SDL 6: hereditary spherocytosis and sickle cell disease
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
anemia when hematopoiesis cannot match pace of RBC destruction, jaundice, cholelithiasis, reticulocytosis
manifestations of hemolysis
-first converted to unconjugated bilirubin within macrophages in the reticuloendothelial system
-then taken up by hepaatocytes and conjugated
what happenns to the heme of lysed cells?
reticuloendothelial system
system composed of tissue macrophages in the spleen, liver, bone marrow and lymph nodes, and their blood- borne counterparts, monocytes
-aka the mononuclear phagocyte system
extravascular hemolysis
Destruction of red blood cells outside of a blood vessel like the spleen, and sometimes the liver
cells of reticuloendotheliail system
-similar to physiologic removal of senescent RBCs
in extravascular hemolysis, RBCs are cleared from circulation by
splenomegaly
main consequence of chronic extravascular hemolysis
intravascular hemolysis
hemolysis associated with cell membrane damage by autoantibodies, microorganisms, direct trauma, shear stress, or toxins
hemoglobinemia, decreased plasma haptoglobin, hemoglobinuria, and hemosiderinuria.
the principle features of intravascular hemolysiis
Fenton reaction
reaction of free hemoglobin promoting formation of hydroxyl radicals---> oxidative tissue damage
spleen and liver macrophages
haptoglobin hemoglobin complex is removed by
Hemosiderin
an iron-storage protein primarily made in times of iron overload secondary to intravascularr hemolysis
no
is splenomegaly associated with intravascular hemolysis?
severe
extramedullary hematopoiesis is a sign of ______ annemia
iron containing pigment hemosiderin, particularly in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow
phagocytosis of red cells leadsd to the accumulation of
pigment gallstones
gallstone type associated with chronic hemolysis
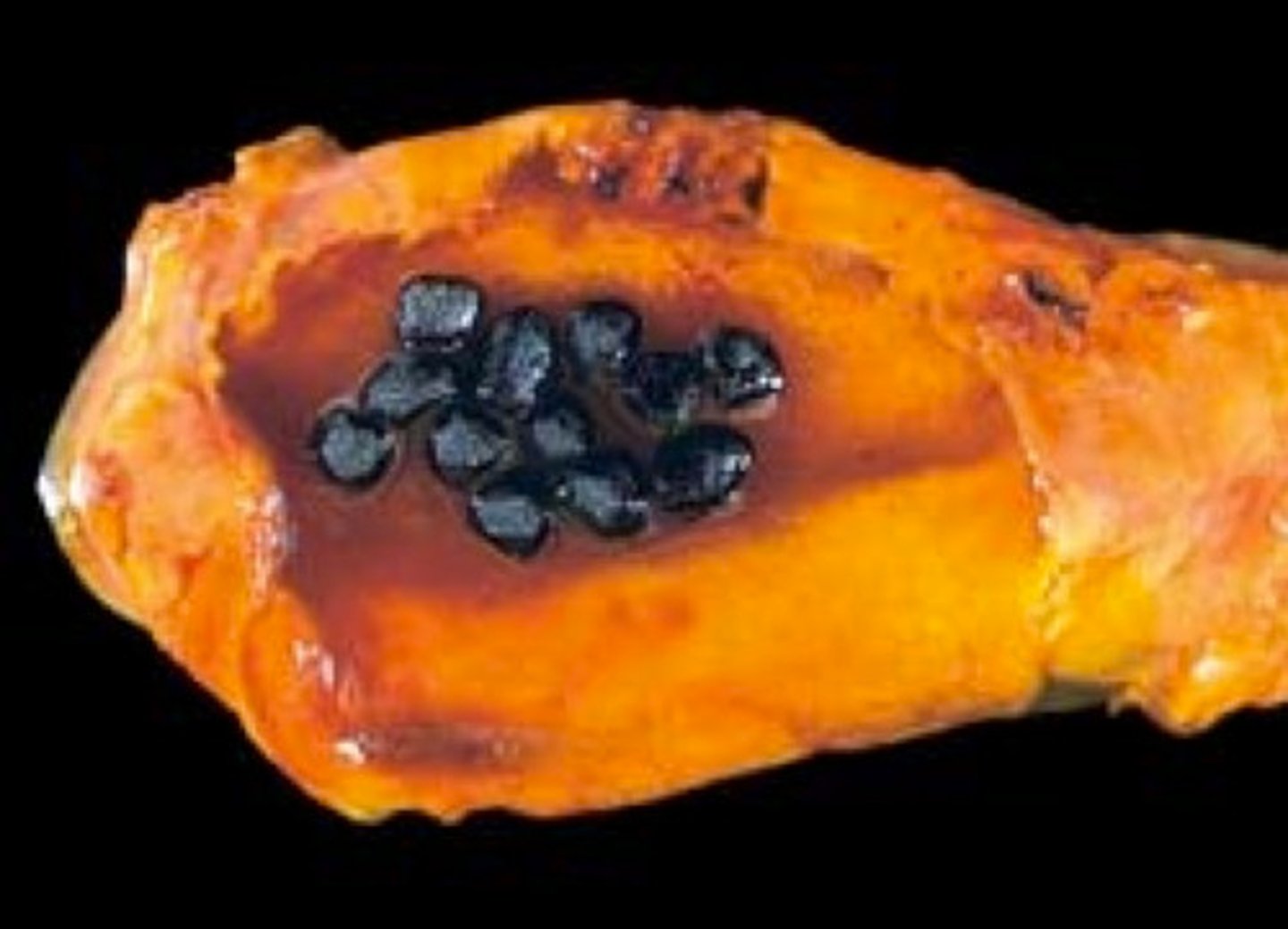

Hereditary spherocytosis
an inherited disorder caused by mutations in the genes encoding erythrocyte membrane protein
hereditary spherocytosis
the most common hereditary hemolytic anemia in people of northern European descent
ANK1, encoding ankyrin
most common gene mutation of hereditary spherocytosis
autosomal dominant
inheritance of hereditary spherocytosis
microvesicles
-splenic sequestration also promotes the spheres
young spherocytosis cell's destabilized lipid bilayer sheds membrane fragments which form ______ which reduces RBC surface area, making spheroid
splenectomy
