carboxylic acids and esters
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
isomerism
exhibit functional group isomerism with esters
exhbiti chain isomerism
physical properties
carboxylic acid molecules have an alkyl group as well as -COOH
in addition to intermolecular forces of attraction, hydrogen bonds between the molecules are present as well
hydrogen bond between carboxylic acid molecules refer to the electrostatic forces of attraction between a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to the oxygen atom and a lone pair of electrons on an oxygen atom from another carboxylic acid molecule
dimer formation
in the liquid state or in organic solvents, pairs of carboxylic acids molecules are joined together by strong hydrogen bonds to form dimers
carboxylic acids do not form dimers in aqueous state: water molecules preferentially form hydrogen bonds with the carboxylic acid molecules, disrupting the formation of carboxylic acid dimers
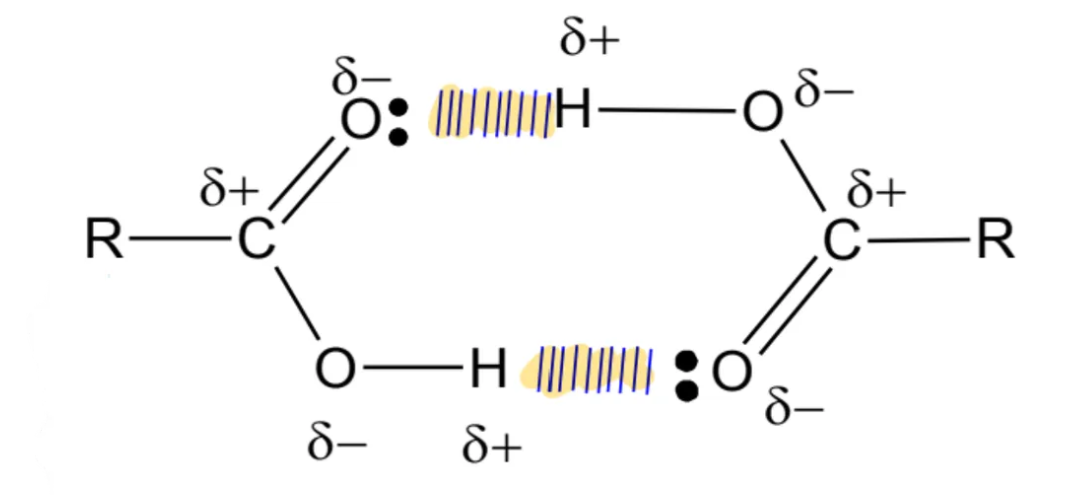
boiling point
boiling points of carboxylic acids are higher than alcohols of similar Mr
more extensive hydrogen bonding formed between carboxylic acid (RCOOH) molecules compared to alcohol (ROH) molecules due to the greater number of hydrogen bonding sites per molecule
boiling points increases with increasing total number of electrons present
the larger the molecule → greater electron cloud size → stronger and more extensive intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules → greater amount of energy required to overcome this attraction
straight chain isomers have higher boiling points than their branched isomers
extent of surface area of contact of straight chain isomers is greater than the branched isomers → extensiveness of weak intermolecular forces of attraction is greater → energy required to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules is greater
preparation of carboxylic acids from alcohols
primary alcohols can undergo oxidation to form carboxylic acids
general equation: RCH2OH + 2[O] → RCOOH + H2O
reagents and conditions:
KMnO4 (aq), dilute H2SO4, heat under reflux
K2Cr2O7 (aq), dilute H2SO4, heat under reflux
observation:
purple KMnO4 solution is decolourised
orange K2Cr2O7 turns green
breaking of O-H bond
carboxylic acid acting as an acid
carboxylic acids can undergo reactions with metals, bases and carbonates
reaction with metals
carboxylic acids react with reactive metals like sodium to give carboxylate salt and hydrogen gas
general equation: R-COOH + Na → R-COO-Na+ + 1/2 H2
reagents and conditions: Na (reactive metal), r.t.p.
observation: effervescence of H2 observed that extinguishes a lighted splint with a ‘pop’ sound
reaction with bases → neutralisation
carboxylic acids react with alkalis to yield a carboxylate salt and water
general equation: R-COOH + NaOH → R-COO-Na+ + H2O
reagents and conditions: NaOH (aq) or KOH (aq), r.t.p
reaction with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates
carboxylic acids react with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates to give a carboxylate salt, water with the liberation of carbon dioxide
general equations
carbonates: 2RCOOH + Na2CO3 → 2R-COO-Na+ + H2O + CO2
hydrogencarbonates: RCOOH + NaHCO3 → R-COO-Na+ + H2O + CO2
reagents and conditions: Na2CO3 (aq)/(s) OR NaHCO3 (aq)/(s), r.t.p.
