The Americans: Chapter 18
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
Boxers
Secret Chinese group that rebelled against foreigners in China (Boxer Rebellion)

2
New cards
Hawaii
Kingdom of Queen Liliuokalani, eventually becomes part of the United States when she is overthrown by Sanford Dole.
3
New cards
Teddy Roosevelt
Gave up his Assistant Secretary of the Navy position to lead the group of volunteers, later became president, "spoke softly and carried a big stick"
4
New cards
Pearl Harbor
U.S. Naval base in Hawaii - excellent deep water port.
5
New cards
William Randolph Hearst
Pulitzer's competitor in fueling Spanish-American war Yellow Journalist.

6
New cards
Panama Canal
Manmade waterway made by the U.S. to connect the Atlantic and Pacific - sign of American prowess in the Western Hemisphere
7
New cards
Open Door Policy
Hay's policy for accessing Chinese market, meant that no single nation would have a monopoly on trade with any part of China. - The US's way into China

8
New cards
USS Maine
The destruction of this ship fueled the Cuban crisis, ordered to Cuba to bring home American citizens in danger from the violence, blew up in the harbor of Havana, more than 260 men killed

9
New cards
Rough Riders
Volunteer cavalry led by Teddy Roosevelt.
10
New cards
Imperialism
Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories

11
New cards
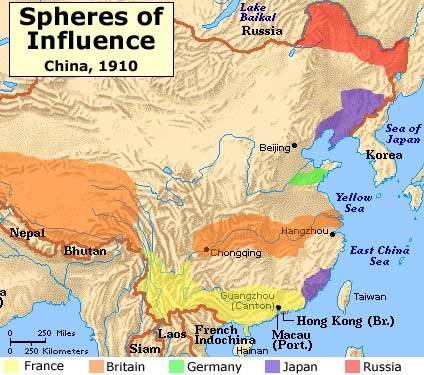
China
Where the Boxer Rebellion took place, also a place where several European Nations exercised control . (Spheres of Influence)
12
New cards
Cuba
Spanish would rather see it sunk that sold to U.S., rebelled against Spain, freed from Spain in the Treaty of Paris. Led Jose Marti was the revolutionary leader.

13
New cards
Guam
Given to the U.S. in the Treaty of Paris, (Island in the Pacific)
14
New cards
Anti-Imperialism League
All agreed that it was wrong for the United States to rule other people without their consent . Against US Imperialism.
15
New cards
Protectorate
A country whose affairs are partially controlled by a stronger power, but not fully a colony - Puerto Rico is a protectorate of the US.
16
New cards
Spheres of Influence
Areas where each nation claimed special rights and economic privileges - most notably in China.
17
New cards
Boxer Rebellion
This was a revolt were the native Chinese fought against the European and Japanese 'invaders'.

18
New cards
John Hay
U.S. Secretary of State, 1899 issued a series of policy statements called Open Door Notes

19
New cards
Yellow Journalism
Style of writing which exaggerates the news to lure and enrage readers. Ex. Pulitzer and Hearst

20
New cards
Admiral George Dewey
Gave the command to open fire on the Spanish navy in the Pacific (Manila Bay - Philippines), U.S. victory, his men destroyed every Spanish ship.

21
New cards
San Juan Hill
U.S. victory, Roosevelt and the Rough Riders called a heros. Most important land battle of the war.
22
New cards
Treaty of Paris
Ended the SPAM war. Spain freed Cuba, turned over islands of Guam in the Pacific and Puerto Rico in the Caribbean, and sold the Philippines to U.S. for $20 million - (against the wishes of the Filipinos)

23
New cards
Alfred T. Mahan
U.S. Naval Admiral, urged government to build naval power

24
New cards
3 factors that fueled new American imperialism
1. Desire for military strength
2. thirst for new markets
3. belief in cultural superiority
2. thirst for new markets
3. belief in cultural superiority

25
New cards
William Seward
Secretary of State under president Lincoln and president Johnson. 1867 arranged for U.S. to buy Alaska from Russians for $7.2 million
26
New cards
Midway Islands
refueling station, taken over by the U.S. in 1867, 1300 miles north of Hawaii
27
New cards
Queen Liliukalani
Queen of Hawaii, overthrown by Sanford DOle.

28
New cards
Sanford B. Dole
Set up a government in Hawaii after the queen was overthrown

29
New cards
General Valeriano Weyler
Sent to Cuba to restore order, herded people into concentration camps, 300,000 cubans and thousands died from hunger and disease - The BUTCHER!!

30
New cards
Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine
Roosevelt had the right to exercise military force in Latin American countries in order to keep European countries out - "Big Stick Diplomacy"

31
New cards
Dollar Diplomacy
President Taft's (1909-1913) policy with Latin America. Replaced TR's Big Stick Diplomacy. Used loans and economic support to justify US involvement in our 'backyard'.

32
New cards
Moral Diplomacy
President Wilson's (1913 - 1921) policy with Latin America. Replaced Taft's Dollar Diplomacy. As its name implies, justifies the use of morals to explain foreign policy - THe United States would only deal with countries who shared our views of Morality.