*1.4 Internet Protocols
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
ICMP
Sends messages between devices to try to get responses back to ensure it’s on/alive
Ex. the ping command uses this
Can give response or TTL expiration warnings
TCP
Connection-oriented
Reliable
Flow speed control
Can resend/reorder packets
UDP
Connectionless
Unreliable
No flow speed control
No error recovery/verification/resending of data
GRE
Creates a tunnel between two devices connected with a VPN
Encapsulates data in an IP packet and send it over a GRE tunnel
This doesn’t do the encryption
Concentrator
Purpose-built device or software (or built into firewall) for encrypting/decrypting VPN connections
Has cryptographic hardware
IPSec
Protocol that provides VPN encryption
Standardized; firewalls on either side of convo can communicate over the VPN tunnel
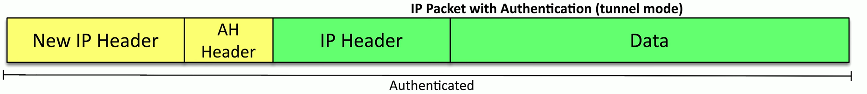
Authentication Header (AH)
An IPSec protocol
Validates info sent over an IPSEC tunnel
Everything is sent unencrypted, but with hashing for integrity
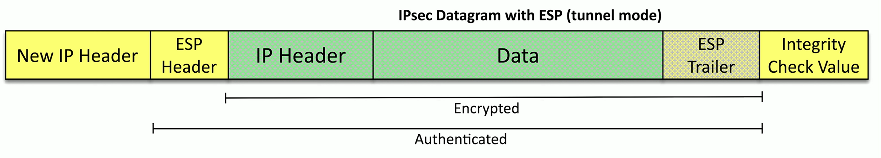
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
An IPSec protocol
Encrypts the original packet and the ESP trailer, and then we put a new IP header, an ESP header, and an integrity check value at the end of the packet
Encrypts and authenticates data
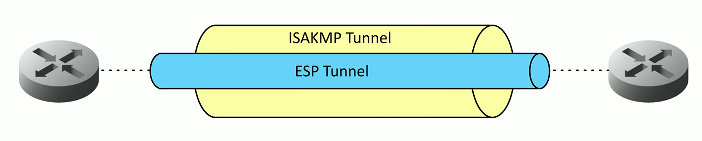
Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
Steps for both side of convo to agree on encryption/decryption keys
This agreement is the Security Association
Has 2 phases
IKE Phase 1 (ISAKMP)
Uses Diffie-Hellman to create shared secret key
UDP/500; ISAKMP protocol

IKE Phase 2
Coordinates ciphers and key sizes
IPSec transport mode
IPSec header/trailer surround the data portion; only the data is encrypted
IP Header is in the clear; can see destination of the packet if captured
Less secure

IPSec tunnel mode
IPSec header and trailer put around both the original data and the original IP header; encrypts everything
Much more secure; used more often
Nothing from the original packet is sent in the clear; even if captured, you’d never see the destination/data
