Sinuses
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
paranasal sinuses
mucosa-lined, air-filled cavities located in 4 of the orbital bones; decrease weight of skull and add resonance to voice; communicate with nasals cavity via small aperatures
frontal
sinus located in frontal bone, on each side of the midline and superior to the orbit
A
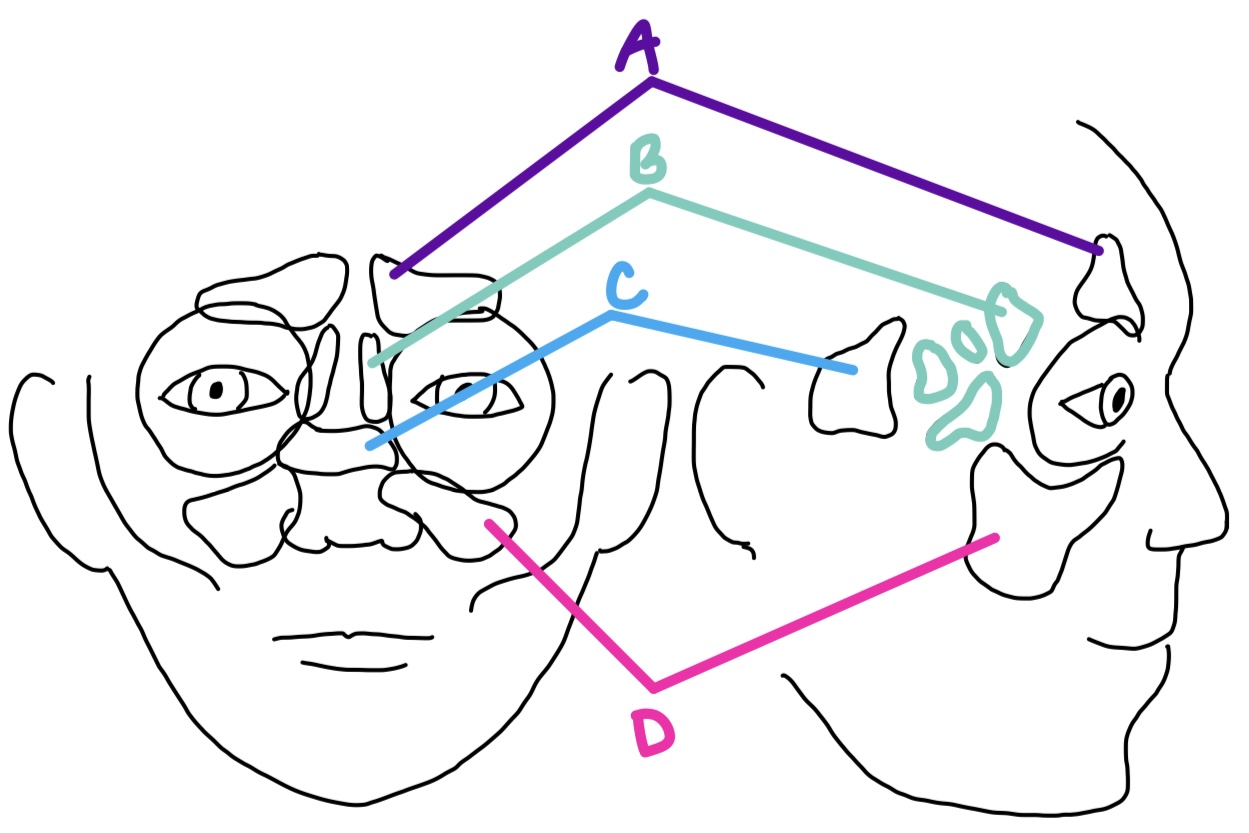
maxillary
largest sinus, located in each maxillary bone and inferior to the orbits
D
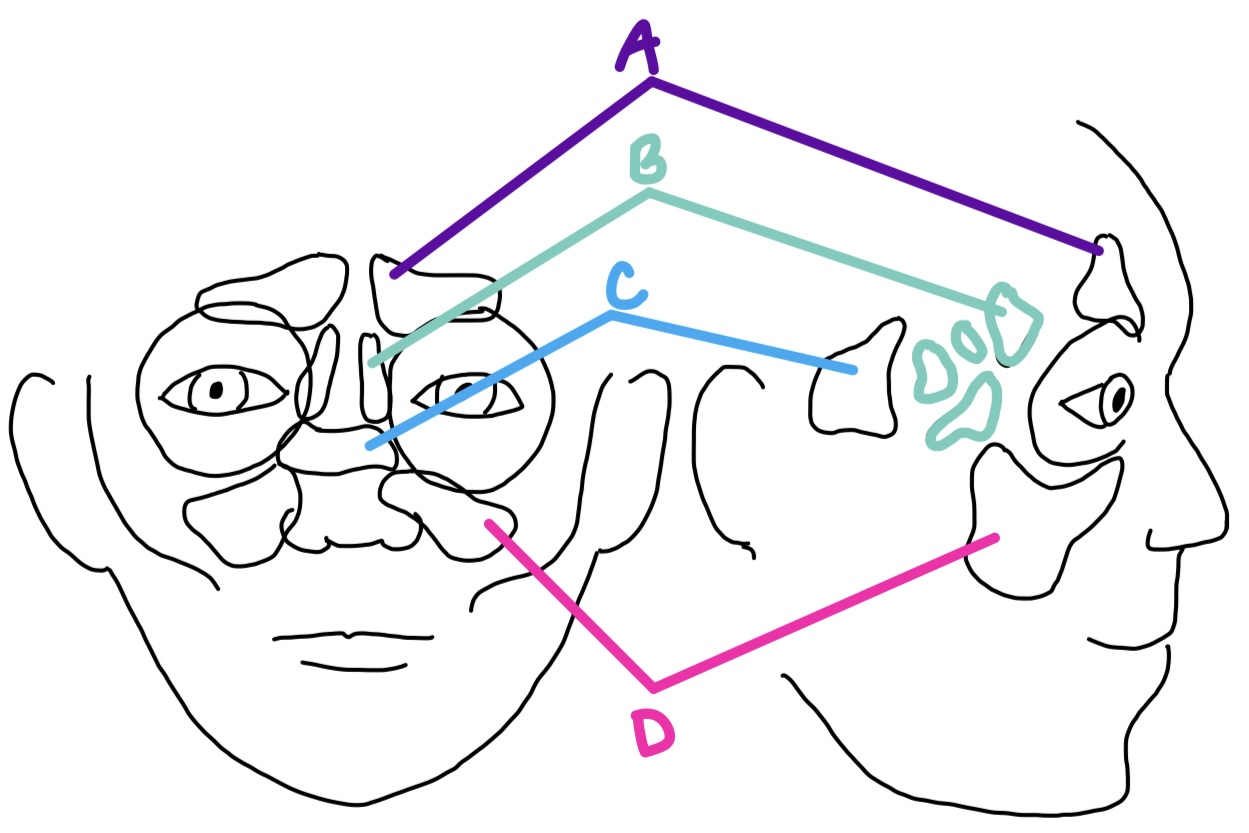
ethmoid
sinus with several air cells on both sides of perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, medial to the orbits
B
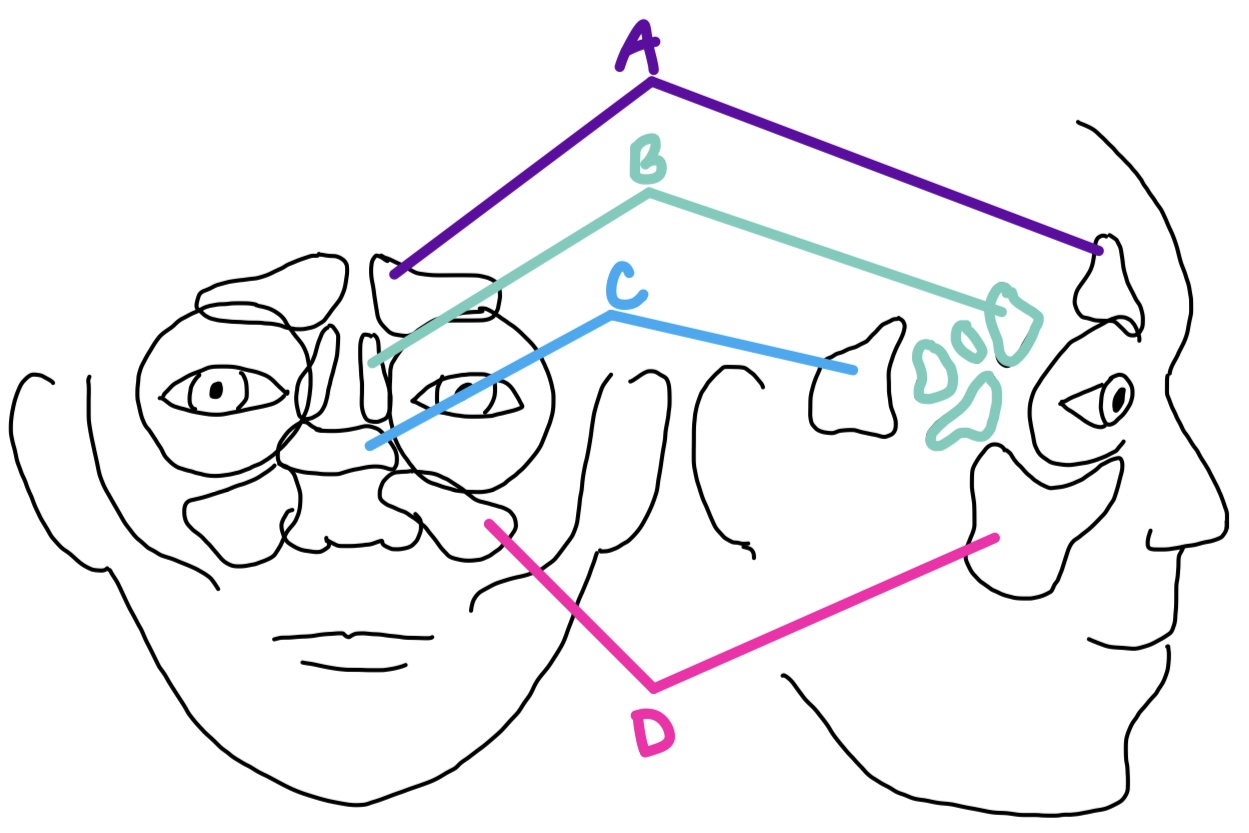
sphenoid
sinus in the body of the sphenoid, posterior & medial to orbits
C
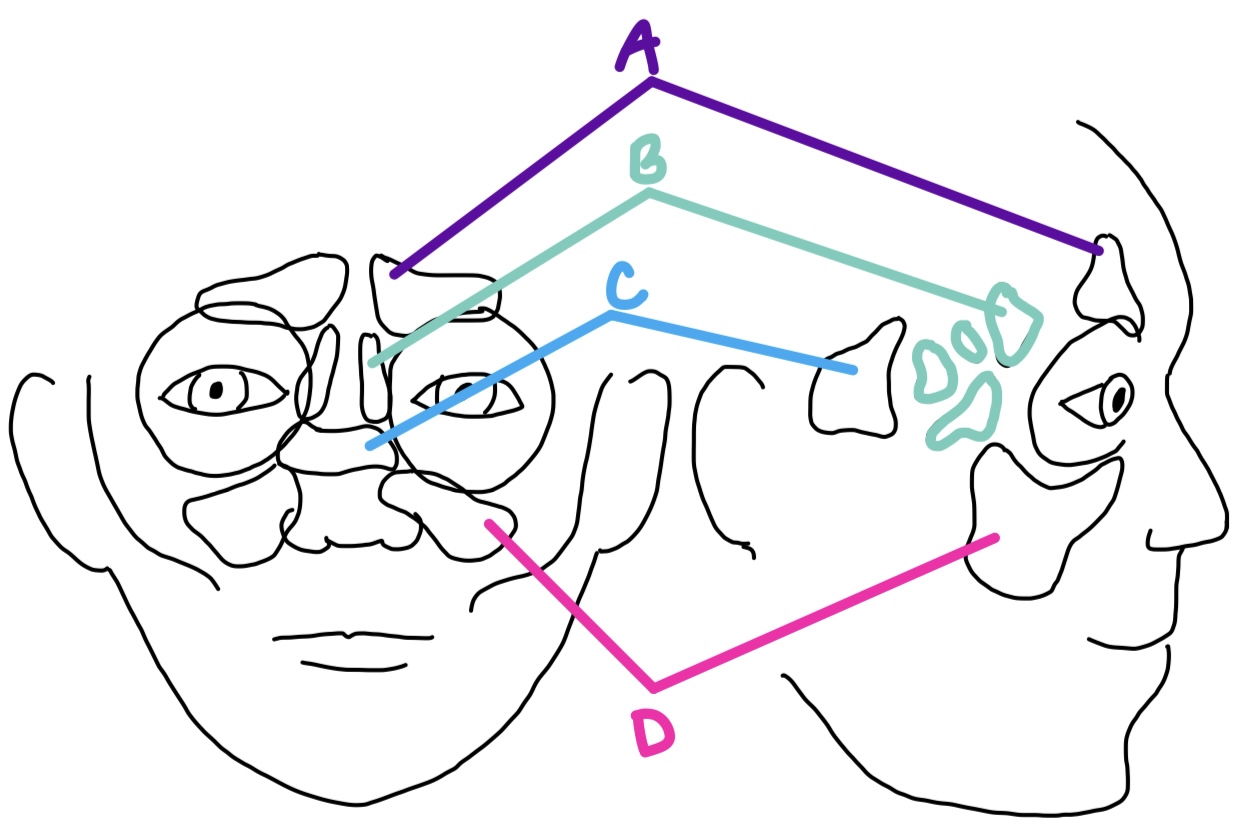
orbital cellulitis
