Intro to Earth Science
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What is a mineral?
Naturally occurring
Inorganic solid
Definite chemical composition
Highly ordered atomic arrangement
The 6 properties of Minerals
Color
Streak
Hardness
Cleavage/Fracture
Reaction to acid
Density
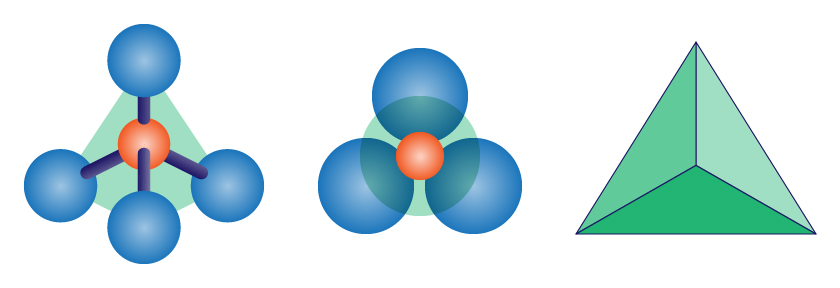
The two elements in a silicate tetrahedron
Silicon (1)
Oxygen (4)
Polymorphs
Minerals with the same composition but different atomic structures.
The 9 main mineral groups
Native elements
Oxides
Hydroxides
Sulfides
Sulfates
Carbonates
Phosphates
Halides
Silicates
The two most abundant elements in the earth’s crust
Oxygen
Silicon
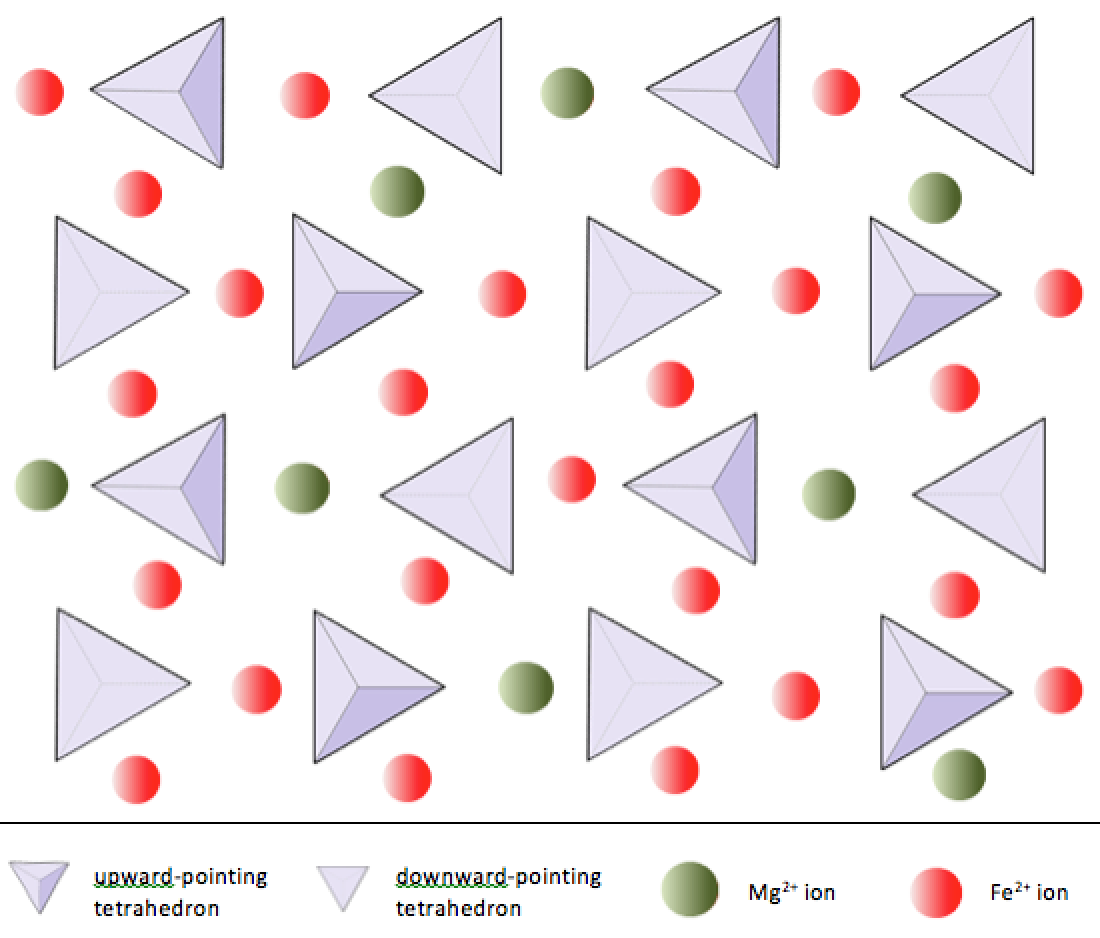
Isolated tetrahedrons
Where the tetrahedrons are not bonded to each other instead they are bonded to different elements (i.e. olivine).
Single chain tetrahedrons
Where the tetrahedrons are bonded into a chain (i.e. pyroxine)
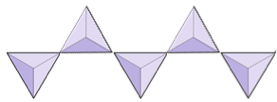
Double Chain tetrahedrons.
Where the tetrahedrons are in two chains bonded to each other. (i.e. amphiboles)
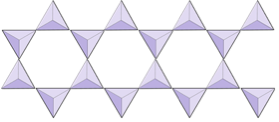
Sheet tetrahedrons
Where the tetrahedrons are bonded into sheets (i.e mica, biotite, and clay)
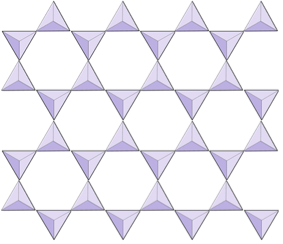
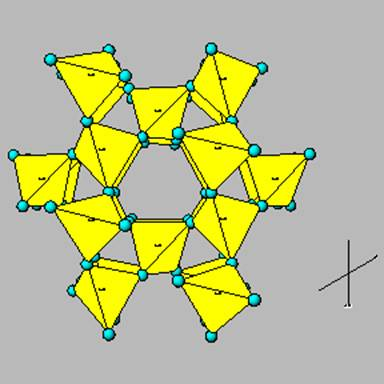
3-D Network tetrahedrons
Where the tetrahedrons are bonded in a complex three dimensional network (i.e. felspar, quartz)
Solid solution series
Where an ion substitutes for another in the crystal structure.
