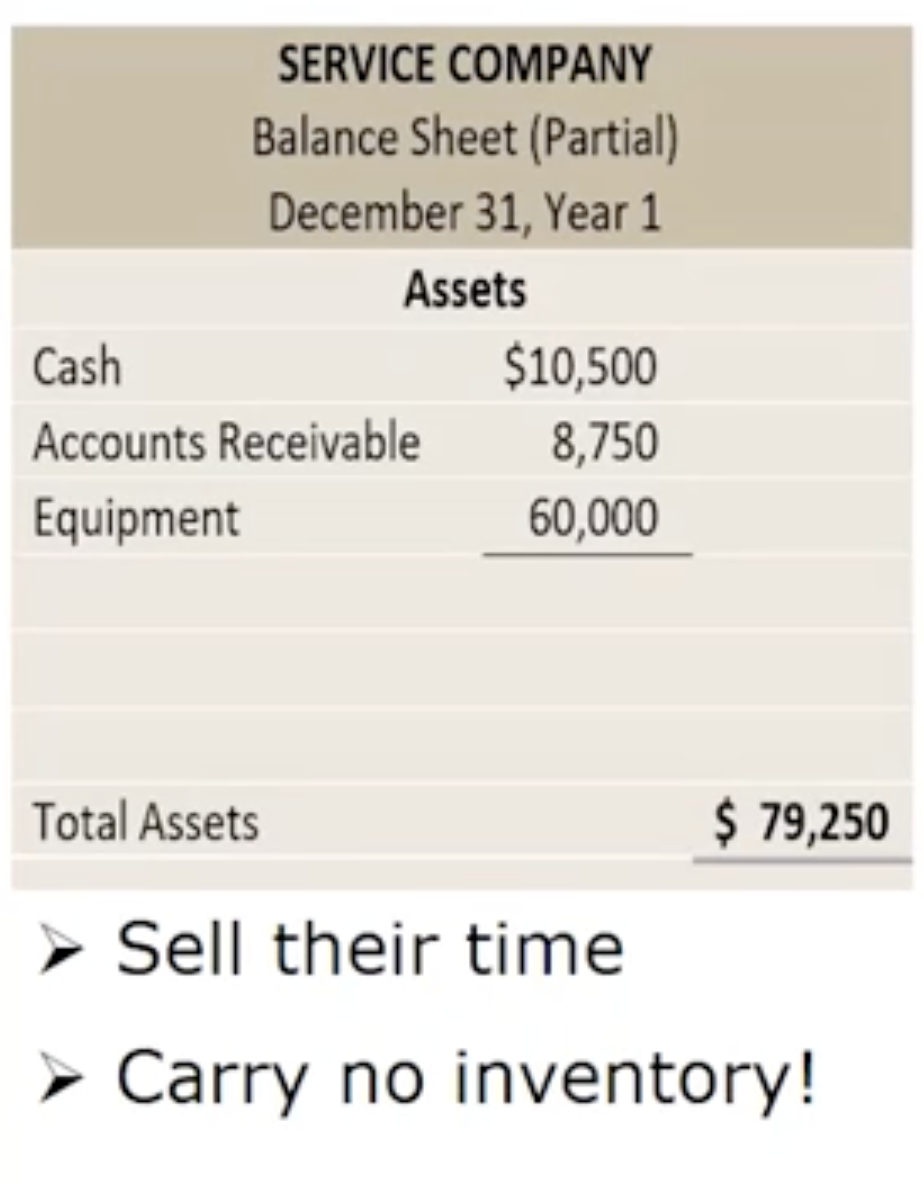
How are costs classified: Service company

They DO NOT carry any inventor7
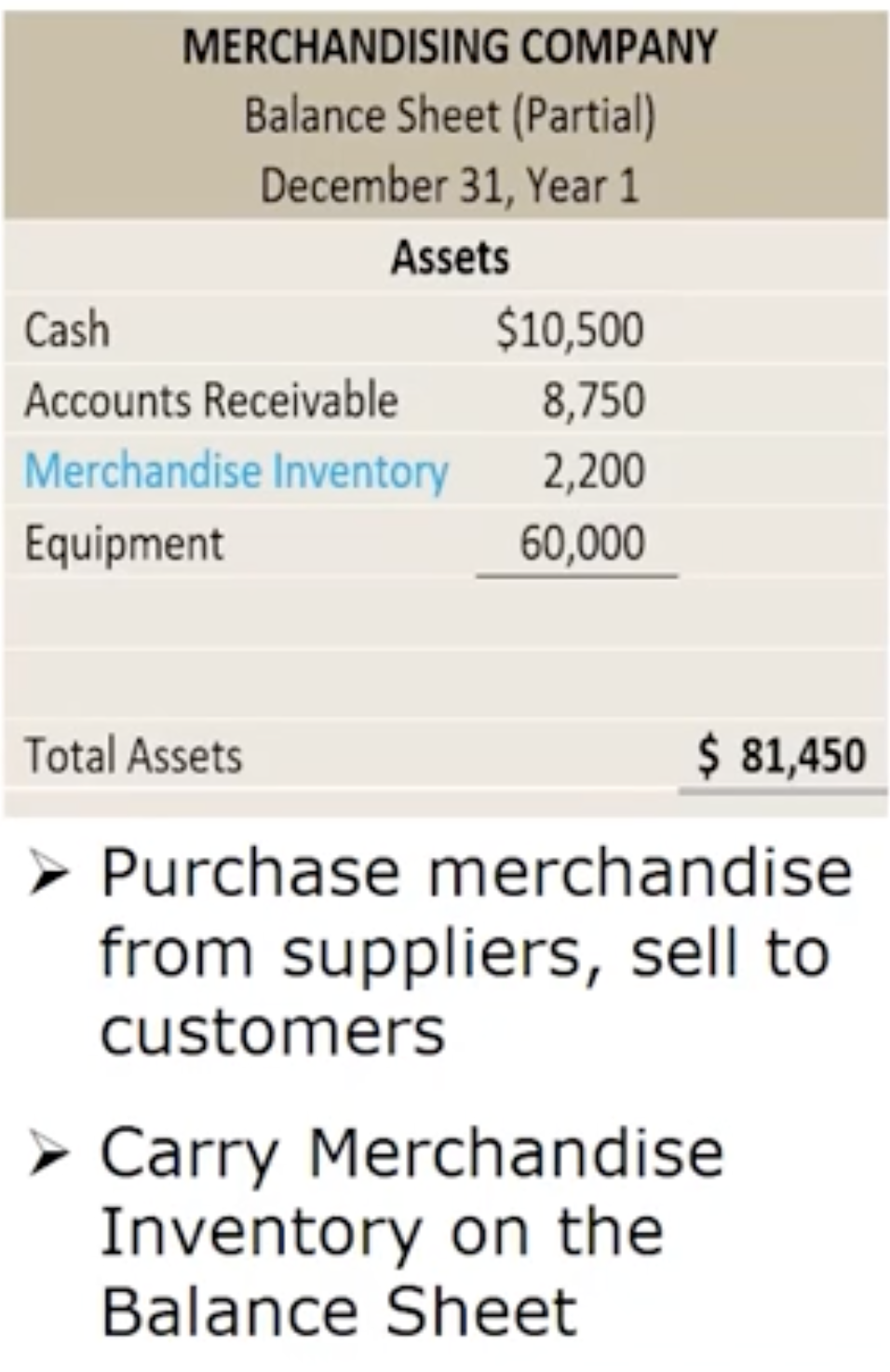
How are costs classified: Merchandising company

