Lecture 2 (1/20) - Cellular Biology Review
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Phospholipids
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tail
The Body Cavities
Cranial
Pleural + Pericardial= Thoracic
Diaphragm
Abdominal+ Pelvic= Abdominopelvic
Pericardial sac
tissue that surrounds the heart
How can phospholipids arrange themselves?
Bilayers
Micelles
Liposomes
Bilayer
forms a sheet
Micelles
droplets of phospholipids
Liposomes
have an aqueous center
Fluid Mosaic Model
describes the plasma membrane as a highly flexible, two-dimensional liquid (fluid) composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates arranged in a constantly shifting pattern (mosaic)
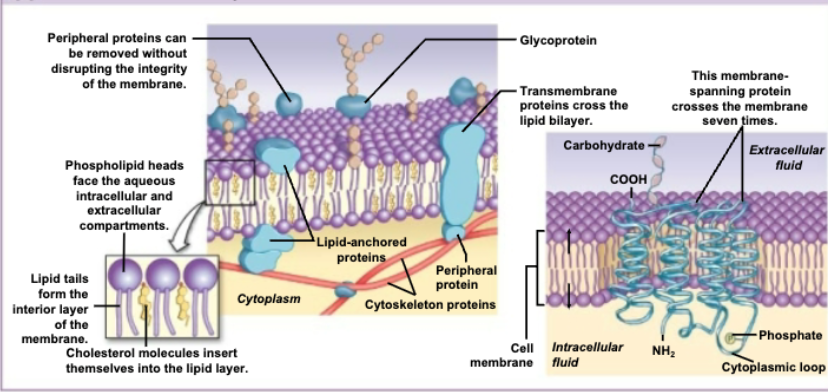
Cell Membrane Components
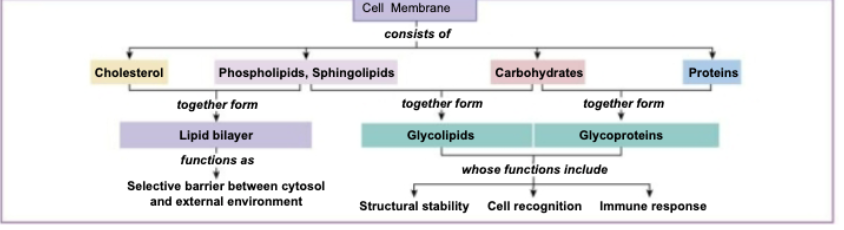
Cell Membrane consists of…
Cholesterol, Phospholipids, Carbohydrates, and proteins
Cholesterol + Phospholipids
Lipid bilayer- selective barrier between cytosol and external environment
Phospholipids + carbohydrates
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates + Proteins
Glycoproteins
Glycolipids + Glycoproteins
Structural stability
Cell Recognition
Immune Response
Cell Strcuture
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm Components
Cytosol
Membrane Organelles
Inclusions
Protein fibers
Membrane organelles
Mitochondria
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Inclusions
Lipid droplets
Glycogen granules
Ribosomes
Protein fibers
Cytoskeleton
Centrioles
Cilia
Flagella
Microvilli
Increase cell surface area
Microfilaments
form a network just inside the cell membrane
Microtubules
the largest cytoskeleton fiber
Intermediate fialments
myosin and keratin
Peroxisomes
contain enzymes that break down fatty acids and some foreign materials
Lysosomes
small spherical storage vesicles that contain powerful digestive ensymes
Centrioles
are made from microtubules and direct DNA movement during cell division
Mitochondira
ATP production
Golgi Apparatus and Vesicles
participates in protein modification and packaging.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
is a network of interconnected membrane tubes that are a continuation of the outer nuclear membrane.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
main site of protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
synthesizes lipids and, in some cells, concentrates and stores calcium ions.
Protein Synthesis: Step 1
mRNA is transcribed from genes in the DNA
Protein Synthesis: Step 2
mRNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to cytosolic ribosomes, initiating protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis: Step 3
Some proteins are released by free ribosomes into the cytosol or are targeted to specific organelles.
Protein Synthesis: Step 4
Ribosomes attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum direct proteins destined for packaging into the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Protein Synthesis: Step 5
Proteins are modified as they pass through the lumen of the ER
Protein Synthesis: Step 6
Transport vesicles move the proteins from the ER to the Golgi Apparatus
Protein Synthesis: Step 7
Golgi cisternae migrate towards the cell membrane.