Rules for mineral construction
Similar ionic radius
Similar charge
Igneous rock formation
The cooling and solidification of molten liquid rock.
What does Igneous rock color tell you?
Chemical composition.
What two things does Igneous grain size tell you?
Speed of cooling
Intrusive or extrusive cooling
Where do intrusive igneous rocks form?
Inside the earth’s crust.
Where do extrusive igneous rocks form?
On the surface of earth’s crust.
Igneous Phaneritic rock
An igneous rock with large crystals that can be seen by the naked eye. (i.e. granite)
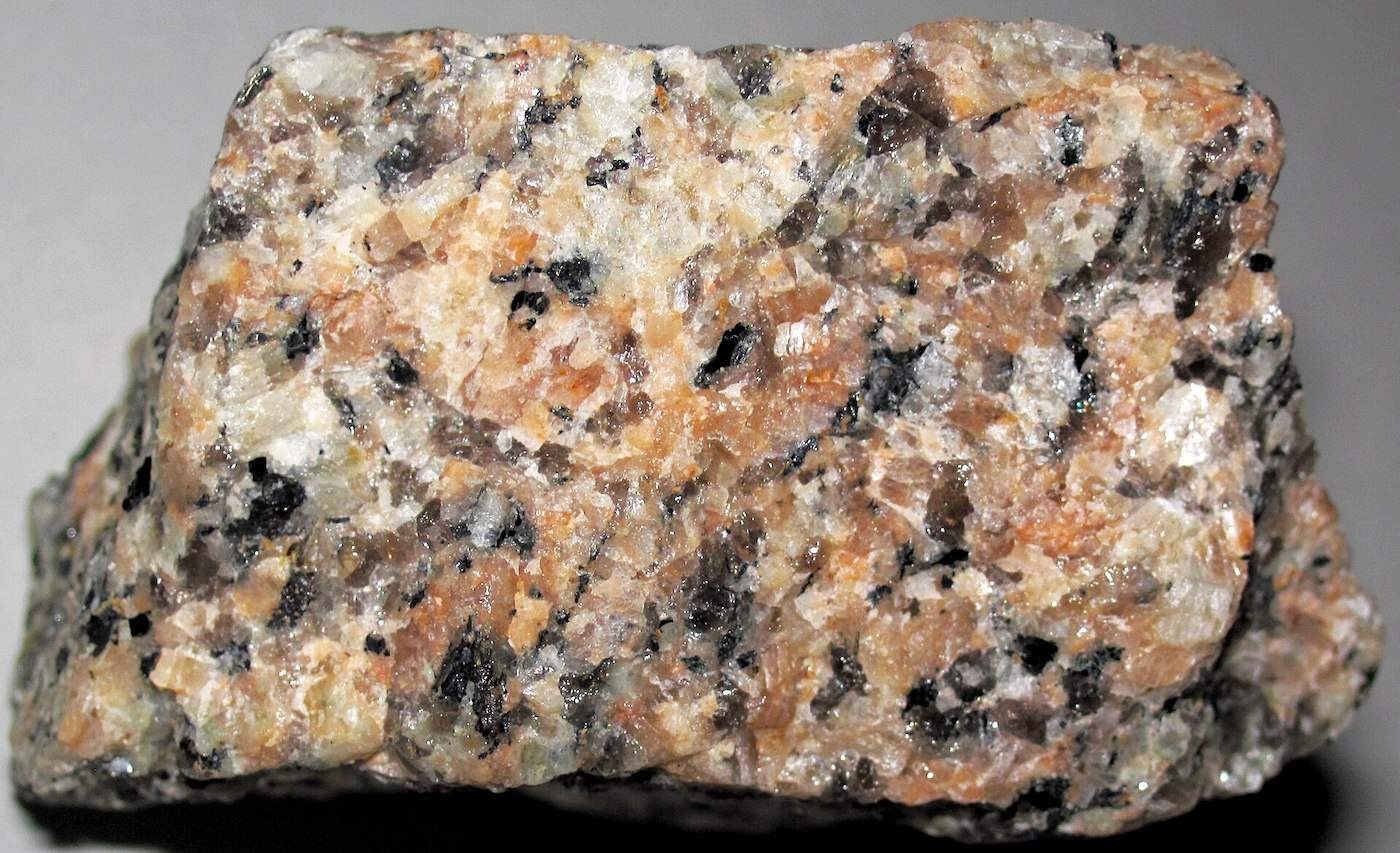

Igneous Aphanitic rock
An igneous rock with fine crystals that cannot be seen by the naked eye. (i.e. andesite, basalt)
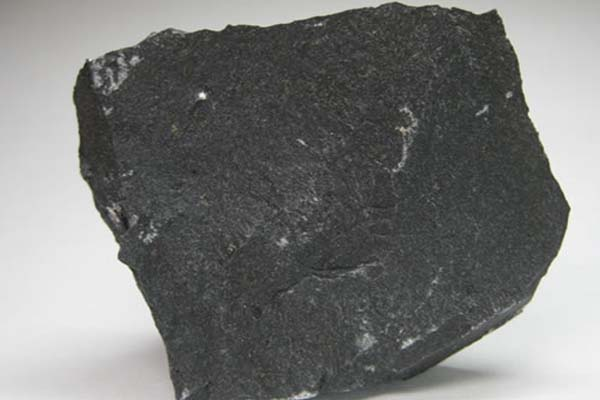

Igneous Pegmatitic rock
An igneous rock with exceptionally large crystals (i.e. topaz, fluorite)

Igneous Glassy rock
An igneous rock without specific crystal grains and has a glassy texture (i.e. obsidian)

Igneous Vesicular rock
