Genetics Unit Test Part 1
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Grade 11u genetics review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
The haploid chromosome number in humans
23
The term phenotype may be defined as
An observable expression of the genotype
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, including all its genes.
Phenotype
The physical traits or characteristics of an organism resulting from its genotype and environment.
A gene exists in two different forms (A and a), which type of gamete can a homozygous recessive individual produce
a
The gene makeup of an organism for a particular trait is its:
genotype.
To determine if an organism with a dominant phenotype is heterozygous, the organism is mated to a:
homozygous recessive for the trait.
During meiosis, genetic variation in the gametes is achieved by
crossing over and random assortment.
If a human has two X chromosomes, it will normally produce:
Females
Colour-blindness is a sex-linked characteristic because the gene is:
carried on a sex chromosome
How many chromosomes does someone with Down Syndrome have
47
If a sperm cell contains 18 chromosomes, a muscle cell from the same organism will contain
18 pairs of chromosomes
If one pair of your 23 chromosomes does not separate during anaphase I of meiosis, it would result in the production of:
four cells with 22 chromosomes and two with 24 chromosomes
Sexual and asexual reproduction are alike in that:
They can both occur in multicellular organisms
in sexually reproducing species, the chromosome number remains stable over time because _____ and _____ always alternate
meiosis, fertilization
Humans possess:
22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes
What is the result when a diploid cell undergoes meiosis:
Four haploid cells
Synapsis occurs during:
prophase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and migrate towards opposite poles
Anaphase I
A tetrad is made up of:
four chromatids from two homologous chromosomes
The major contribution of sex evolution is:
a method to increase genetic variation
The law of independent assortment:
alleles for different traits separate randomly, leading to a 9:3:3:1 ratio. This happens only for genes on different chromosomes
Why is a test cross used:
To determine the genotype of an individual with an unknown phenotype
What is the probability that a male will inherit an X-linked recessive allele from his father:
0%
Karyotypes are useful for
Checking if the chromosome count and structure are normal and determining sex
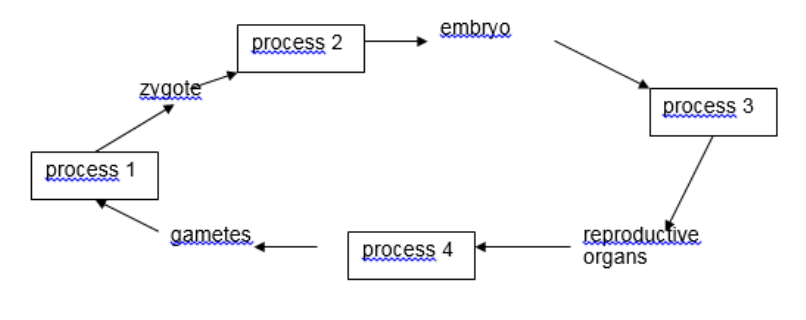
which process does meiosis division occur
process 4
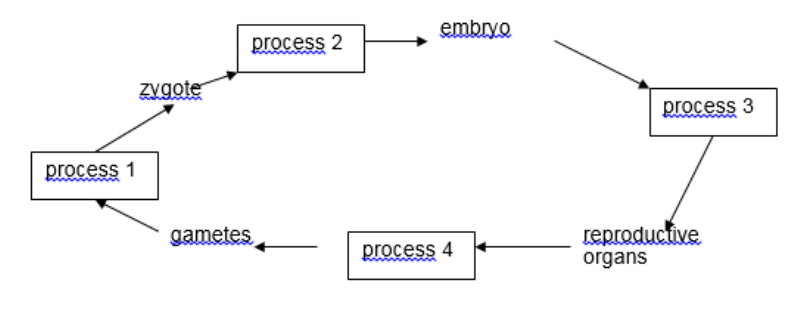
What process represents a return to a diploid chromosome number
process 1
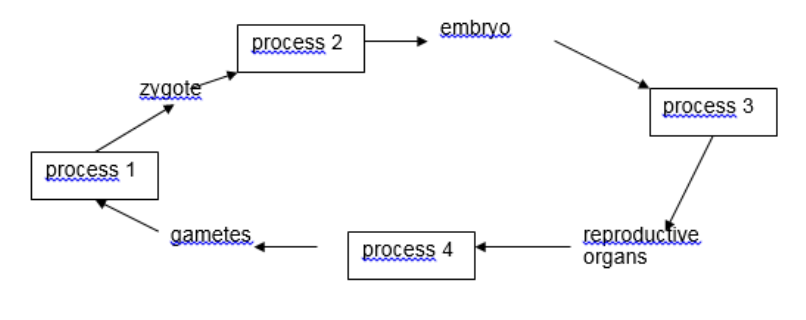
Which process represents mitosis
process 2 and 3
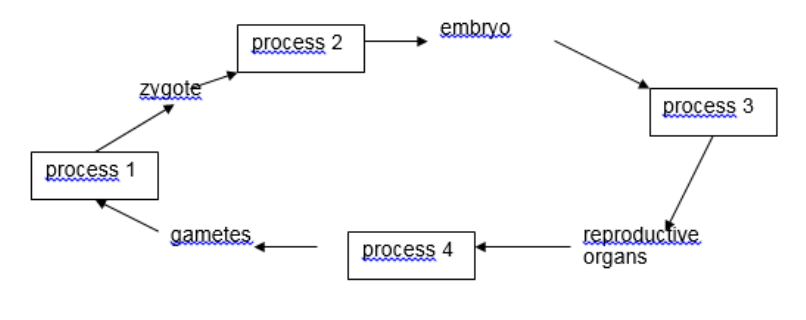
which cells are considered sex cells
gametes
mit or mei, daughter cells are genetically identical to each other andd parent cell
mitosis
mit or mei, results in two daughter cells
mitosis
cells are haploid
meiosis
mit or mei, introduces genetic variation into a species
meiosis
mit or mei, daughter cells are different from each other and parent cell
meiosis
mit or mei, cells are diploid
mitosis
mit or mei, results in four cells
meiosis
mit or mei, involves two divisions
meiosis