They carry inventory which they sell to consumers
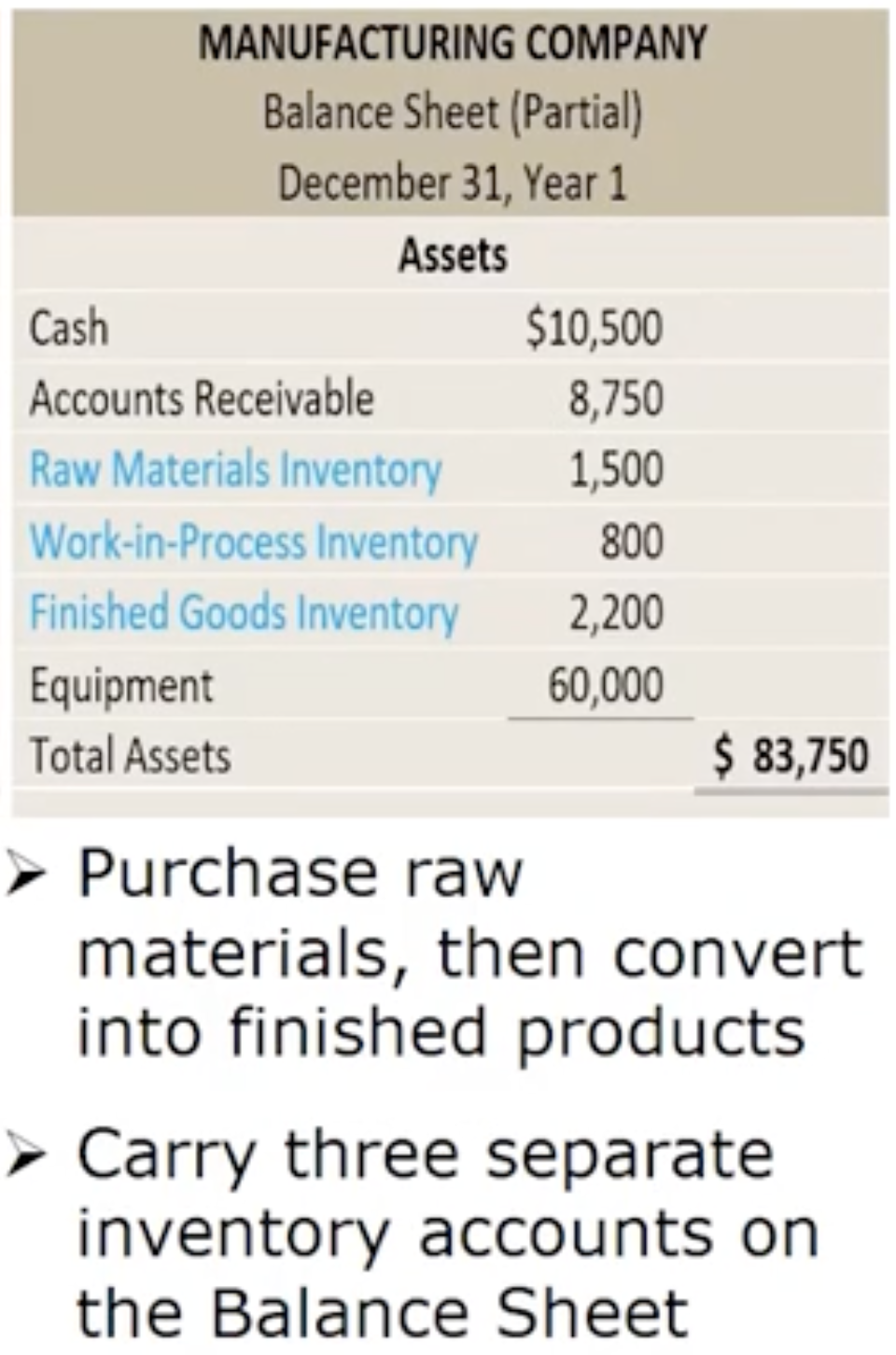
How are costs classified: Manufacturing company
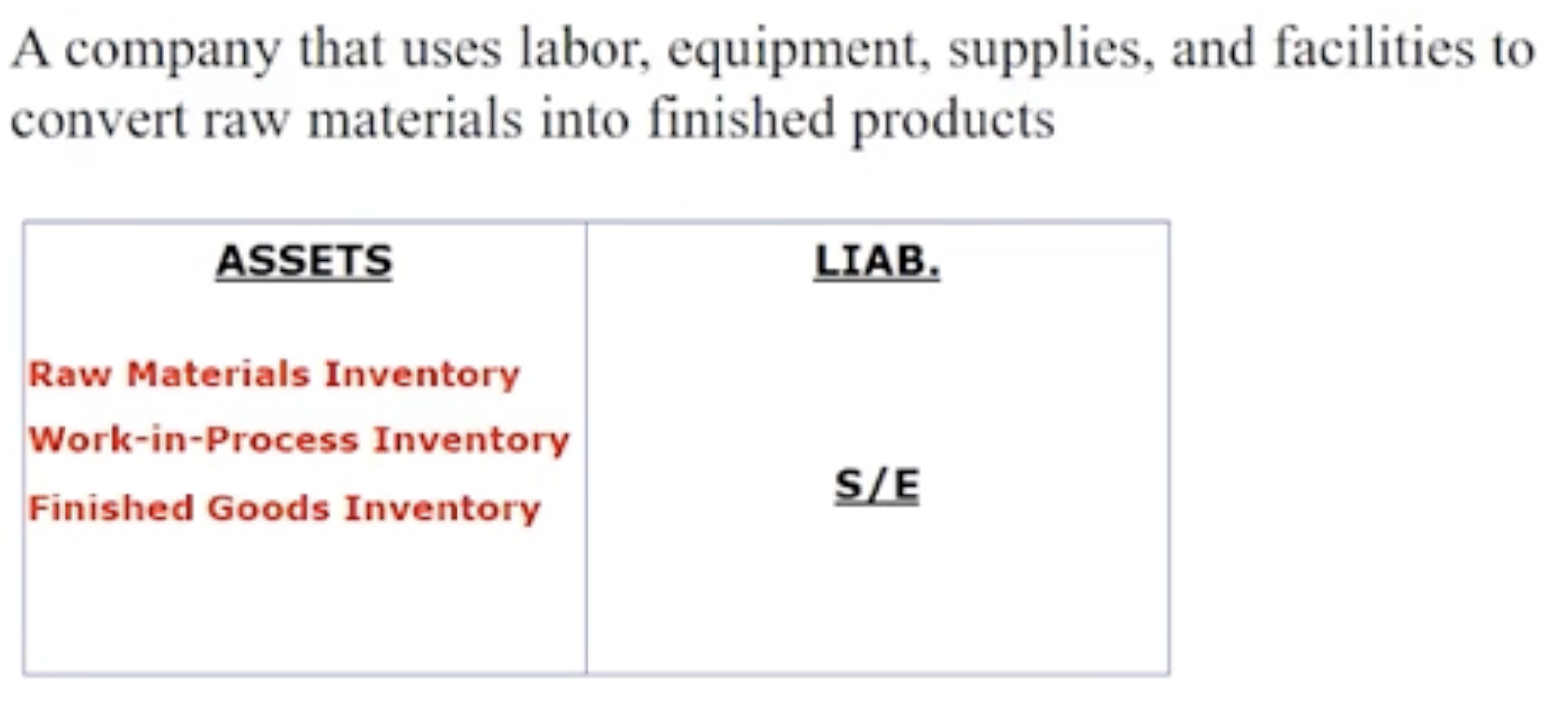
How are costs classified: Manufacturing company— Raw materials inventory
Materials used to manufacture a product
How are costs classified: Manufacturing company— Work- in- process inventory
Goods that have been started in the manufacturing process but not yet complete
How are costs classified: Manufacturing company— Finished goods inventory
completed goods that have not yet been sold
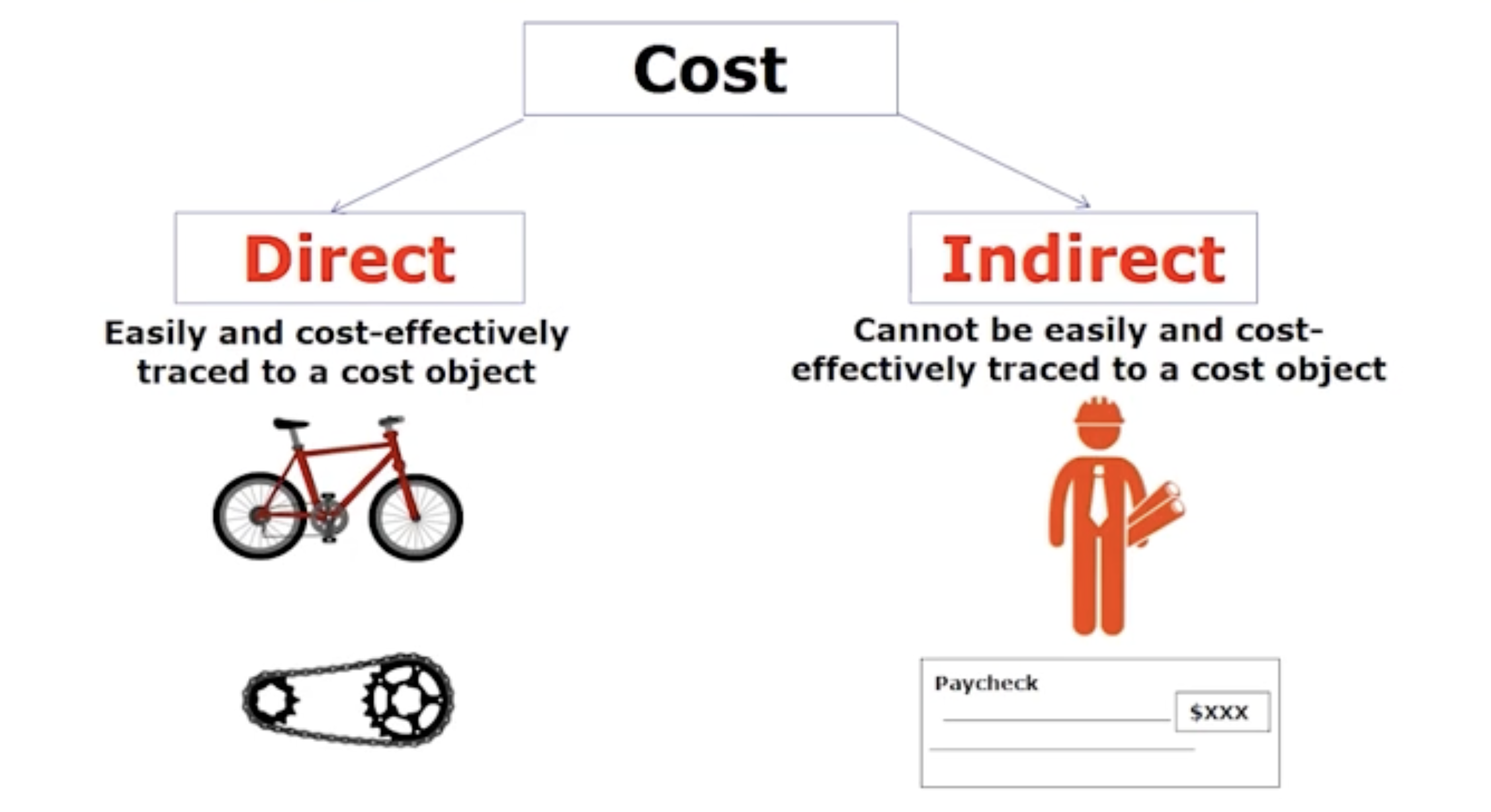
How are costs classified: Direct and indirect costs
