Histology 802 Cytology Lecture and Lab Review
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards encompass key vocabulary and concepts related to cytology and histology based on the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Cell membrane
Consists of three laminae: outer dense, middle light, and inner dense; total thickness is 7-9 nm.
Glycocalyx
Formed from chains of sugars or glycolipids attached to peripheral proteins on the plasma membrane.
Transmembrane proteins
Proteins that span the membrane and constitute a significant portion of the membrane's weight.
Acinar cells
Cells in the pancreas that have basally located nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm due to protein secretory granules.
Lysosomes
Organelles containing enzymes that digest cellular waste and are formed from the Golgi complex.
Microvilli
Apical cell membrane evaginations that increase surface area for absorption in epithelial tissues.
Cilia
Hair-like structures on the surface of certain cells, containing microtubules, that aid in movement.
Desmosomes
Structures that provide adhesion between adjacent epithelial cells, visible as dense bodies between cells.
Mitosis
The process of cell division that includes stages such as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Cell cycle
Divided into four phases: G1, S, G2, and M, with G1 being the pre-duplication phase and M the mitotic phase.
Static cells
Cells that never divide, such as neurons and cardiac cells, remaining in the G0 phase for life.
Renewing cells
Cells that are continuously replaced at fixed intervals, such as blood cells and gastrointestinal epithelium.
Euchromatin
Less condensed form of chromatin; appears lightly basophilic under the microscope.
Heterochromatin
More condensed form of chromatin; appears darkly basophilic under the microscope.
Glycogen granules
Energy storage particles found in liver cells, seen as beta and alpha particles in electron microscopy.
Melanocytes
Cells that synthesize melanin and transfer it to keratinocytes in the skin.
Secretory granules
