Photosynthesis in BIOL 225: Chloroplast Structure, Light Reactions, and Calvin Cycle
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are the main energy and electron carrying molecules in photosynthesis?
ATP and NADPH
What is the overall chemical reaction for photosynthesis?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Where does photosynthesis occur in plant cells?
In chloroplasts
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
Light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle)
What is the function of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy
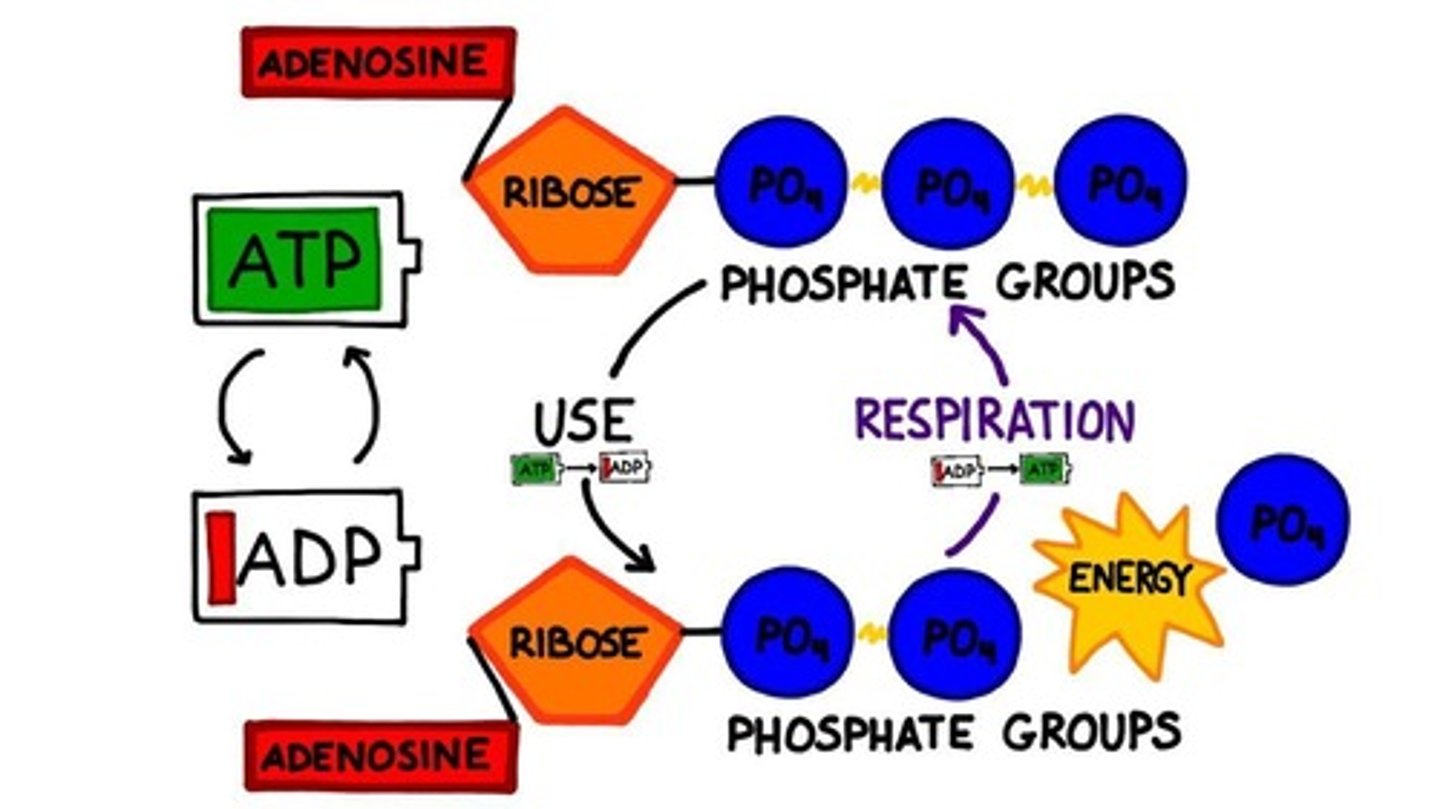
What is the role of ATP in photosynthesis?