A costs is often traced to a costs object: a product, department, sales territory, or activity
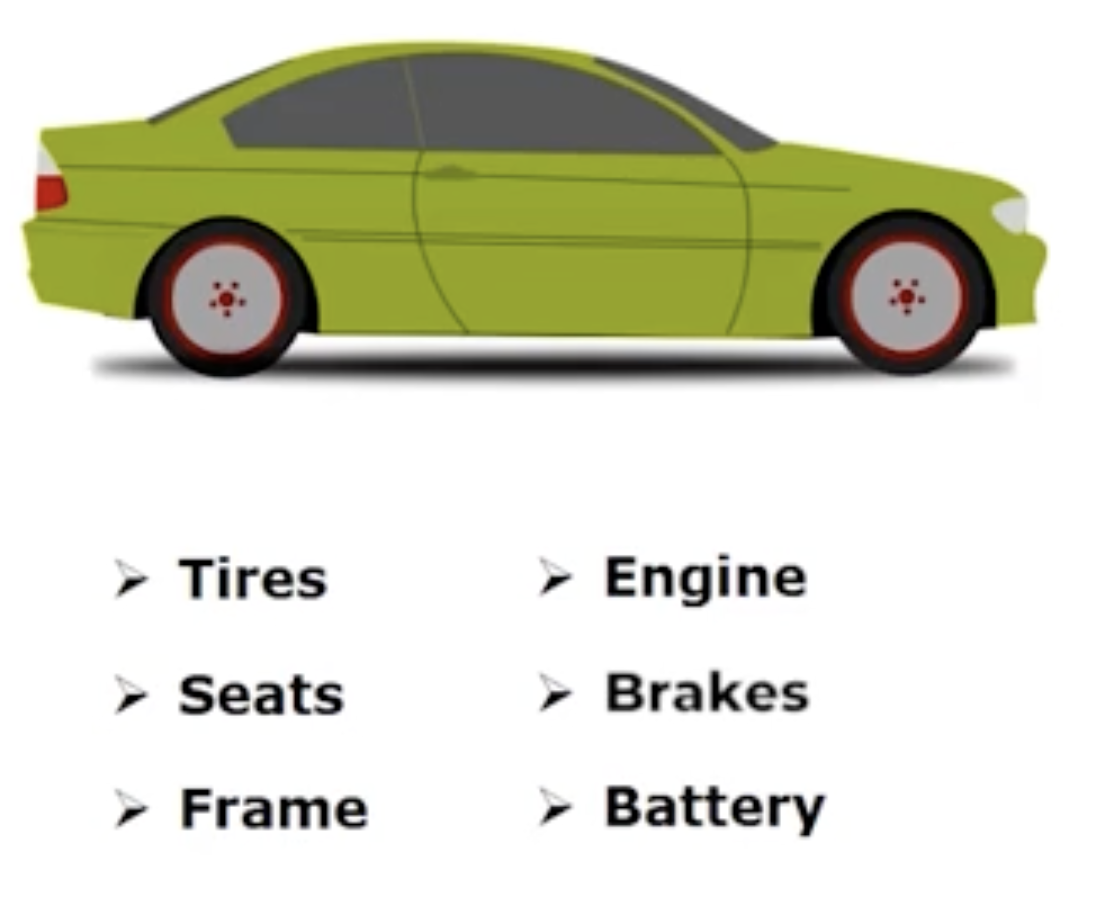
How are costs classified: Manufacturing costs— Direct materials
Materials that become a physical part of a finished product and whose costs are easily traced t the finished product
Ex:
How are costs classified: Manufacturing costs— direct labor
The labor costs of employees who convert raw materials into finished products
Ex: Assembly workers in a car dealership, those who actually work on the assembly line and convert the raw materials into a finished car, are considered direct labor.
How are costs classified: Manufacturing costs— Manufacturing overhead

