unit 5
1/345
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
346 Terms
1st step of urine formation
blood is filtered in the glomerulus
2nd step of urine formation
substances like water and electrolytes are reabsorbed
3rd step of urine formation
secretion, additional waste products are added to the forming urine
4th step of urine formation
Only waste and excess fluid leave the body as urine
Arterial blood gas (ABG)
the most accurate test for oxygen and breathing status
Absorption speed rule
if stool moves too fast there is less absorption
Accessory muscle use
using neck, shoulder, or chest muscles to help breathe because normal breathing isn't enough.
Aerosol therapy
Liquid med to mist
Helps open airways
Loosens mucus
Goes straight to lungs
Aerosol therapy
a machine or inhaler turns liquid medication into a fine mist so it goes straight into your lungs
Afterload
how hard the heart has to push against to get blood out
more resistance = harder to pump
Airway hyperactivity
airways react strongly and constrict
airway obstruction Causes
mucus
plugs
inflammation
Alveoli
tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen goes into the blood and CO₂ comes out.
Anal fissures
small cuts or tears in the skin around the anus that cause sharp pain and bright red blood on the toilet paper
Angiography
uses dye to outline blood vessels and find blockages or aneurysms
Anticholinergic medications
used for slowing things down in the body
blocks the parasympathetic system
cause urinary retention bc they relaxes bladder
Anuria
No urine output
< 4 cc/hr
aorta
comes out of the left ventricle and sends blood to every part of the body except the lungs
biggest artery of body
Apnea
when a person stops breathing completely for a moment.
arterial (artery) blood
measured to see how much oxygen is really being delivered to the body
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)
blood test from an artery that measures oxygen, CO₂, and pH.
Arterial blood gas (ABG)
measures oxygen, CO₂, and pH from arterial blood
Arterial Oxygen Saturation (SpO₂)
percentage of oxygen in the blood measured by pulse ox.
Ascending colostomy
stoma created in the ascending colon producing liquid stool with strong odor
asphyxiation
when the airway gets blocked and the person cannot get enough oxygen to breathe, leading to suffocation
Asystole
no electrical activity in the heart, causing a flatline and no heartbeat
Atelectasis
alveoli collapse, so oxygen can't pass into blood easily
Atelectasis
collapsed alveoli (air sacs), meaning they don't open, so no gas exchange happens.
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
receives the impulse from the SA node and delays it slightly,
can fire at 40-60 bpm if needed
Automaticity
the heart can create its own electrical impulses
Autonomic nervous system
body system that controls automatic actions like bowel movement speed
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
a hormone that increases when the heart is stretched from heart failure
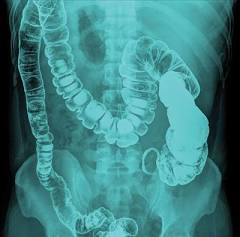
Barium studies
test w/ X-ray used to visualize the digestive tract
by having the patient drink a thick, white liquid,
which coats the organs and shows up clearly on the images.
Barrel chest
the chest looks rounded and enlarged front-to-back,
lungs stay over inflated for a long time (like in COPD/emphysema), so the rib cage stays expanded.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Enlargement of the prostate gland
blocks urine flow and causes retention or overflow incontinence
Bilirubin in urine
waste from broken RBC
if found in urine means liver problems
Bilirubin
waste from broken red blood cells
Bladder capacity
The bladder stores about 250-400 mL before you feel the urge
Bladder training
Teaching the bladder to hold urine longer by scheduled voiding
Bladder
A muscular sac that stores urine until it is released
Hematuria
Blood in urine
Means conditions like kidney stones, UTIs,
also kidney/bladder cancer but rare
Blood lipid profile
a test that measures cholesterol and triglycerides to check heart disease risk
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
Measures protein waste still sitting in the blood
shows how well kidneys filters
range 8-25 mg/dl
Blood vessels
veins, arteries, and capillaries carry blood for perfusion
Bolus
a soft ball of chewed food mixed with saliva that moves from the mouth to the stomach
Borborygmi
stomach gurgling sounds
Bronchoscopy
a scope inserted through the nose or mouth into the airways to see the trachea and bronchi.
