Histology 7: oral mucosa
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Oral Mucosa
The lining of the oral cavity, composed of various types of epithelium, including lining, masticatory, and specialized mucosa.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue characterized by multiple layers of cells, providing protection in areas such as the oral cavity.
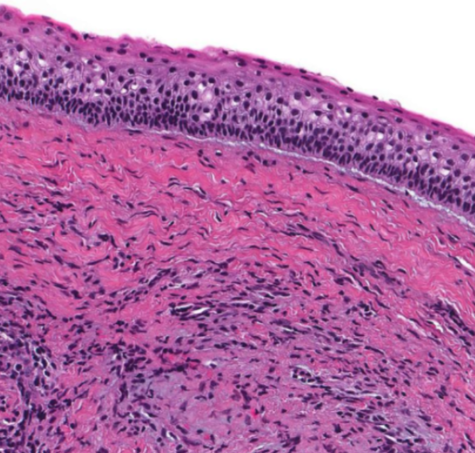
Lining Mucosa
The type of oral mucosa that covers areas like the floor of the mouth and cheeks, typically nonkeratinized and flexible.
Masticatory Mucosa
Oral mucosa that is keratinized and withstands the mechanical stress of chewing, located in areas like the hard palate.
Specialized Mucosa
Mucosa found on the surface of the tongue, containing papillae that have specialized functions such as taste.
Lamina Propria
The connective tissue layer beneath the epithelium, composed of papillary and reticular layers, providing support and nourishment.
Seromucous Glands
Glands that produce both serous (watery) and mucous (viscous) secretions, found in various locations in the oral cavity.
Vermilion Border
The red margin of the lips where the nonkeratinized mucosa meets the skin.
Keratinization
The process by which cells in the epidermis become filled with keratin and move upwards to form a tough, protective layer.
Free Gingival Groove
The groove that separates the free gingiva from the attached gingiva.
Dentogingival Epithelium
The epithelium that lines the sulcus and connects the gingiva to the tooth surface.
Parakeratin
A form of keratinized epithelium where nuclei are retained in the keratin layer.
Orthokeratin
A type of keratinized epithelium that lacks nuclei in the keratin layer.
Gingival Sulcus
The space between the tooth and the free gingiva, where plaque and bacteria can accumulate.
Periodontal Disease
An inflammatory disease affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth, which can lead to apical migration of gingiva.
Keratinized Mucosa
Mucosa that is covered with a layer of keratin, providing a barrier to protect underlying tissues.
Nonkeratinized Mucosa
Mucosa that does not have a keratin layer, often found in areas subject to less mechanical stress.
Von Ebner Glands
Serous glands associated with the circumvallate papillae that help wash away substances on the tongue to enhance taste.
oral cavity is lined by
stratified squamous epithelium
three variations of oral mucosa
lining mucosa- floor of mouth cheeks lips
masticatory mucosa- hard palate and gums
specialized mucosa- tongue surface.