ATP serves as the main energy currency molecule
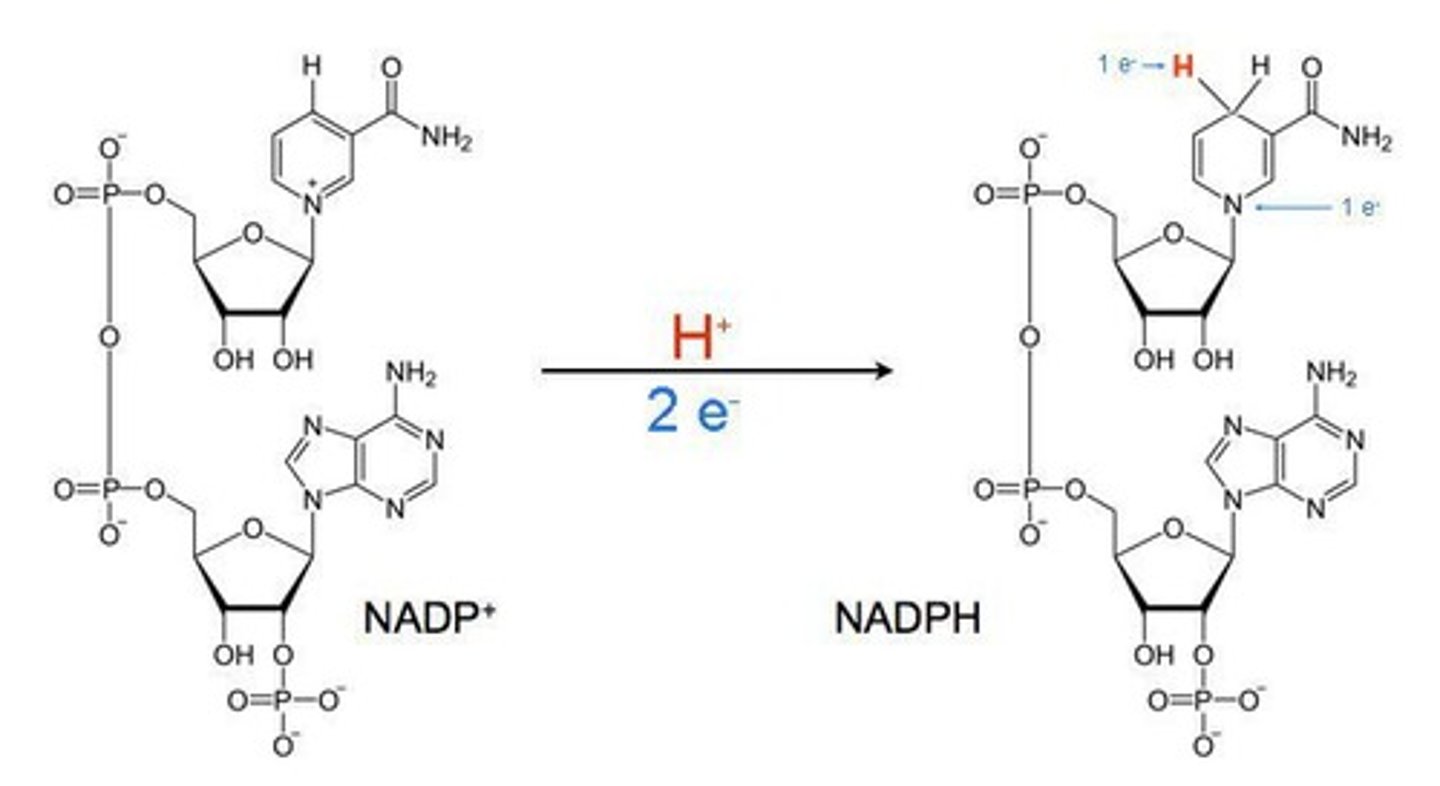
What is NADPH used for in photosynthesis?