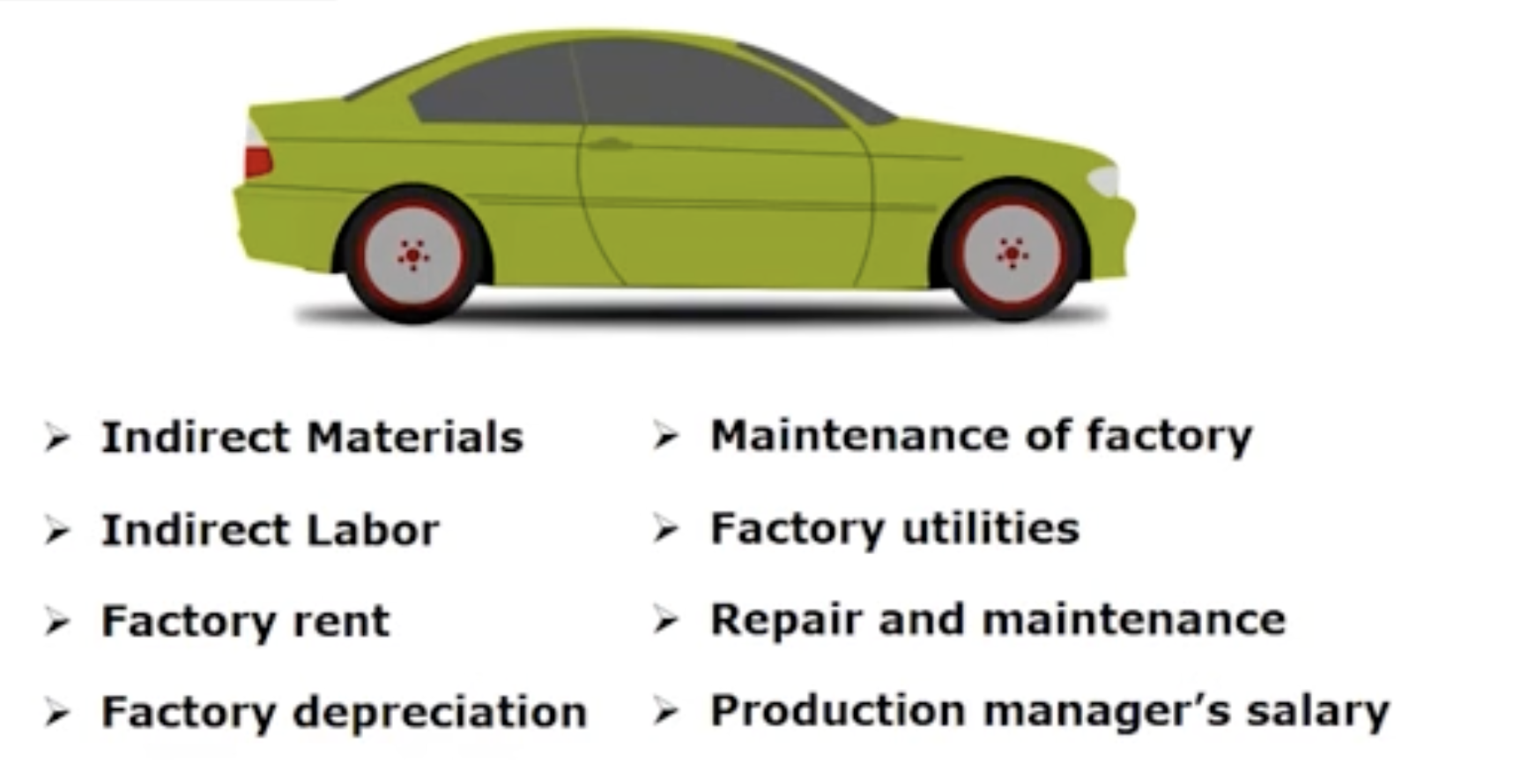
How are costs classified:


