BE 354 Chapter 5 Tissues
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
four primary types of tissue
epithelial tissue function
protection, secretion, absorption, excretion
epithelial tissue location
cover body surface, cover and line internal organs, compose gland
epithelial tissue characteristics:
lack blood vessels, cells readily divide, cells tightly packed
connective tissue function
bind, support, protect, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells
connective tissue location
widely distributed throughout the body
connective tissue characteristics
mostly have good blood supply, cells are far apart than epithelial cells, with extracellular matrix in between
muscle tissue function
movement
muscle tissue location
attached to bones, in the walls of hollow internal organs, heart
muscle tissue characteristics
able to contract in response to specific stimuli
nervous tissue function
conduct impulses for coordination, regulation, integration, and sensory reception
nervous tissue location
brain, spinal cord, nerves
nervous tissue characteristics
cells communicate with each other and other body parts
epithelial tissue
general characteristics: covers organs and body surface/lines cavities and hollow organs, have a free surface on one side and are anchored to a basement membrane on other, cells are tightly packed and contain little intercellular material, usually lack blood vessels, cells readily divide
stratified
two layers of cells
simple
one layer of cells
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
shape of cells
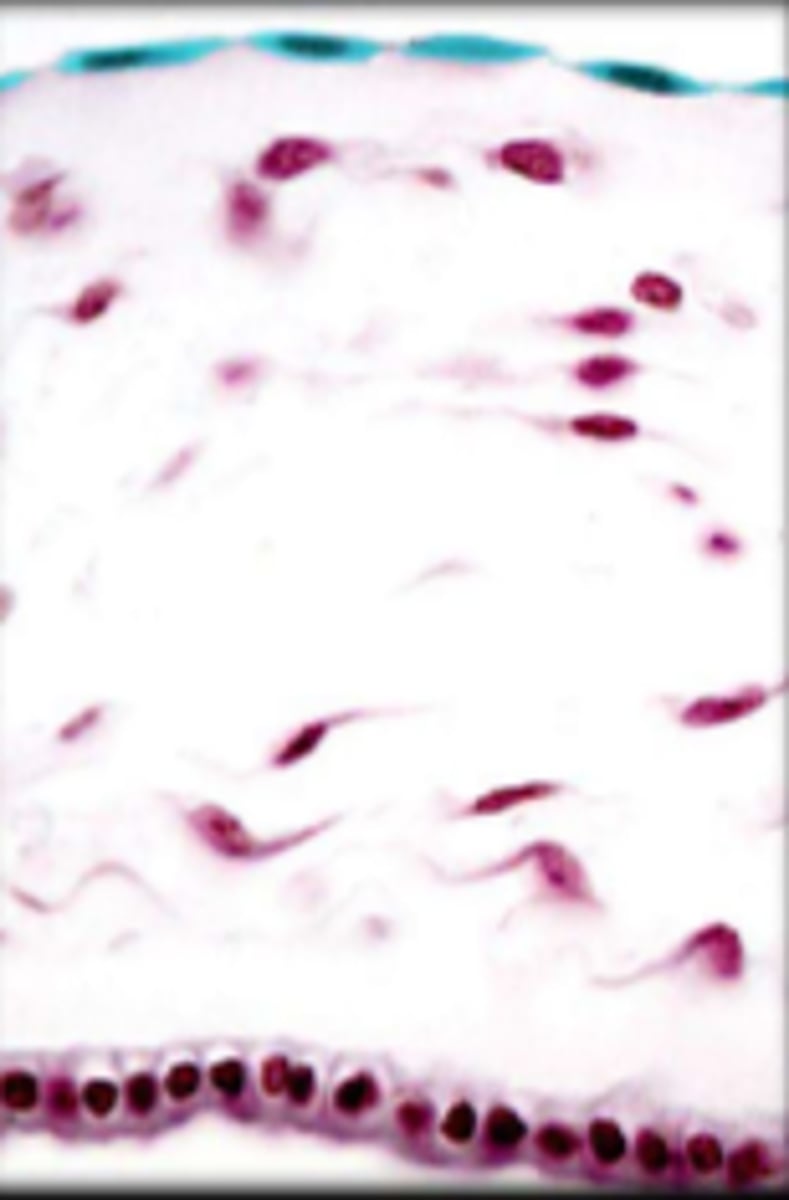
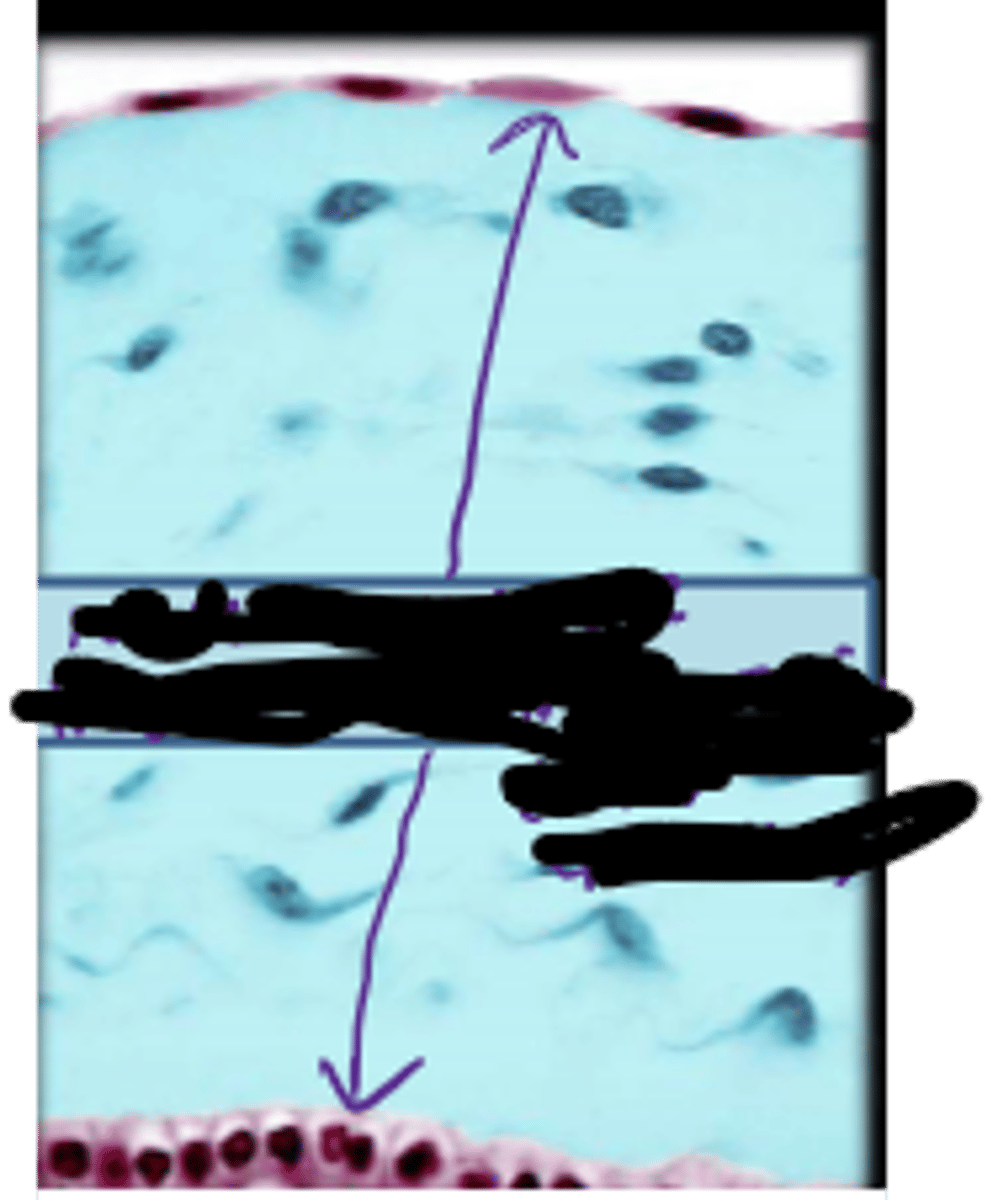
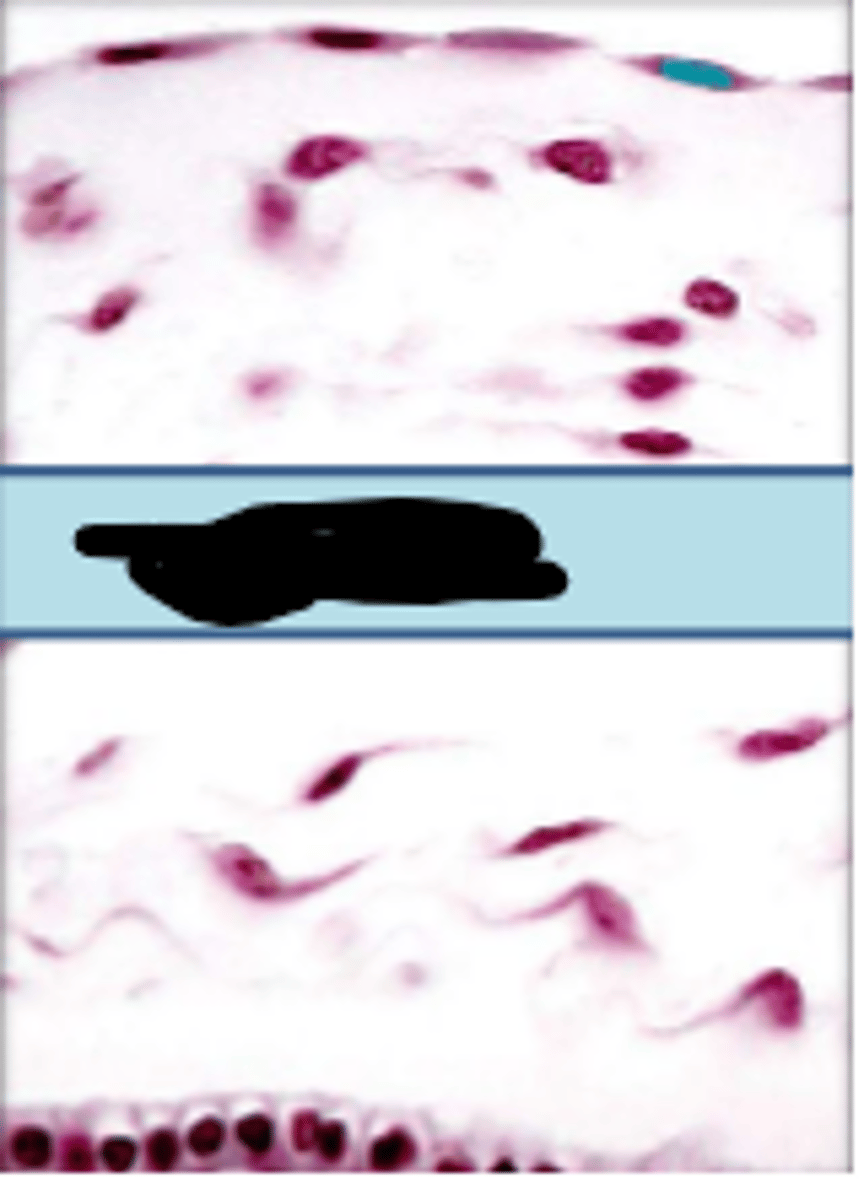
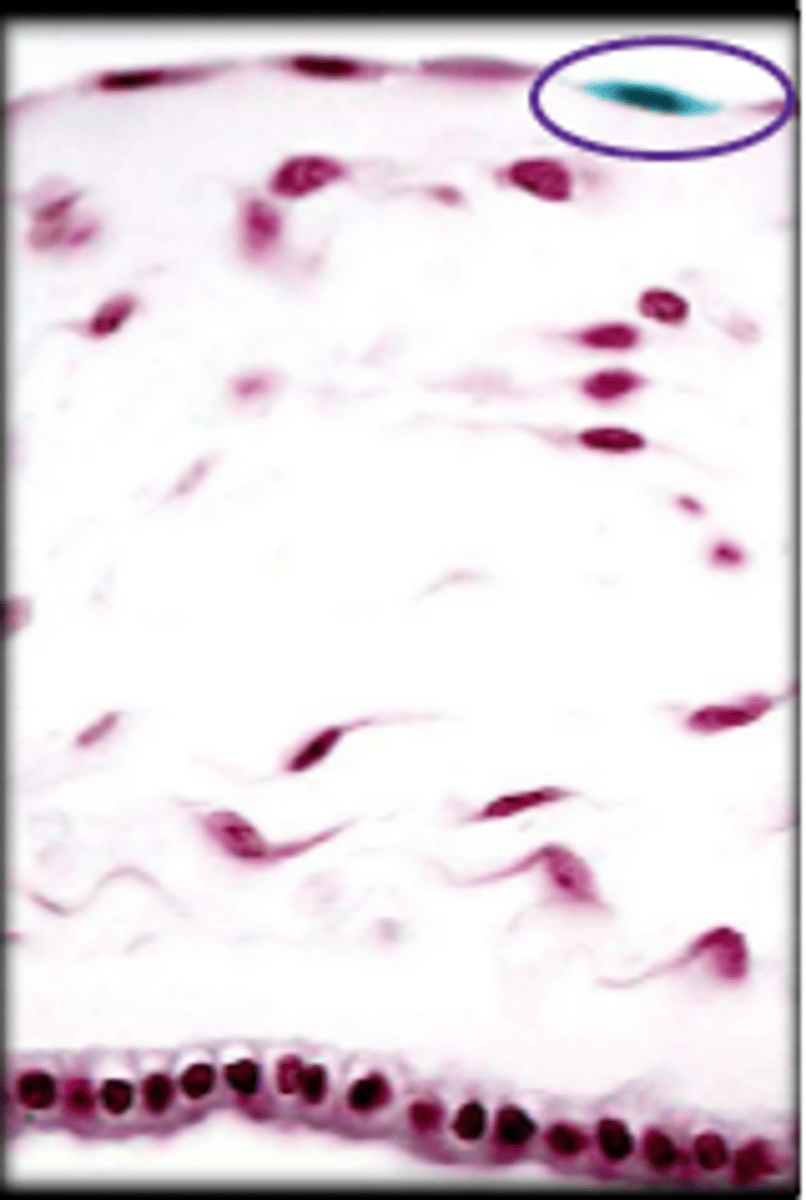
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of thin and flattened cells, substances pass easily through, lines air sacs, lines blood vessels, lines lymphatic vessels
simple squamous epithelium
loose connective tissue (lamina propia)
nucleus
simple squamous epithelia cell
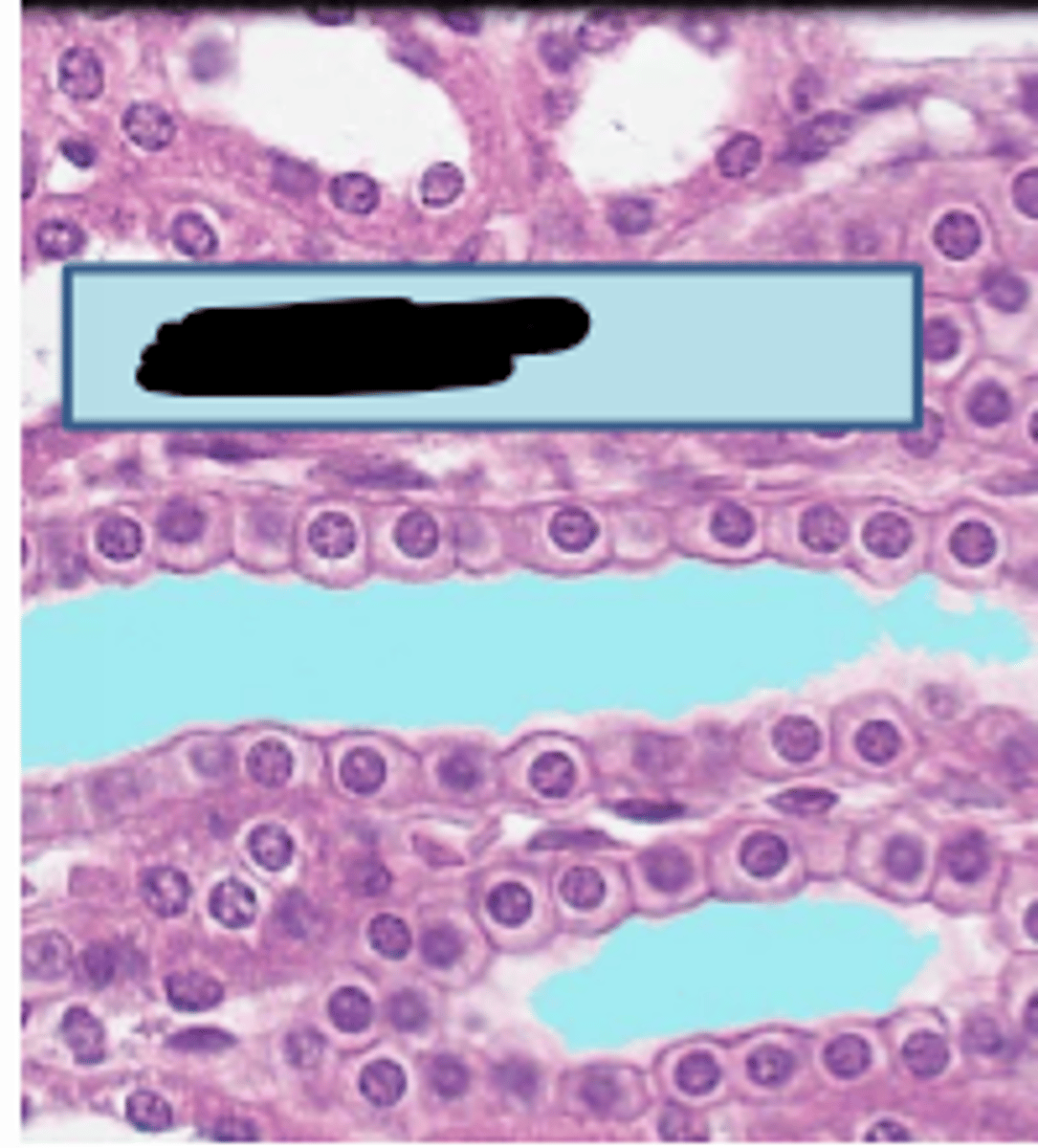
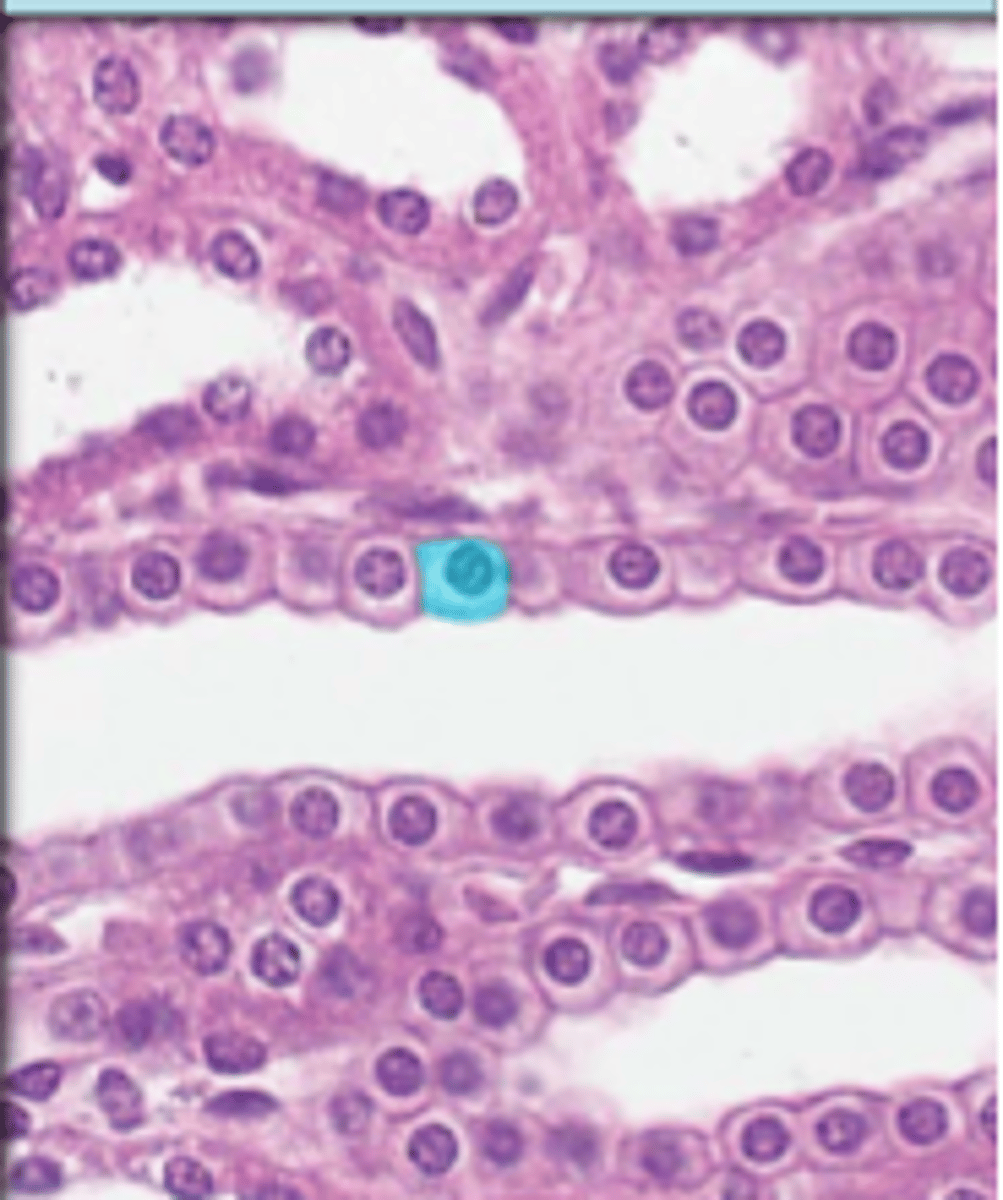
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube-shaped cells with centrally located nuclei, functions in secretion and absorption, lines kidney tubules, covers ovaries, lines ducts of some glands
simple cuboidal epithelium
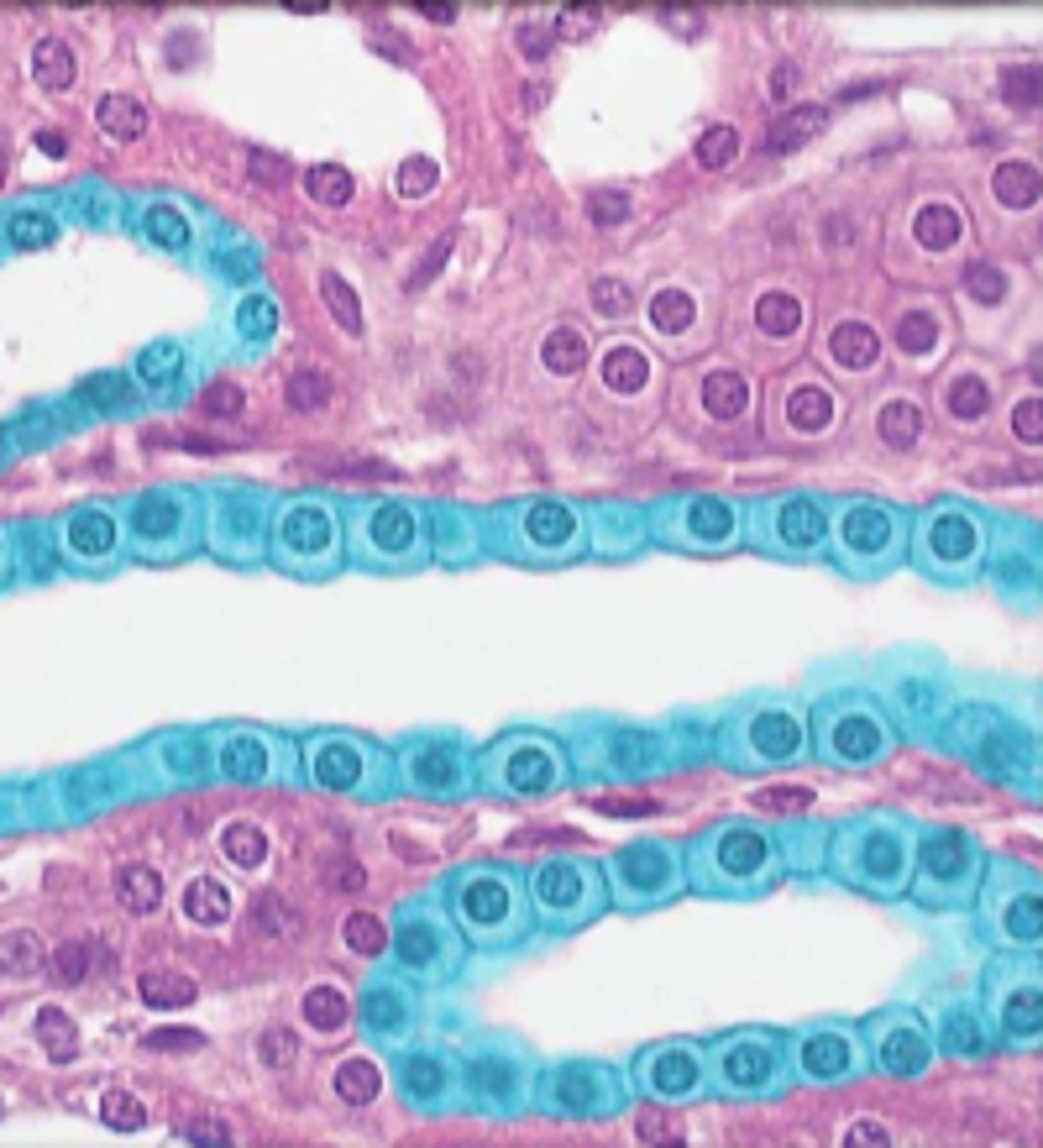
lumen