NADPH is used to transfer electrons and provides reducing power
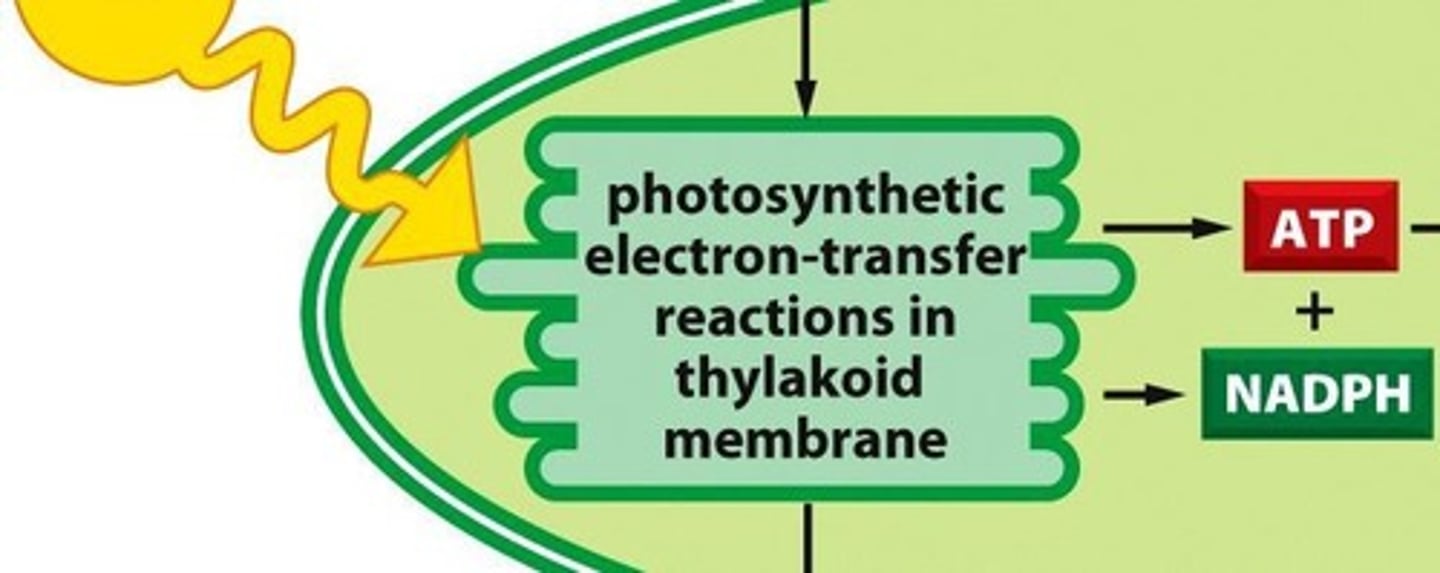
What happens during the light-dependent reactions?
Solar energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH
What is the Calvin Cycle?
The light-independent reactions that synthesize glucose from CO2 using ATP and NADPH
What are the three stages of the Calvin Cycle?
Carbon fixation, sugar formation, and regeneration of RuBP
What is the role of the enzyme Rubisco in photosynthesis?
Rubisco attaches CO2 to RuBP during carbon fixation
What is produced during the reduction phase of the Calvin Cycle?
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (PGAL), which can be used to form glucose
How are electrons replenished in chlorophyll during photosynthesis?