An igneous rock that contains holes that were caused by gas (i.e. pumice)

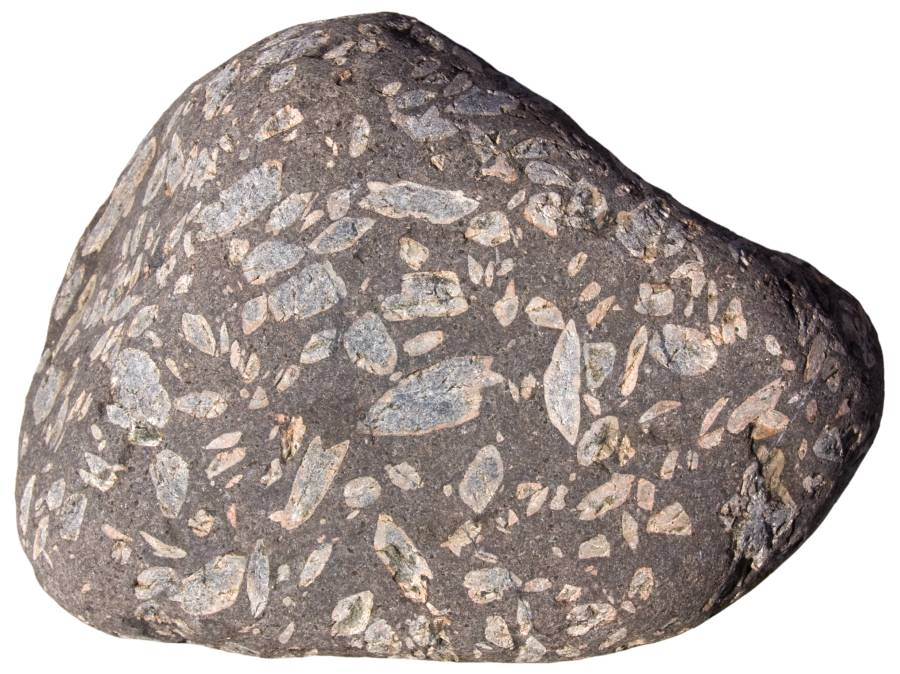
Igneous Porphyritic rock
An igneous rock with larger crystals visible crystals and finer groundmass (i.e. andesite)

Ultramafic Igneous Rocks
Rocks that are made of mostly mafic materials like olivine and extremely little in felsic materials.
What color are mafic rocks usually?
Dark to Black
What color are felsic rocks usually?
Light to medium grey
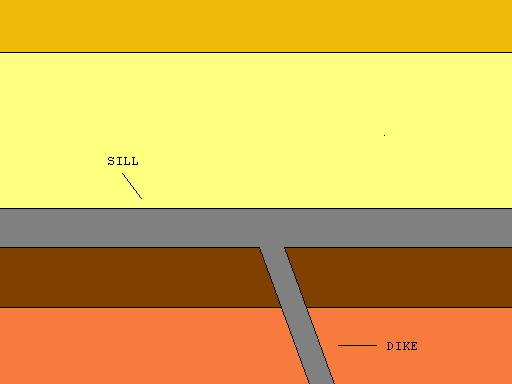
Sill intrusion
When magma intrudes between layers of rock.
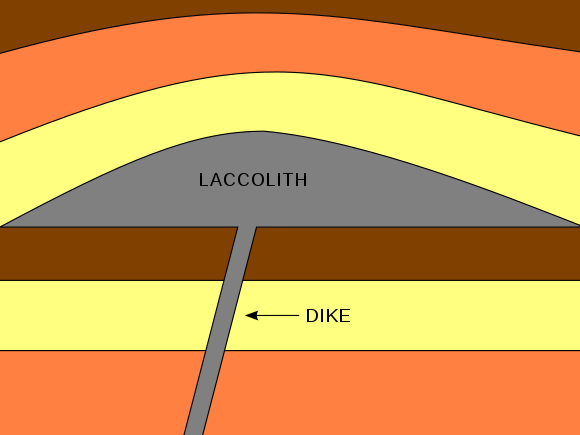
Laccolith intrusion
A upper-crust intrusion that creates a dome shape.
Batholith intrusion
A very large lower-crust intrusion.
Dike intrusion
An intrusion that usually runs perpendicular they can also feed magma into other intrusions.
Bowen’s Reaction Series
A series that describes which minerals crystalize first when magma cools.
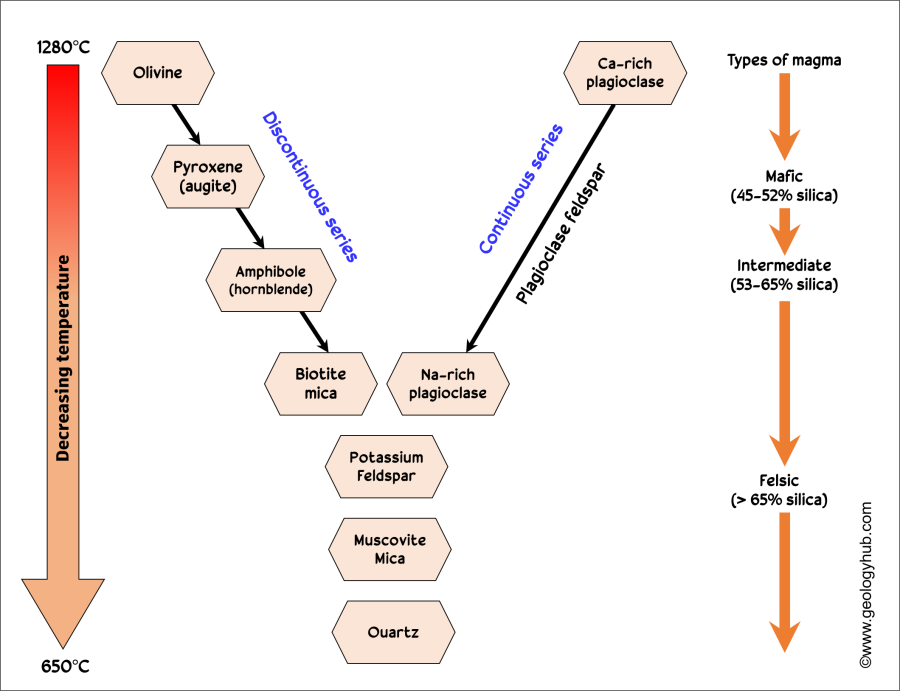
What is the first to crystalize in Bowen’s Reaction Series?