simple cuboidal epithelial cell
nucleus
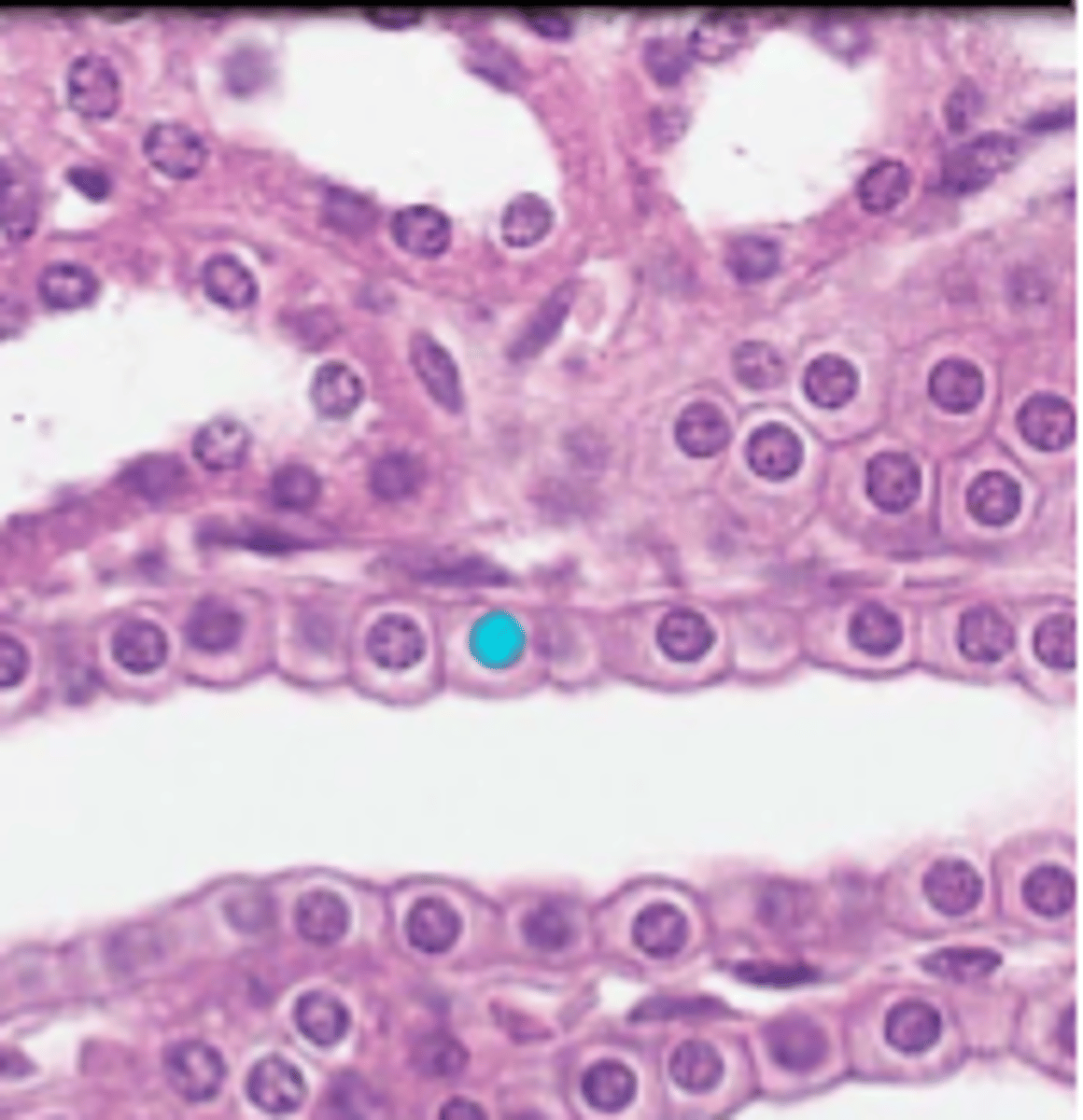
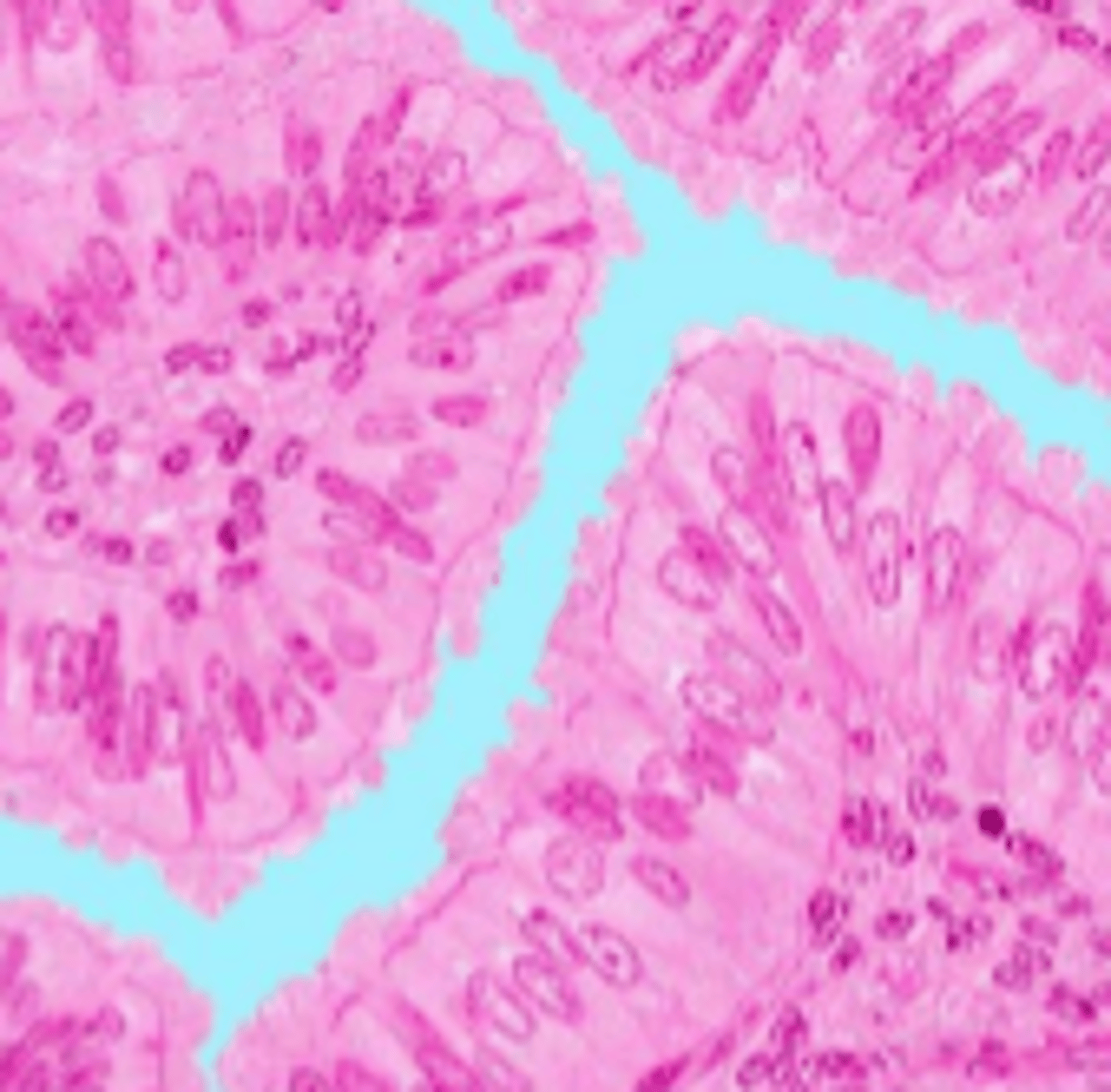
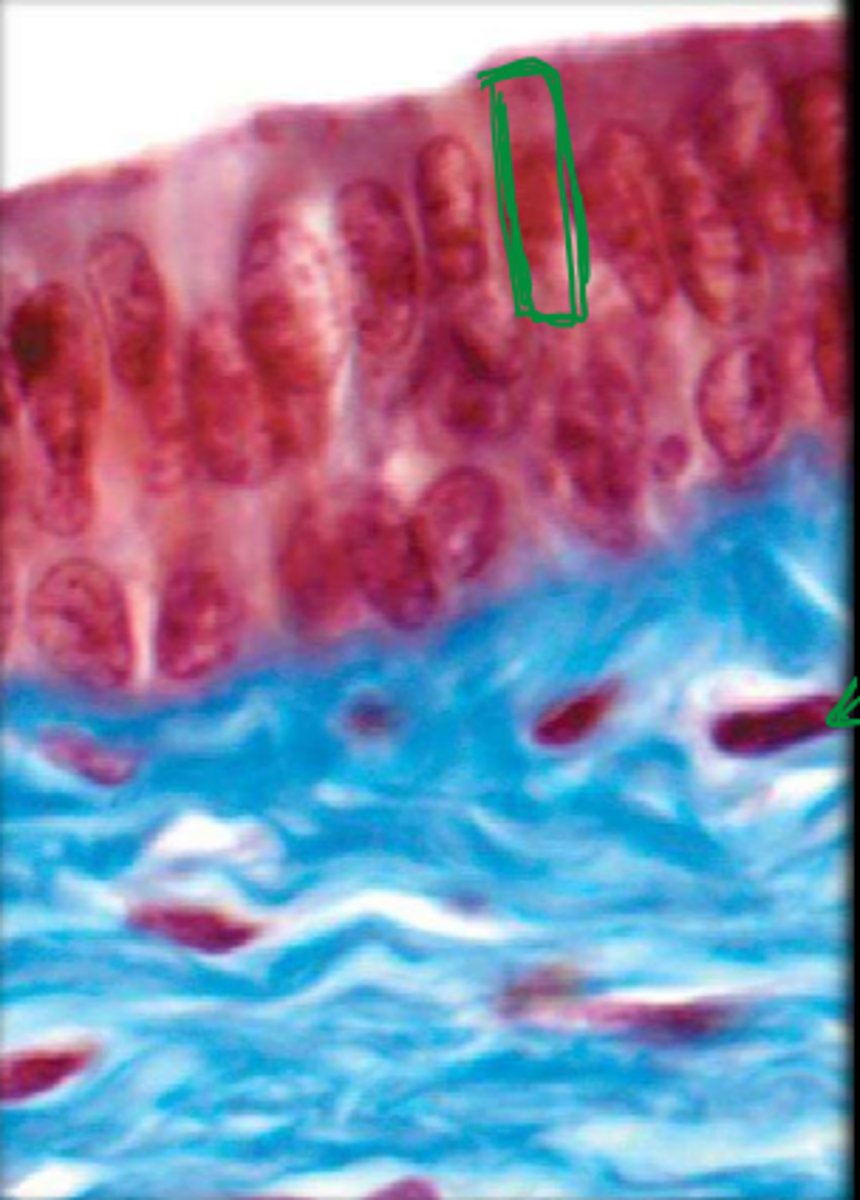
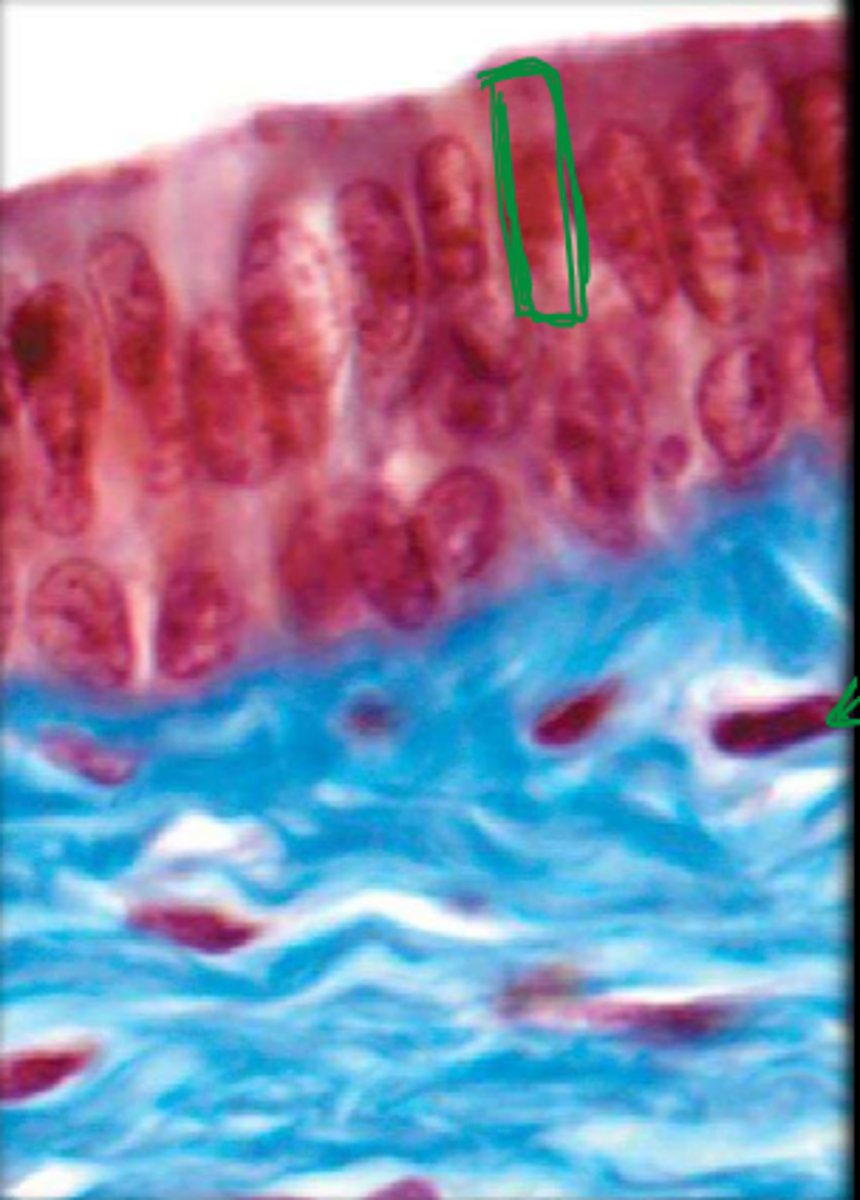
simple columnar epithelium
single layer of elongated cells, nuclei usually near the basement membrane, sometimes possesses cilia, lines uterus, stomach, intestines (microvilli), often has goblet cells (secrete mucus)
simple columnar epithelium
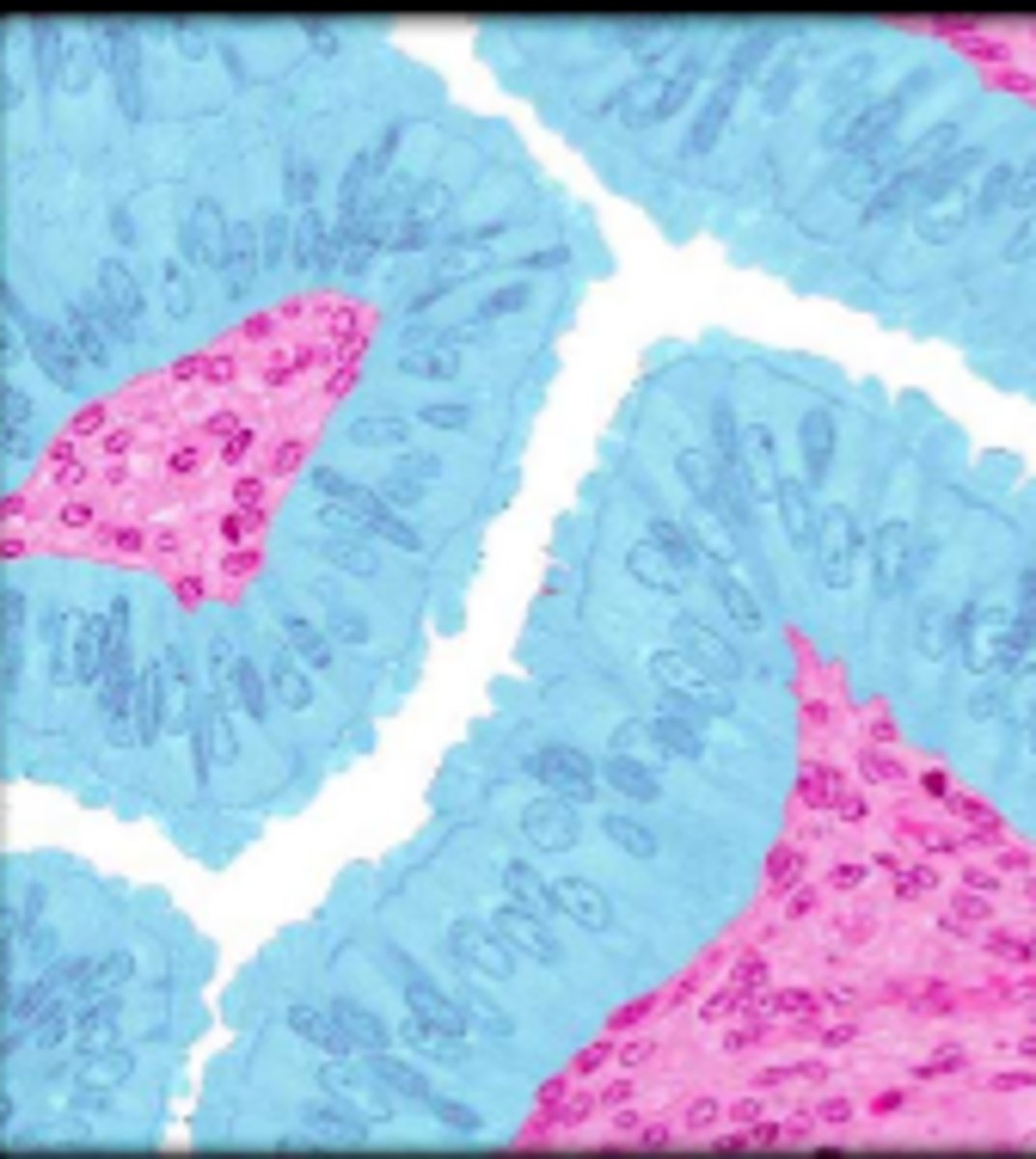
basement membrane
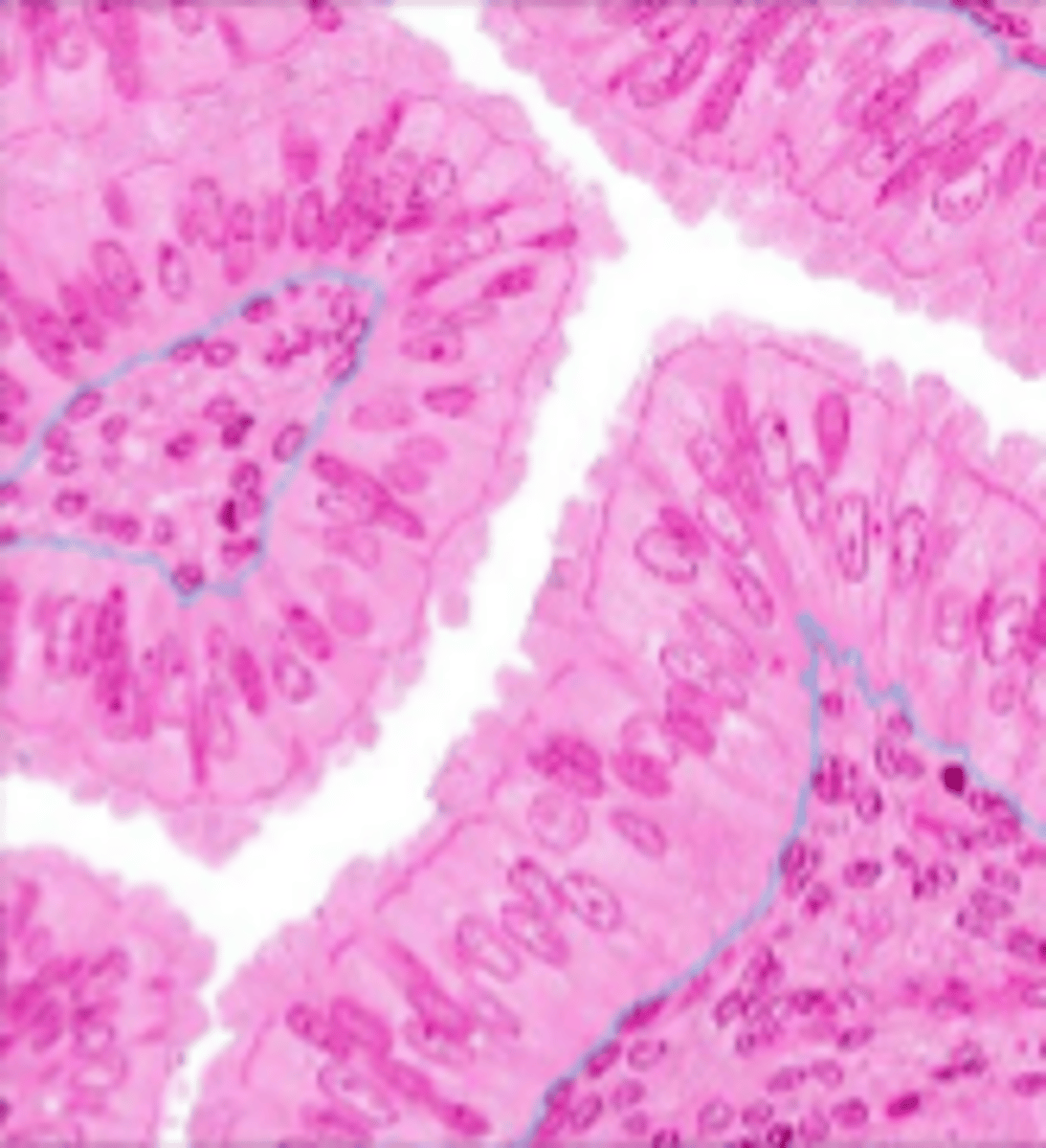
simple columnar epithelial cells
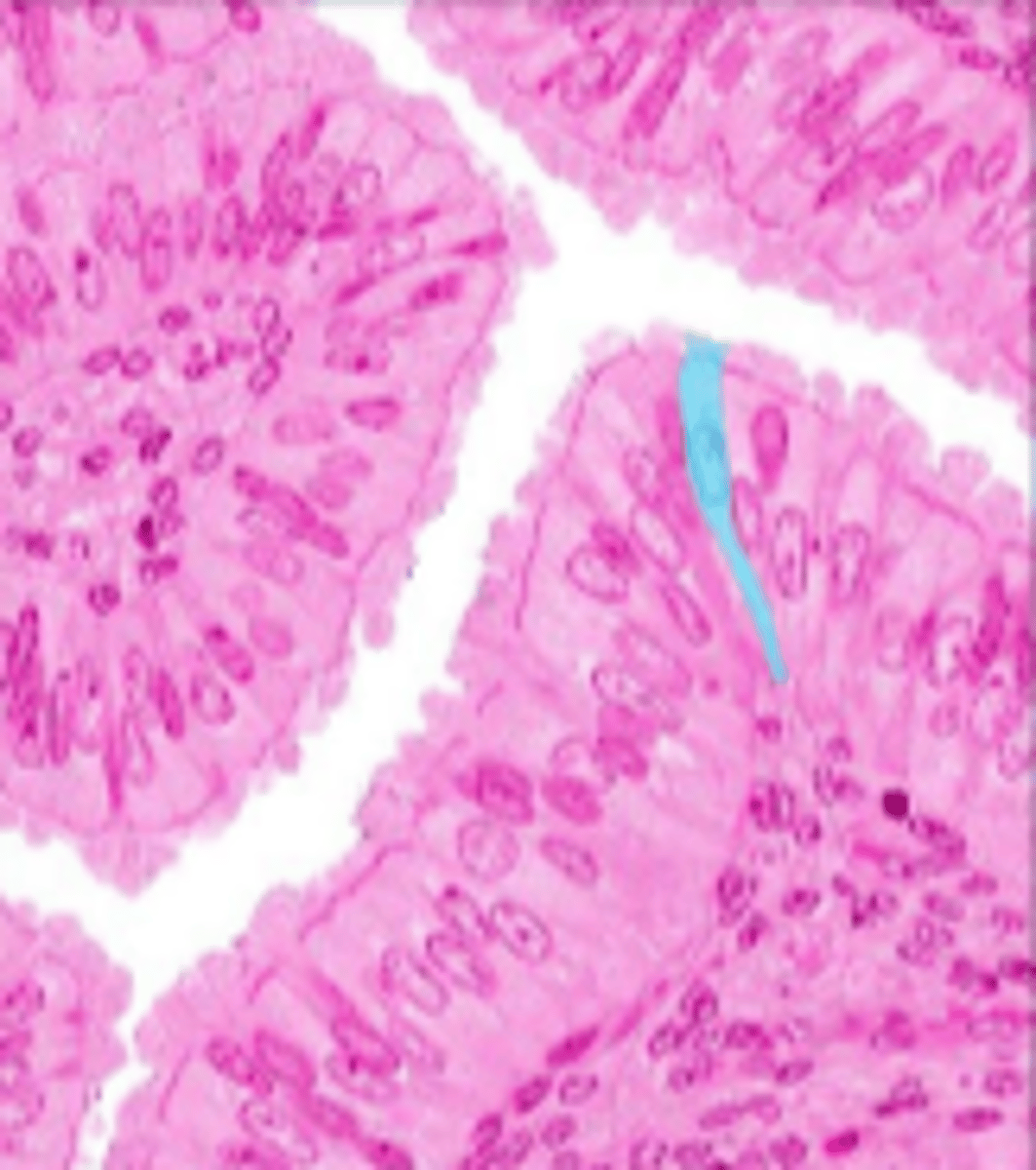
lumen
cilia
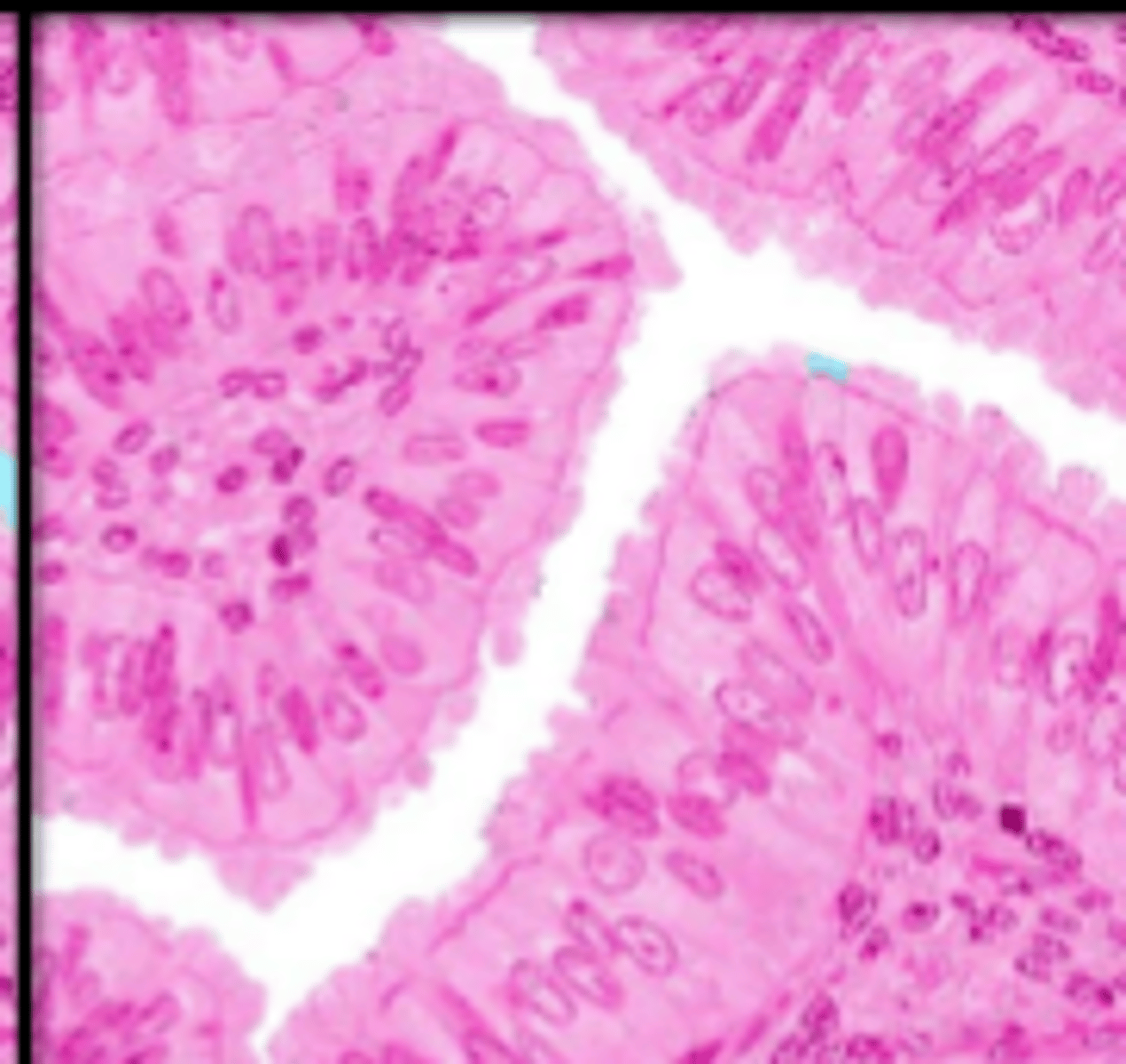
loose connective tissue
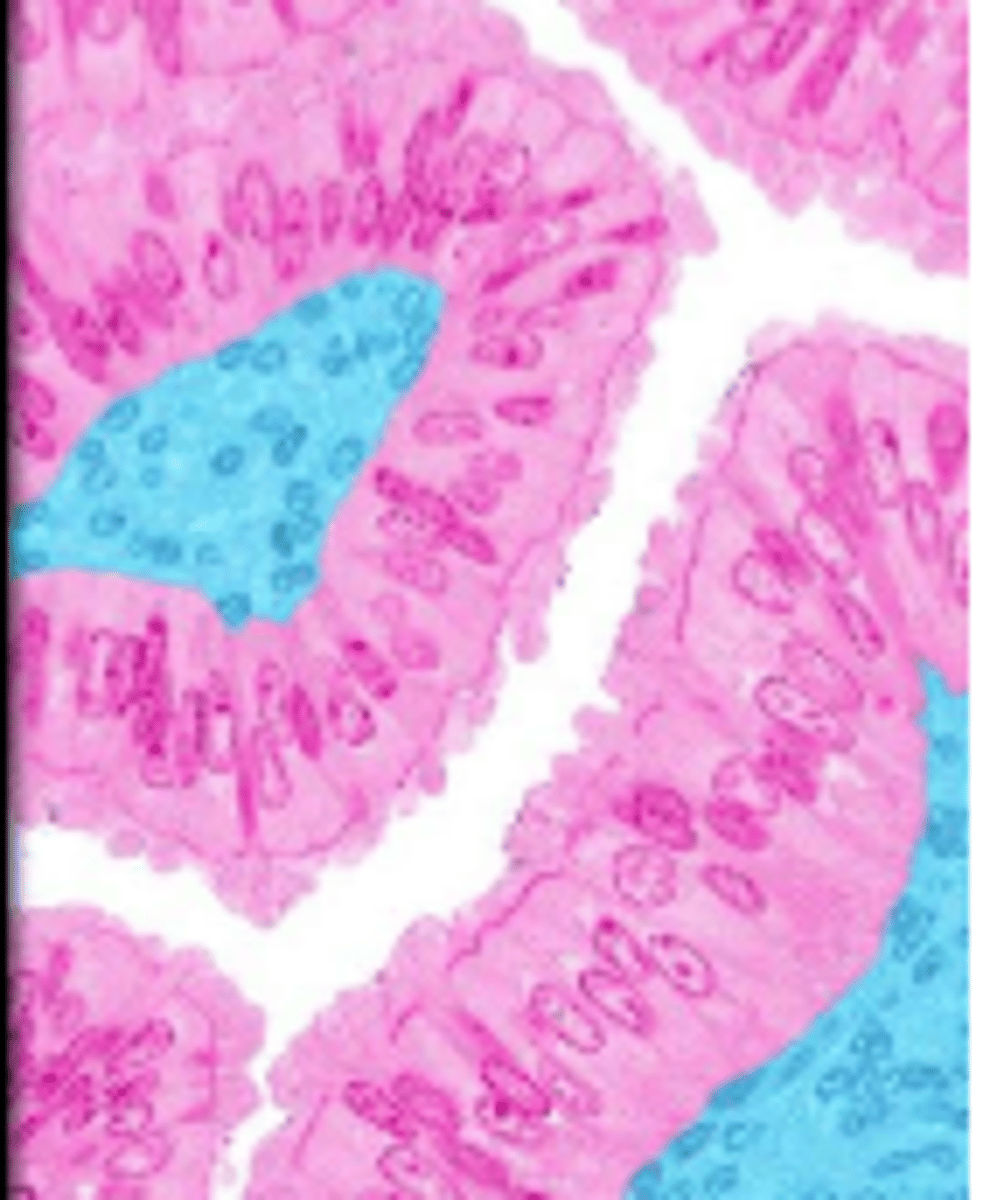
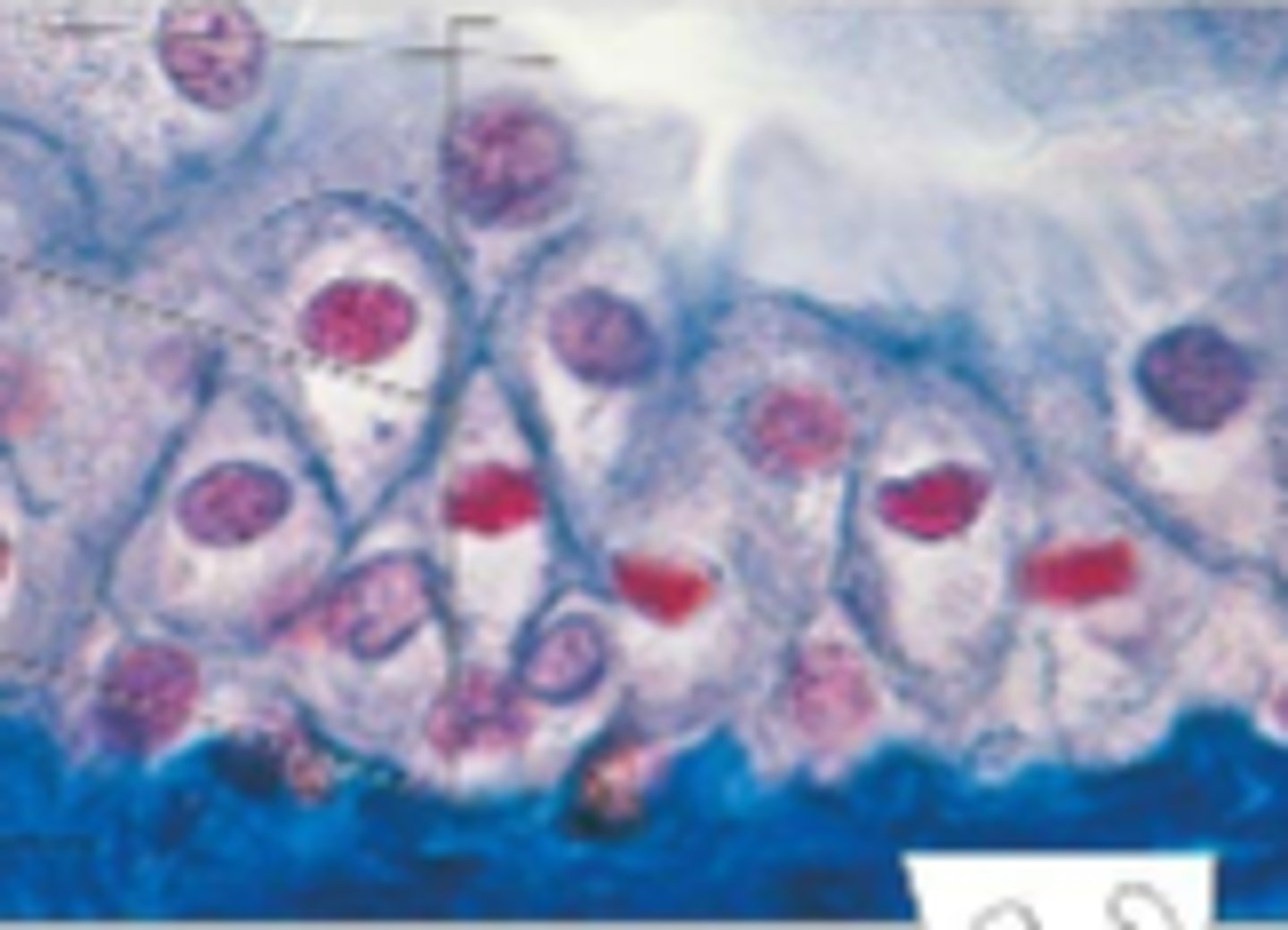
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
single layer of elongated cells, nuclei at two or more levels--giving appearance of being stratified, often has cilia, often has goblet cells, lines respiratory passageways
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
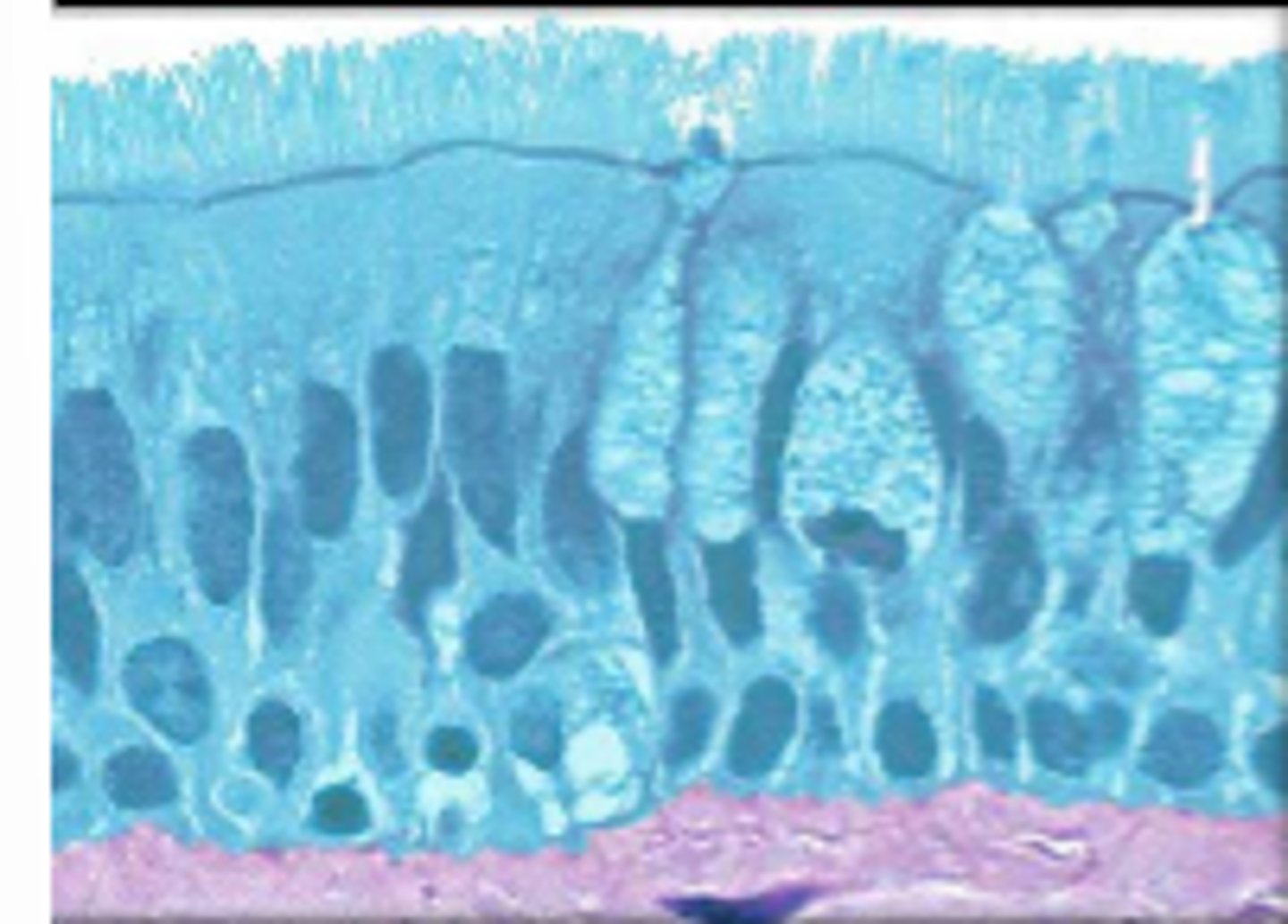
lumen
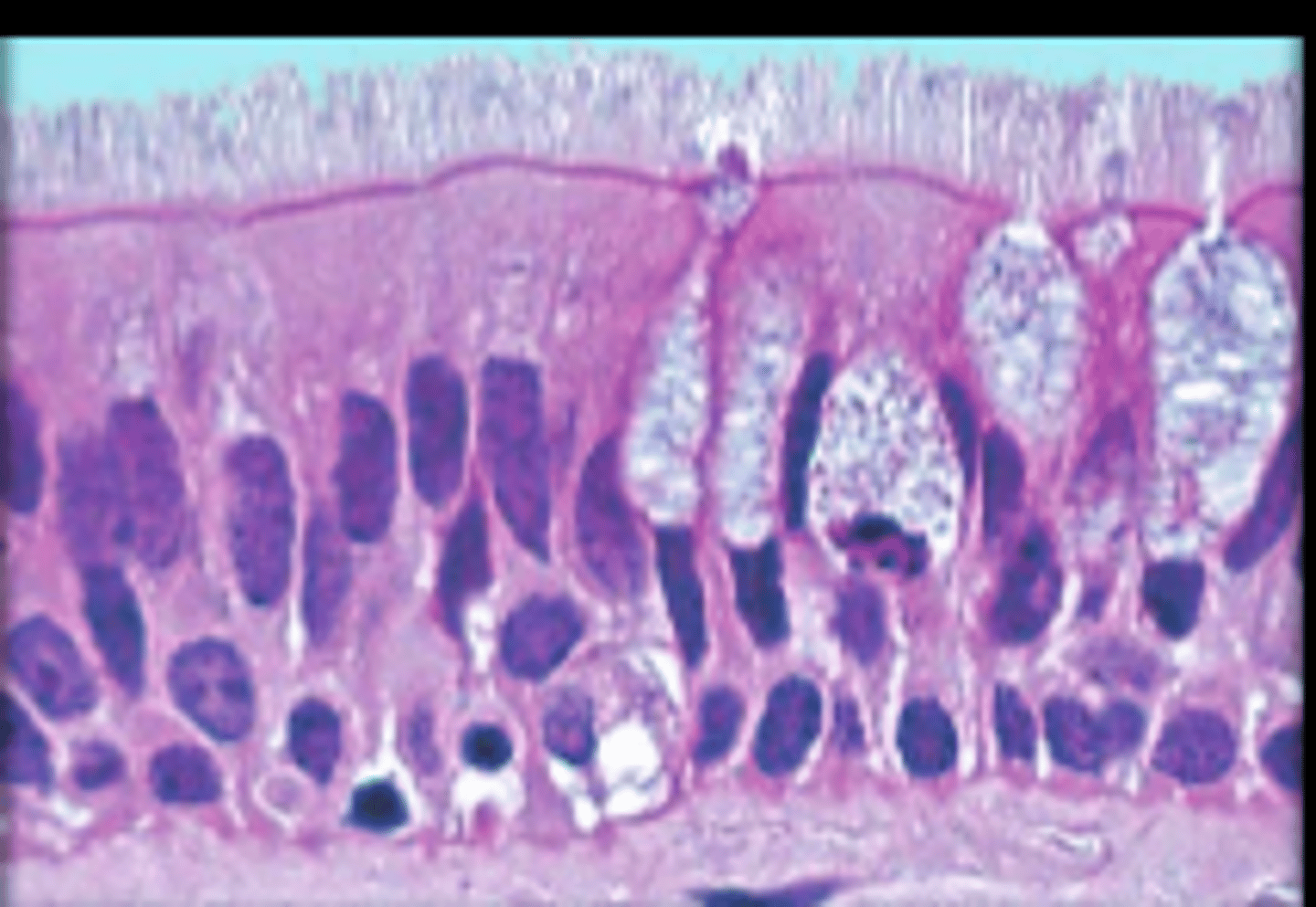
nucleus
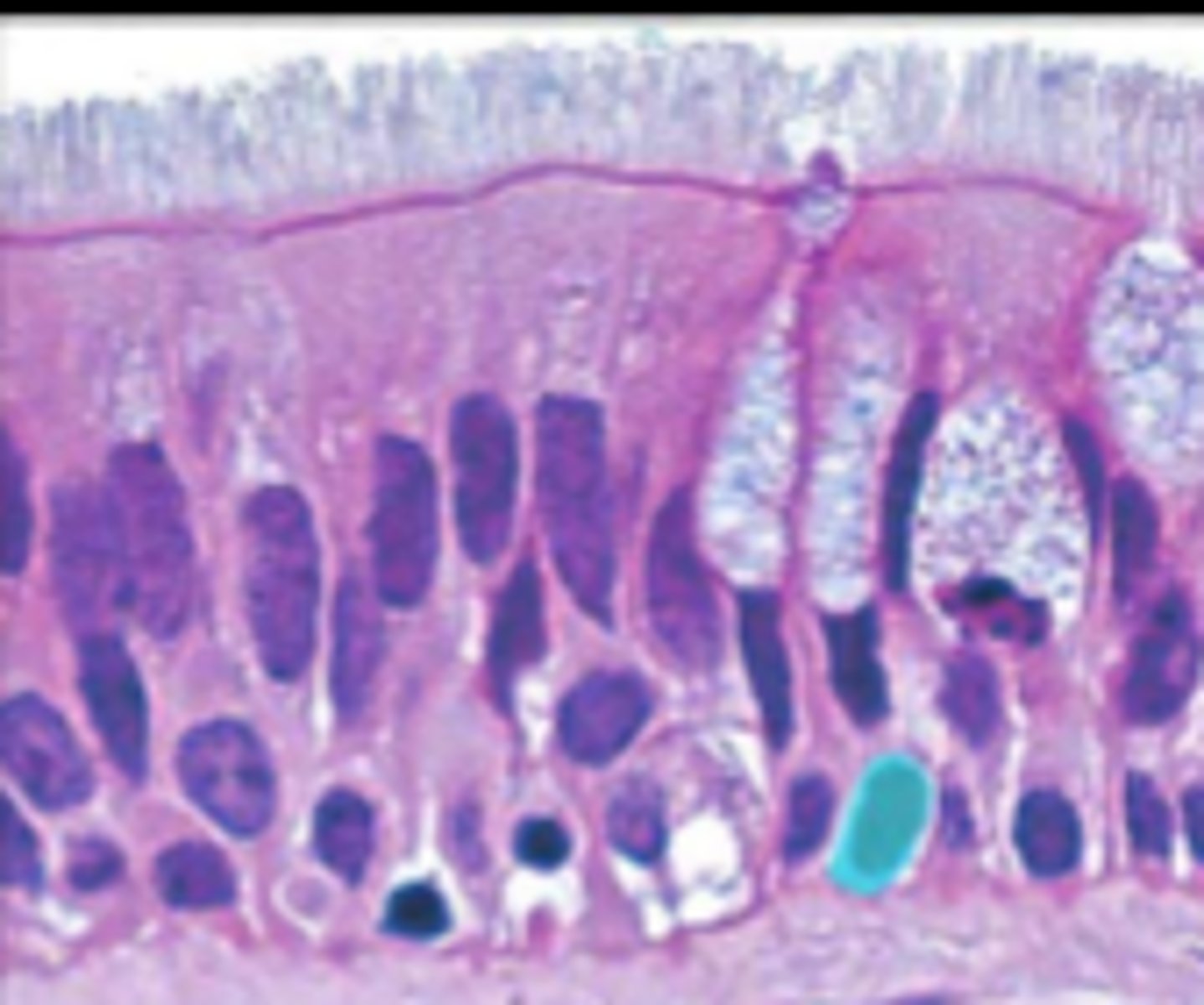
