Thermodynamics
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Momentum
Used to analyze collisions and explosions
Impluse
Change in momentum
In elastic collisions, kinetic energy is a) conserved or b) not conserved.
A) Conserved
In elastic collisions, momentum is a) not conserved or b) conserved.
B) Conserved
What do objects do in elastic collisions? (microscopic)
Bounce off each other
In inelastic collisions, kinetic energy is a) conserved or b) not conserved.
B) Not conserved
In inelastic collisions, momentum is a) conserved or b) not conserved.
A) Conserved
What do objects do in inelastic collisions? (microscopic)
Bounce off of each other
What do objects do in inelastic collisions? (macroscopic)
Stick together
Pressure (Pa)
The amount of force per area
Kinetic Energy (J)
Energy of motion
Heat
The transfer of thermal energy into a system
Cooling
The transfer of thermal energy out of a system
After many collisions of molecules from different systems, it will reach __________ _____________.
Thermal Equilibrium
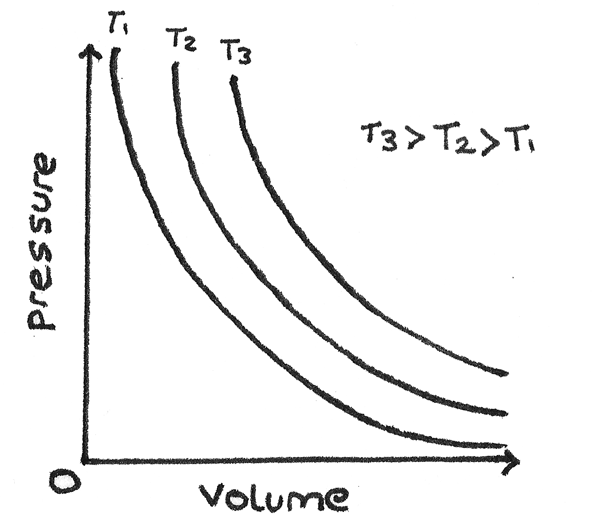
Boyle’s Gas Law
Describes the relationship between pressure and volume
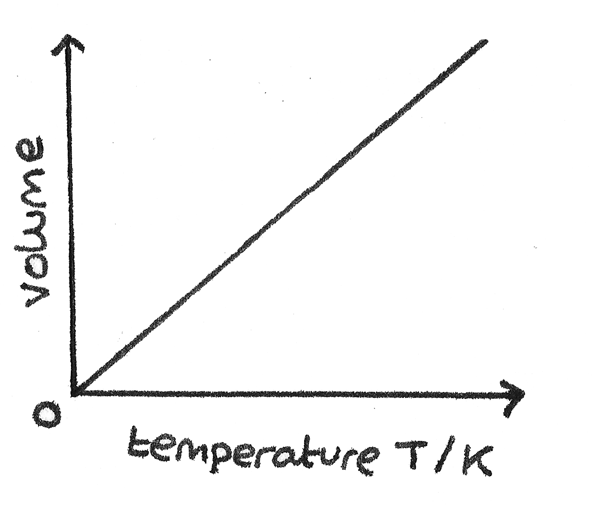
Charles’ Law
Describes the relationship between temperature and volume
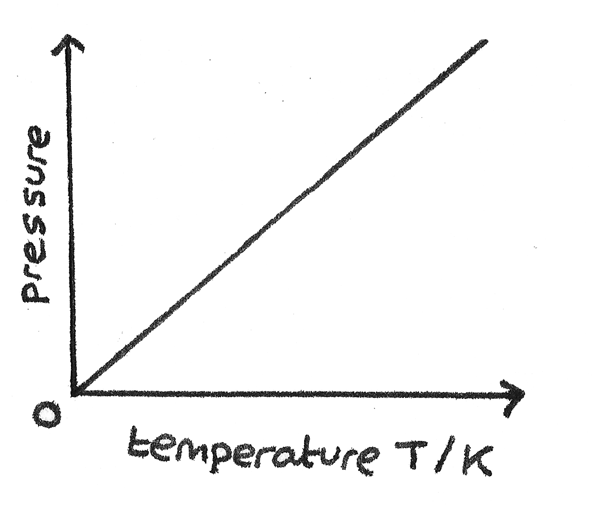
Pressure Law
Describes the relationship between pressure and temperature
Are gas particles a) spaced out , b) close together, or c) somewhere in the middle?
A) Spaced out
Gas particles move _______ in a container.
Randomly
Are collisions between gas particles inelastic or elastic?
Elastic
As the temperature of gas particles increases, the average speed of the particles __________.
