Mass Transport
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Moloney content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are haemoglobins?
large proteins found in red blood cells with a quaternary structure (4 polypeptide chains) that carry oxygen to tissues
group of chemically similar molecules found in many different organisms
What is association/loading?
when an oxygen molecule joins to haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin
What is dissociation/unloading?
when oxygen leaves oxyhaemoglobin to form haemoglobin
What does an oxygen dissociation curve show?
How saturated the haemoglobin is with oxygen at any given partial pressure
Meaning of affinity for oxygen
the tendency of a molecule to bind with oxygen
What is partial pressure (pO2)?
a measure of oxygen concentration
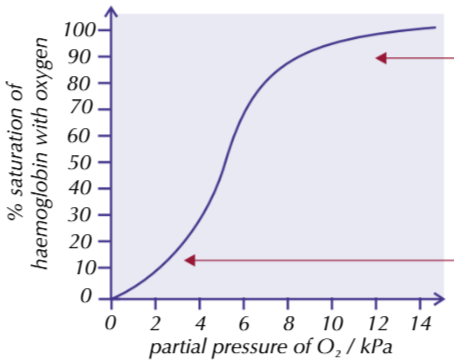
Describe and explain the general shape of a dissociation curve
when haemoglobin first binds with oxygen, its shape alters to make it easier for other oxygen molecules to join too
As haemoglobin becomes more saturated, difficulty for more oxygen molecules o join increases
this is shown by the shallow→steep→shallow dissociation curve
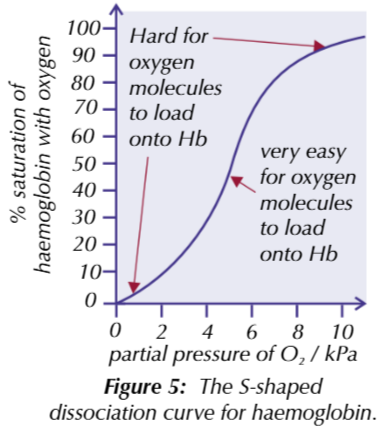
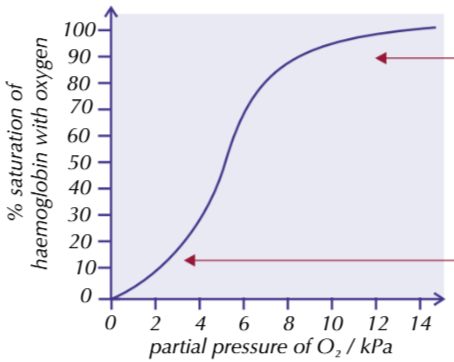
Describe the loading and unlading of oxygen in relation to the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve
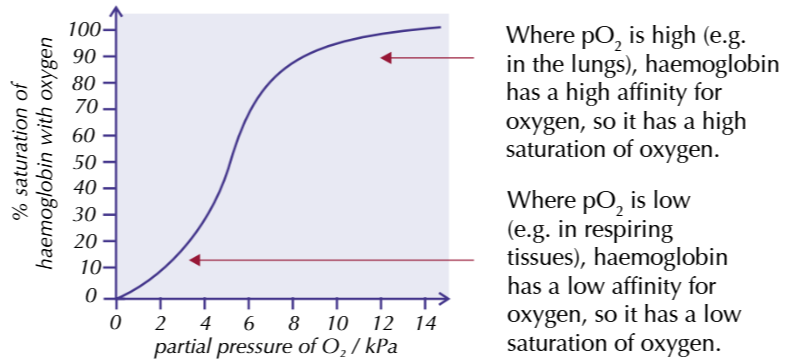
What is partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2)?
What happens to haemoglobin at higher pCO2?
A measure of the concentration of CO2 in a cell
Haemoglobin gives up oxygen more readily at higher pCO2 - gets more O2 to cells during activity
Describe the effects of carbon dioxide concentration on the dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin (The Bohr Effect)
carbon dioxide is produced from cell respiration (pCO2 raises)
rate of oxygen unloading increases
so dissociation curve shifts right but stays the same shape
saturation of blood with oxygen is lower for given pO2, meaning more oxygen is released
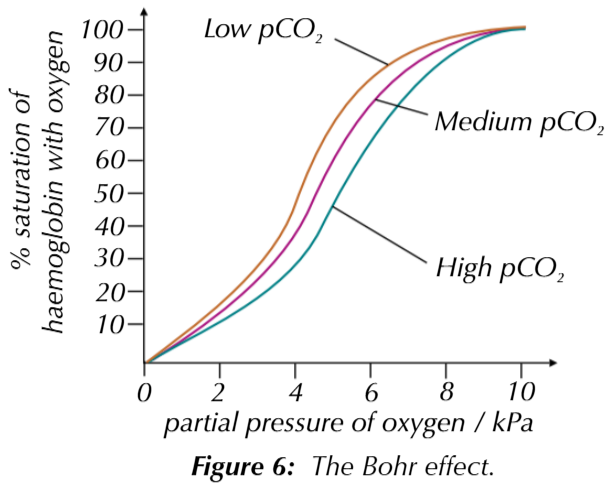
Give three environments that have low oxygen concentration
underground
high altitudes
close to seabed
Describe the difference of the haemoglobin of organisms that live in low oxygen environments compared to human haemoglobin and its dissociation curve
low concentration of oxygen - haemoglobin has higher affinity of oxygen
due to low O2 concentrations, haemoglobin must be good at loading O2
dissociation curve is to left of human