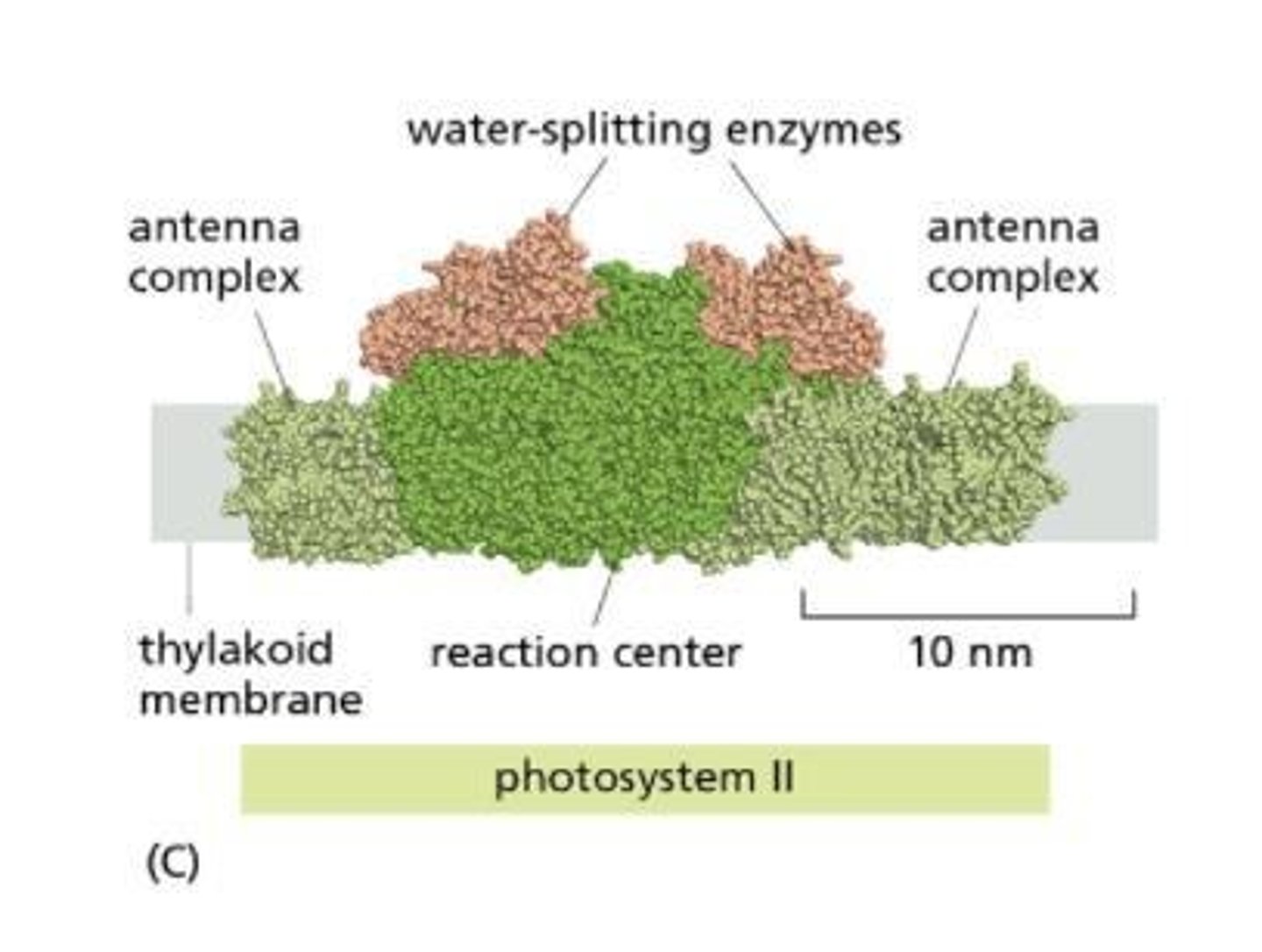
Electrons are replenished by splitting water