procedure that removes the primary 'graveyard' for spherocytes and, thus, eliminates anemia and hyperbilirubinemia.
seen in other disorders associated with membrane loss, such as in autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
besides HS, what other anemias are associated with spherocytes?
reticulocytosis, marrow erythhroid hyperplasia, hemosiderosis, mild jaundice, sometimes cholelithiasis and moderate splenomegaly
-large range of clinical presentatoni
features common to hereditary spherocytosis
-normal or slightly low
must take into account the combined presence of spherocytes (with a low MCV) and reticulocytes (with an increased MCV)
MCV associated with hereditary spherocytosis
increased MCHC
most helpful red cell index in diagnosis hereditary spherocytosis
elevated LDH, unconjugated bilirubiin, and decreased haptoglobin
main three tests for hemolysis
Eosin-5-maleimide binding test
flow cytometric test based on interaction between fluorescent dye EMA and band 3 protein; great test for HS
-lower in HS
osmotic fragility test
if Eosin-5-maleimide binding test results are equivocal, whaat test is done for herediatry spherocytosis diagnosis?
determined by measuring the degree of hemolysis in hypotonic saline solution
how to perform an osmotic fragility test
Fresh normal red cells start to hemolyze at 0.5% NaCl and hemolysis is complete at 0.3% NaCl.
at what tonicity do normal red cells hemolyze?
0.5%
red cell osmotic fragiliity is considered to be increased if hemolysis occurs at NaCl concentration higher than
good
-no specific treatment, treat complications of gallstones
-may rerquire blood traansfusion, EPO, and splenectomy in severe cases
prognosis of hereditary spherocytosis
sickle cell disease
common hereditary hemoglobinopathy caused by a point mutation in β-globin that promotes the polymerization of deoxygenated hemoglobin, leading to red cell distortion, hemolytic anemia, microvascular obstruction, and ischemic tissue damage.
the second half of the first year of life, when fetal Hb falls
at what at is SCD clinically apparent?
point mutation in the sixth codon of β- globin that leads to the replacement of a glutamate residue with a valine residue
mutation associated with SCD
autosomal recessive
-heterozygosity---> asymptomatic sickle cell trait
inheritance of HbS
Sickle cell trait
-polymerization contributes to sickling
40% of the hemoglobin is HbS and the rest is HbA, which interferes with HbS polymerization
HbF>HbA
Hemoglobin types that interfere with polymerization of HbS
Hemoglobin C
hemoglobin of Lysine is substituted for Glutamic Acid at the 6th position on the Beta chain.