How are costs classified: Prime costs
Direct Materials plus direct labor
The primary costs in a labor- intensive manufacturing process meaning in the car ex most of the workers are doing the work
So if its labor intensive, management will focus most of their effort on controlling prime costs
How are costs classified: Conversion costs
Direct labor plus manufacturing overhead
Primary costs in a machine-intensive manufacturing process
If its machine intensive managment will focus most of their attention on conversion costs
How are costs classified: Period costs

How are costs classified: Product costs

How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Service company
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Merchandising company
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Manufacturing company
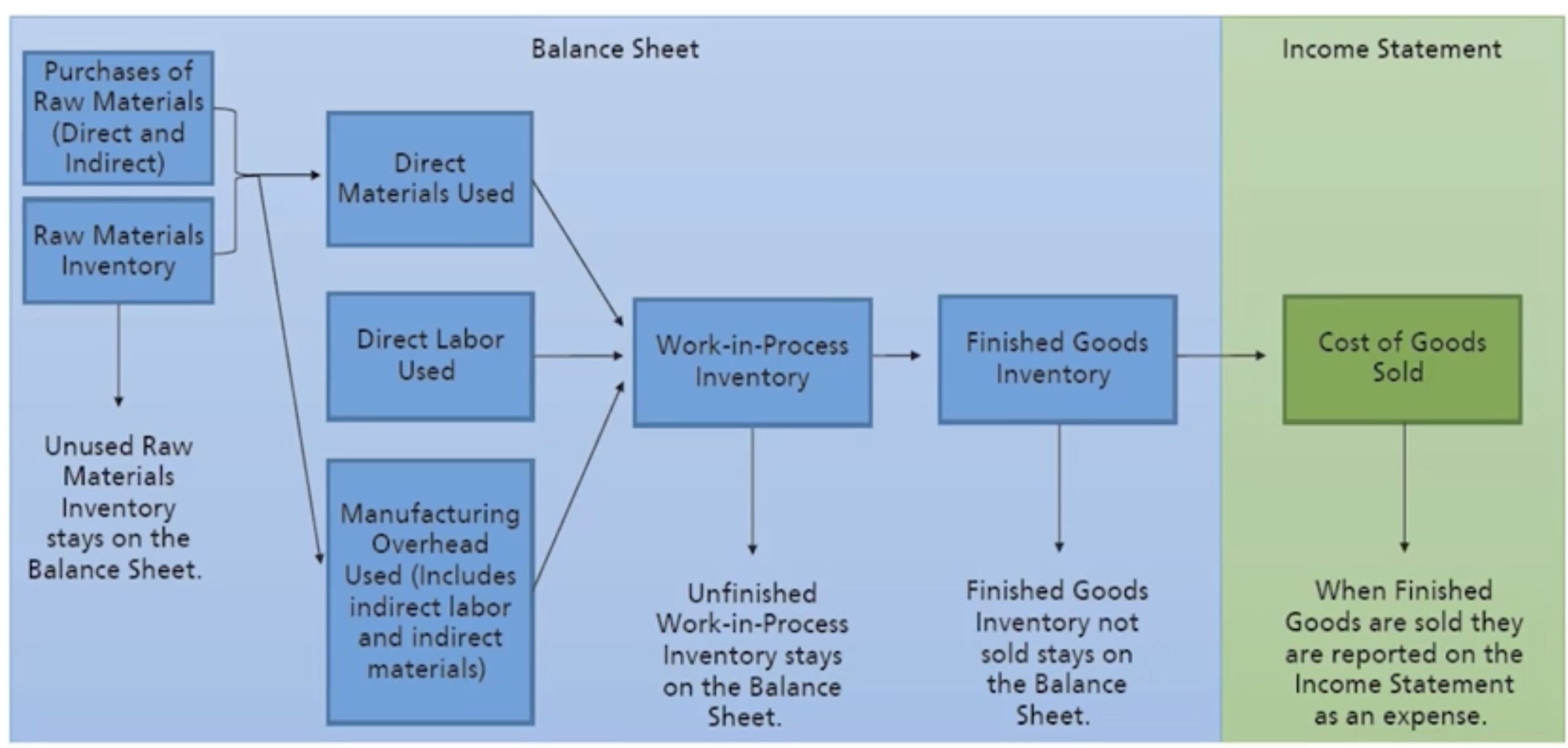
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Product cost flows- manufacturing
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Calculating costs of goods manufactured
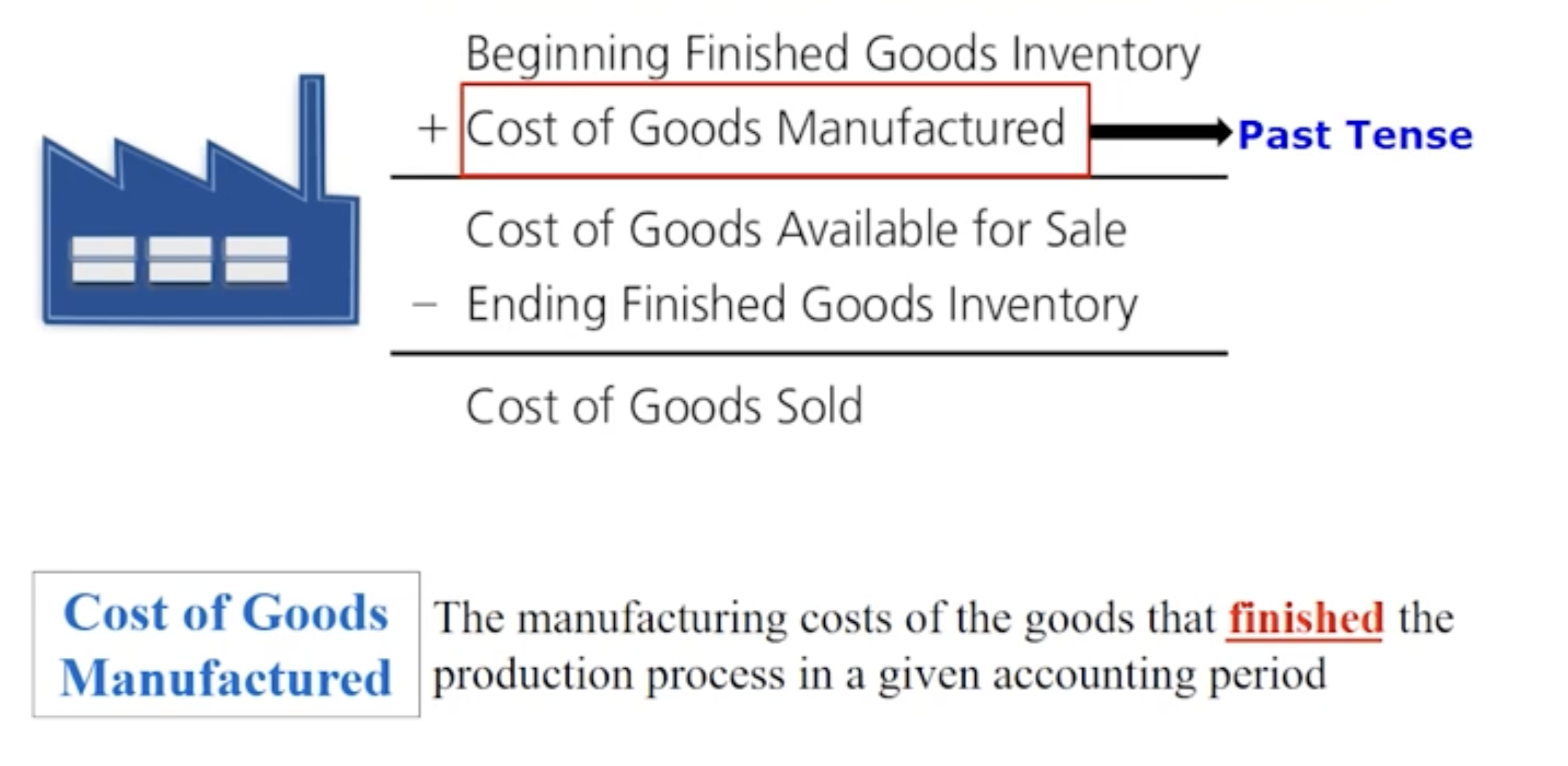
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Step 1. Breakdown of calculating cost of goods manufactured

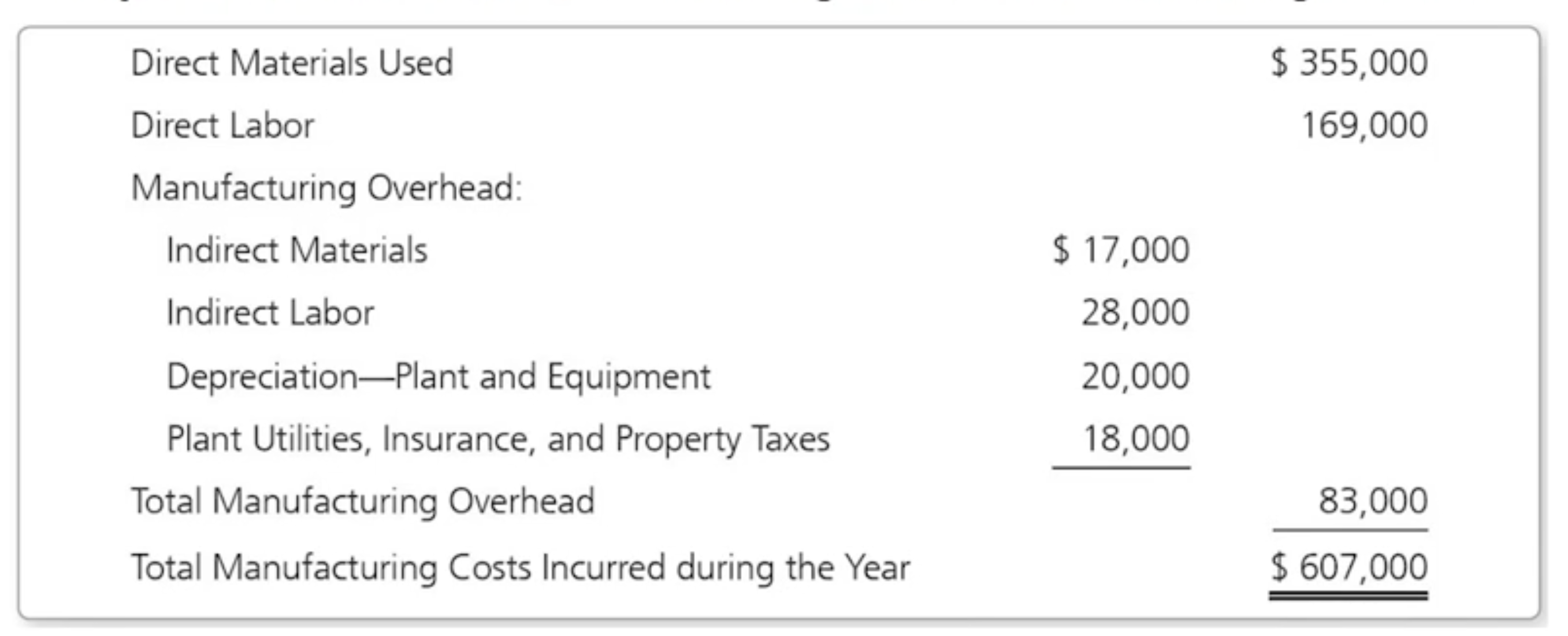
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Step 2. Breakdown of calculating cost of goods manufactured