Olivine
What is the last to crystalize in Bowen’s Reaction Series?
Quartz
The 4 transporting agents of sediment
Water
Wind
Landslides
Glaciers
The 5 properties of sedimentary rocks.
Grain size
Angularity/Roundness
Sorting
Bedding Features
Fossils

What direction is the current flowing?
One direction (unidirectional)

What direction is the current flowing?
Two directions (bidirectional)
What can grain size tell you about a sedimentary rock?
Corse — High energy environment (i.e. fast stream)
Fine — Low energy environment (i.e. slow stream)
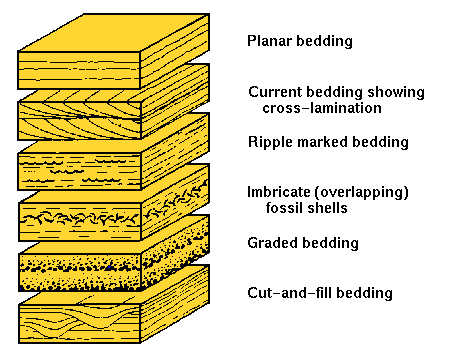
Sedimentary bedding
The layering of sediment to create bedding in the rock produced.
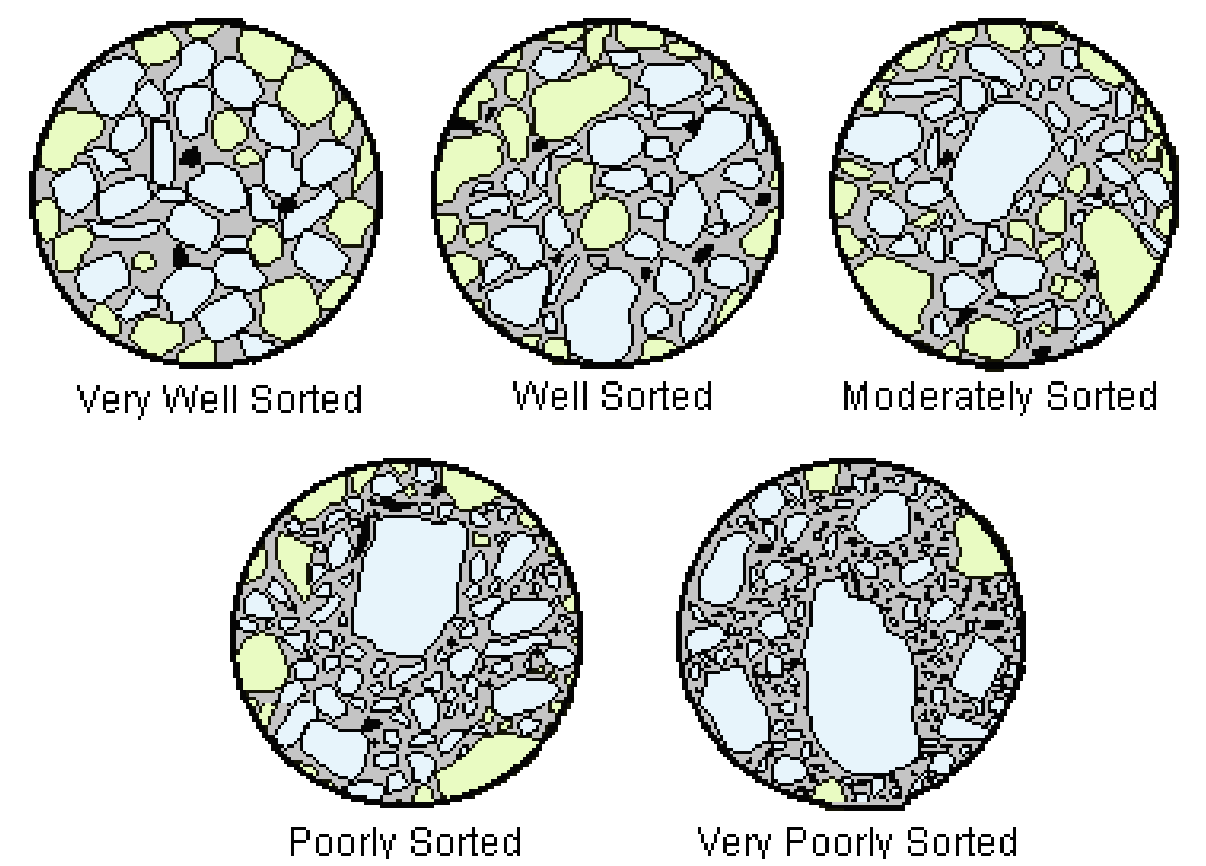
Sorting
A concept that describes the quality of how sediment grains are sorted.
Weathering
Weathering of pre-existing rocks into smaller sediments or ions.
Transport
The movement of sediment from its origin.
Deposition
When sediment is deposited.
Compaction
When the deposited sediment is compacted and packed together.
Lithification
In the process, sediments are converted to rock by pressure.
Shape of sediment grains
Angular — The origin of the sediment is close
Rounded — The origin of the sediment is farther away
Inorganic Chemical Sedimentary Rocks
A rock that is formed when water with dissolved ions evaporates (i.e. rock salt)
Biochemical Sedimentary Rocks
A rock that is formed by organisms pulling ions out of water to form shells. When the organism dies the shells become sediment that becomes compacted (i.e. limestone, coquina)
Detrital Sedimentary Rocks
A rock that is formed by the cementation of solid rock fragments (i.e. conglomerate)
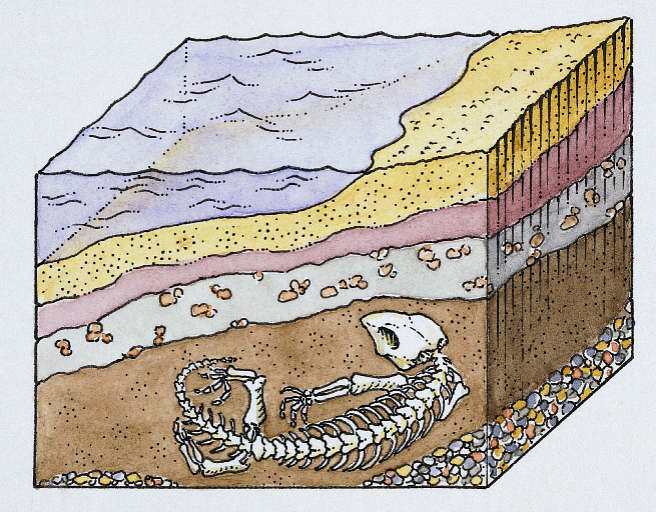
Sedimentary Fossils
The process where remains of organisms get compacted with sediments to become fossils.
