Integumentary System: Skin, Layers, and Accessory Structures
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the integumentary system comprised of?
The skin (cutaneous membrane) and accessory organs (hair, nails, and exocrine glands).
What is the largest organ of the body?
The skin.
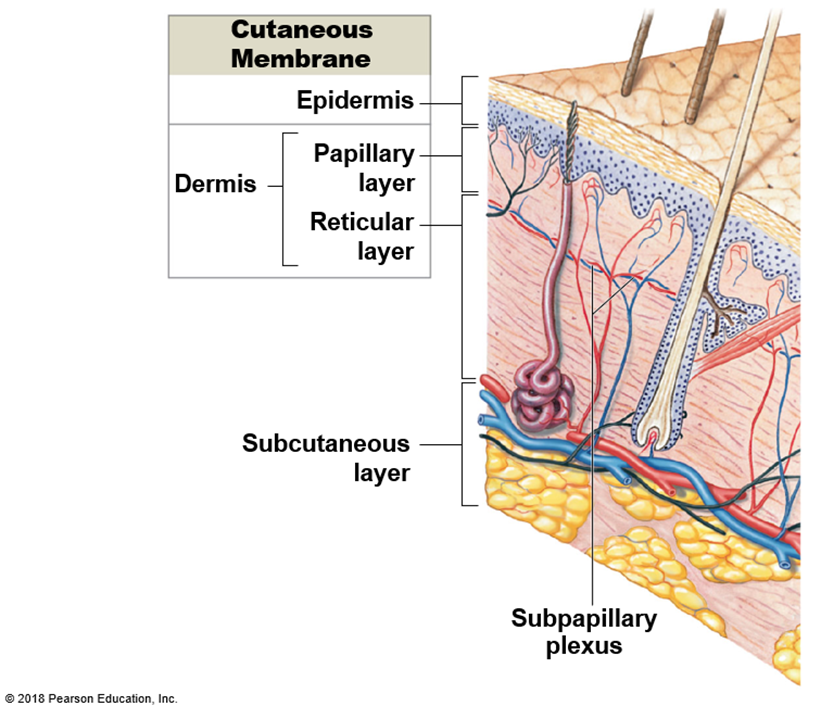
What are the three main layers of the skin?
Epidermis (outer layer), dermis (middle layer), and hypodermis (deepest layer).
What is the primary function of the skin?
To protect internal organs, absorb UV radiation for vitamin D production, and detect stimuli.
What is keratin?
A tough protein produced by keratinocytes that makes skin resilient and resistant to damage.
What are the two types of skin?
Thin skin (four layers of keratinocytes) and thick skin (five layers of keratinocytes).
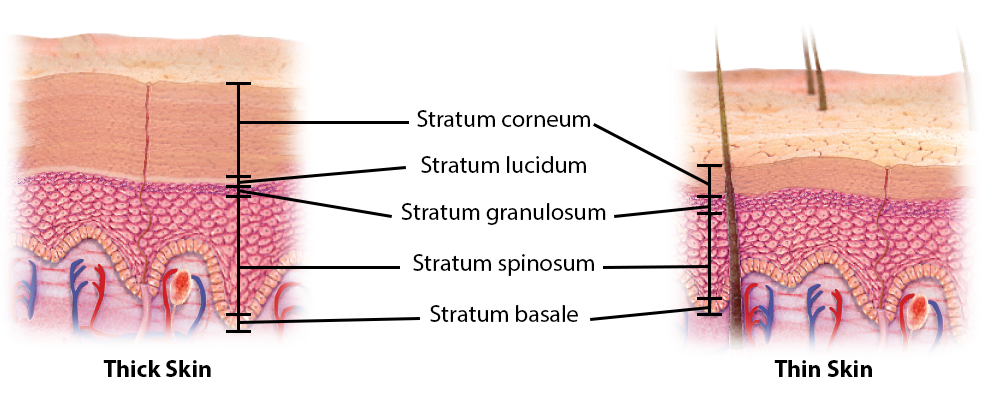
Where is thick skin found?
On the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
What are the four distinct layers of the epidermis?
Stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale.
What is the extra layer found in thick skin?
Stratum lucidum.
What is the function of the stratum basale?
It contains basal cells that constantly divide to rebuild the skin.
How long does it take for a cell to move from the stratum basale to the stratum corneum?
About 7-10 days.