lining mucosa
floor of mouth cheeks lips and soft palate
unattatched
nonkartatinized
soft and pliable
masticatory mucosa
hard palate, alveolar ridges, and gingiva
keratinized
attached mucosa
in primary contact with food when chewing
specialized mucosa
surface of tongue
keratinized papilla
structure of oral mucosa
similar to that of other mucosal tissues
important structures in mucosal tissue
lamina propria
deep reticular layer
submucosa
lining mucosa
thin layer of epithelium and underlying lamina propria
followed by spinous/ stratum spinosum layer
inner oral surface
non keratinized epithelium
seromucous glands (part of minor salivary glands)
lips have a _____ layer that distinguishes them as tissue transitions
vermillion
ectopic sebaceous glands
seen in buccal mucosa
not associated with hair follicles
known as fordyce granules
soft palate
highly vascularized lamina dura and more pink than epithelium of the hard palate
buccal mucosa
similar to lip and soft palate but with fat and mixed seromucous glands
ventral tongue
similar to other mucosa
submucosa has muscle and connective tissue fibers
attatched to floor of mouth loosely in comparison to ventral tongue
minor salivary glands on floor of mouth
right and left sublingual glands present
masticatory mucosa
thicker than nonkeratinized
keratin offers resistance to attrition
granular later (granulosum) and keratin layer (corneum) more prominent
keratin is tough and resistant to
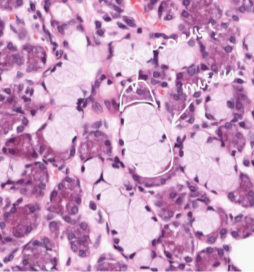
seromucus glands
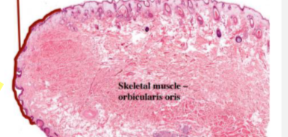
lip
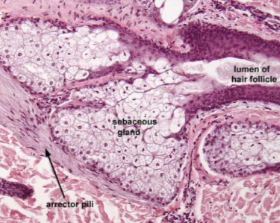
fordyce granule
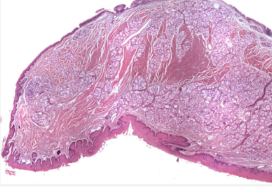
soft palate
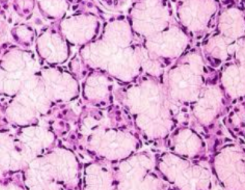
mucus glands with myoepithelium
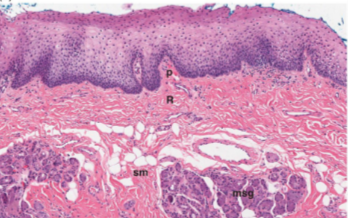
buccal mucosa
ventral tongue
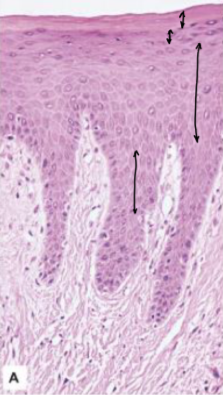
keratinized mucosa
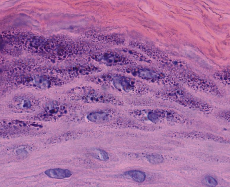
keratohyalin granules
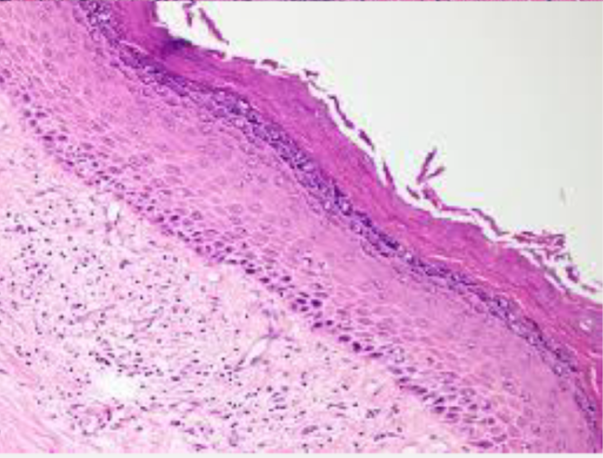
parakeratin
nuclei retained keratin
orthokeratin
nuclei absent from surface keratin
odontogenic keratocyst
lined by parakeratin w/ 25% recurrence rate
Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst
lined by orthokeratin w/ 2% recurrence
parakeratin
orthokeratin
reduced enamel organ epithelium and oral epithelium
fuse as the tooth erupts and result in the production of gingiva as the tooth continues eruption