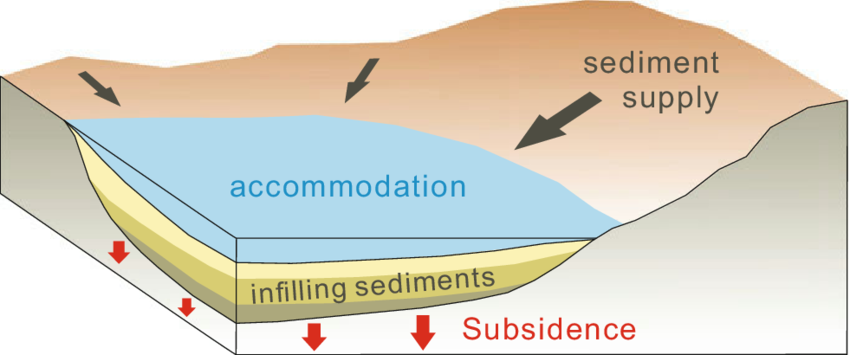
Sedimentary basins
Where parts of the earth’s crust sinks and sediments collect to create a large section of sedimentary rocks.
Metamorphosis
Alteration of pre-existing rock due to increases in pressure/temperature to form a new rock
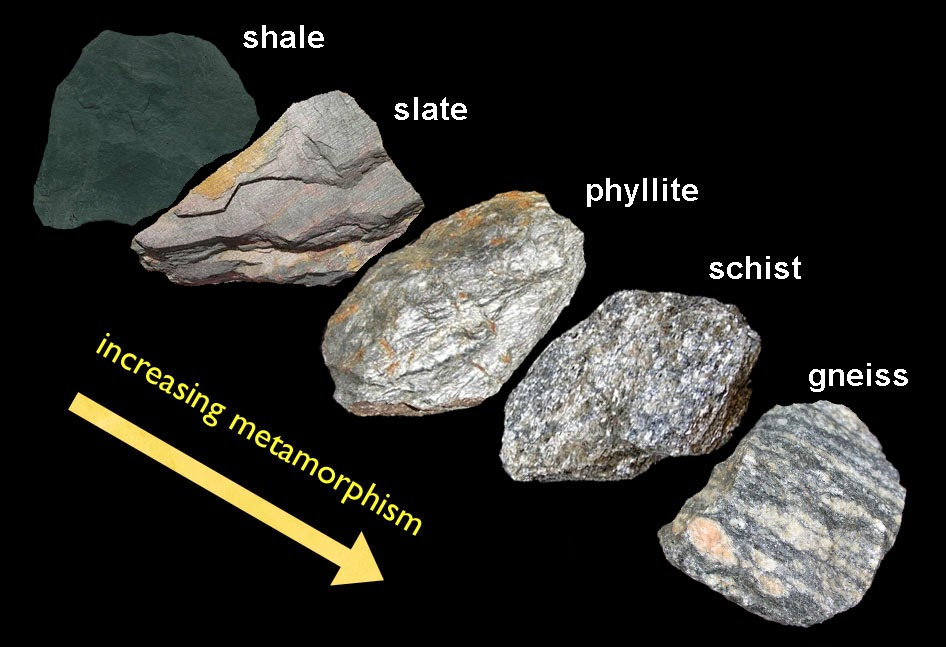

Foliation
Layering due to alignment of the minerals in metamorphic rock

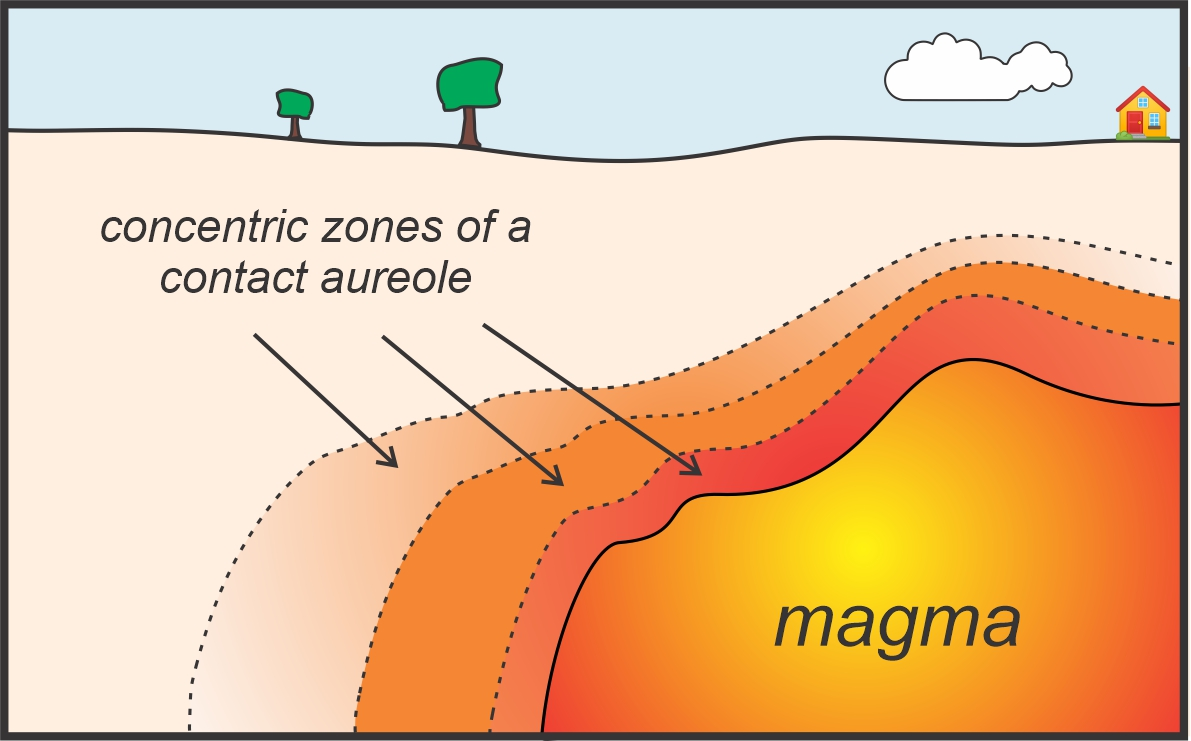
Contact Metamorphism
Small scale metamorphism due to igneous intrusions.