Protein Synthesis: Step 8
Some vesicles bud off the cisternae and move in a retrograde or backward fashion
Protein Synthesis: Step 9
Some vesicles bud oof to form lysosomes or storage vesicles
Protein Synthesis: Step 10
Other vesicles become secretory vesicles that release their contents outside the cell.
Cell Junctions
Connect one cell with another cell with membrane spanning proteins.
Gap junctions
communicating
Tight junctions
occluding
Desmosome
Cell-to-cell anchoring junction
Cell Junctions
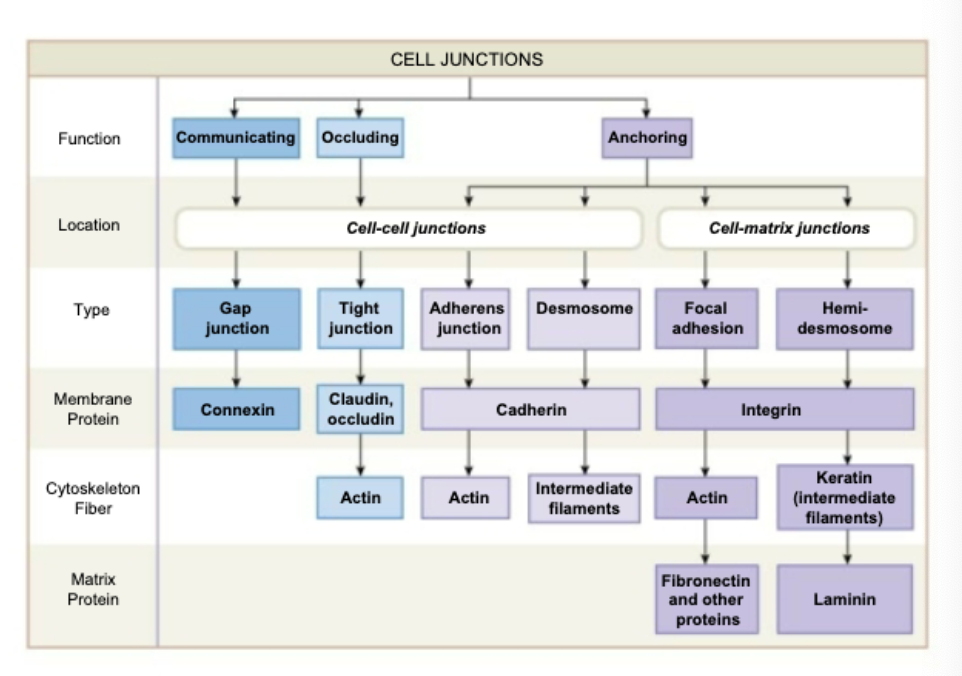
Epithelial tissue
body tissue that covers all internal and external body surface, lines cavities and hollow organs, and form glands.
Exchange epithelium
these thin, flat cells allow movement through and between the cells.
Transporting Epithelium
selectively move substances between a lumen and the ECF
Ciliated Epithelium
Beating cilia create fluid currents
Protective Epithelium
stacked layers of cells that are constantly being replace.
Secretory
make and release a product.
Exocrine Glands
organs that produce and secrete substances directly into an epithelial surface via a duct.
Endocrine Glands
ductless organs of the endocrine system that synthesize and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Loose Connective Tissues
very flexible with multiple cell types and fibers.
Bone and Cartilage
forms when osteoblasts deposit calcium phosphate crystals in the matrix.
firm but flexible matrix secreted by cells called chondrocytes
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
collagen fibers of tendon are densly packed into parallel bundles.
Blood
consists of plasma plus red and white blood cells and the cell fragments called platelets
Adipose tissue
in white fat, the cell cytoplasm is almost entirely filled with lipid droplets.
Hair follicles
secrete the nonliving keratin shaft of hair
Sebaceous gland
exocrine glands that secrete a lipid mixture
Arrector pili muscles
pull hair follicles into a vertical positions when the muscles contracts (goose bumps)
Sweat gland
secrete a dilute salt fluid to cool the body
Empidermis
consists of multiple cell layers that create a protective barrier
Dermis
Loose connective tissue that contains exocrine glands, blood vessels, muscles, and nerve endings.
Hypodermis
contains adipose tissue for insulation
Apocrine glands
release waxy or viscous milky secretions in response to fear or sexual excitement.
Hemidesmosomes
tie epidermal cells to fibers of the basal lamina
Basal lamina
an acellular layer between epidermis and dermis