cilia
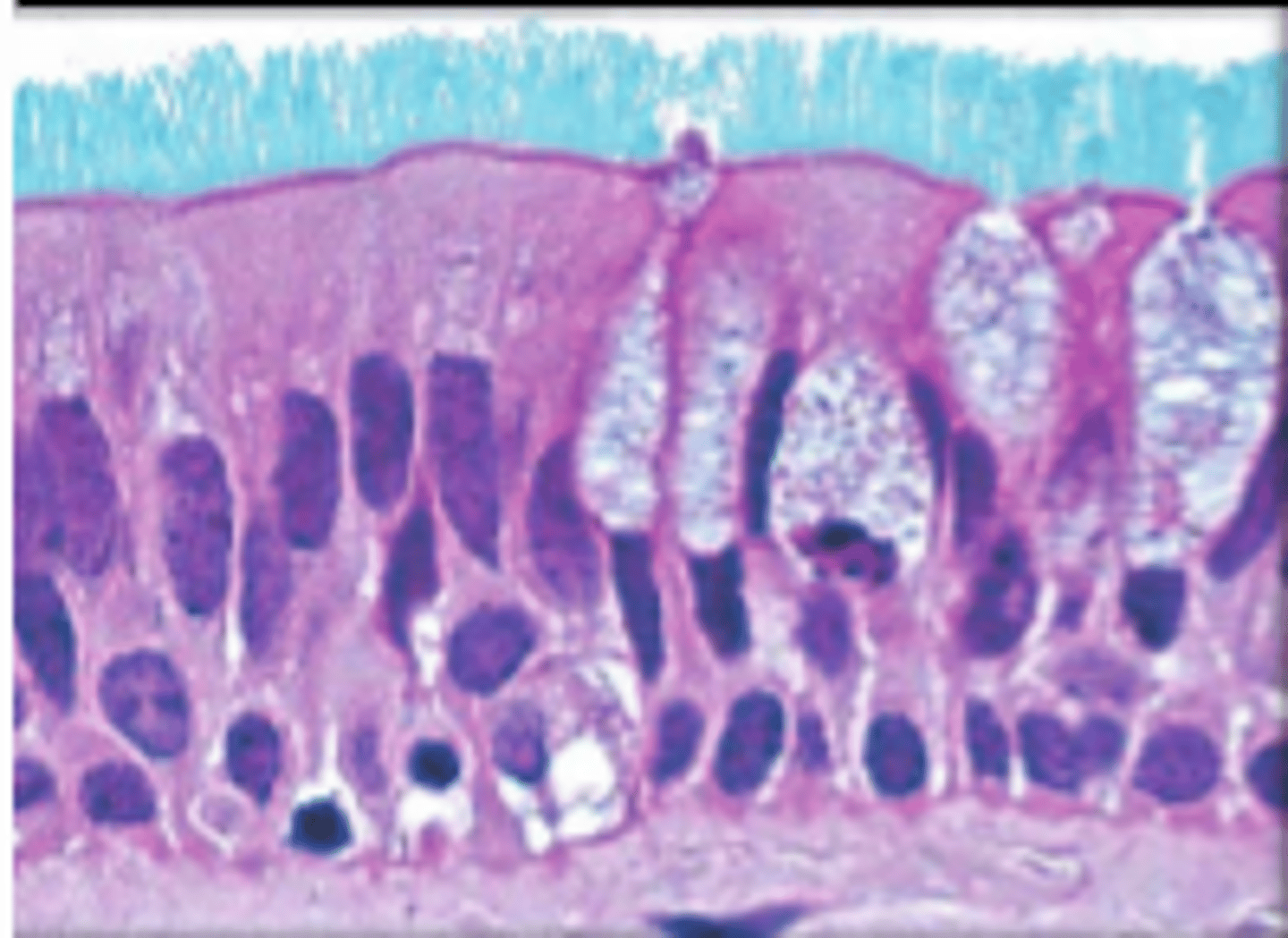
loose connective tissue
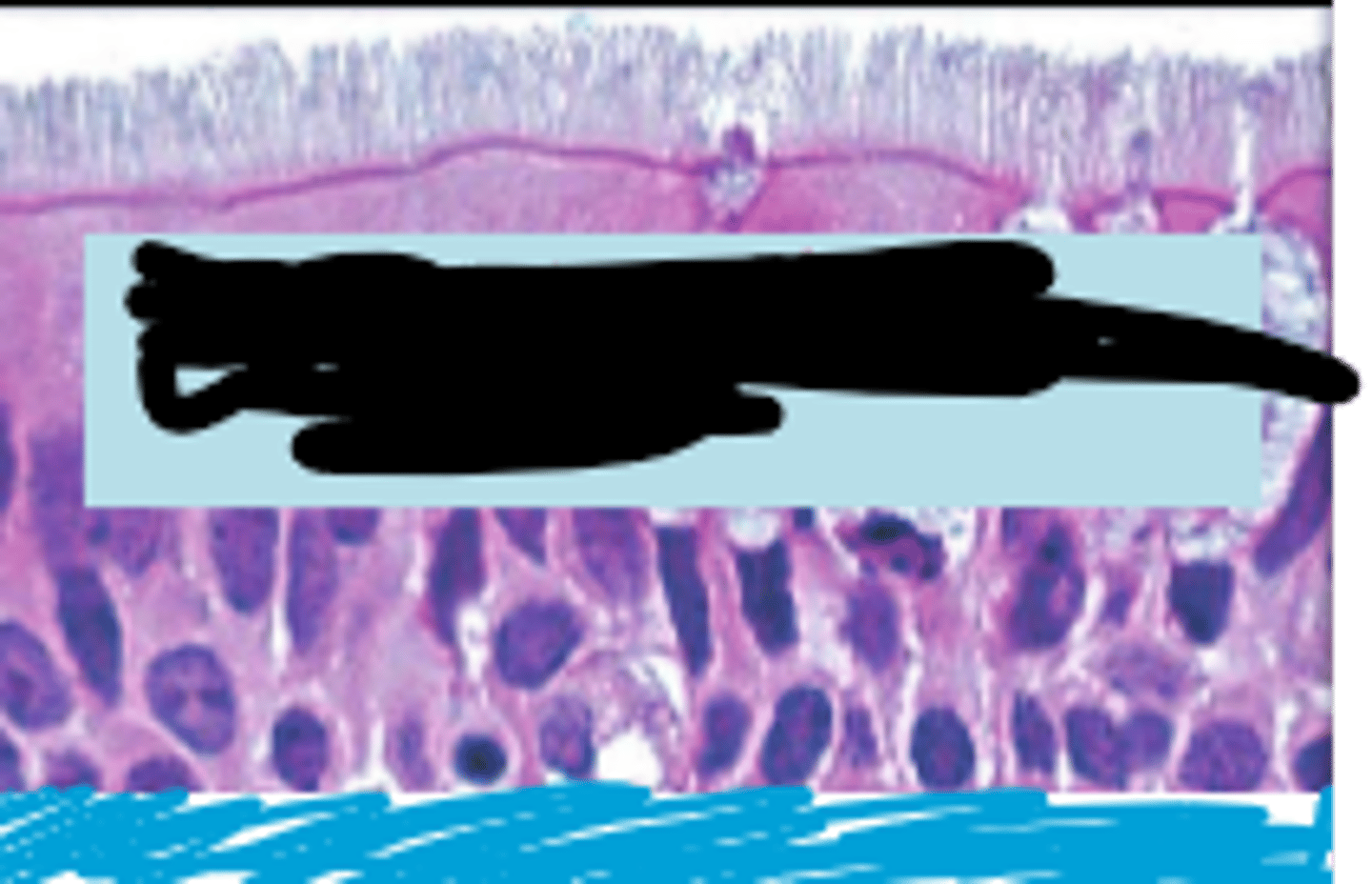
pseudostratified columnar epithelial cell
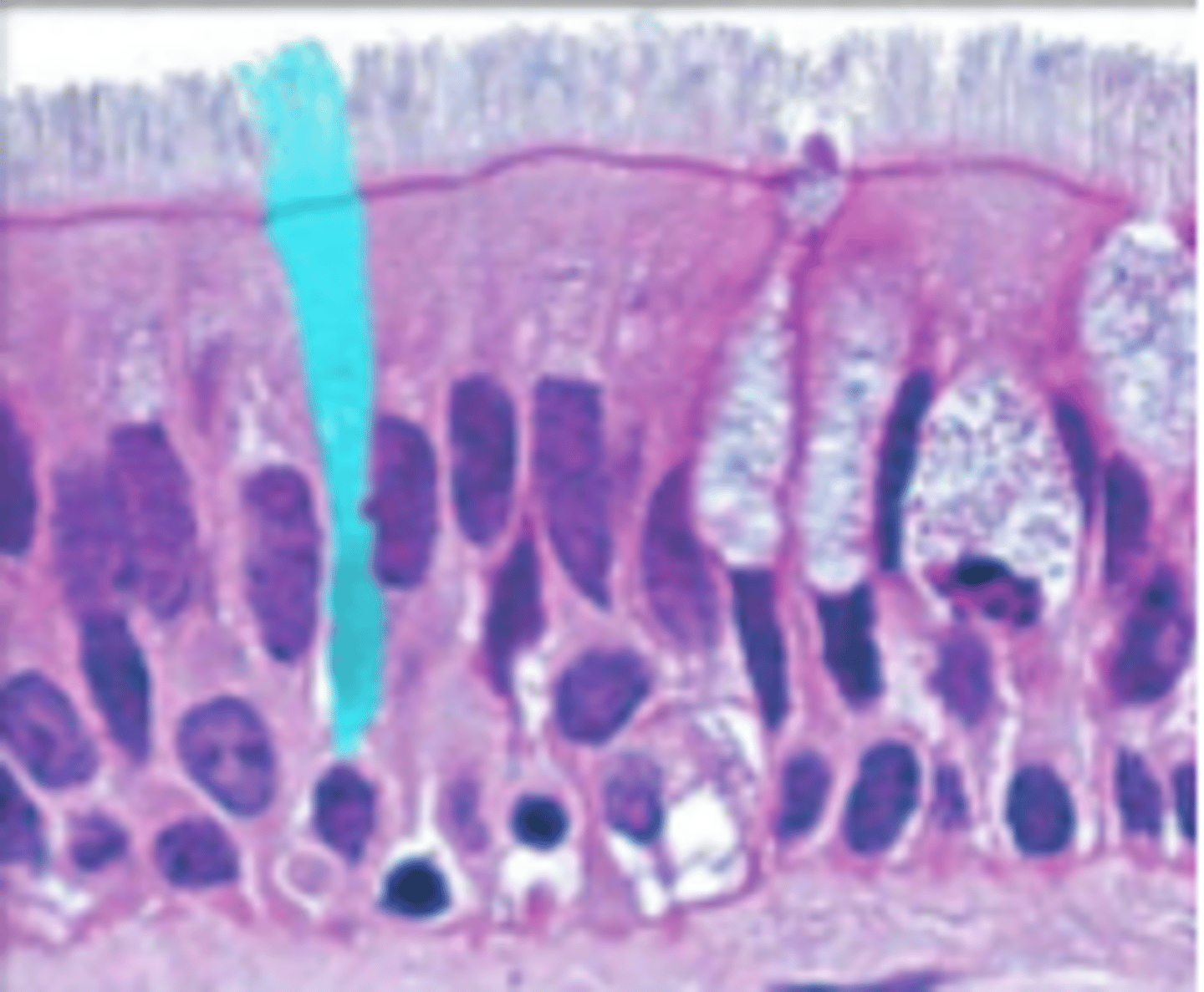
stratified squamous epithelium
many cell layers, top cells are flat, outer layer of skin (can accumulate keratin), lines oral cavity/vagina/anal canal
keratin
portion on top
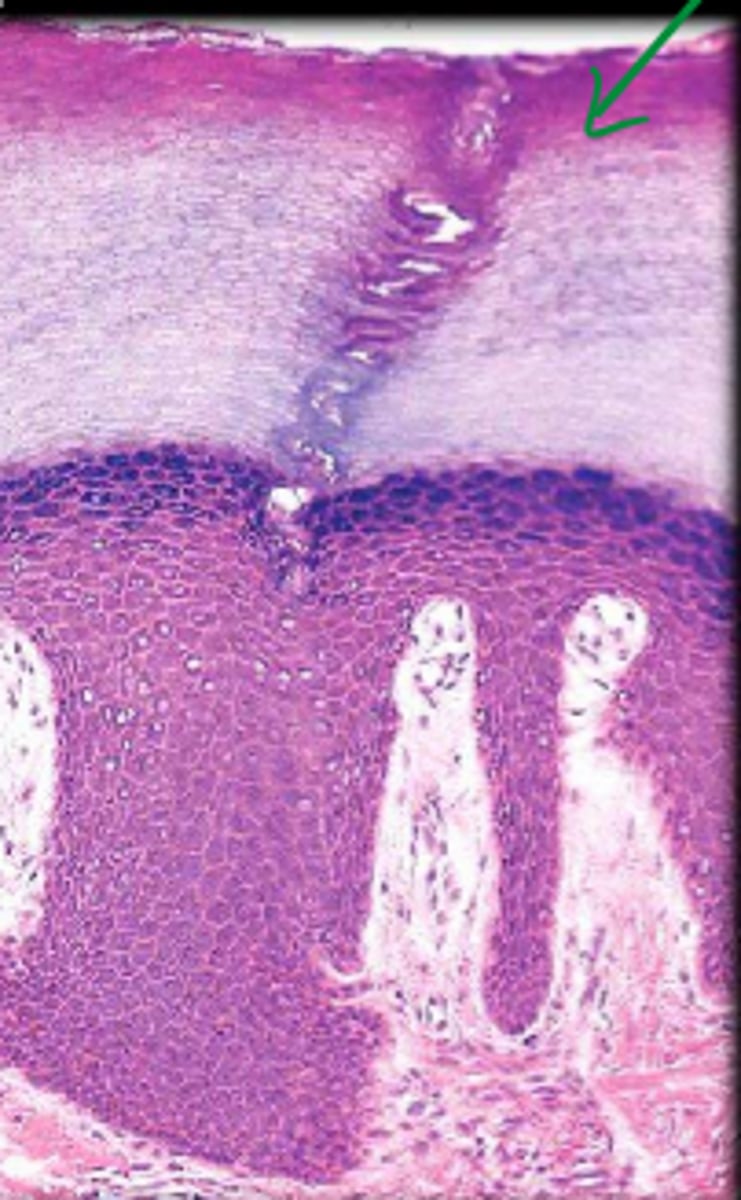
stratified squamous epithelium
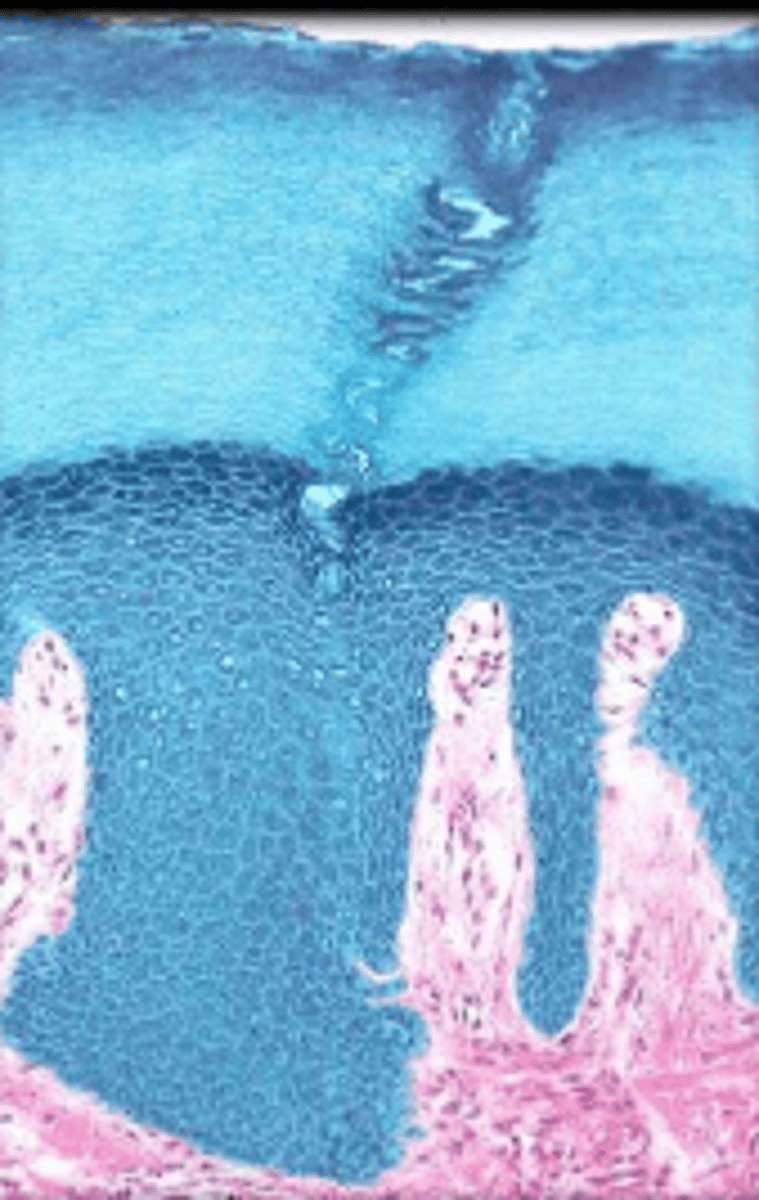
loose connective tissue
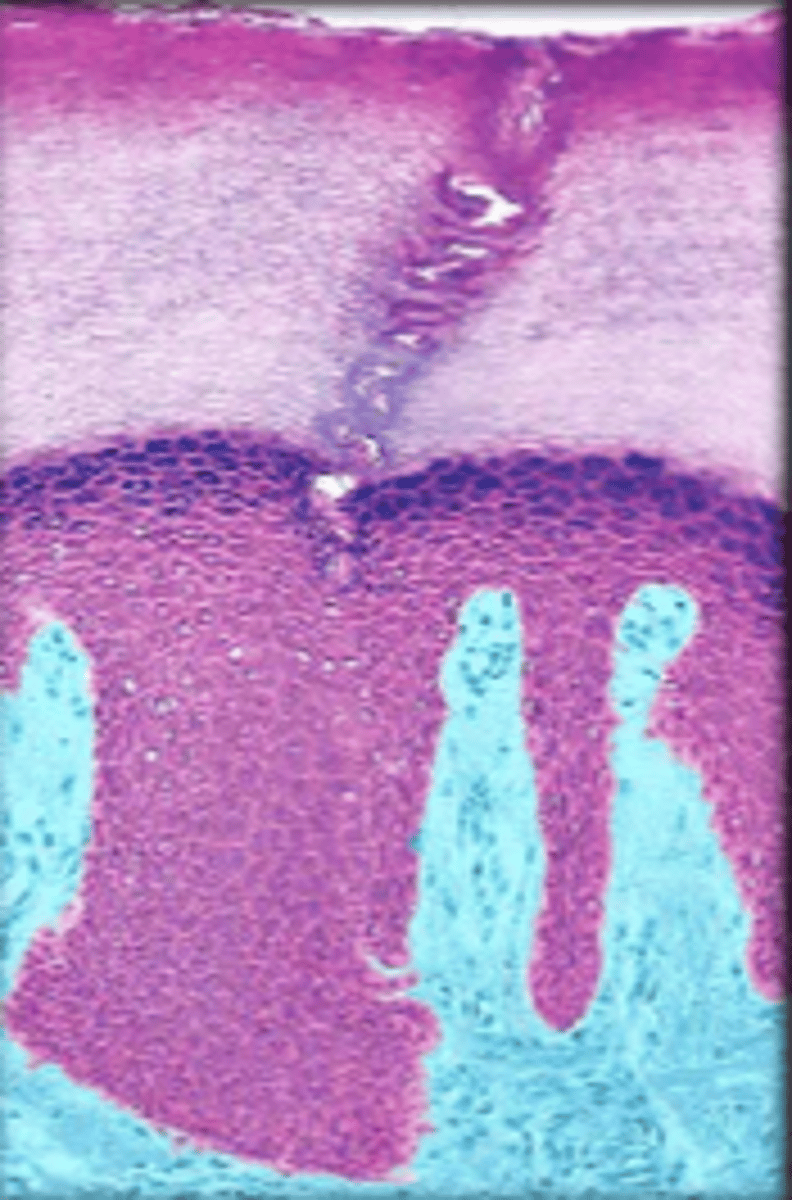
stratified cuboidal epithelium
2-3 layers, cube-shaped cells, lines ducts of mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, and pancreas
stratified columnar epithelium
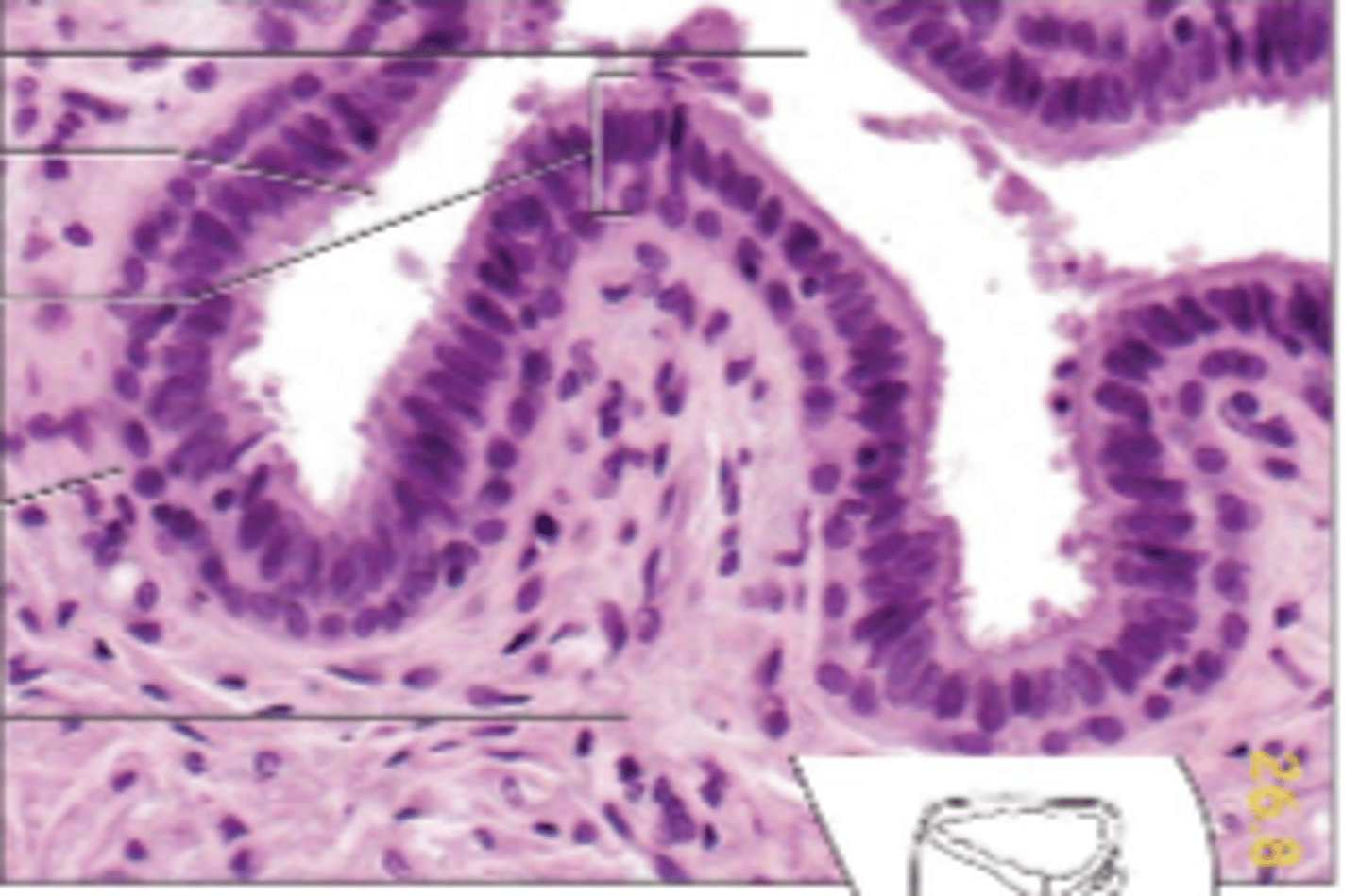
stratified columnar epithelial cell
top portion
connective tissue
bottom portion
transitional epithelium
many cell layers, cube-shaped and elongated cells, designed to distend and return to normal size, line urinary bladder/ureters/part of urethra
transitional epithelium
glandular epithelium
composed of cells that are specialized to produce and secrete substances
endocrine glands, exocrine glands
two types of glandular epithelium