gingiva divisions
free/marginal- encloses tooth and defines sulcus
attached- portion of epithelium attached to neck of tooth
interdental zone/groove- between two contact points
indistinct groove separating free and attached gingiva
free gingival groove
free/ marginal zone
gingival zone that encloses the tooth and defines the gingival sulcus
attached gingiva
portion of epithelium attached to the neck of the tooth
interdental zone/groove
gingival area between two teeth beneath the contact point
gingival sulcus
separates tooth from free gingiva
free and attached gingiva
keratinized
alveolar mucosa
nonkeratinized
attached gingiva is
stippled due to attachment sites to underlying alveolar bone
epithelium of gingiva
naturally sheds and exfoliates over time helping to prevent bacteria build up and form immunity to pathogens
upper gingival sulcus epithelium
not connected to root surface
sulcular epithelium
junctional epithelium
lower gingival sulcus epithelium
attached to root of tooth
dentinogingival epithelium
junction between tooth surface and gingival tissues
made of sulcular and junctional epithelium
sulcular/crevicular epithelium
filled with crevicular fluid
lines gingival sulcus
junctional epithelium
begins at the base of sulcus
attached to tooth surface via hemidesmosomes
hard palate
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
midline raphe with rugae laterally
incisive papilla
mucus glands
traction bands (anchoring palatal mucosa to bone) in the lamina propria of rugae
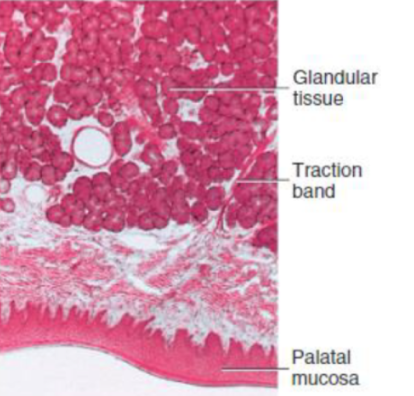
hard palate
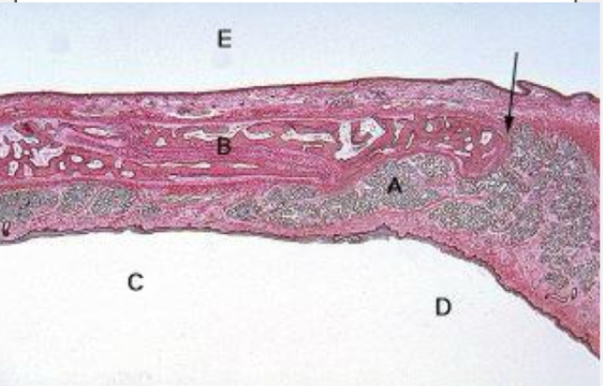
palate
hard palate
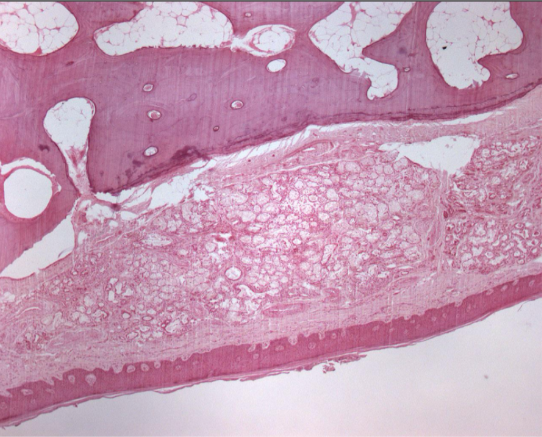
recurrent intraoral herpes
HSV-I
exclusively occurs on keratinized mucosa
aphthous ulcers
idiopathic occurring on nonkeratinized mucosa
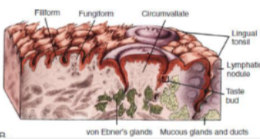
specialized mucosa
anterior of tongue including all epithelial papilla
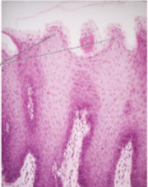
filiform papilla
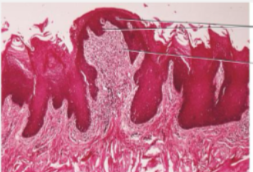
fungiform papilla
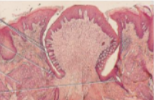
circumvallate papilla
foliate papilla
von ebner glands
under circumvallate papilla
aging affects
oral epithelium becomes thinner and fragile
gradual atrophy of minor salivary glands
fibrosis increases
repair reduces, healing time increased
apical migration of gingiva