molecules in Photosystem II
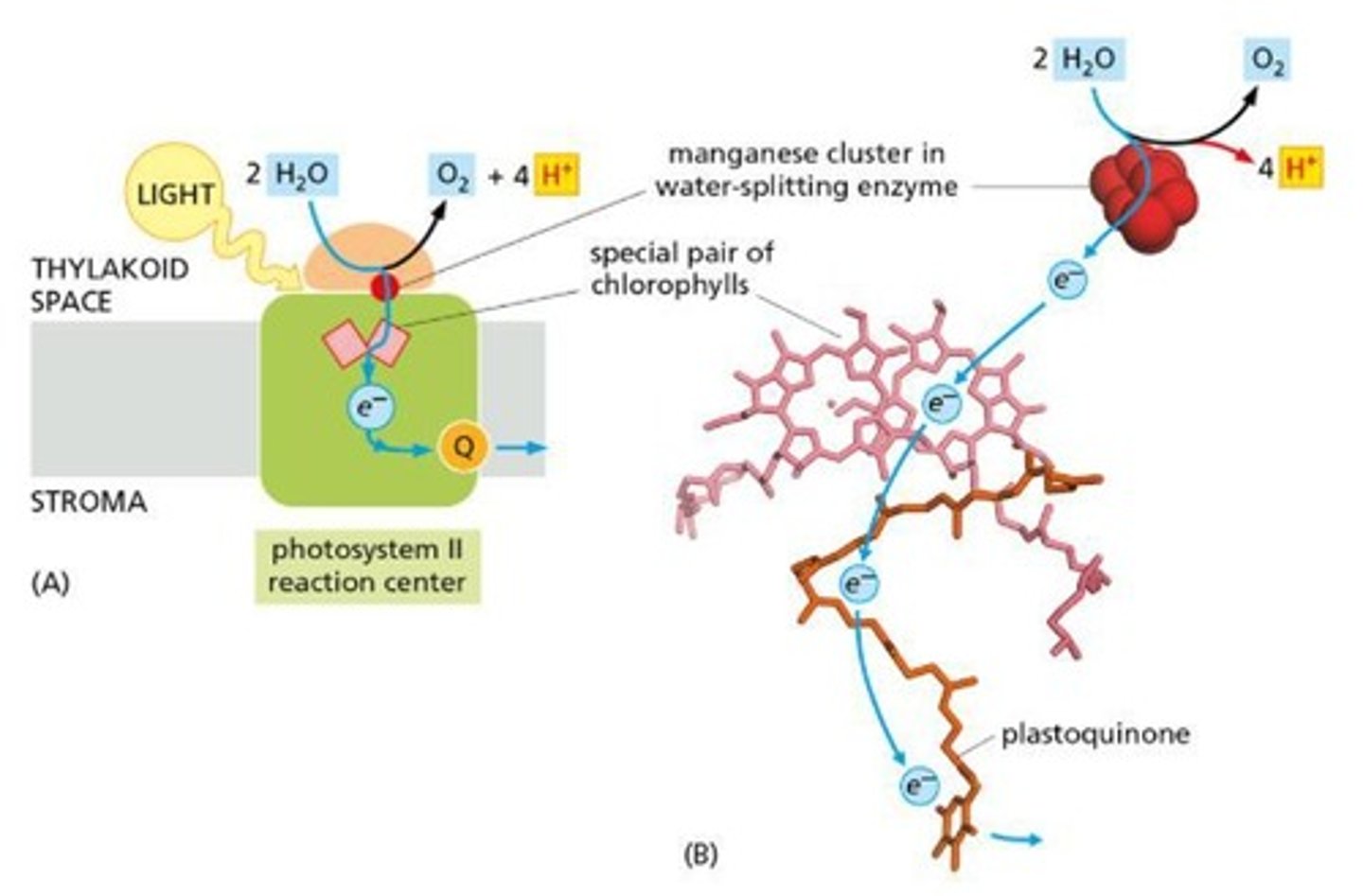
What are thylakoids?