Bronchospasm
sudden tightening of the airway muscles making airways narrow.
Bronchospasm
tightening of airway muscles that narrows the airway
BUN
Measures how much urea nitrogen is in the blood and shows kidney function
Bundle branches
carry the impulse down the left and right sides toward the apex,
can fire at 30-40 bpm
Capillaries
the tiny connection points where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged
Cardiac biomarkers
proteins released into the blood when the heart muscle is damaged
Cardiac catheterization
invasive test using dye to measure valve function and heart muscle strength
Cardiac output
the amount of blood the heart pumps each minute,
ranges 3.5 to 8 liters/min
cardiovascular primary functions
transports oxygen,
transport nutrients,
deliver waste products to organs
Catheter indication (I&O)
Used to accurately measure urine output in critically ill patients
Incomplete retention
Inability to fully empty the bladder
May feel pressure, discomfort and dribbling may occur
Catheter indication (specimen)
Used to collect a sterile urine specimen
Catheter indication (wounds)
Used to keep urine away from Stage III or IV pressure ulcers
Catheter specimen
Sterile urine sample taken directly from a catheter port
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI)
A UTI caused by bacteria entering the bladder through an indwelling urinary catheter.
CAUTI prevention
PureWick and condom catheters are used to avoid this
Clostridioides difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD)
diarrhea caused by C diff bacteria
antibiotics kill the good bacteria in the gut, and C. diff overgrows
Celiac disease
autoimmune reaction to gluten that damages the small intestine and causes diarrhea and malabsorption
Cellulose
indigestible plant fiber that adds bulk to stool
helps promote normal bowel movements
Central cyanosis
blue color around lips/mouth, very serious low oxygen.
Chest x-ray
shows heart size/shape and pulmonary congestion or edema
Clean-catch / midstream
Urine sample collected after cleaning the urethra and catching midstream urine
Cleansing enema
solution given to empty the colon before tests or procedures
Cloudy urine
↑ chance of infection
Clubbing
fingertips get round and bulb like from longterm low oxygen levels.
CO formula
cardiac output equals stroke volume x HR
Colitis
means inflammation of the colon (large intestine)
Colon sections
ascending colon transverse colon descending colon sigmoid colon
Colonoscopy
scope that visualizes the colon up to the ileocecal valve, anus to rectum to colon
Colonoscopy
test that looks inside the entire colon with a camera
Colostomy
can be temporary or permanent opening created from the colon to the abdomen for stool drainage
Colostomy
opening from the colon to the abdomen to pass stool
Complete blood count (CBC)
a blood test that measures red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
Constipation
hard, dry, stool
difficult to pass
Contractility
how strong the ventricle squeezes during the beat
Coronary blood flow increase
coronary flow can increase up to six times to meet higher oxygen demands
Coronary vessels
these vessels supply oxygen to the myocardial cells
Coude catheter
A catheter with a curved tip used to pass around an enlarged prostate
Cough reflex
clears irritants from lower airway
Crackles
short popping sounds caused by fluid in the small airways or alveoli.
Creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB)
an enzyme from heart muscle that increases with heart damage
Creatinine (Cr)
delet
Creatinine
Waste from skeletal muscle breakdown
most accurate indicator of kidney function
Culture & sensitivity (C&S)
Test that identifies bacteria/type of infection in the urine, must be sterile
CXR (chest x-ray)
checks lungs for infection, fluid, or collapsed areas
Cyanosis
bluish color of skin/lips from low oxygen.
Cyanosis
bluish lips, skin, or nails caused by low oxygen in the blood.
Cystic fibrosis
condition where thick mucus affects digestion
can cause diarrhea constipation or steatorrhea
Cystoscopy
A scope is inserted through the urethra to look inside the bladder
Dark amber urine
↑ dehydration
Decreased sphincter control
older adults may have reduced control of anal sphincters leading to incontinence
Deep cough
strong cough to remove mucus deep in the lungs
Defecation reflex
body signal that tells you to have a bowel movement