Increase
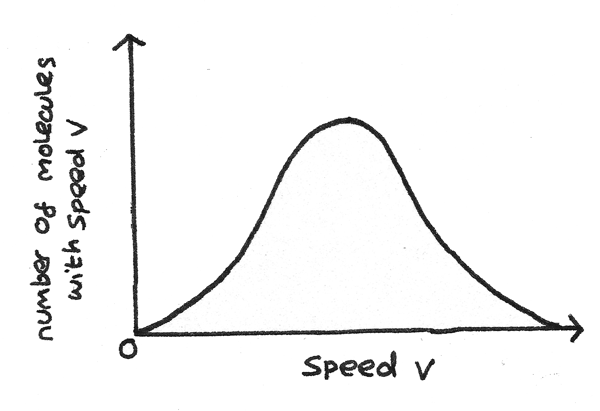
Maxwell Speed Distribution
Describes the distribution of speeds among particles in a gas
Mass (kg)
Amount of matter
Volume (m3)
Space occupied
Density (kg/m3)
Amount of matter per space
Solids
Constant shape
Constant mass
Constant volume (cannot be compressed)
Liquids
Takes shape of container
Constant mass
Constant volume (cannot be compressed)
Gas
Constant mass
Can be compressed
Ideal Gas Laws (List Four)
Gas particles move in random straight lines
Collisions between particles are elastic
The temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy
No intermolecular attraction between particles
At absolute zero, pressure is _______.
Zero
At absolute zero, ________ and _______ are at an all time low.
Entropy; Enthalpy
Conduction
Faster moving particles collide with slower moving particles and speed them up, increasing their temperature
Buoyancy
Force that pushes up on an object in water or air
Archimedes’ Principle
Buoyant force is equal in magnitude to the weight of the fluid displaced
Convection
Hot air rises
As a temperature of a fluid increases, its density _________.
Decreases
As the density of a fluid decreases, it experiences a larger ________ ________ and _____.
Buoyant force; rises
Radiation
Energy that moves from one place to another in a form that can be described as waves or particles
Internal Energy
Total energy of the systems
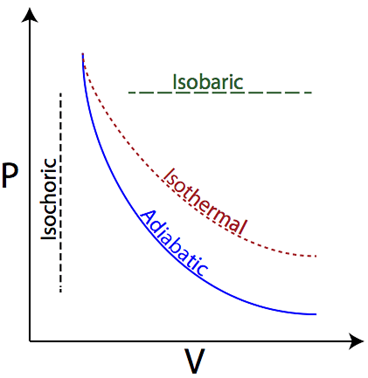
Isobaric
Pressure is constant
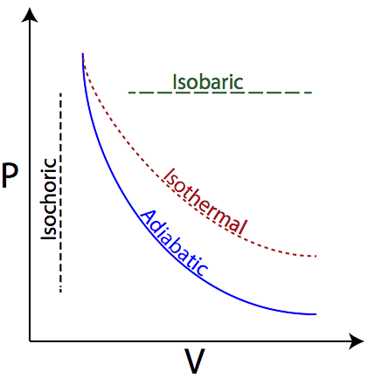
Isothermal
Temperature is constant; internal energy (U) = 0
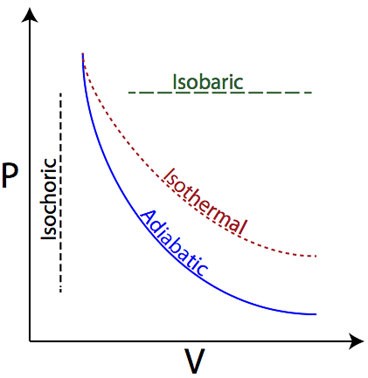
Isovolumetric (Isochoric)
Volume is constant; Work = 0
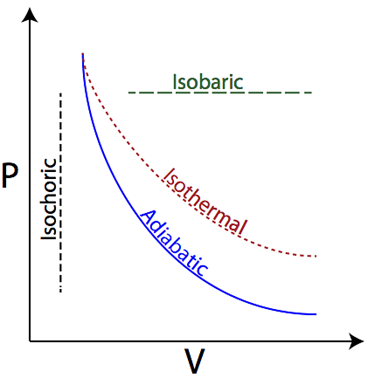
Adiabatic
No heat is exchanged
What sign is work when gas is expanding? (Work done on the gas)
Negative
What sign is work when gas is being compressed? (Work done on the gas)
Positive
When a closed system is moving clockwise, work is ____________.
Negative
When a closed system is moving counterclockwise, work is ____________.
Positive
In a close system, the internal energy (U) is A) Equal to the amount of work done on the gas, B) Equal to the amount of temperature, or C) Zero.
C) Zero
How do you figure the net work based off of a graph? (closed system)
It is the area inside the closed shape.
Specific Heat
Amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of a substance by one degree Celsius (or one Kelvin)
The rate at which energy transfers by conduction depends on…(Three Things)
The material
The physical dimensions
Temperature difference
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
If system A and B are in thermodynamic equilibrium with system C, then systems A and B are in thermal equilibrium with each other
Entropy
Measure of the disorder or randomness in a system
When does maximum entropy occur?
When a system is in thermodynamic equilibrium
Second Law of Thermodynamic
Any energy transfer or transformation, the total entropy of a closed system will either increase or remain the same; it cannot decrease
When is the work being done on the gas?
When the volume is decreasing or being compressed
When is work being done by the gas?
When the volume is increasing or being expanded