spreading of sinusitis to the orbit, typical of ethmoid sinuses: ocular motility is affected; proptosis is key sign
connective tissue
arranged in a complex network that serves to line, cover, and separate orbital structures; to anchor soft tissue structures to bone, and to compartmentalize areas
periorbita (orbital periosteum, orbital fascia)
covers bones of orbit; serves as attachment site for muscles, tendons, and ligaments & is a support structure for the blood supply to the orbital bones
loose, sutures, foramina
periorbita connection to orbital bones is _______ except at _______ & _______
annulus of Zinn
where the periorbita is continuous with the fascial epimysium that envelops each rectus muscle along its entire length
orbital septum
dense connective tissue sheet, circular, runs from entire rim of orbit to tarsal plates; helps prevent facial infections from entering the orbit and maintains orbital fat in its place
Tenon’s capsule
sheet of dense connective tissue that encases the globe; lies b/t conjunctiva & episclera & merges with them anteriorly in the limbal area; acts as a barrier to prevent the spread of orbital infections into the globe
suspensory ligament of Lockwood
hammocklike sheet of dense connective tissue that runs from its attachment on the lacrimal bone at the medial orbital wall to the zygomatic bone at the lateral wall; helps support the globe, particularly in the absence of bones on the orbital floor
fat
spaces not occupied by ocular structures, connective tissue, nerves, or vessels are filled with ______
4
how many adipose tissue compartments are normally located within muscle cone surrounding optic nerve?
exophthalmos (proptosis)
protrusion of the globe; can be caused by a number of pathological conditions, inflammation, edema, tumors, and injuries
thyroid ophthalmopathy
what is the most common type of exophthalmos?
thyroid ophthalmopathy
causes proliferation of orbital fat and connective tissue, and lymphoid infiltration, hypertrophy of the EOMs, and protrusion of the globe and eyelid retraction
exophthalmometer
assesses the amount of protrusion of each eye from the orbital rim
preseptal cellulitis
inflammatory condition that affects tissues of eyelid; characterized by swelling, tenderness, and erythema; swelling is confined to the eyelid; no proptosis; ocular motility is unaffected
floor
which part of the orbit is most susceptible to a classic blow-out fracture?
blow-out fracture
causes damage to inferior EOMs; clinical signs include orbital swelling, ecchymosis, anesthesia of area innervated by infraorbital nerve, diplopia; typically occurs in thin region along infraorbital canal