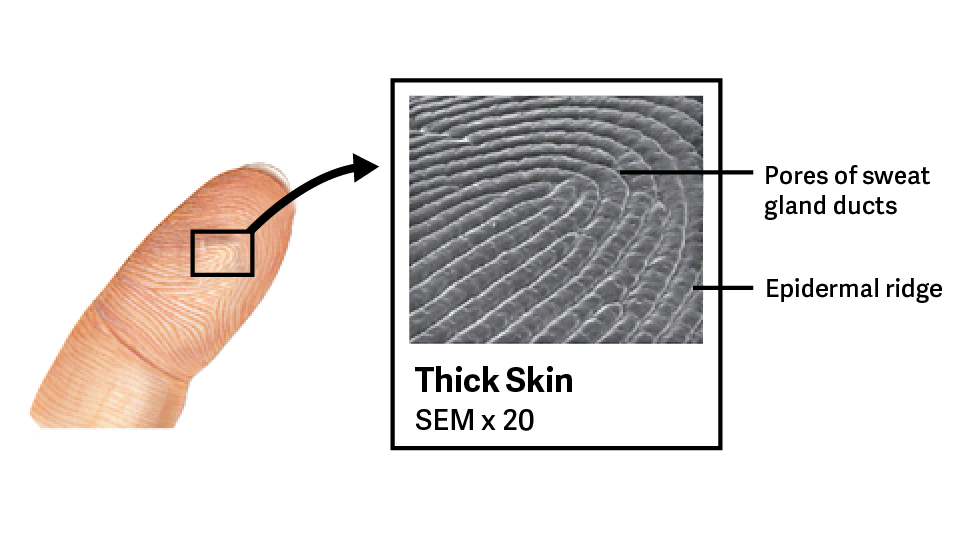
What are epidermal ridges?
Projections formed by dermal papillae that create unique patterns, commonly known as fingerprints.
What role do Langerhans cells play in the skin?
They help in the immune response against pathogens and skin cancers.
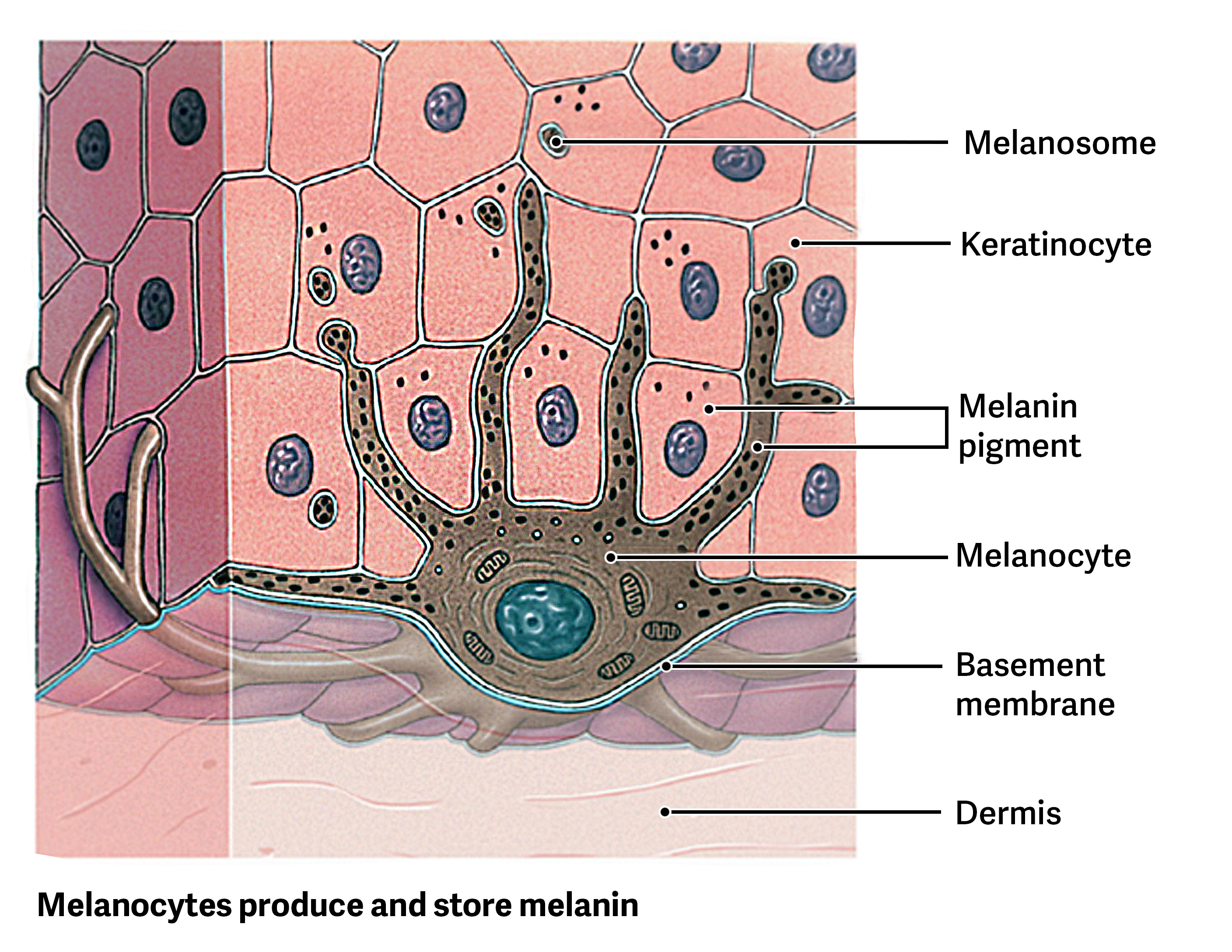
What pigment do melanocytes produce?
Melanin, which gives skin its color and protects against UV radiation.