Vesicles that contain substances to be secreted by the cell, formed from the Golgi apparatus.
Nucleoli
Structures within the nucleus responsible for ribosome synthesis.
Cytoplasmic:nuclear ratio
The ratio of the volume of the cytoplasm to that of the nucleus; important in cell morphology assessment.
Perinuclear location
The positioning of the Golgi body surrounding the nucleus within nerve cell bodies.
Autophagosomes
Lysosomes fused with the cell’s old organelles for degradation.
Hematoxylin Stain
basic dye with positive (+) charge
stains acidic structures with net negative (-) charge
ex: nucleus & ribosomes
Eosin Stain
acidic dye with negative (-) charge stains
stains basic structures with net positive (+) charge
ex : most cytoplasmic structures (EXCEPT ribosomes)
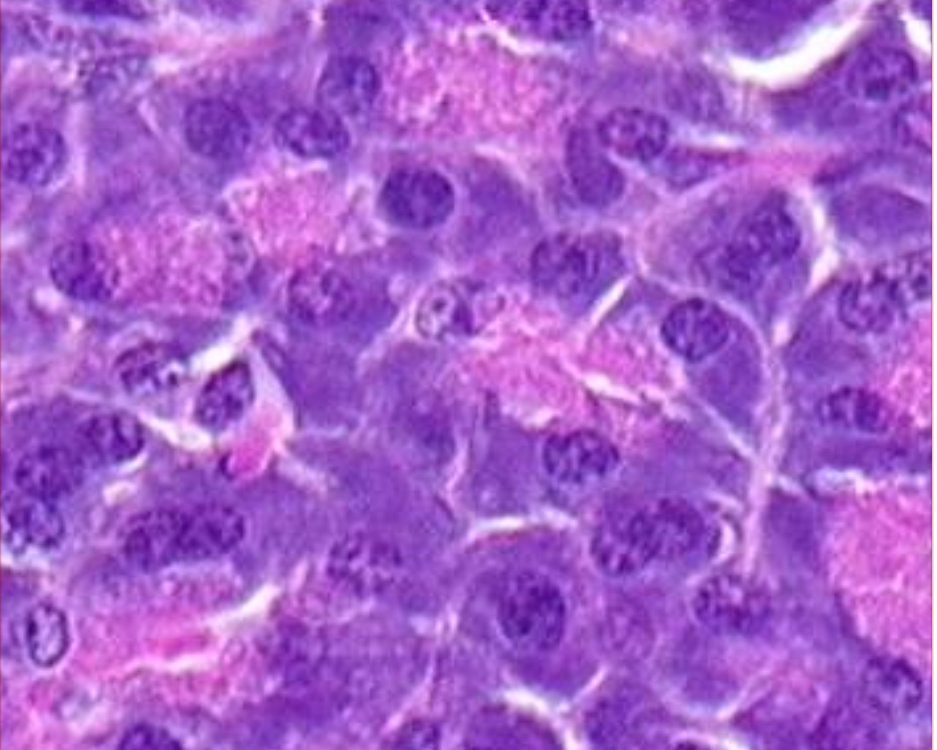
Pancreas Acinar Cells - basophilic
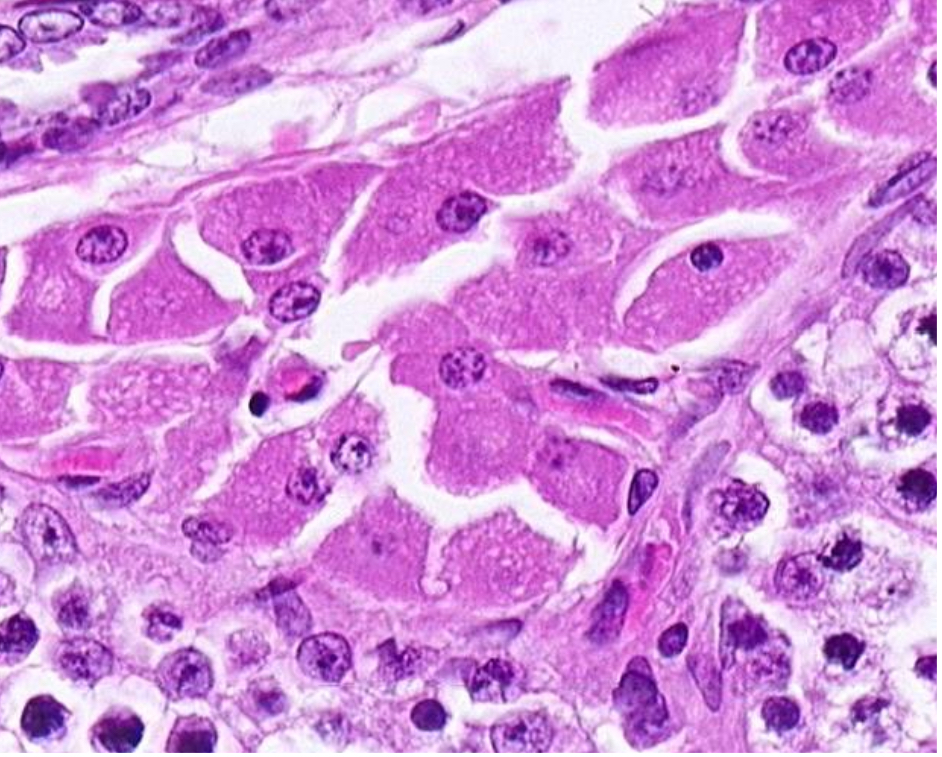
Leydig Cells - eosinophilic
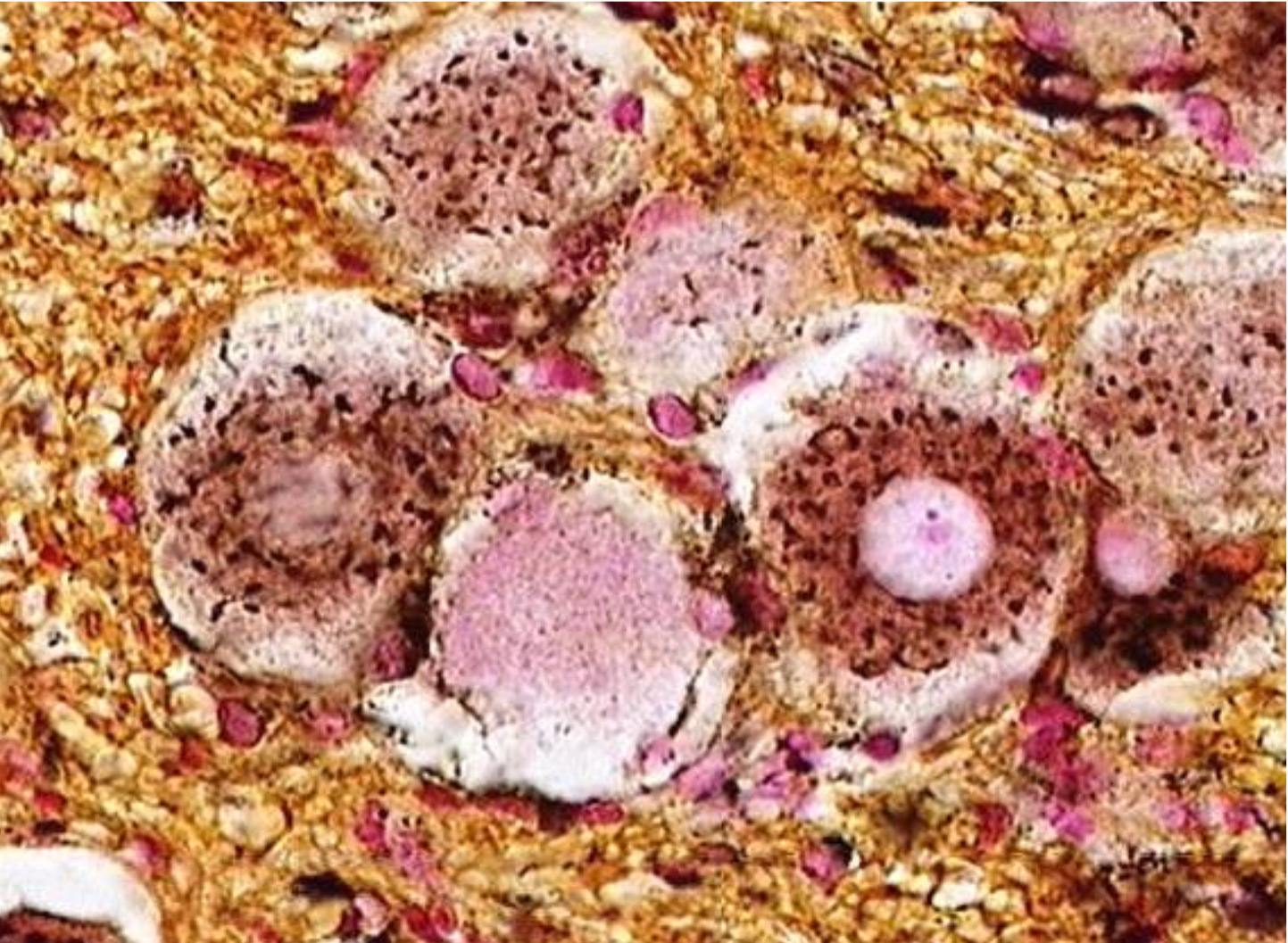
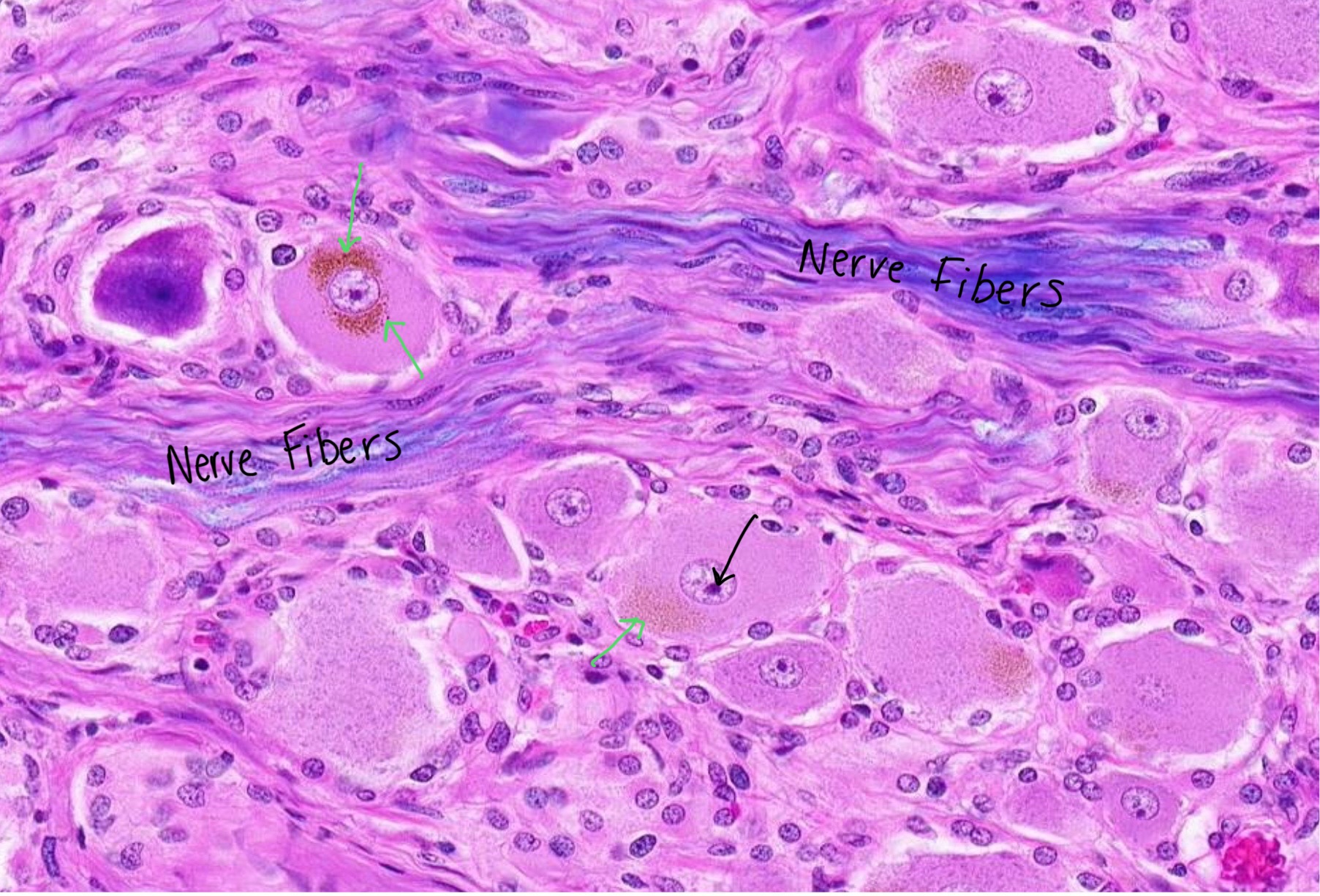
green arrows - aggregated lipofuscin pigments
black arrow - nucleoli