observation: effervescence of CO2 observed that forms white precipitate in Ca(OH)2
condensation reaction with alcohols
condensation reaction with alcohols
carboxylic acids react with alcohols to form sweet-smelling liquids, esters, RCOOR
reagents and conditions: concentrated H2SO4 catalyst, heat
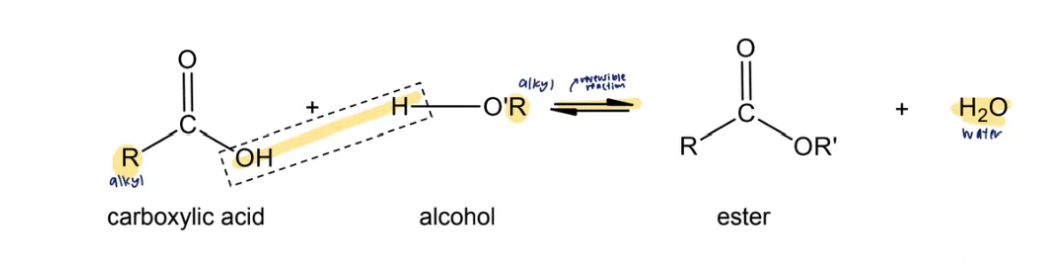
nomenclature of esters
first part: alcohol used (alcohol → alkyl)
second part: carboxylic acid used (carboxylic acid → carboxylate)
guidelines:
write out formula ⇒ write acid group first followed by the alcohol group
name the ester ⇒ name the alcohol group first followed by the acid group
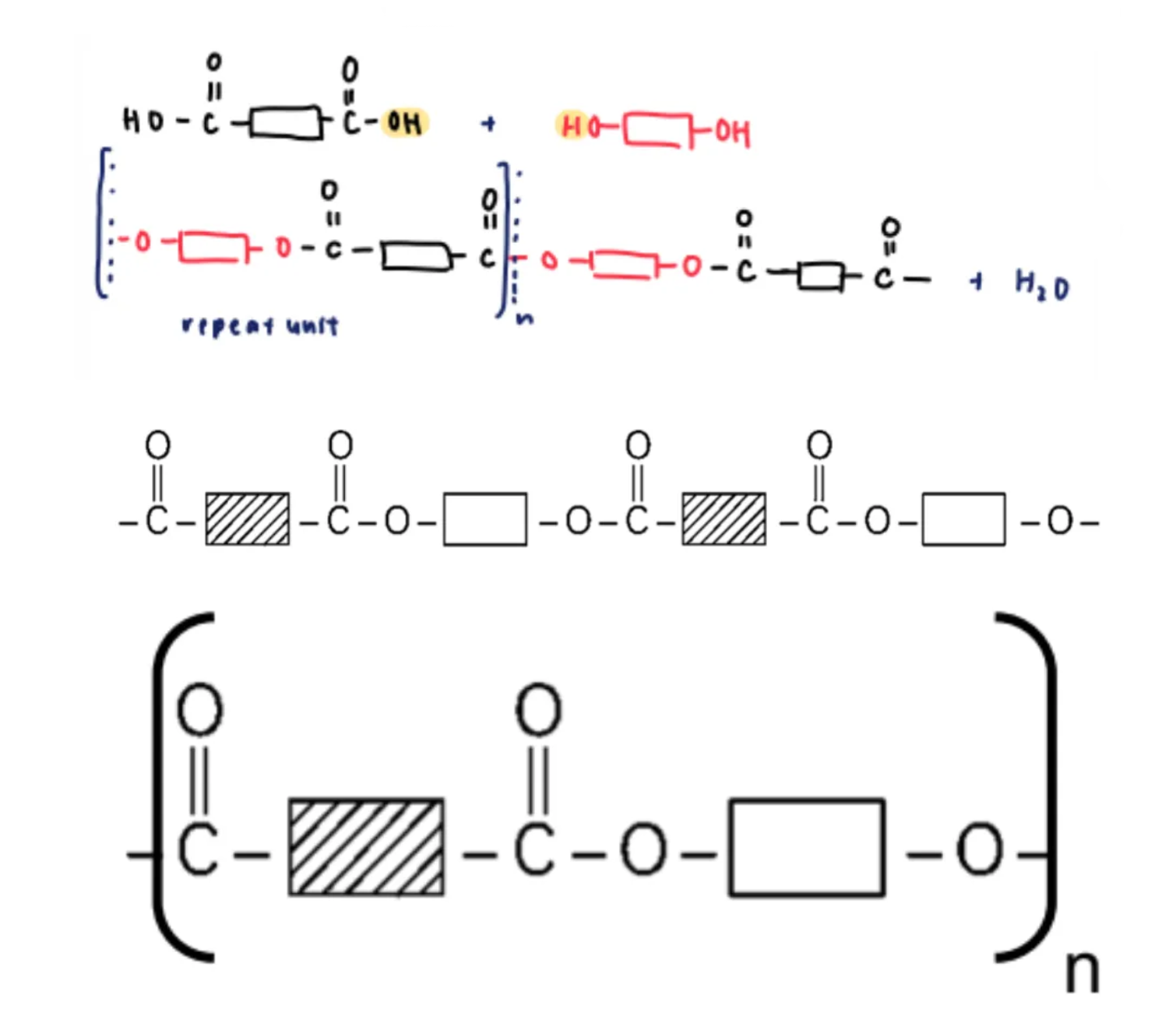
condensation polymerisation
occurs when monomer units join together to form a larger structural unit while releasing smaller molecules as a byproduct such as water or methanol
formation of polyesters
esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols → dibasic acid and diol
resulting polymer: polyester → a polymer where the individual units are held together by ester linkages
e.g.: terylene → poly(ethylene terephthalate)
monomer units: benezene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid and ethane-1,2-diol
after condensation occurs between the carboxylic acid and alcohol functional groups, a polyester with the following partial structure will be formed
uses
used as a fibre to make clothes → polyester
used to make bottles → PET
formation of polyamides
polyamide is a polymer where individual units are held together by amide linkages
amide functional group is -CONH2
amide link is -CONH-
e.g.: nylon
two monomer units
after condensation occurs between the carboxylic acid and amine (-NH2) functional groups, a polyamide with the following partial structure will be formed
uses:
used in textiles for clothing and carpets, ropes and fishing lines