What is the role of Merkel cells?
They are sensory receptors that respond to light touch.
What do fibroblast cells produce?
Collagen, which helps adhere epidermal cells and provides skin elasticity.
What are the two main regions of the dermis?
The superficial papillary region and the deeper reticular region.
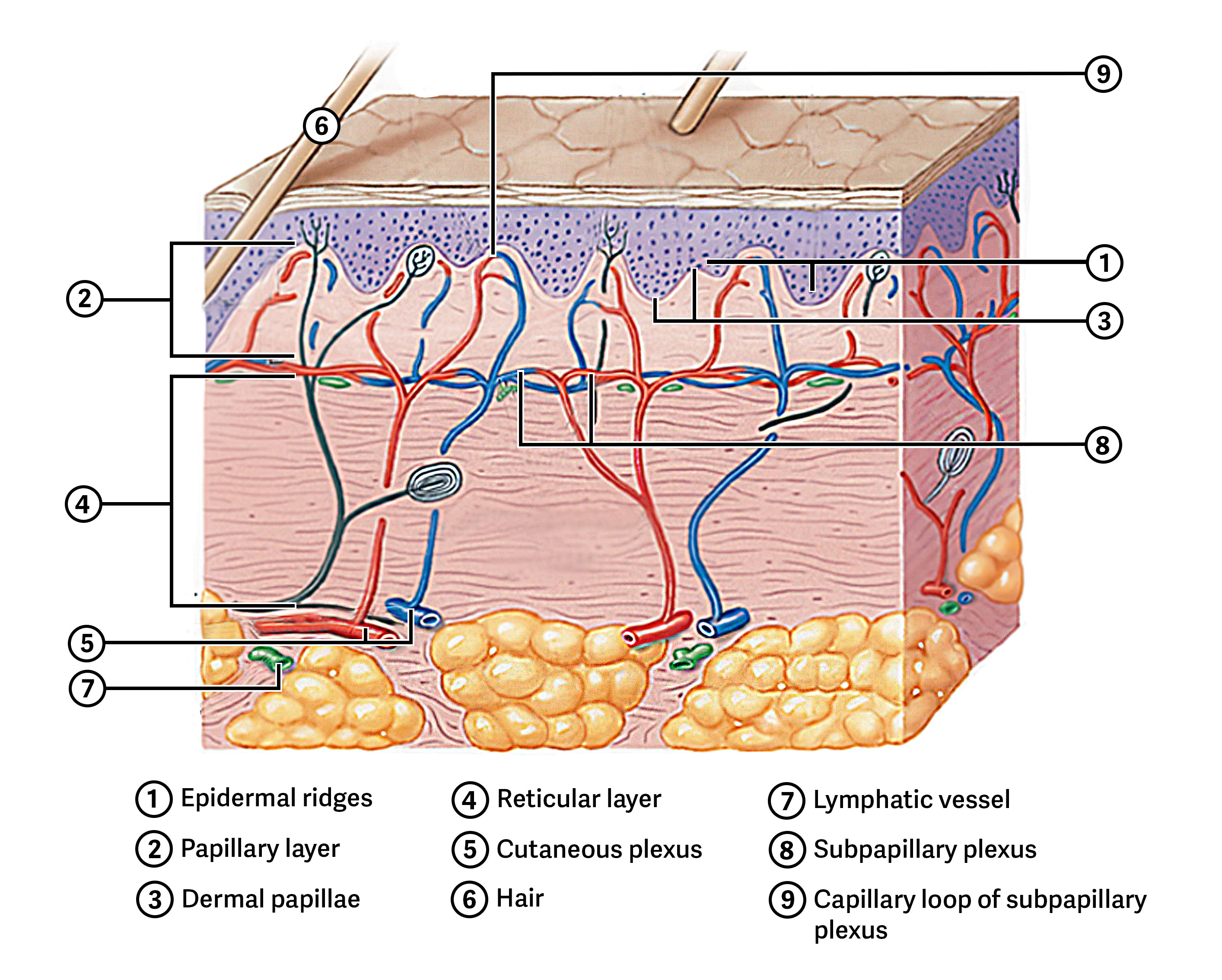
What types of sensory organs are found in the dermis?