endocrine glands
glands that secrete into body fluids or blood
exocrine glands
glands that secrete into ducts
merocrine, apocrine, holocrine
types of glandular secretions
merocrine glands
glandular secretions: fluid product, salivary glands, pancreas gland, sweat glands
apocrine glands
glandular secretions: cellular product, portions cells, mammary glands, ceruminous glands
holocrine glands
glandular secretions: secretory products, whole cells, sebaceous glands
serous membranes, mucous membranes, cutaneous membranes, synovial membranes
types of membranes
serous membranes
membranes: line body cavities that do not open to the outside, reduce friction, inner lining of thorax and abdomen, cover organs of thorax and abdomen, secrete serous fluid
mucous membranes
membranes: line tubes and organs that open to outside of body, lining of digestive/respiratory/urinary/reproductive tracts, secrete mucus
cutaneous membranes
membranes: covers body, skin
synovial membranes
membranes: composed entirely of connective tissue, lines joints
connective tissue
general characteristics: most abundant tissue type, cells are farther apart than epithelia cells, contain matrix between cells, lots of functions, most have good blood supply and are well-nourished but vascularity varies among tissue types
extracellular matrix
consists of protein fibers and ground substance; consistency varies from fluid to semisolid to solid
fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells
connective tissue major cell types
fibroblasts
connective tissue cell types: most common cell, large, secretes, extracellular matrix fibers
macrophages
connective tissue cell types: wandering cell, phagocytic, important in immunity and prevent of infection
mast cells
connective tissue cell types: large cell, located near blood vessels, release heparin (anticoagulant), release histamine (promotes inflammation)
collagenous fibers
connective tissue fibers: thick, composed of collagen, great tensile strength, abundant in dense connective tissue, hold structures together
elastic fibers
connective tissue fibers: bundles of microfibrils embedded in elastin, elastic
reticular fibers
connective tissue fibers: very thin collagenous fibers, highly branched, form delicate supportive networks
connective tissue proper
connective tissues: includes loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue
areolar, adipose, reticular
types of loose connective tissue
dense regular, dense irregular, elastic
types of dense connective tissue
specialized connective tissue
connective tissues: includes cartilage, bone, blood
areolar connective tissue
connective tissue: mainly fibroblasts, gel-like ground substance collagenous fibers and elastic fibers, thin and delicate membranes, binds skin to structures, beneath most epithelia (laminar propia)
areolar connective tissue
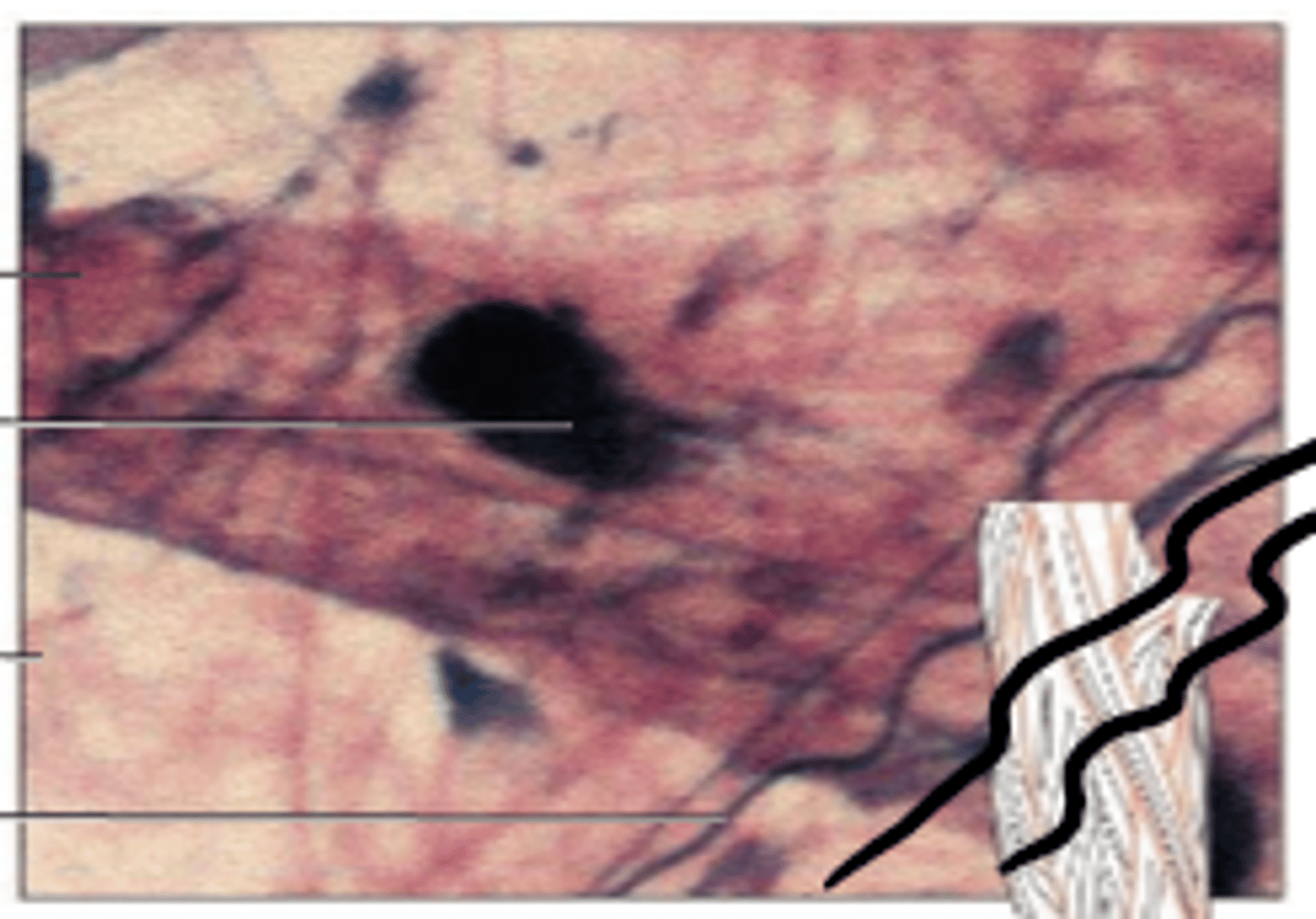
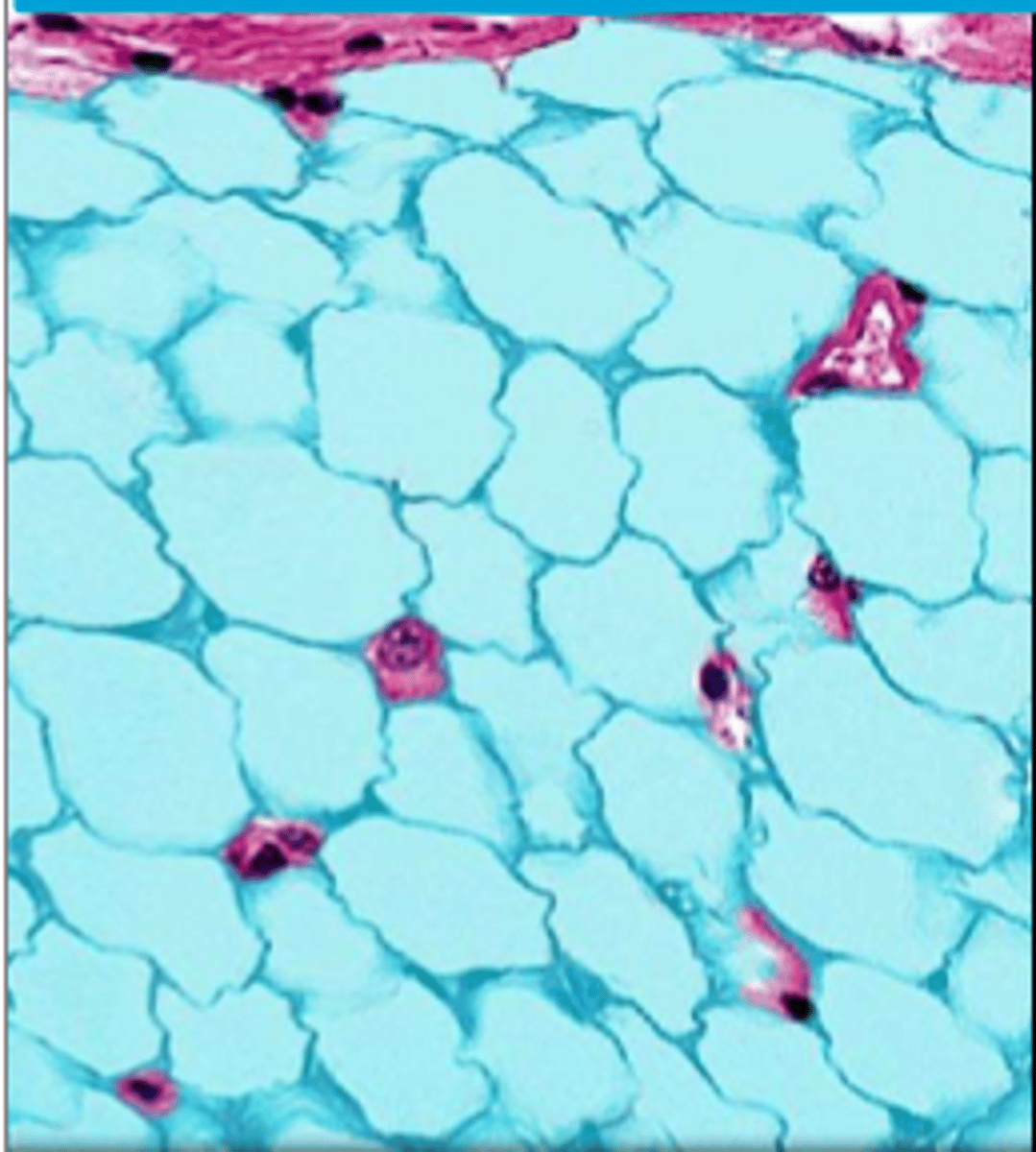
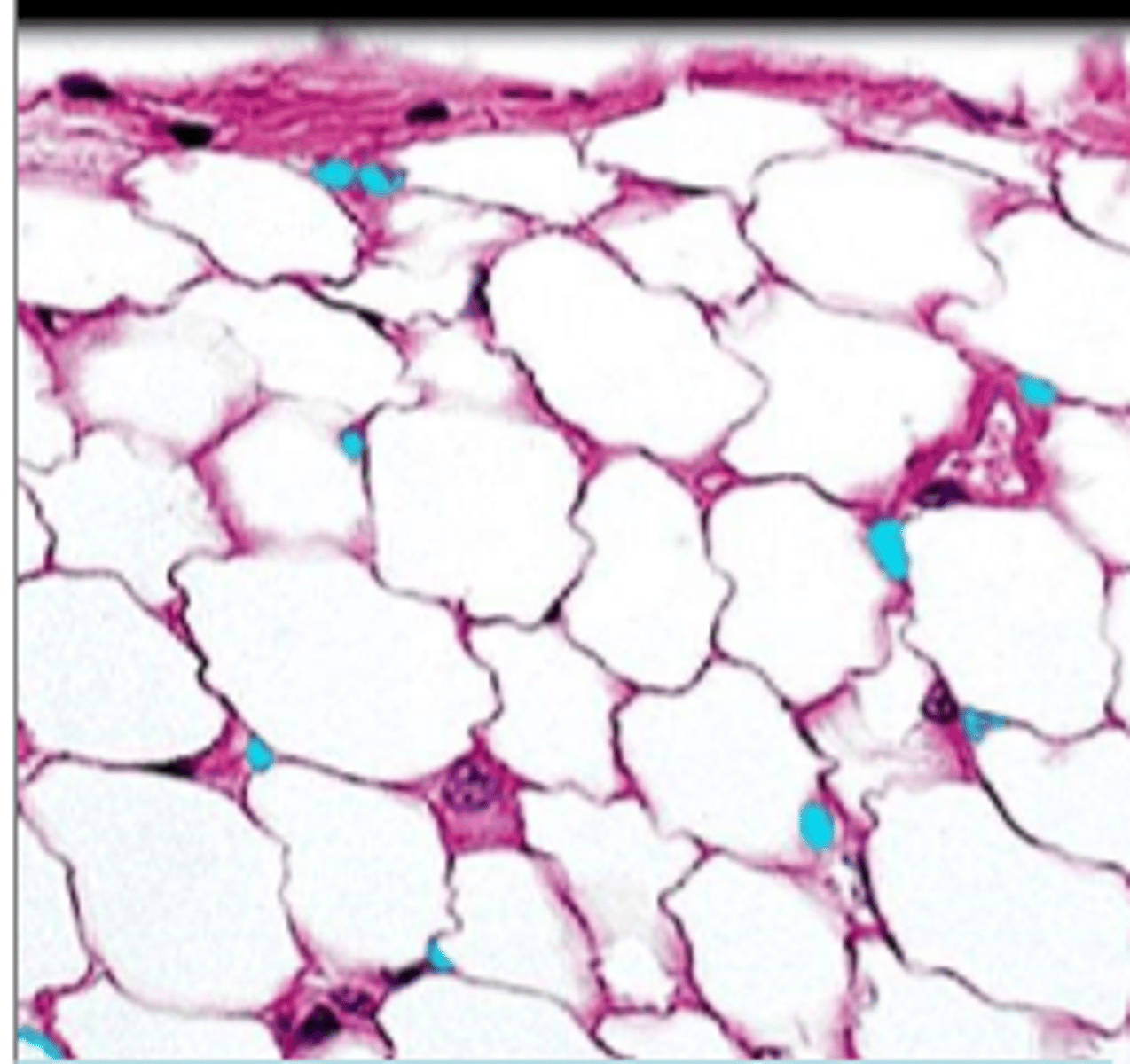
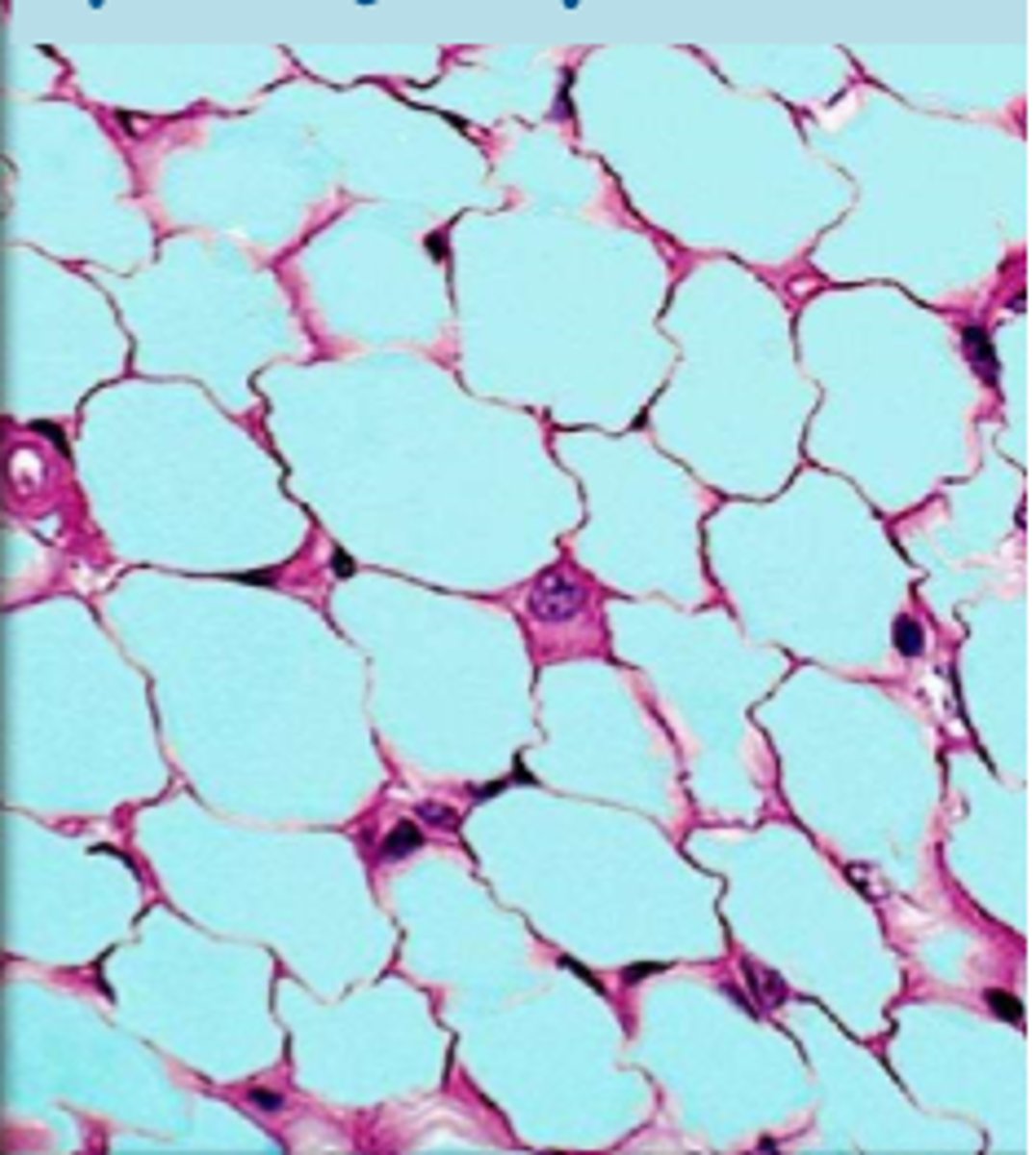
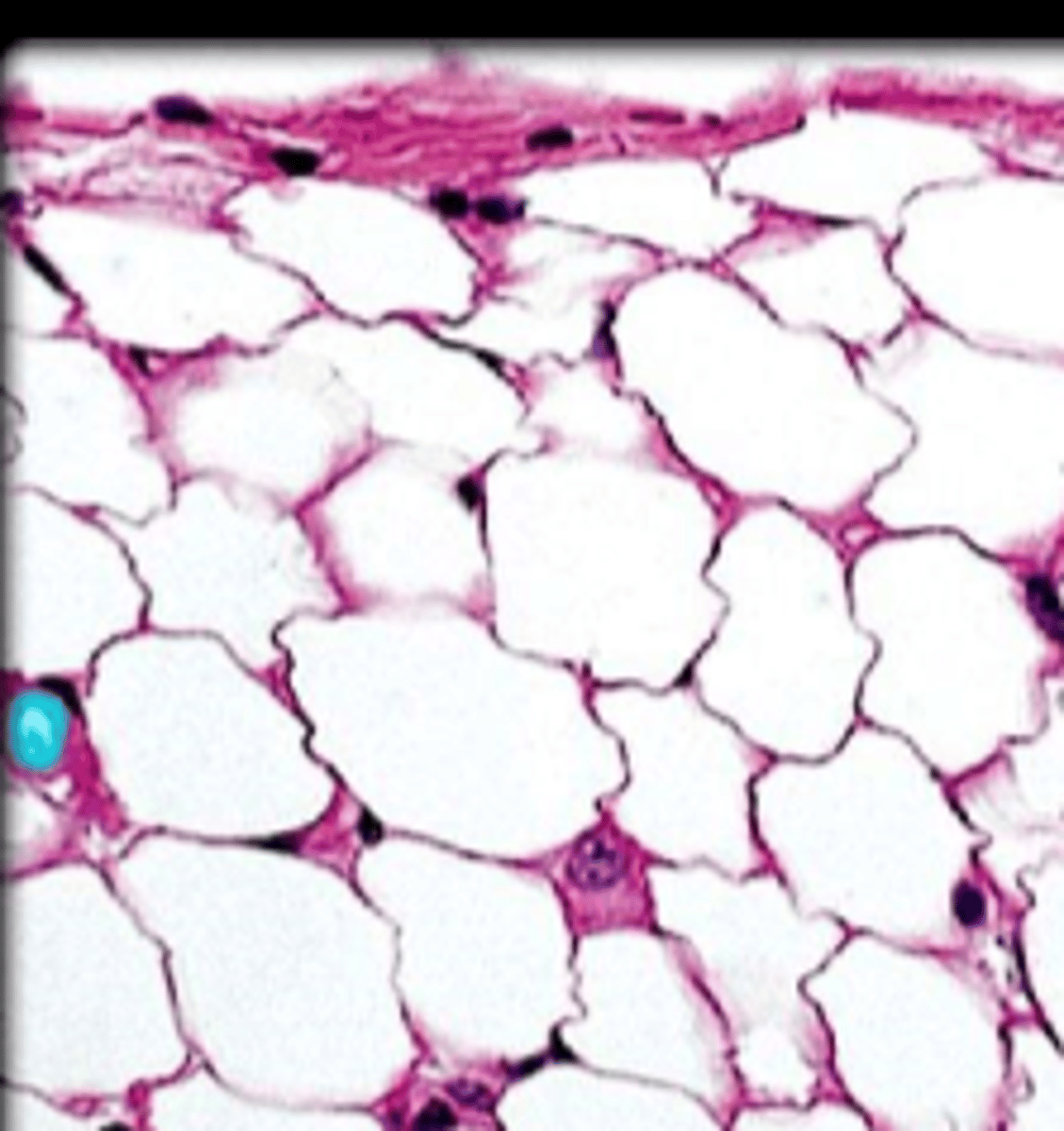
adipose connective tissue
connective tissue: adipocytes, functions: stores fats, cushions, insulates, beneath skin, around joints, padding the kidneys/heart/other internal organs, between muscles
adipose connective tissue
nuclei
fat droplets
capillaries
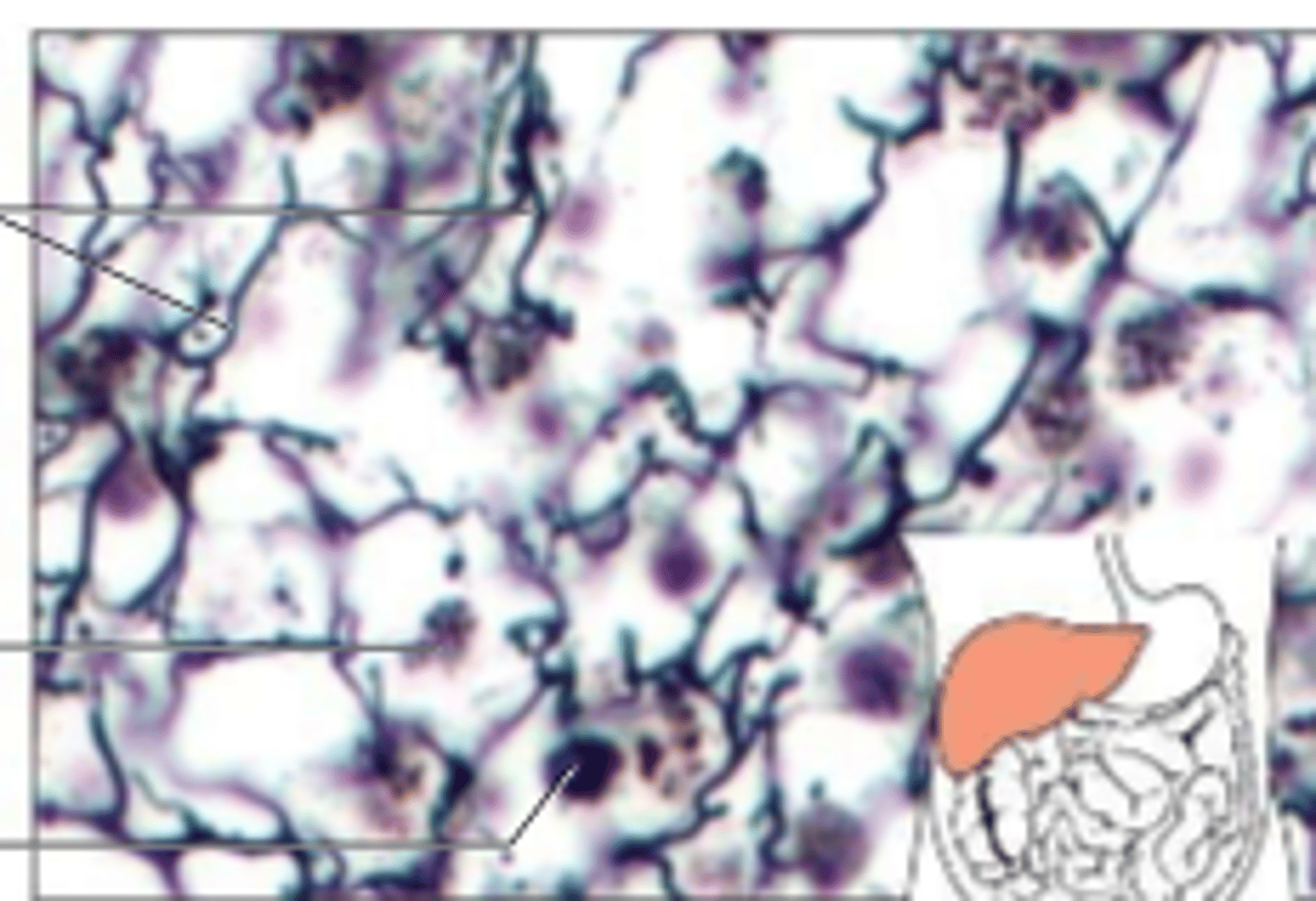
reticular connective tissue
connective tissue: composed of reticular fibers, supports internal organ walls, walls of liver/spleen
dense regular connective tissue