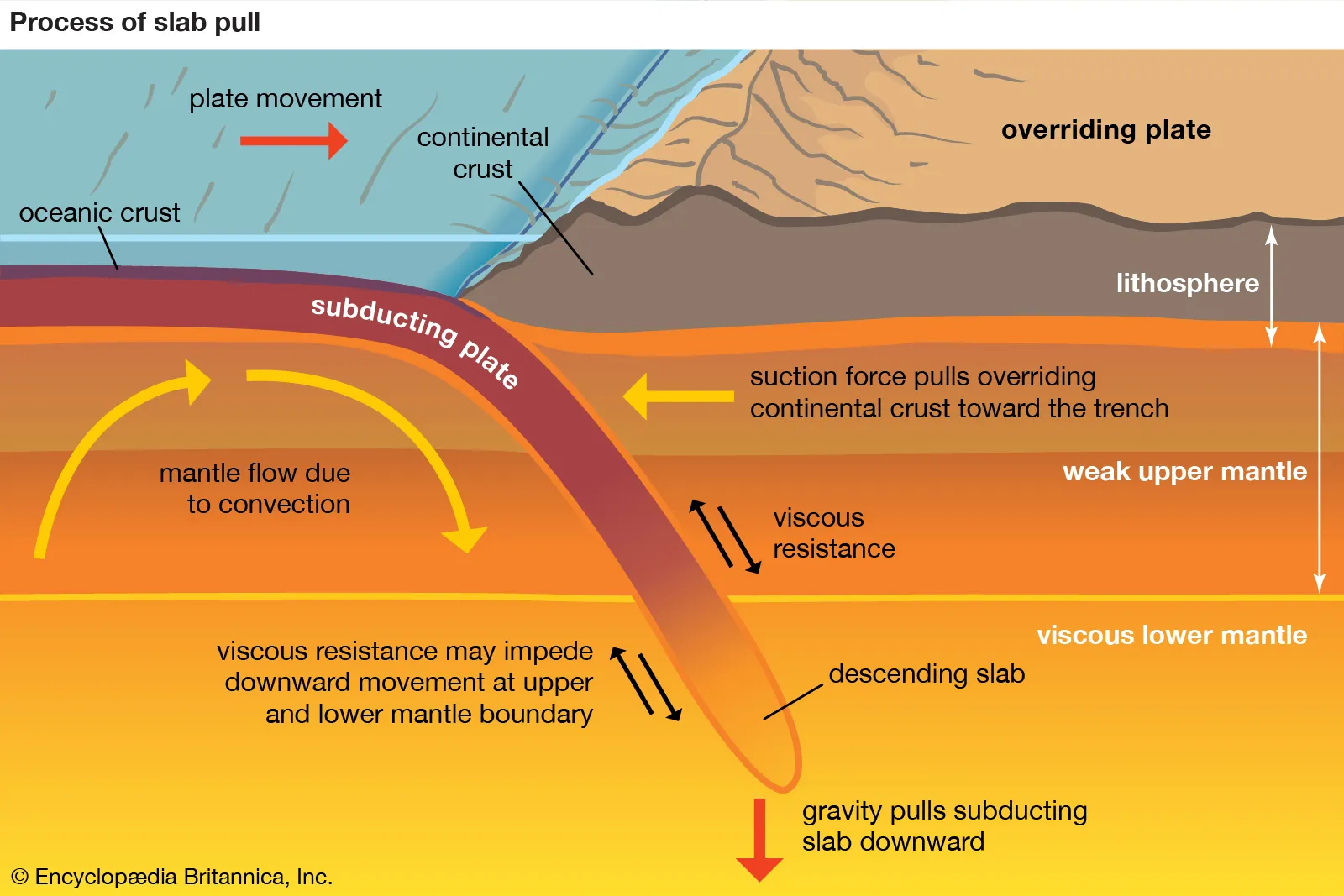
Regional Metamorphosis
Large scale metamorphism due to plate tectonics and compressional stress.
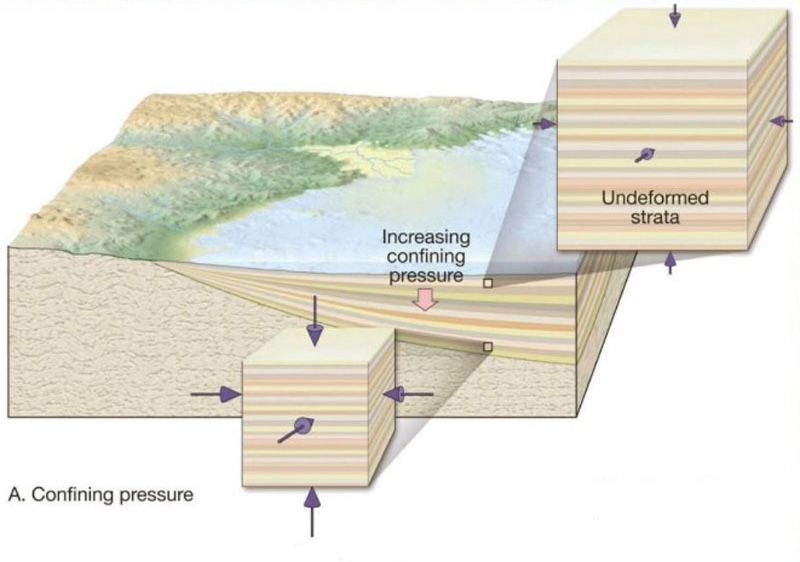
Burial metamorphism
When sedimentary rocks are burried deep enough to expierence heat and pressure
Parent rock
Rocks that existed before the process of metamorphosis.