Meissner corpuscles (light touch and vibration) and Pacinian corpuscles (pressure and vibration).
What indicates dehydration in the skin?
Skin that does not recoil back to its normal shape after being pinched.
What is the primary connective tissue in the dermis?
Dense irregular connective tissue.
What is the function of the dermis in relation to the epidermis?
It provides nutrients to the epidermis through diffusion.
What is the significance of the stratum corneum?
It is the outermost layer made of dead, keratinized cells that provides a water-resistant barrier.
How many layers of keratinized cells does the stratum corneum hold?
15-30 layers.
What is the role of antimicrobial peptides in the stratum corneum?
They limit microbial growth and form an antimicrobial barrier.
What happens to dead cells in the stratum corneum?
They remain for about two weeks before sloughing off.
What is an indicator of dehydration related to skin?
When the skin does not recoil back to its normal shape but stays pinched.
What is the reticular region of the dermis responsible for?
It contains the main blood supply for the skin through an extensive network of blood vessels called the cutaneous plexus.
What causes the color of a bruise?
Blood leaking out of a damaged blood vessel into the dermis.
What are the two layers of the hypodermis?
Subcutaneous fat and subcutaneous tissue.
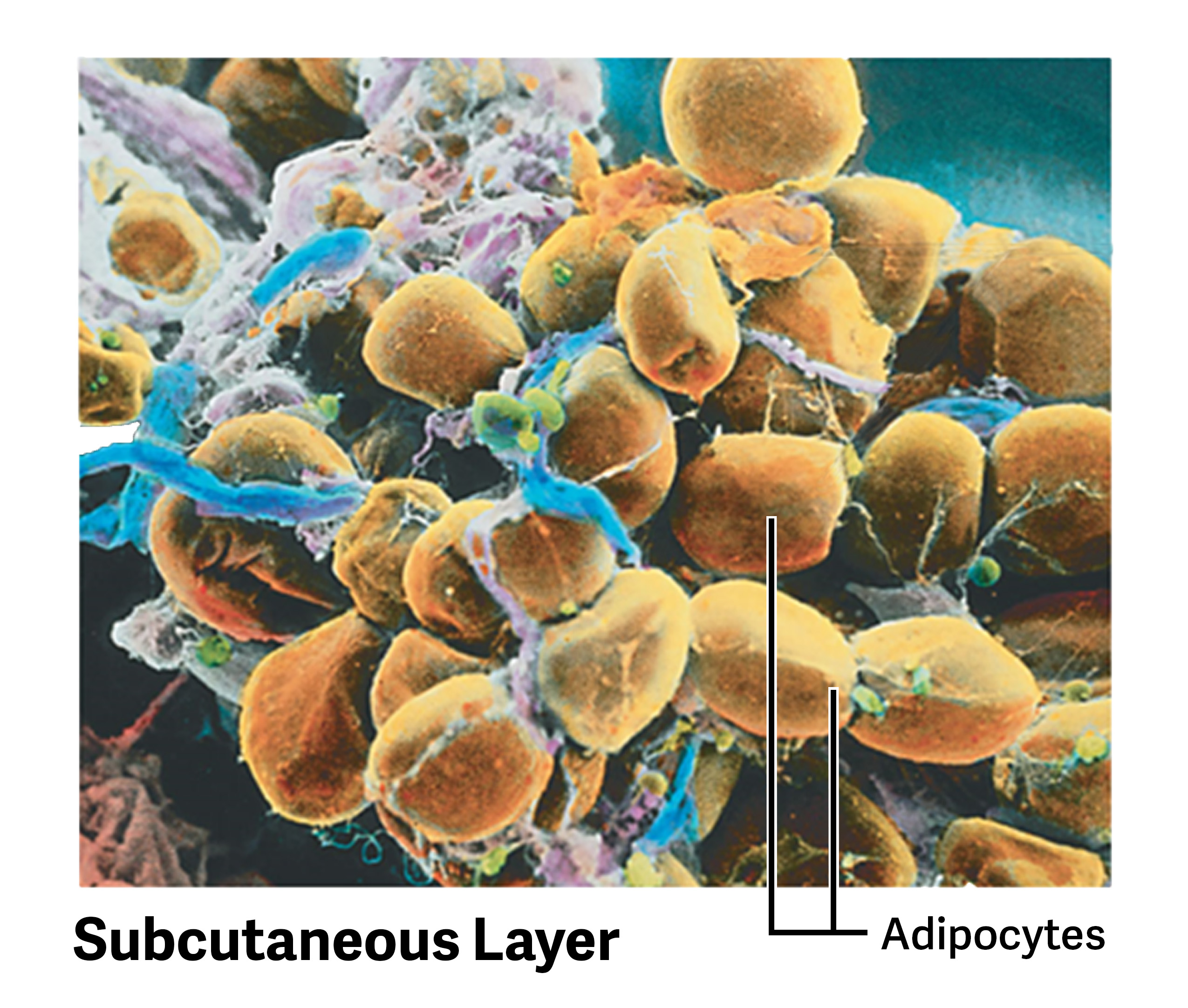
What is the primary function of the hypodermis?
To anchor the dermis to a layer of fat cells, providing insulation and protection for deeper tissues.
What is a subcutaneous injection?
An injection given in a needle that reaches the hypodermis layer, allowing for slower absorption than intravenous administration.
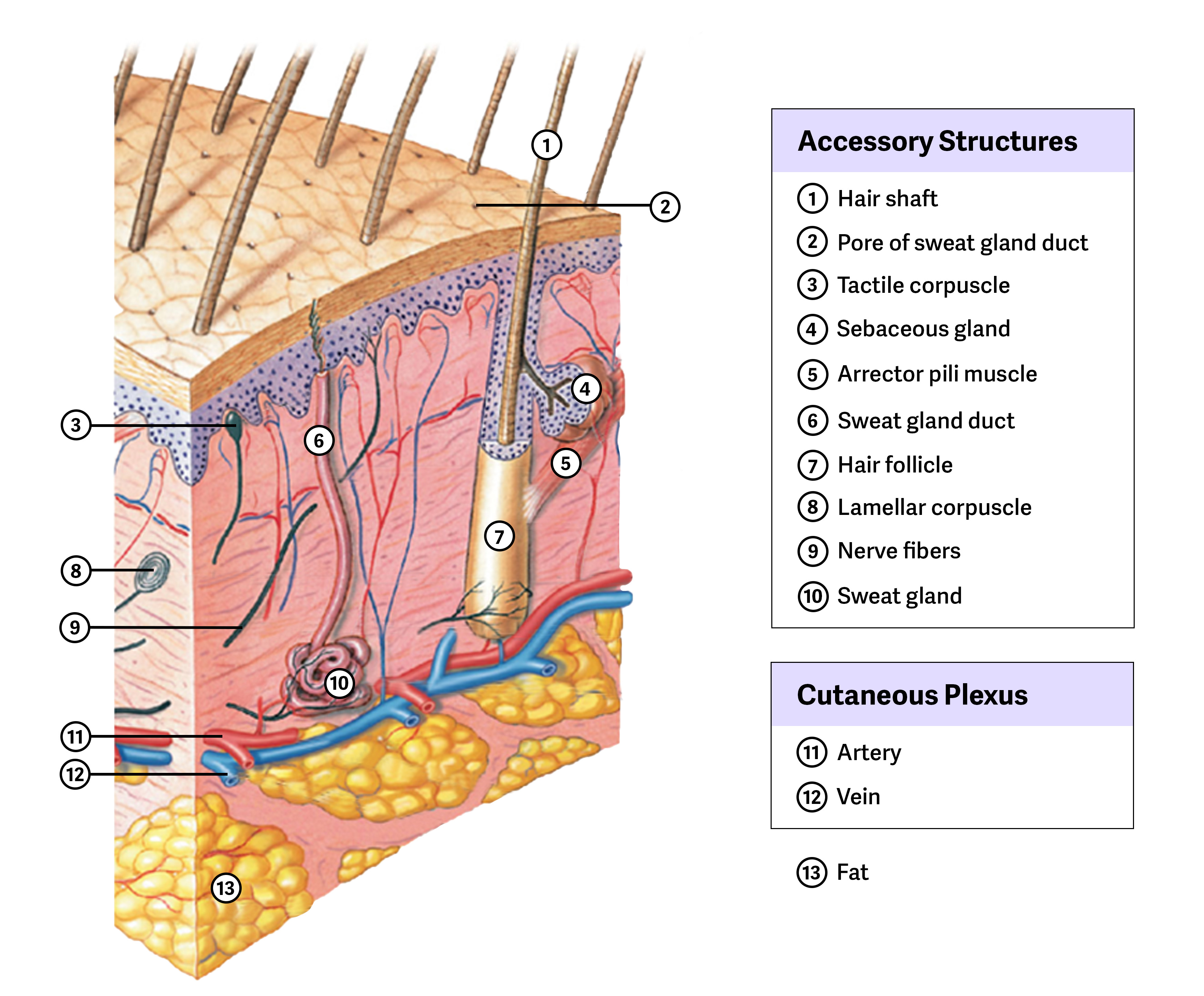
What are the two main parts of hair?
The root (in the dermis) and the shaft (extending through the epidermis).
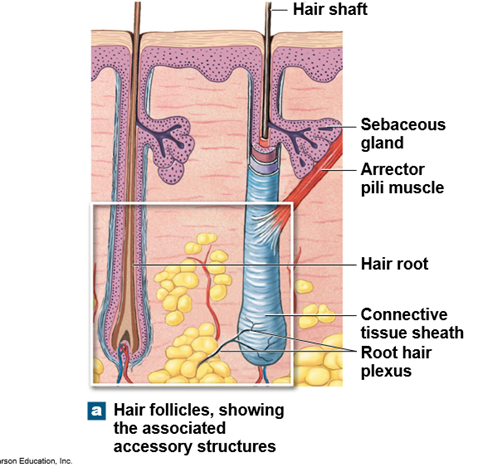
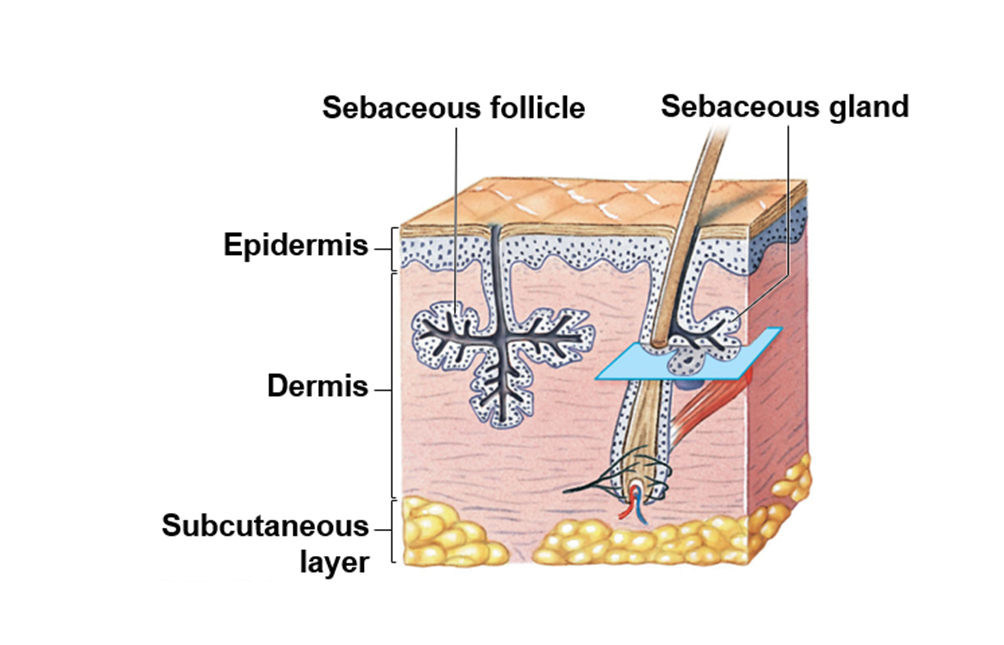
What is the role of sebaceous glands?