Thylakoids are internal membrane structures in chloroplasts where light-dependent reactions occur
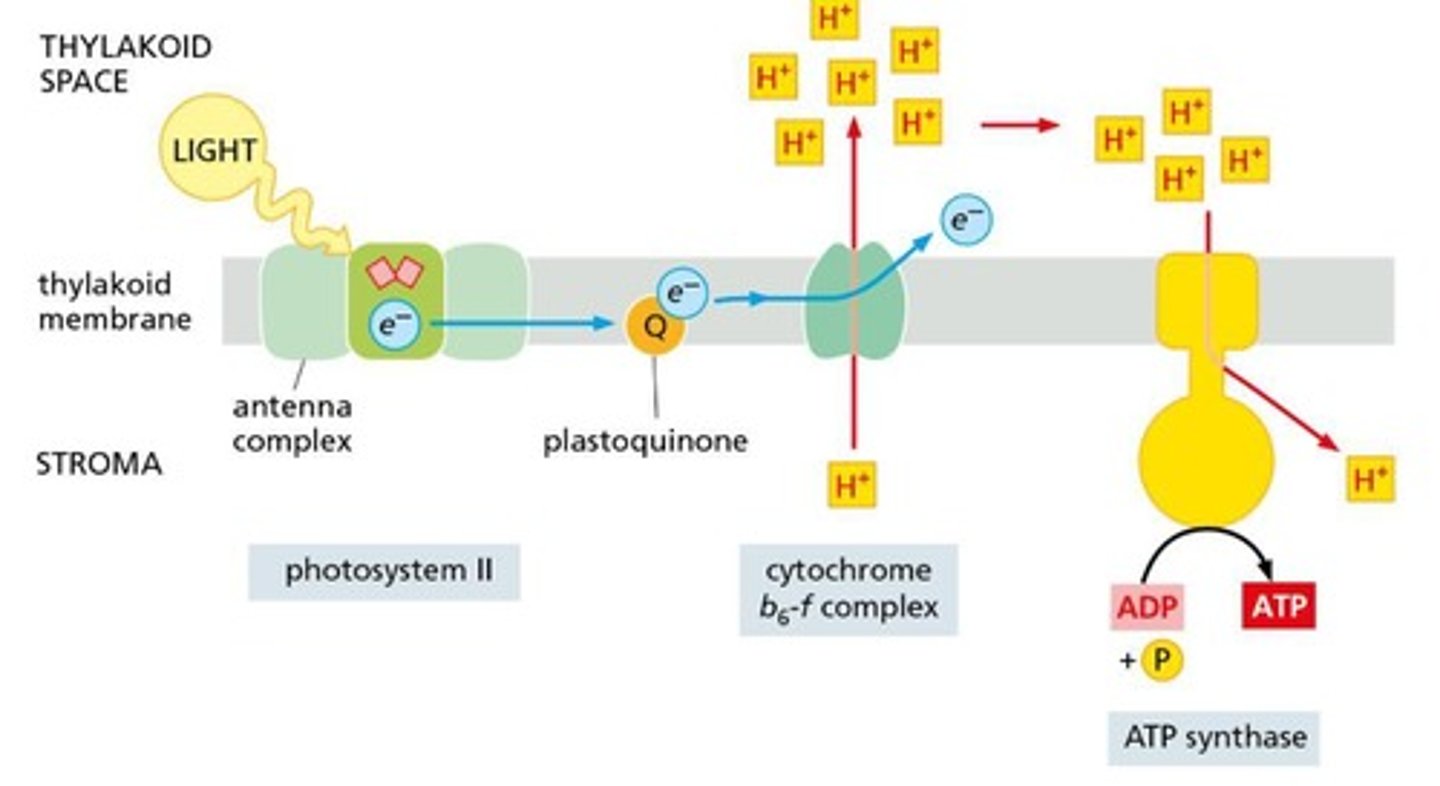
What is the significance of the antenna complex in photosynthesis?
The antenna complex contains chlorophyll molecules that capture light energy
What is the role of the electron transport chain (ETC) in photosynthesis?
The ETC transfers electrons and helps generate ATP and NADPH
What is the hydrophobic tail of chlorophyll responsible for?