Recrystallization
The process where crystals are packed together which creates a new crystal structure.
Scientific Method
The process used by scientists to acquire knowledge through the usage of observation and skepticism.
What are the steps in the scientific method?
Observation
Problem or Question
Hypothesis
Testing and Observations
Presenting and Publish Findings
Scientific theory
Hypothesis
An explanation based on limited evidence that serves as a starting point for research.
Observation
The act of perceiving something and registering its significance.
Scientific Theory
A well-supported explanation of some aspect of the natural world with repeatable results.
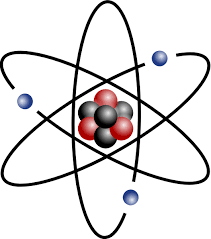
The 3 parts of an atom.
Proton
Neutron
Electron
Proton
A subatomic particle with a positive charge and an atomic mass of about 1. Found in the nucleus of the atom.
Neutron
A subatomic particle with a neutral charge and an atomic mass of about 1. Found in the nucleus of the atom.
Electron
A subatomic particle with a negative charge with a very small atomic mass. Found on the electron shells of the atom.
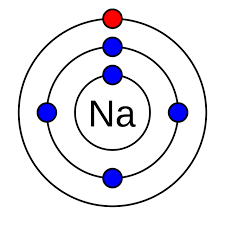
Valance shell
The outermost shell of an atom.
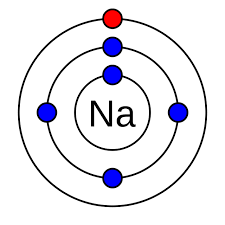
Valance electrons
The outermost electrons in the valance shell.
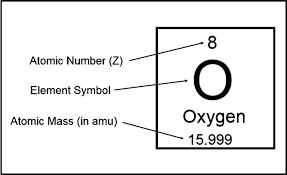
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element. Atoms are neutral, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons.
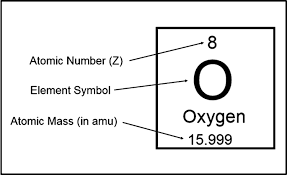
Atomic Mass
The mass of an atom is a weighted average that is largely determined by the number of its protons and neutrons
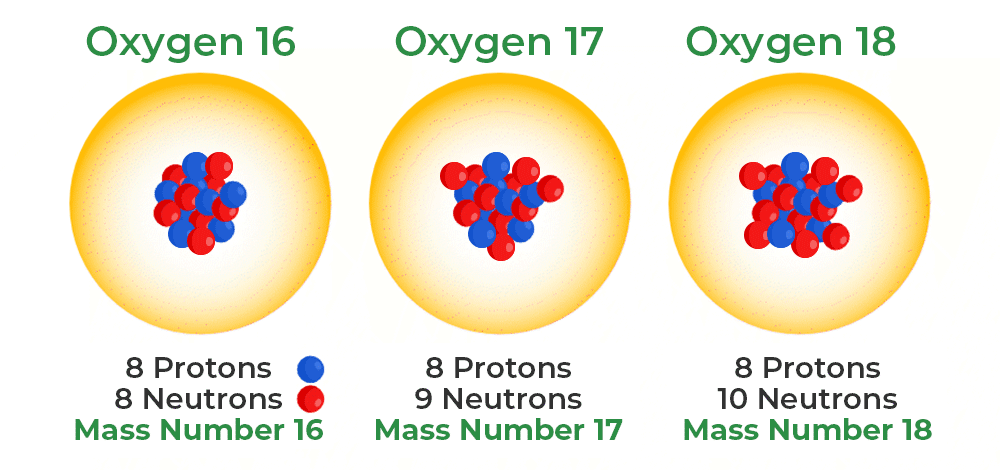
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with the same amount of electrons but a different amount of neutrons.
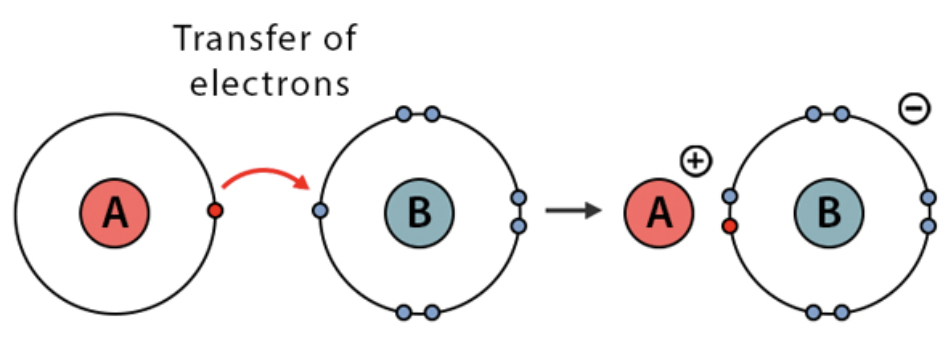
Ions
An atom with a net charge due to the loss/gain of electrons.
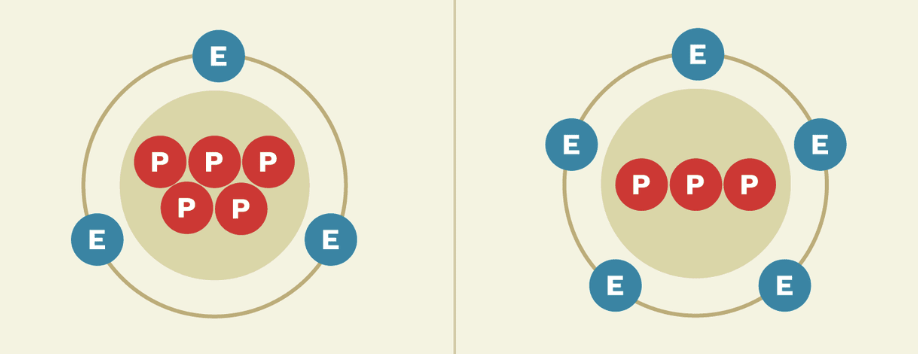
Cation
A positively charged ion that has more protons than electrons.