To hydrate hair with oil and keep the skin from drying out.
What happens to hair follicles after puberty?
They change their properties, particularly in areas like the armpits, groin, and head.
What is the visible portion of a nail called?
The nail body.
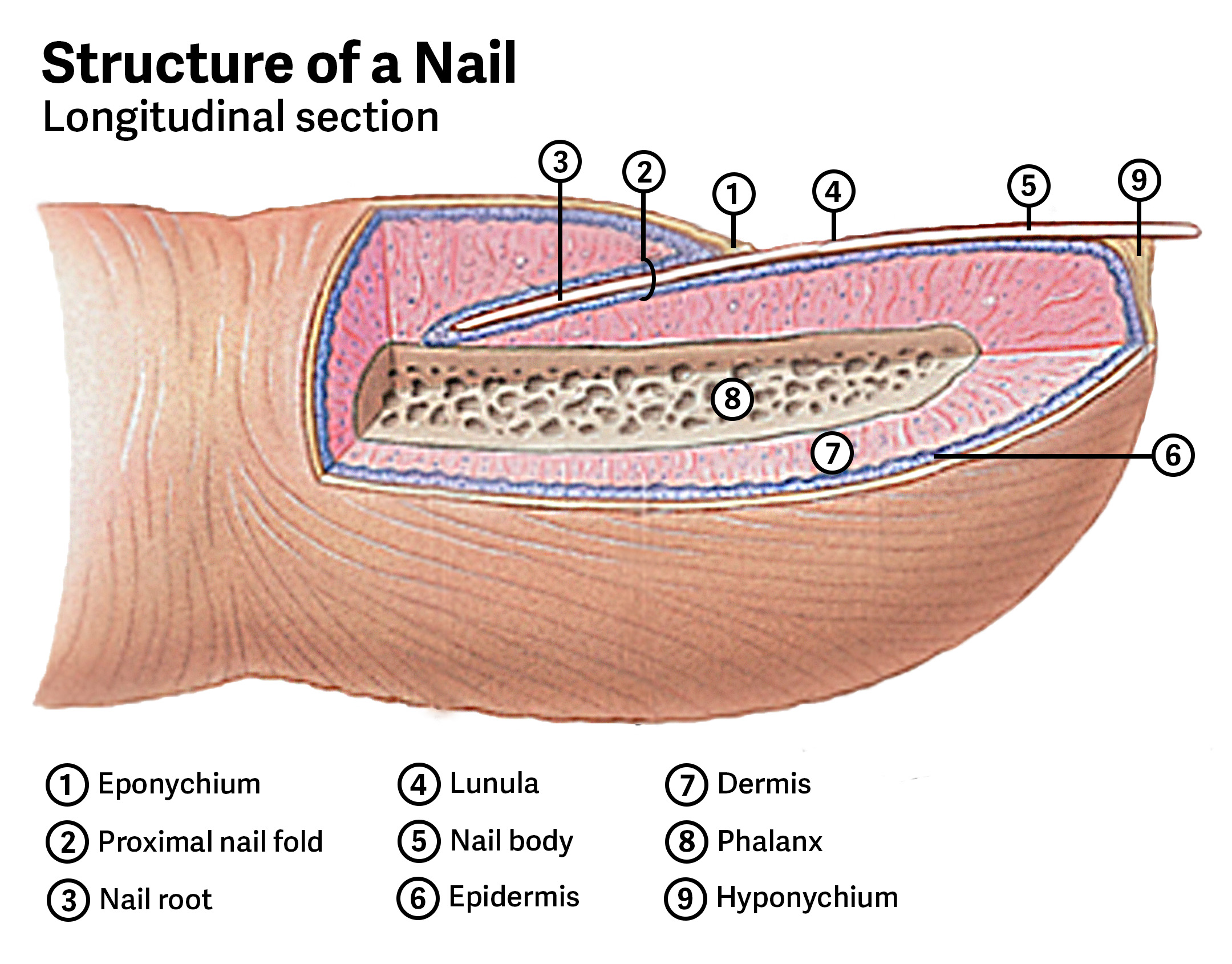
What is the lunula?