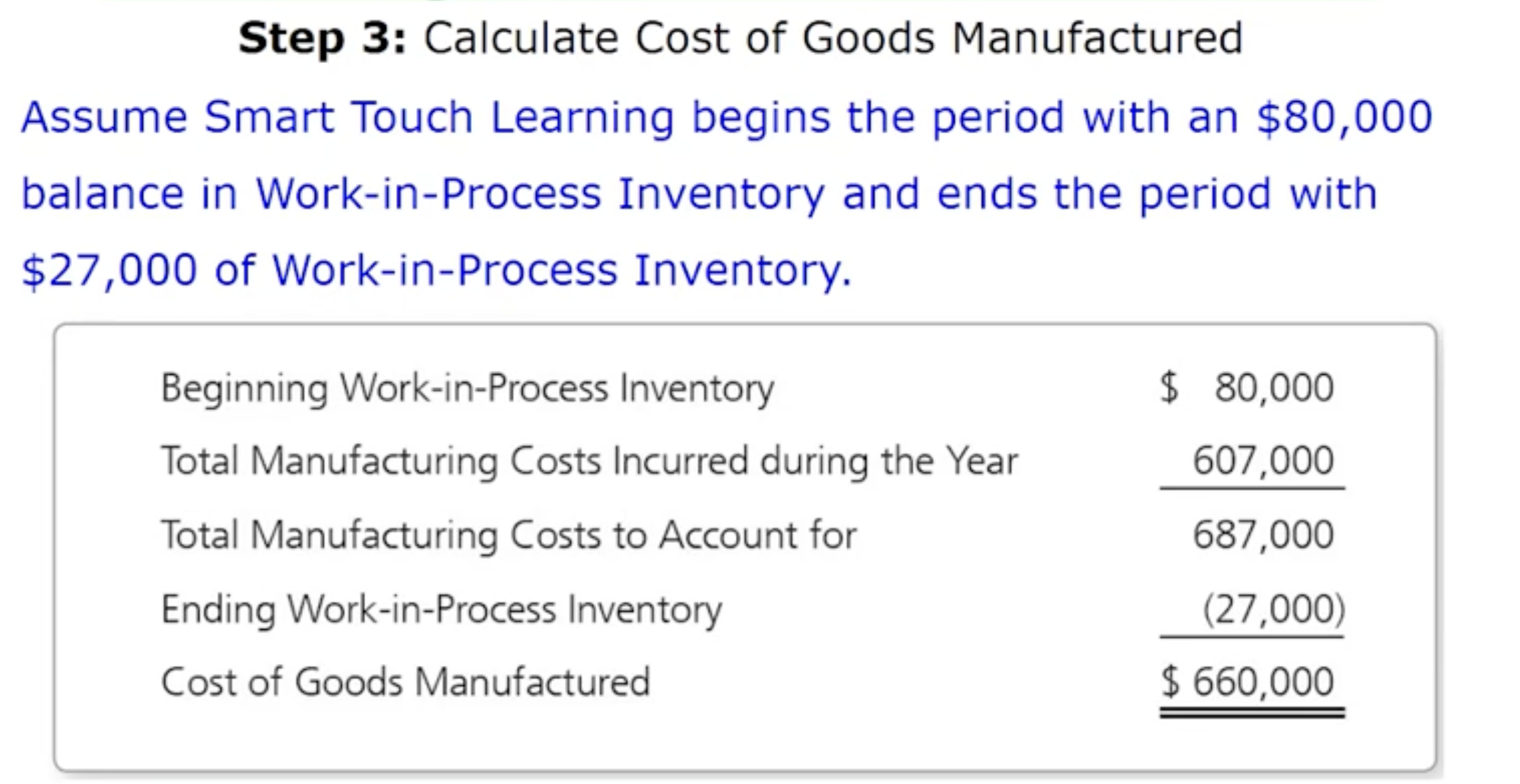
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Step 3. Breakdown of calculating cost of goods manufactured
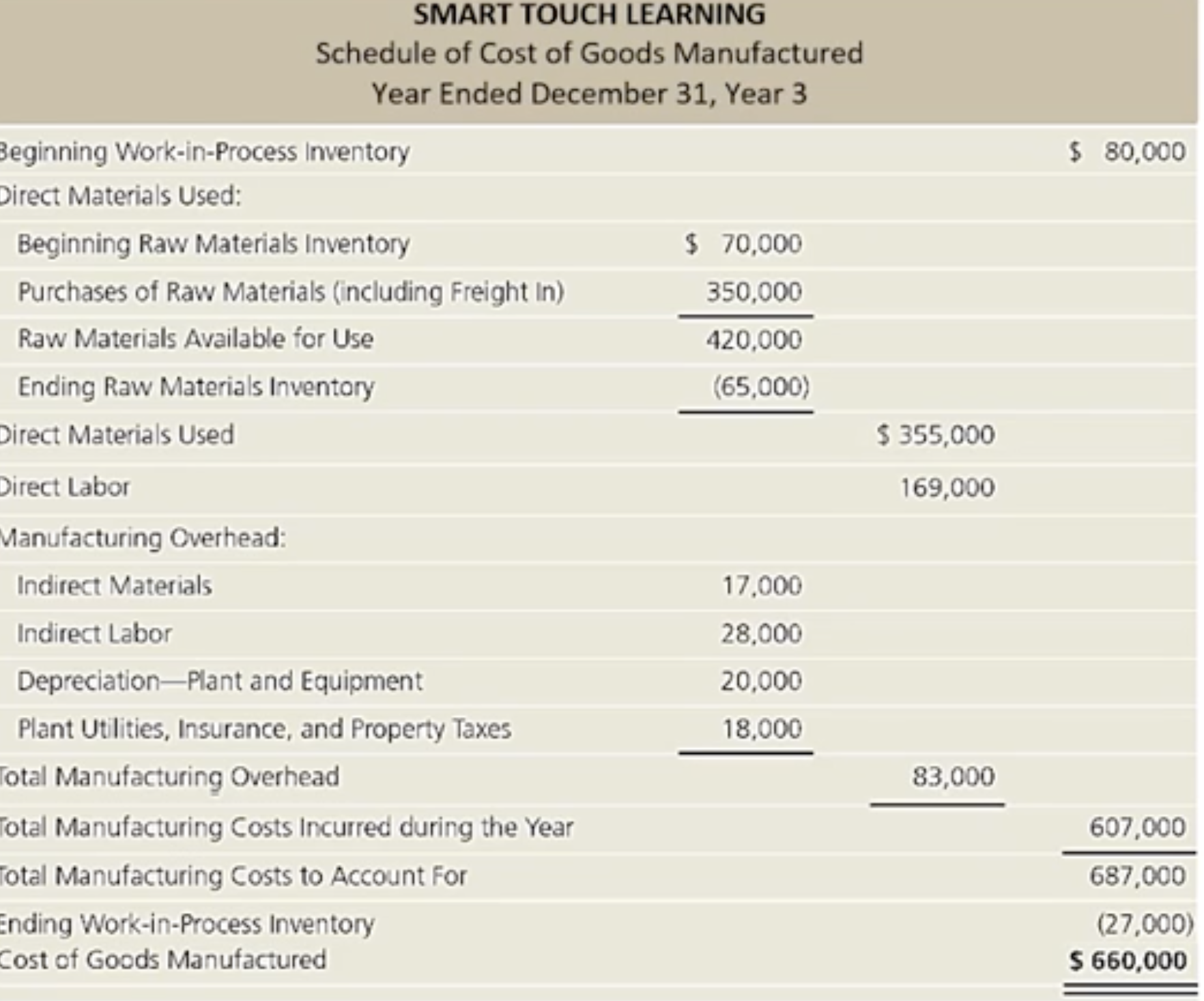
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Final summary of the 3 steps of costs of goods manufacturing
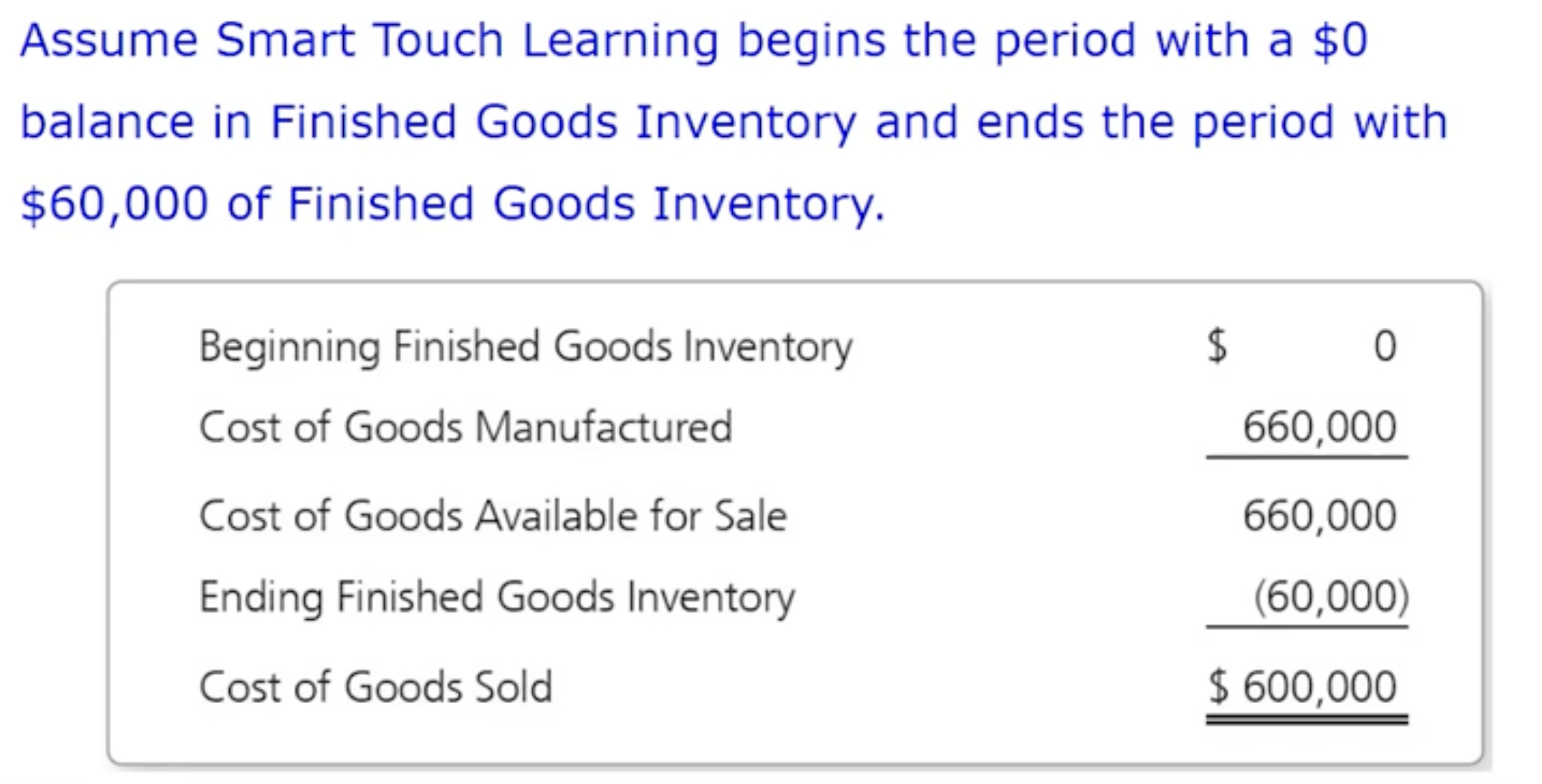
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Calculating cost of goods sold