HbSC disease
heterozygous for HbbC and HbS---> symptomatic sickling disorder
end-stage, nondeformable, irreversibly sickled cells, which retain a sickle shape even when fully oxygenated.
the most severely damaged sickled cells are converted to
-chronic hemolytic anemia (mean lifespan 20 days)
-widespread microvascular obstrructiton---> ischemic tissue crisis
what are the two major consequences that arise from sickling of red cells
free radicas and oxidative damage
reperfusion of ischemic tissue due to SCA generates
damaged erythrocytes release free hemoglobin into the plasma, which strongly bind to nitric oxide, causing functional nitric oxide deficiency and contributing to the development of vasculopathy.
how is SCA associated with functional nitric oxide deficiency?
irreversibly sickled cells, reticulocytosis, and target cells
-howell jolly bodies
findings of peripheral blood smear of SCA pt
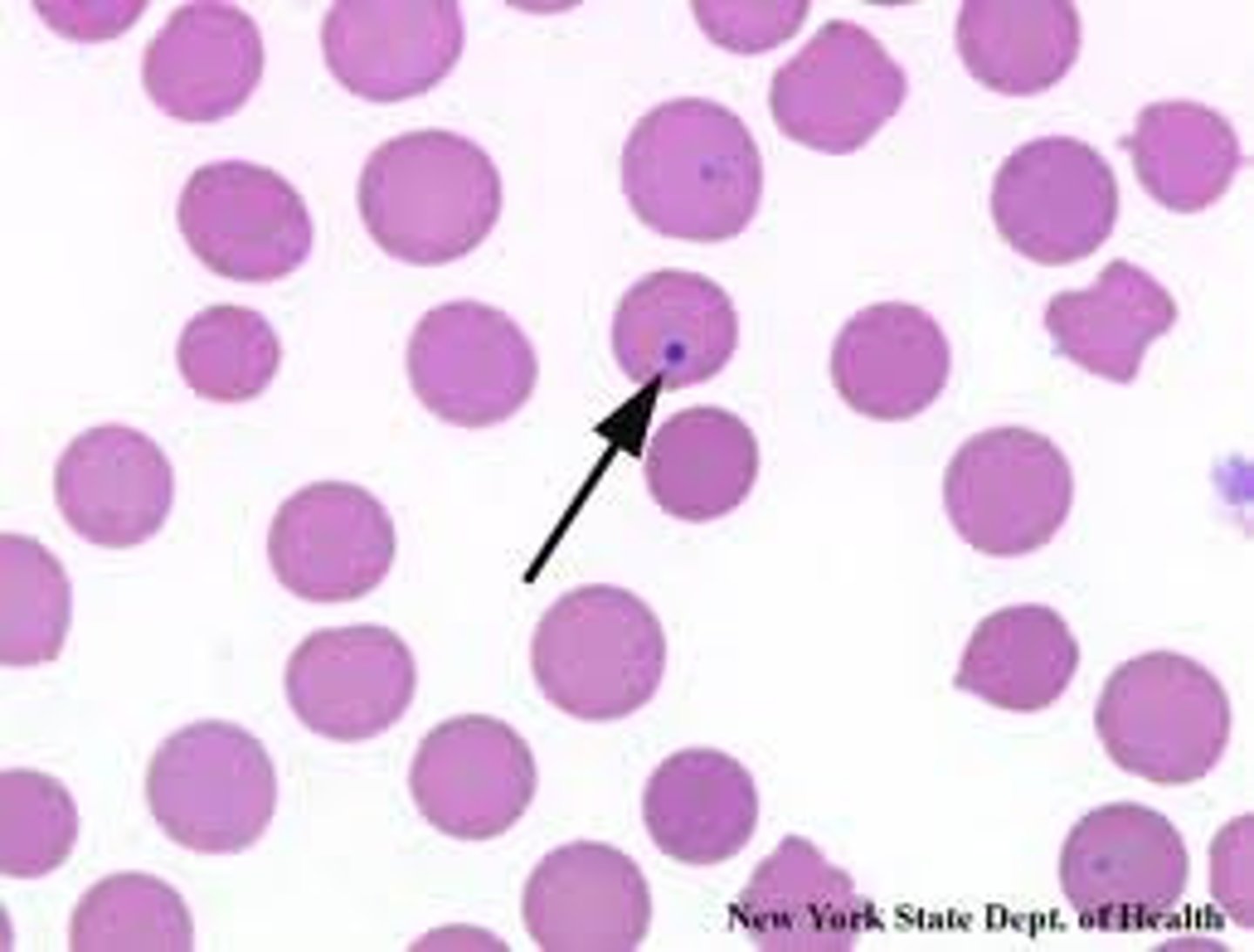
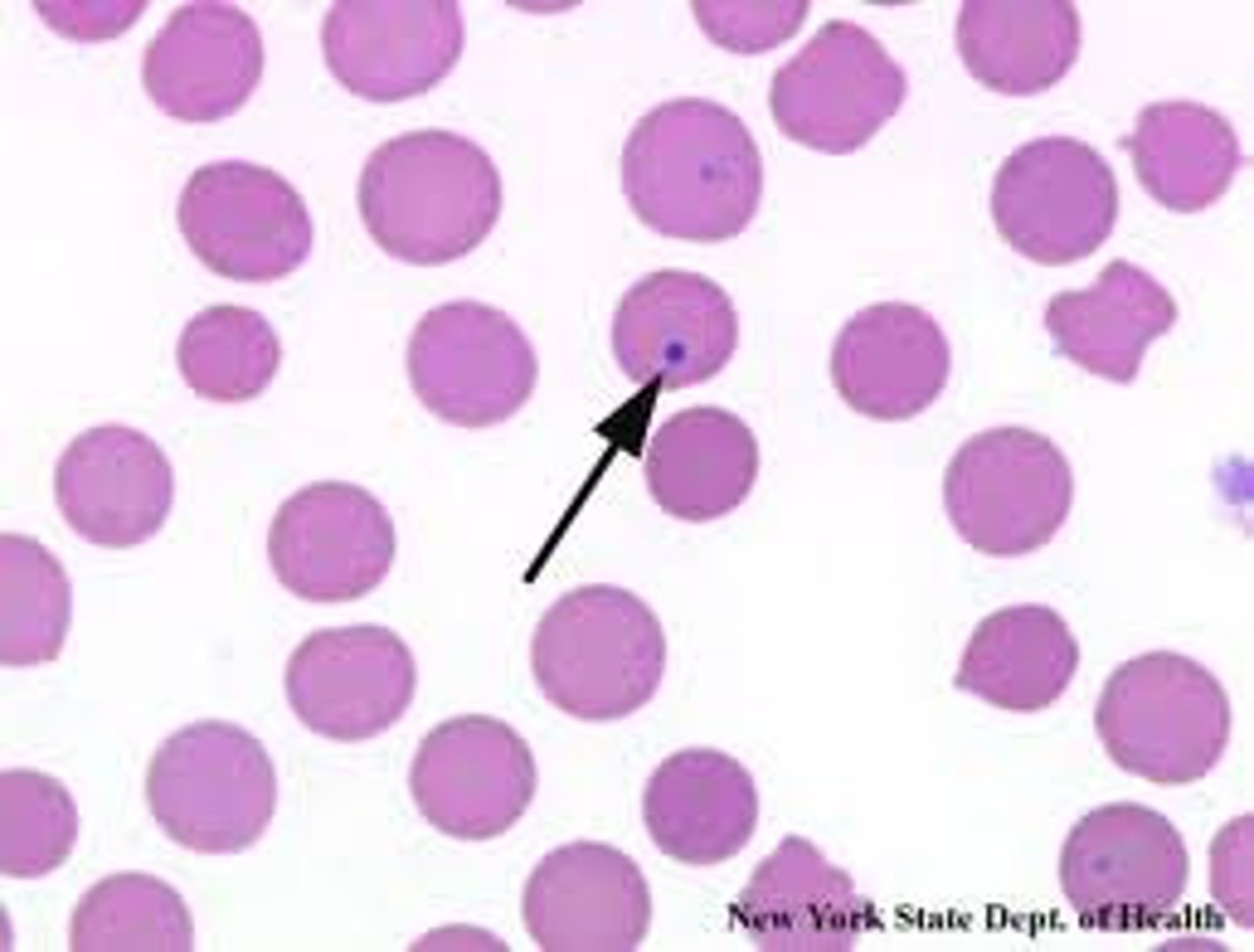
howell-jolly bodies
small nuclear remnant RBCs due to asplenia
-associated with SCA
Autosplenectomy
the gradual fibrosis and dysfunction of the spleen secondary to SCA
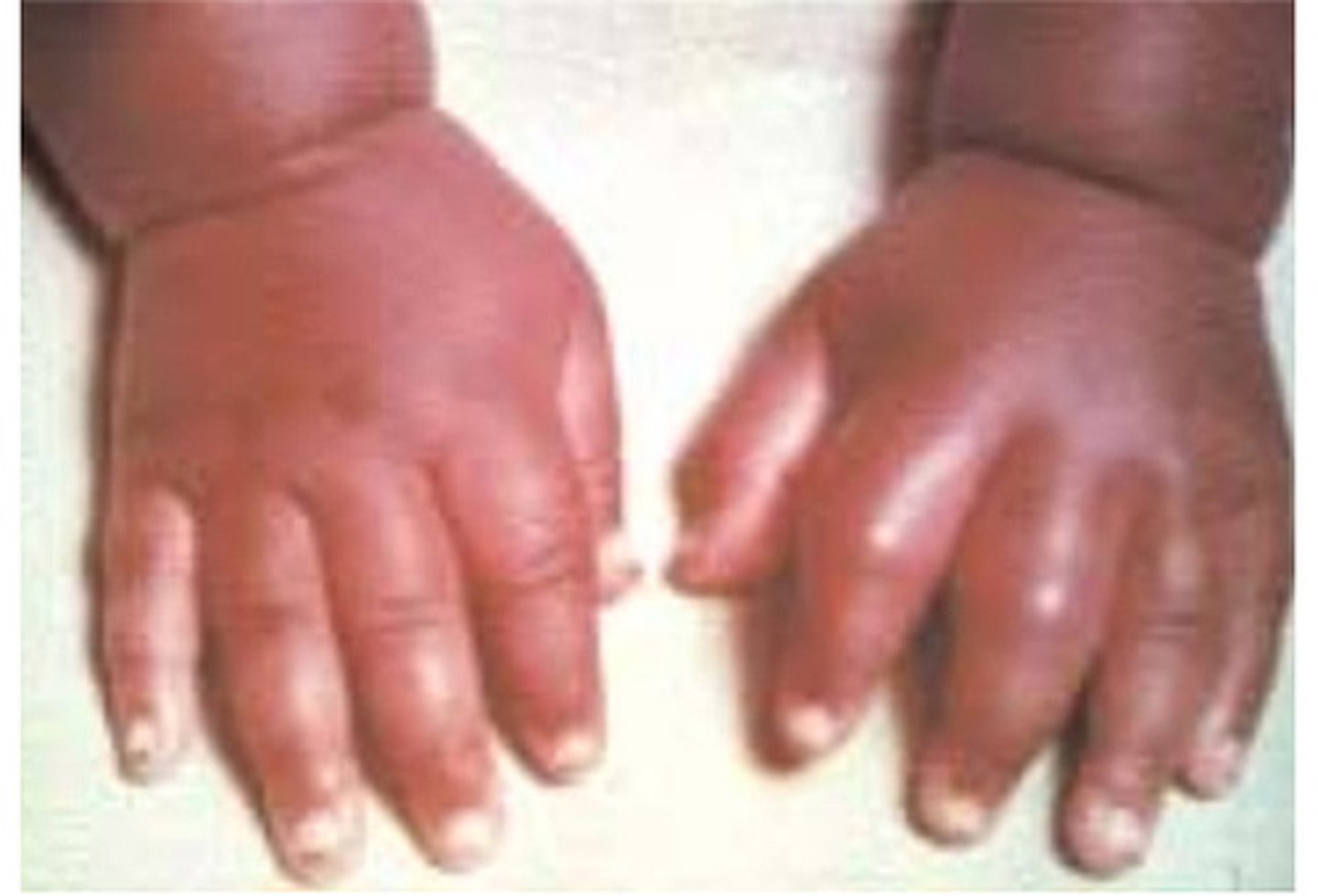
dactylitis
a special manifestation of an acute pain crisis in young children in which the hands or feet are swollen, tender, and erythematous.
encapsulated organisms
children with SCD are at an increased risk of infection from _______ organisms due to functional asplenia
salmonella
children with SCD are at an increased risk of osteomyelitis by what causitive organism?
aplastic crisis
complication of children with SCD who get parvovirus B19
sudden onset of acute anemia (pallor), and splenomegaly and may present as sudden circulatory collapse due to the rapid sequestration of circulating red cells in the spleen.
signs of acute splenic sequestration crisis
acute chest syndrome
acute pulmonary process that occurs exclusively in pts with SCD
-presence of new pulmonary infiltrate that involves at least one complete lung segment
leukocyte count is elevated with predominance of nneutrophils
-platelets increased
WBC of pt with SCD
low
ESR associated with SCD
Howell-Jolly bodies
this finding indicates the pt is asplenic
gel electrophoresis process
diagnosis of SCD is confirmed by
sickle trait
heterozygous state with 35-45% of hemoglobin being HbS, 50-60% is HbA and <3.5% is HbA2 on electrophoresis
sickle cell disease
85-90% of hemoglobin being HbS, 2-15% HbF and <3.5% HbA2 on electroporesis
cardiac and infectious
primarry cause of death among pts with SCD
hydroxyurea (myelosuppressive agent)
-raises the level of HbF and generates NO
the only effective drug proven to reduce the frequency of painful episodes