The crescent-shaped visible portion of the nail bed near the nail root.
What are mechanoreceptors in the skin responsible for?
Detecting mechanical sensory information such as light touch and vibration.
What do nociceptors detect?
Pain, such as from a pinprick.
What is the function of thermoreceptors?
To detect hot and cold temperatures.
What type of glands produce secretions onto an epithelial surface?
Exocrine glands.
What is sebum?
An oily substance produced by sebaceous glands that helps keep skin and hair moisturized.
What are the two types of sweat glands?
Merocrine (eccrine) sweat glands and apocrine sweat glands.
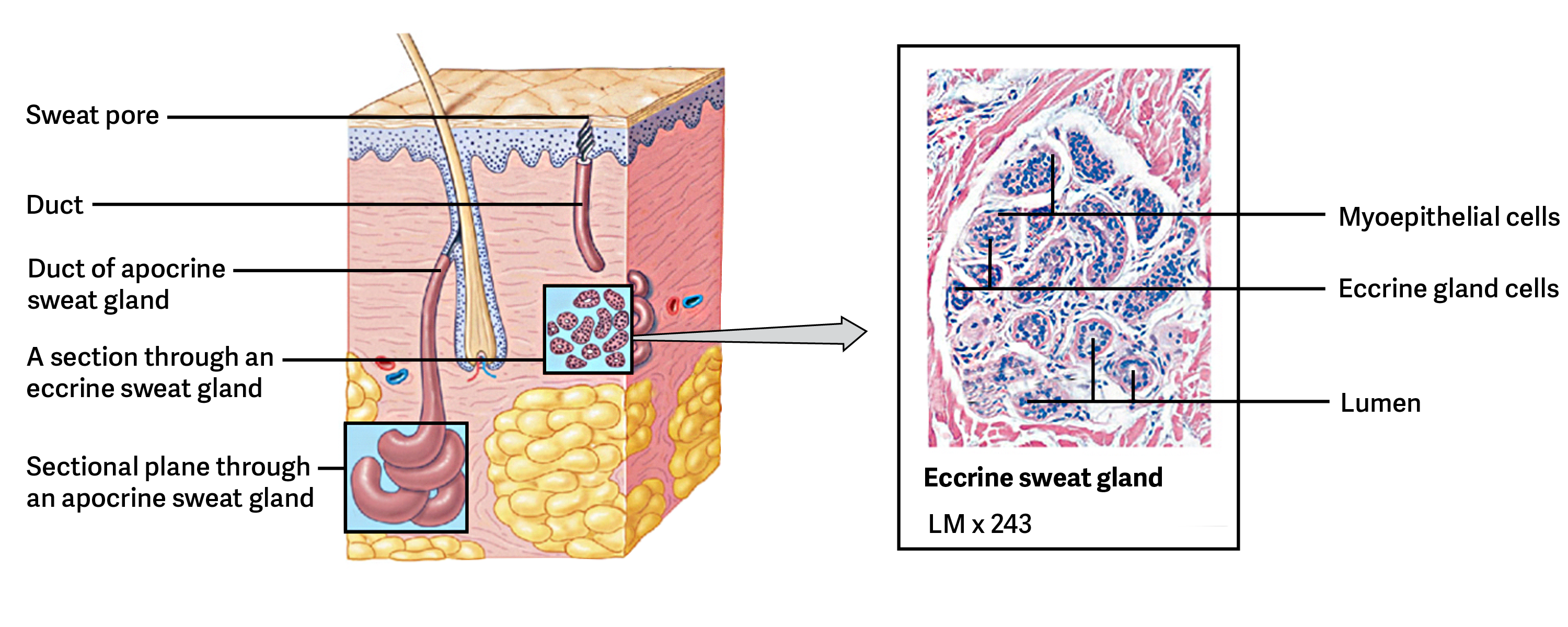
Where are apocrine sweat glands primarily located?
In the armpits and around the nipples.
What is the composition of sweat produced by merocrine glands?
99% water with a few salts.
What do ceruminous glands secrete?
Ear wax, which is a combination of sweat and sebaceous secretions.