Describe the difference of the haemoglobin of organisms that have higher activity levels compared to human haemoglobin and its dissociation curve
high oxygen demand - haemoglobin has low affinity for oxygen
because haemoglobin must unload oxygen easily so it’s available
Dissociation curve is to right of human

Describe the difference of the haemoglobin of organisms that are small compared to human haemoglobin and its dissociation curve
small mammals have higher surface area : volume ratio than larger mammals
they lose heat quickly so have a higher metabolic rate to keep warm
meaning they have high oxygen demand
small mammal haemoglobin have lower affinity for oxygen than human haemoglobin because their oxygen needs to unload easily to meet high oxygen demand

heart, cariovascular stuff
check class notes and compare with textbook
What are causal relationships?
Where a change in one variable causes a change in the other
What is the xylem?
tissue that transports water and mineral ions in solution in the stem and leaves of the plant (up from roots to leaves)
What is the phloem?
tissue that transports organic substances/solutes like sugars in solution both up and down the plant
Describe the structure of the xylem
xylem vessels are part of xylem tissue that transports water and ions
they are long, tube-like structures formed from dead cells joing end-to-end
no end walls which makes uninterrupted tube allowing water to pass up through middle easily
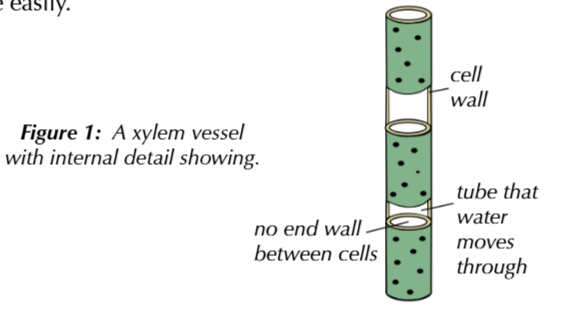
Explain the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem [5 marks]
water lost from leaf because of transpiration/evaporation of water (molecules)
this lowers water potential of the mesophyll/leaf cells
water pulled up the xylem which creates tension
water molecules cohere/’stick’ together by hydrogen bonds
this forms continuous water column
adhesion of water molecules to walls of xylem vessel
What is transpiration?
the evaporation of water from a plant’s surface, especially the leaves
(water evaporates and leaves cells and leaves via stomata down water potential gradient)
What factors affect transpiration rate?
light intensity
stomata open when it’s light to let CO2 in for photosynthesis
they close in the dark - little transpiration
temperature
warmer molecules = more energy = evaporate from cell faster
humidity
lower humidity = faster transpiration rate (water potential)
wind
windier = fast transpiration rate (water potential)
estimating transpiration rate - potometers
plant mass transport dissection (require practical 5)
do
Describe the structure of the phloem
formed from cells arranged in tubes
sieve tube elements are living cells that form the tube for transporting solutes, and have no nucleus and few organelles so
there are companion cells for each sieve tube element to carry out living functions for sieve cells e.g. energy for active transport of solutes
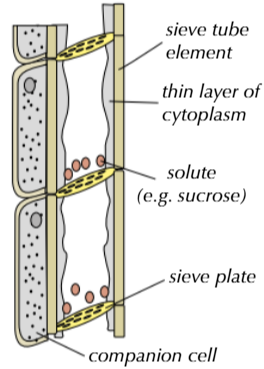
What is translocation?
The movement of solutes to where they are needed in the plant
(solutes sometimes called assimilates
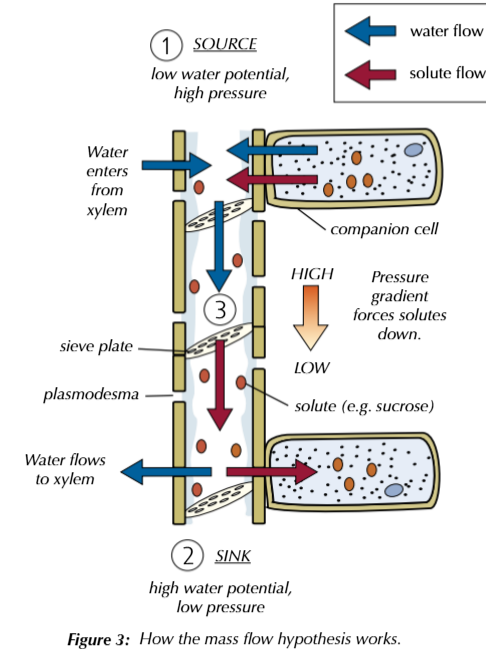
Explain the mass flow hypothesis for the mechanism of translocation in plants
Source (where assimilates/solutes produced)
active transport used to actively load solutes from companion cells into sieve tubes of phloem at source
water potential in sieve tube lowers, so water enters from xylem and companion cells via osmosis
high pressure created at source end of phloem
Sink (where assimilates used up)
at sink end, solutes are removed from phloem to be used up
water potential increased inside sieve tube so water leaves via osmosis , lowering pressure
Flow
results in pressure gradient from source end to sink end
gradient pushes solutes along sieve tubes towards sink to be used
higher concentration of sucrose at source = higher rate of translocation
finish flashcards - add evidence for mass transport hypothesis stuff
duh