connective tissue: densely packed collagenous fibers, very strong, poor blood supply--slow to heal, fibroblasts, tendons, ligaments, dermis
reticular connective tissue
dense regular connective tissue
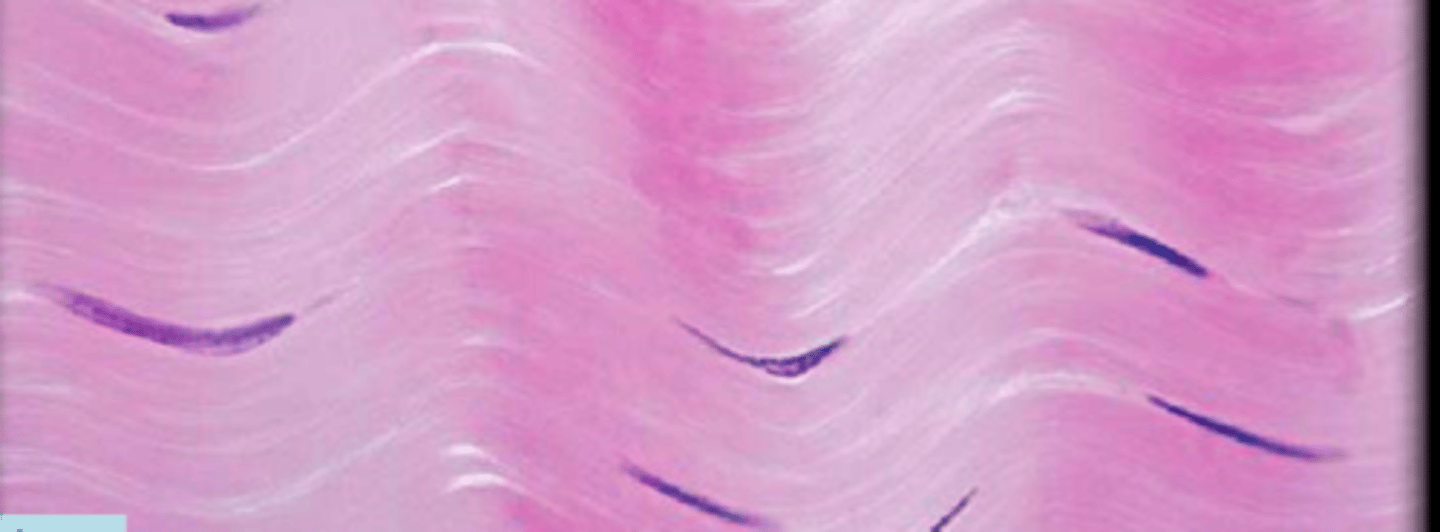
collagen fibers/ECM
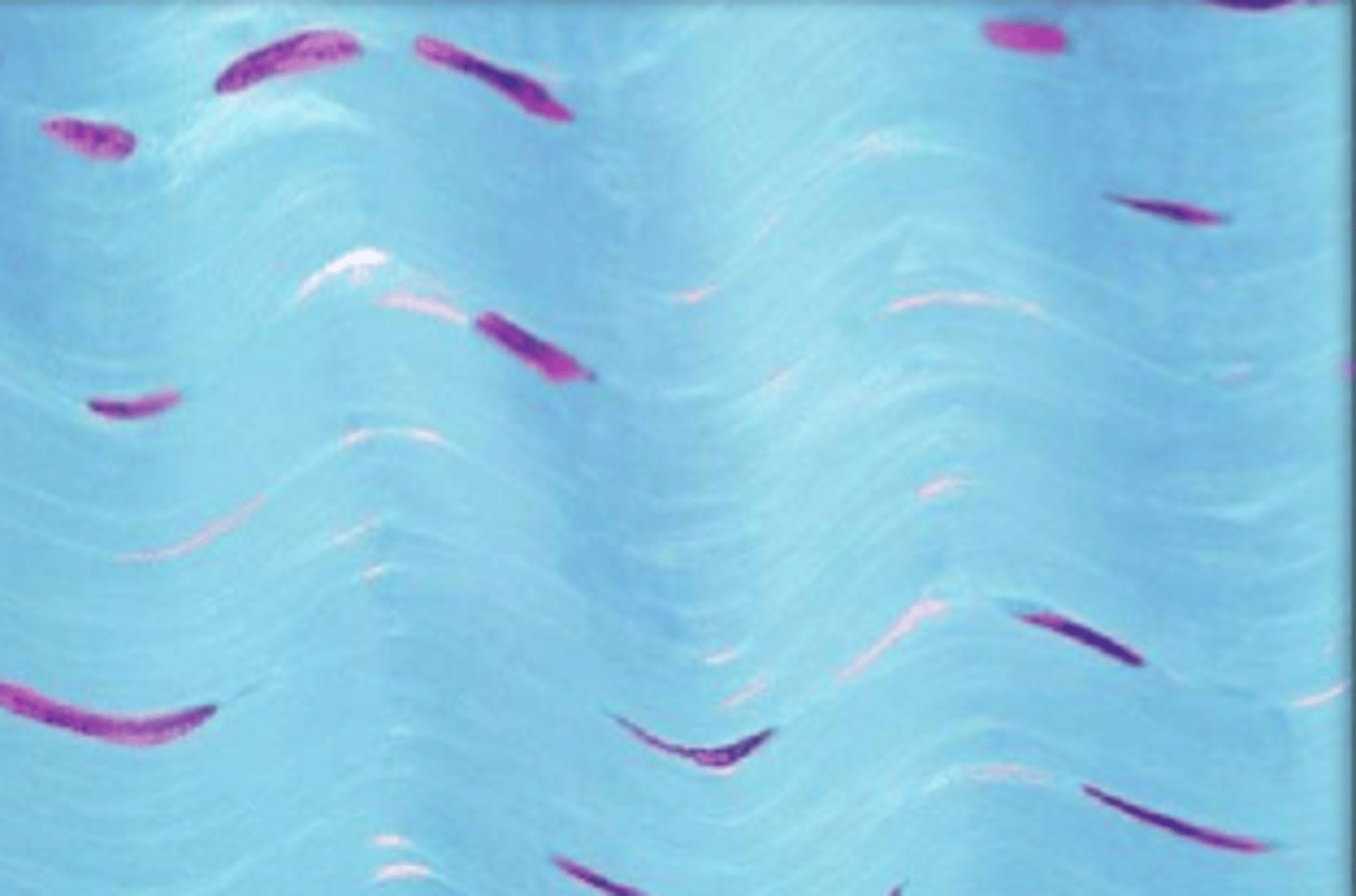
nuclei of fibroblasts
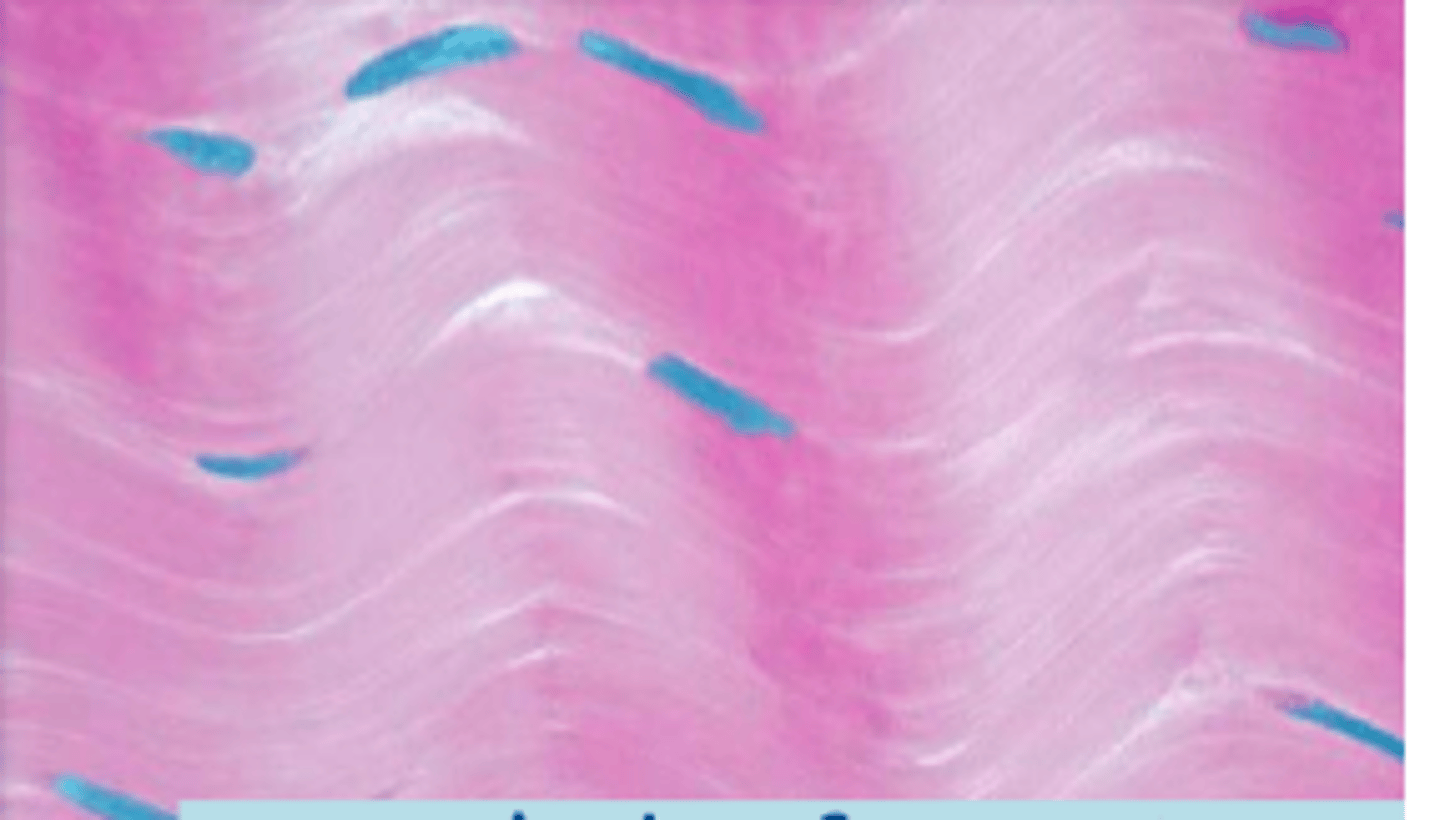
cartilage
connective tissue: rigid matrix that provides framework for various structures, chondrocytes located in lacunae in this gel-like matrix, poor blood supply, covered by pericohondrium
lacunae
outlined discoloration in cartilage
hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, fibrocartilage
three types of cartilage
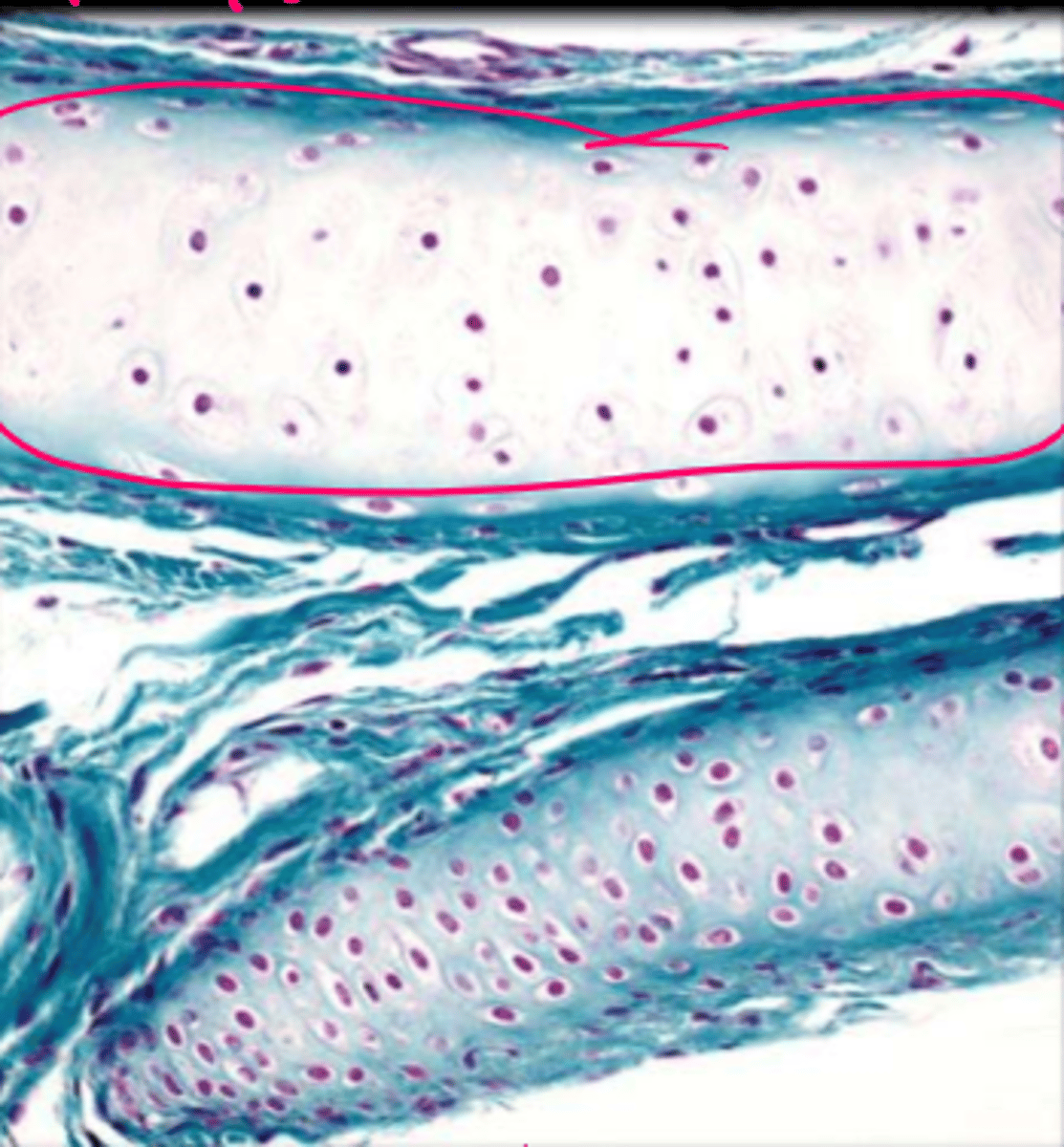
hyaline cartilage
cartilage: most abundant, fine collagenous fibers, ends of bones, nose, respiratory passages
elastic cartilage
cartilage: flexible--elastic fibers, external ear, larynx
fibrocartilage
cartilage: very tough--many collagenous fibers, shock absorber,, intervertebral discs, pads of knee, pelvic girdle
hyaline cartilage
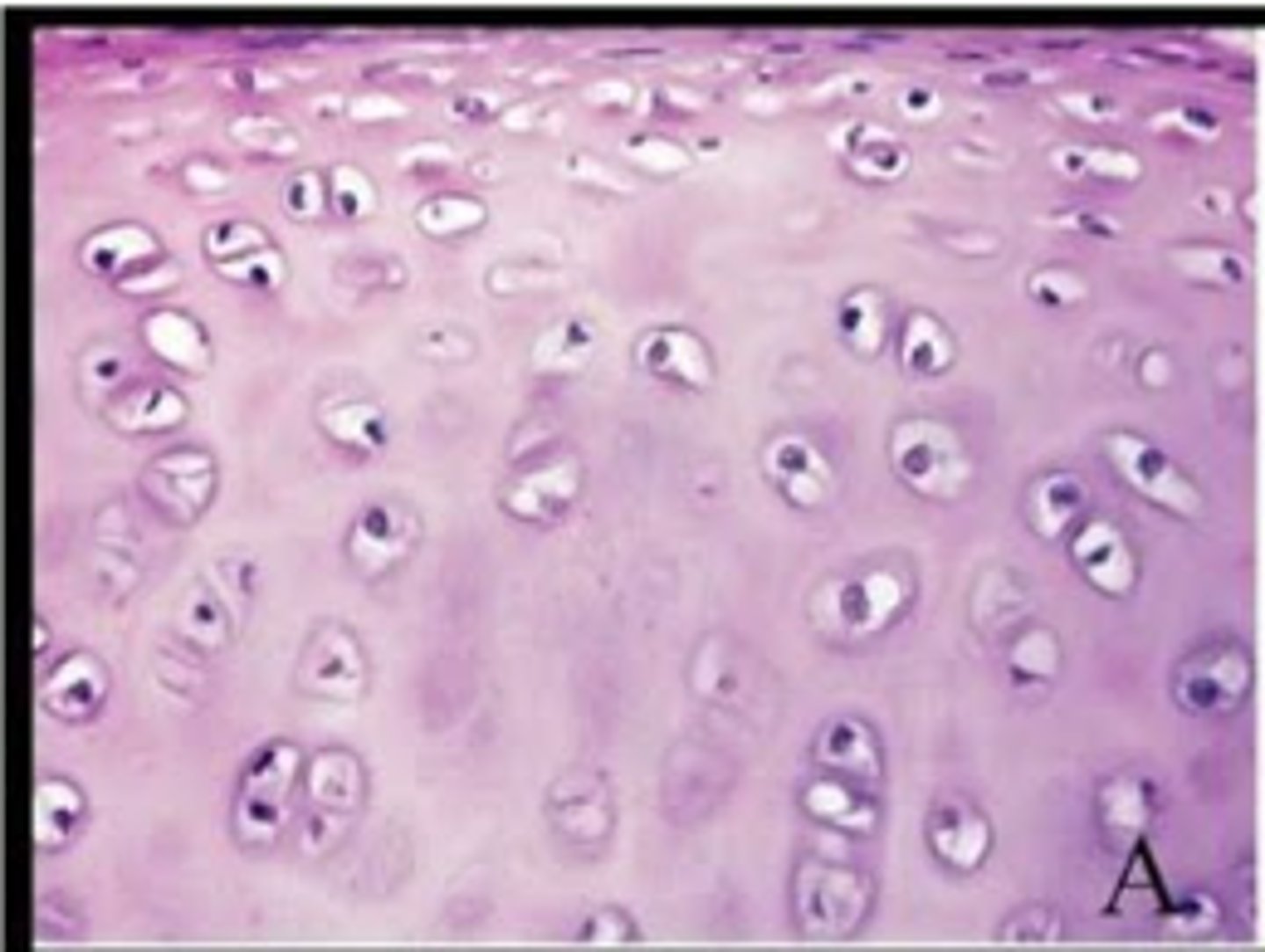
elastic cartilage
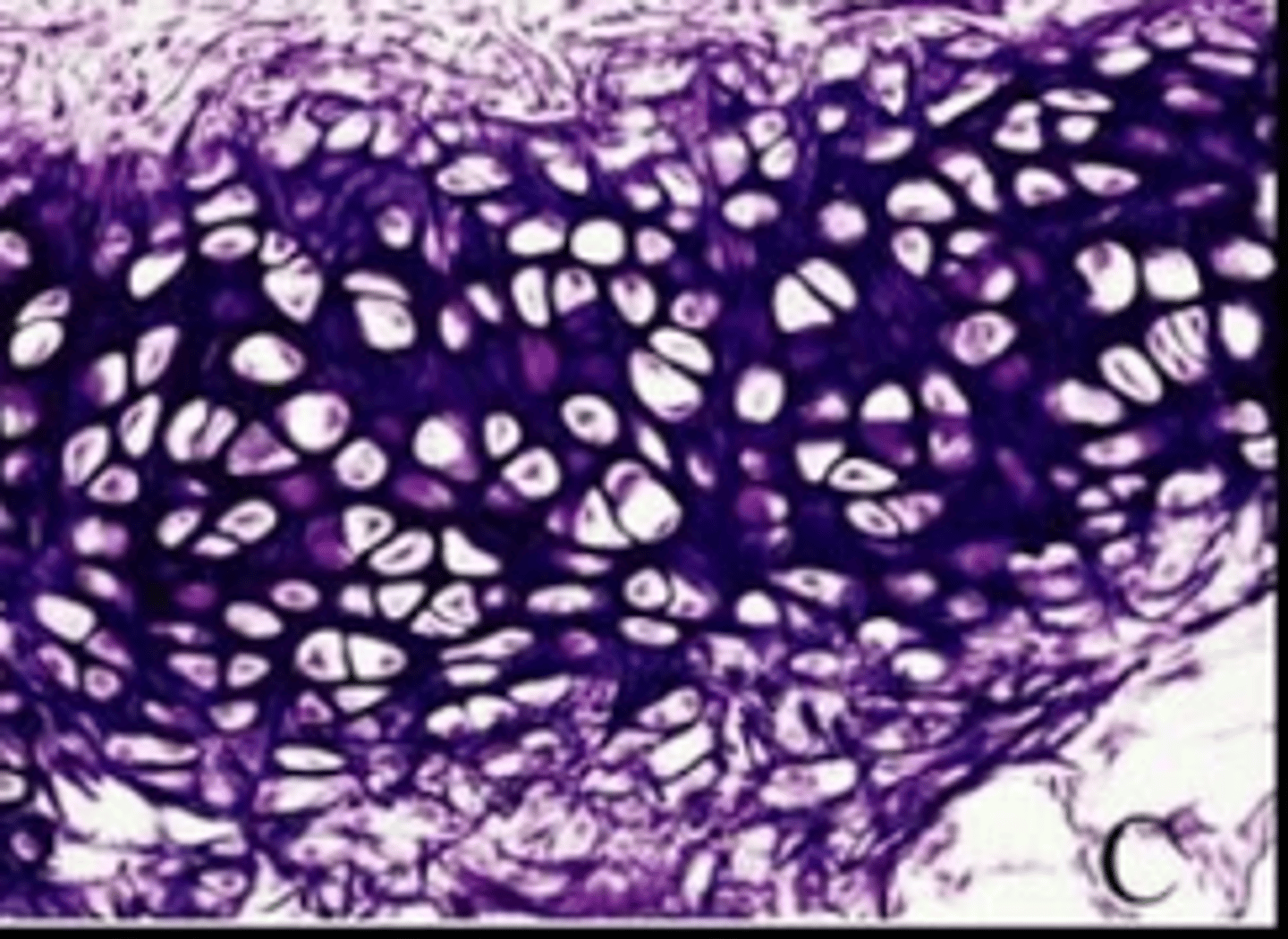
fibrocartilage
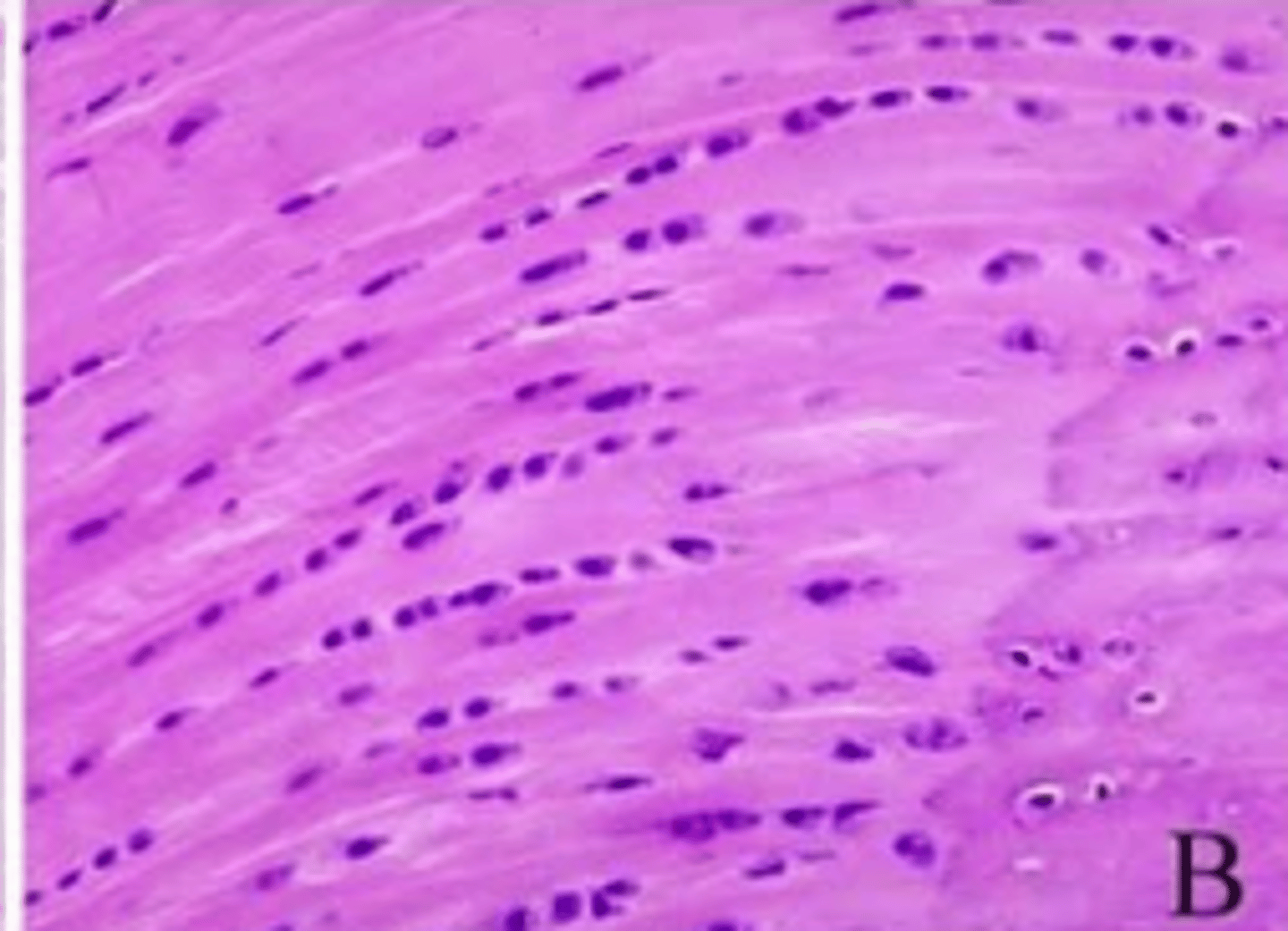
hyaline cartilage