How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Calculating cost of goods sold
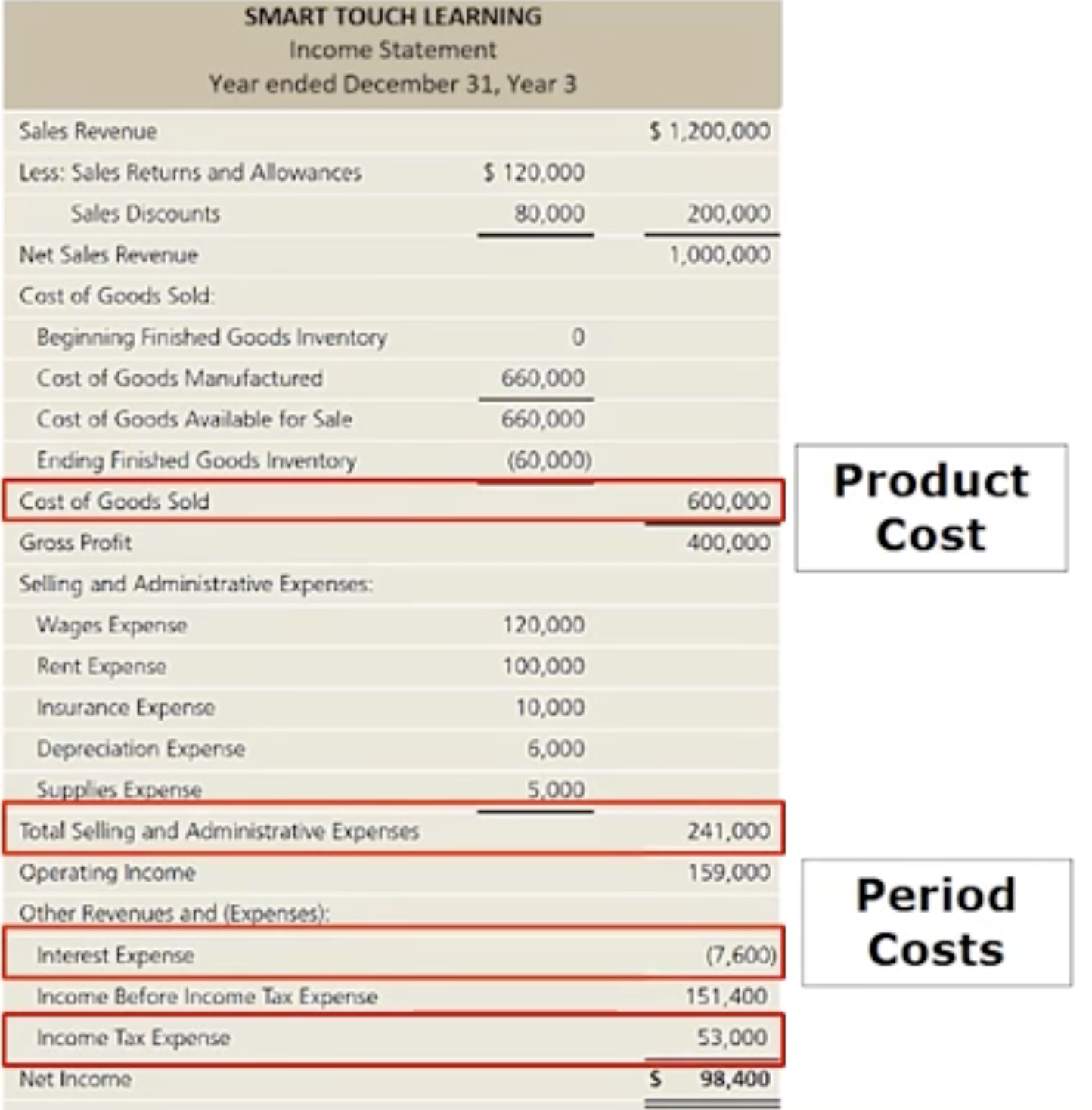
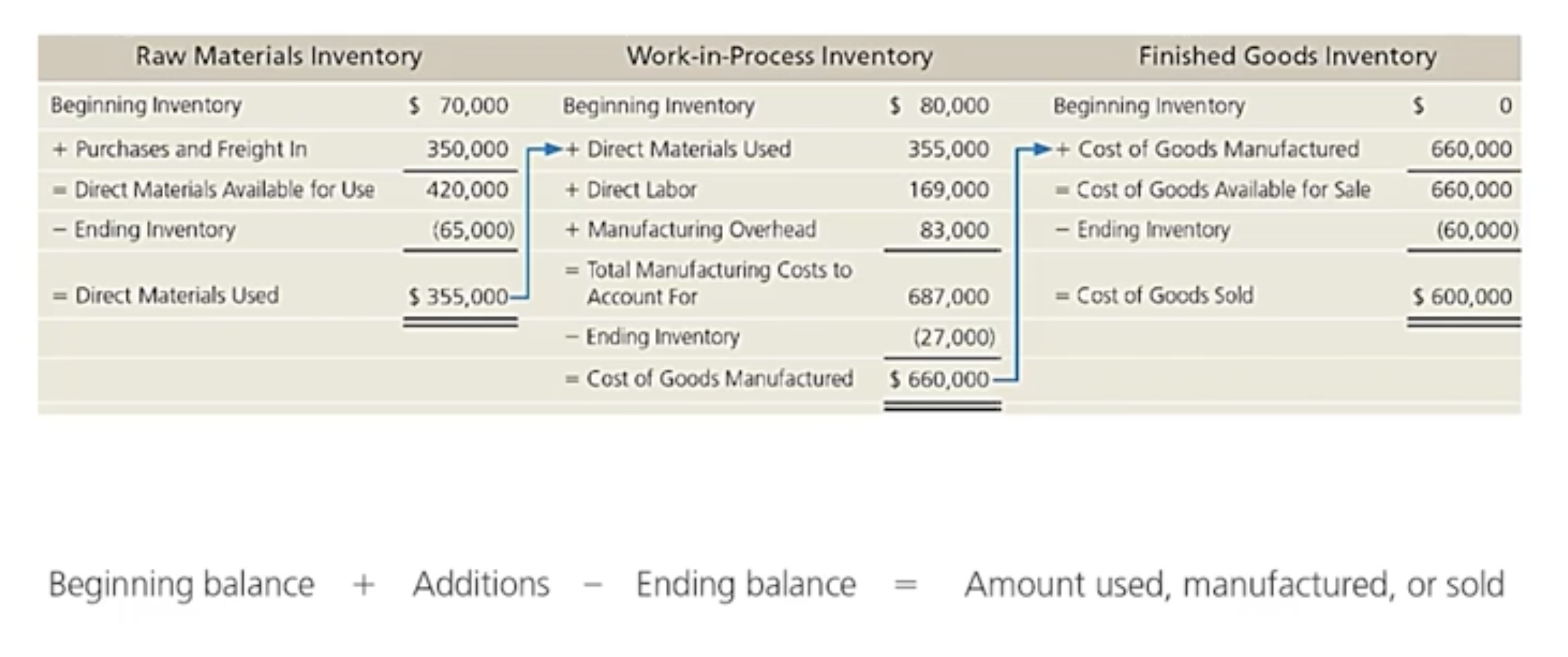
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Flow of costs through inventory accounts
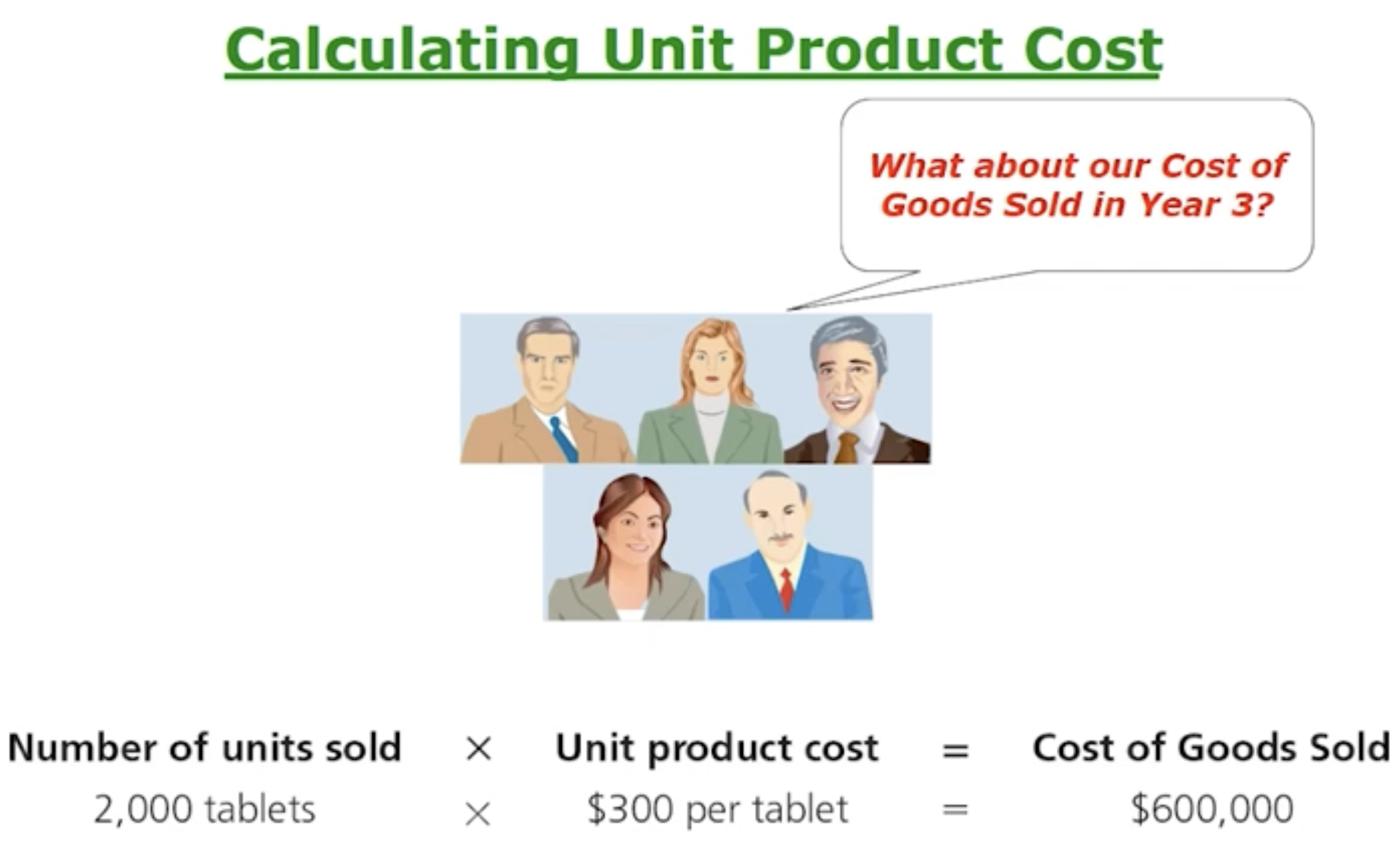
How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Calculating unit product cost example Part 1

How do manufacturing companies prepare financial statements: Calculating unit product cost example part 2
What business trend are affecting managerial accounting: Enterprise resource planning
A software system that can integrate all of a company’s functions, departments, and data into a single system
E- commerce
What business trend are affecting managerial accounting: Just in time management
Producing products just in time to satisfy needs (limit inventory)
What business trend are affecting managerial accounting: Emerging technologies
Recent advances in technology can equal competitive advantage

What business trend are affecting managerial accounting: Cloud-based services

What business trend are affecting managerial accounting: Total quality management

What business trend are affecting managerial accounting: The triple bottom line

How is managerial accounting used in service and merchandising companies: Calculating cost per service

How is managerial accounting used in service and merchandising companies: Calculating cost per item