It anchors chlorophyll molecules in the thylakoid membrane
What happens to the excess oxygen produced during photosynthesis?
Excess oxygen is released into the atmosphere
What is the primary purpose of the light-independent reactions?
To synthesize organic compounds (glucose) from inorganic CO2
What are the inputs and outputs of the Calvin Cycle?
Inputs: CO2, NADPH, ATP; Outputs: NADP+, ADP, Glucose
What is the function of ATP synthase in photosynthesis?
ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate during the light reactions
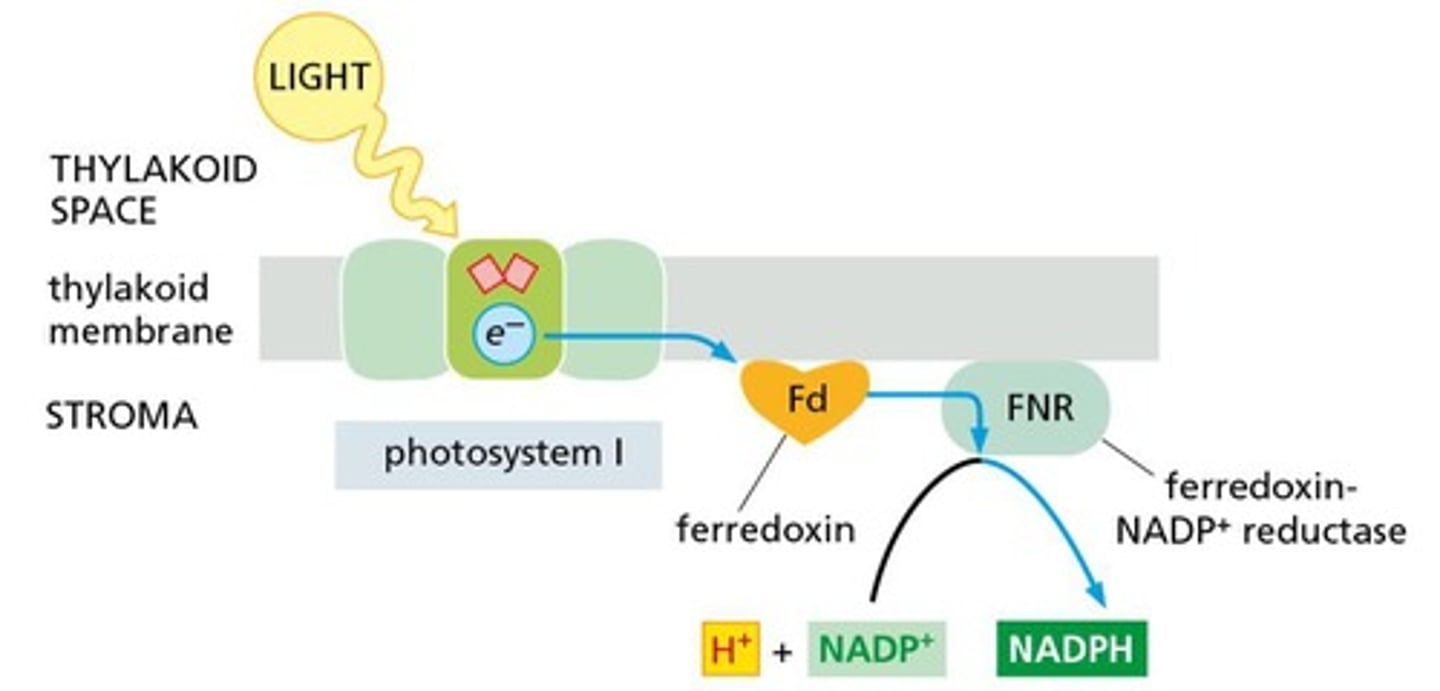
What is the role of ferredoxin in the light reactions?
Ferredoxin transfers electrons to NADP+ to form NADPH
How do plants utilize kinetic energy from sunlight?
Plants use it to combine CO2 and H2O to form glucose