Chapter 24: AP Biology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Speciation
Origin of new species; key evolutionary process.
Evolutionary Theory
Explains species origin and population evolution.
Microevolution
Allele frequency changes within a population.
Macroevolution
Large-scale evolutionary changes above species level.
Biological Species Concept
Species defined by interbreeding and viable offspring.
Reproductive Isolation
Biological barriers prevent species from interbreeding.
Hybrid
Offspring from crosses between different species.
Prezygotic Barriers
Prevent fertilization before zygote formation.
Postzygotic Barriers
Prevent hybrid offspring from developing or reproducing.
Hybrid Breakdown
F1 hybrids fertile; later generations less viable.
Hybrid Sterility
Viable hybrids that are sterile due to chromosomal differences.
Hybrid Inviability
Hybrid embryos fail to develop or survive.
Habitat Isolation
Species prefer different habitats, reducing encounters.
Temporal Isolation
Different breeding schedules prevent reproduction.
Behavioral Isolation
Species fail to recognize each other as mates.
Mechanical Isolation
Incompatible sexual organs prevent reproduction.
Gametic Isolation
Sperm and egg incompatibility prevents fertilization.
Morphological Species Concept
Defines species by shared structural traits.
Ecological Species Concept
Species defined by ecological niche and interactions.
Phylogenetic Species Concept
Species as smallest group sharing a common ancestor.
Allopatric Speciation
Geographic isolation leads to new species formation.
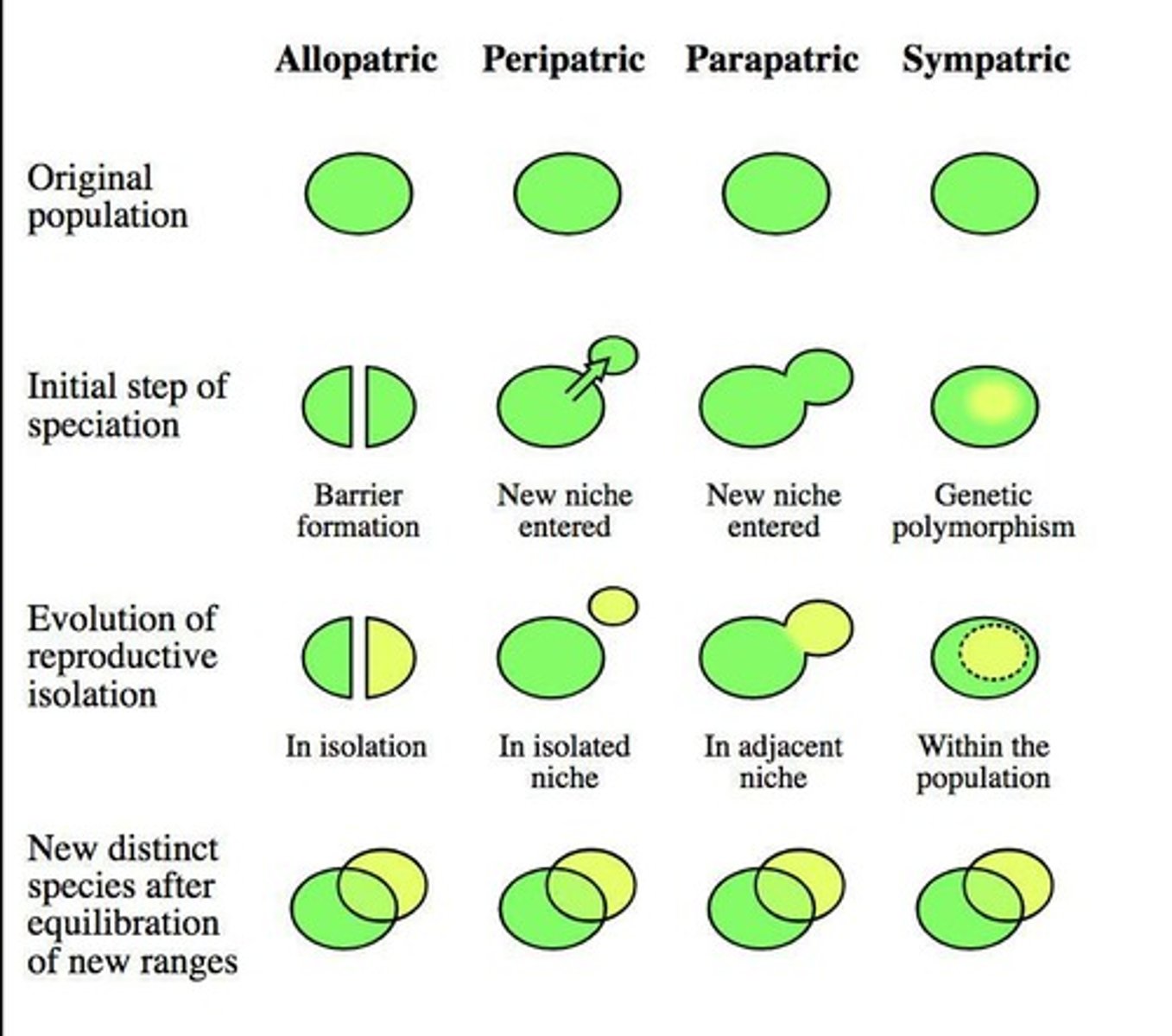
Sympatric Speciation
New species form without geographic separation.
Punctuated Equilibrium
Long periods of stasis interrupted by rapid change.
Gradualism
Continuous, slow evolutionary changes over time.
Polyploidy
Organisms with extra chromosome sets due to meiosis errors.
Autopolyploidy
Extra chromosome sets arise within a single species.
Allopolyploidy
Extra chromosome sets from hybridization between species.
Habitat Differentiation
Population exploits new niche, leading to isolation.
Sexual Selection
Mate choice based on specific traits influences speciation.
Genetic Basis of Speciation
Speciation results from changes in one or many genes.