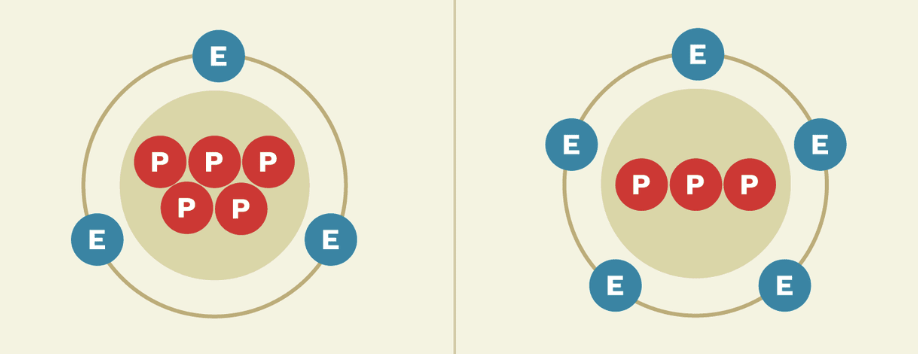
Anion
A negatively charged ion that has more electrons than protons
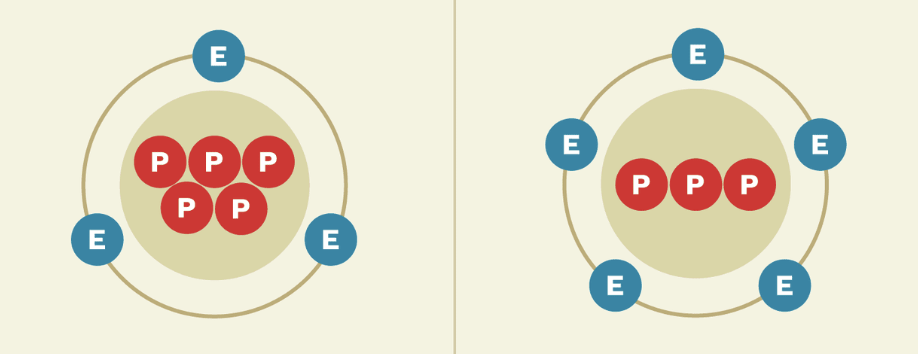
Covalent bonding
When atoms bond and share electrons to form electron pairs.
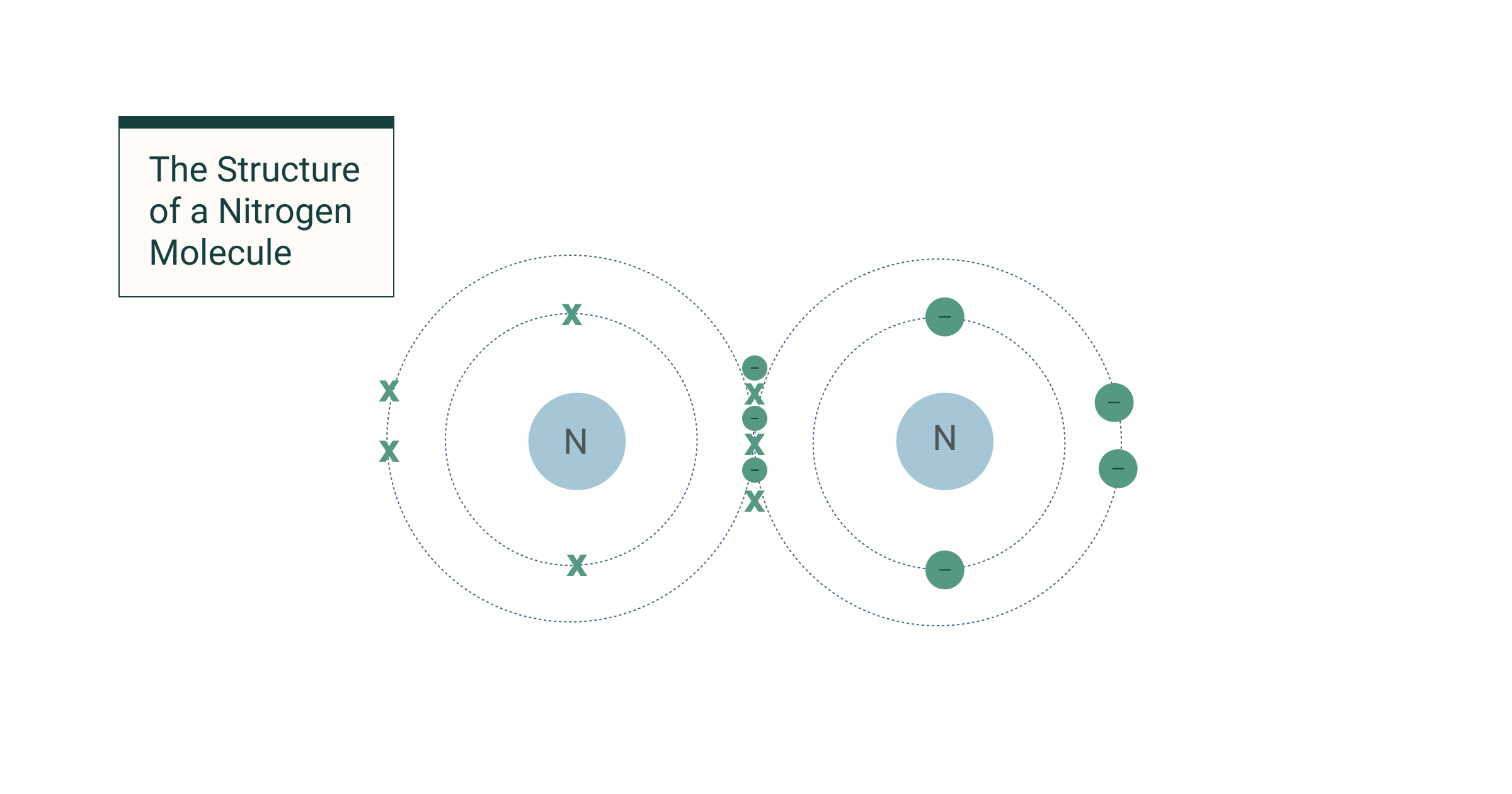
Ionic bonding
When atoms with opposite electrical charges are attracted to each other.