Anatomy Quiz- Skeletal System
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Tendon
dense tissue that connects muscles to bones
Ligament
strong tissue that connects bone to bone and stabilizes jointed
sacrum
Cartilage
flexible tissue that protects your joints and bones
Joint
where 2 or more bones meet, allows flexibility
clavicle
humerus
ulna
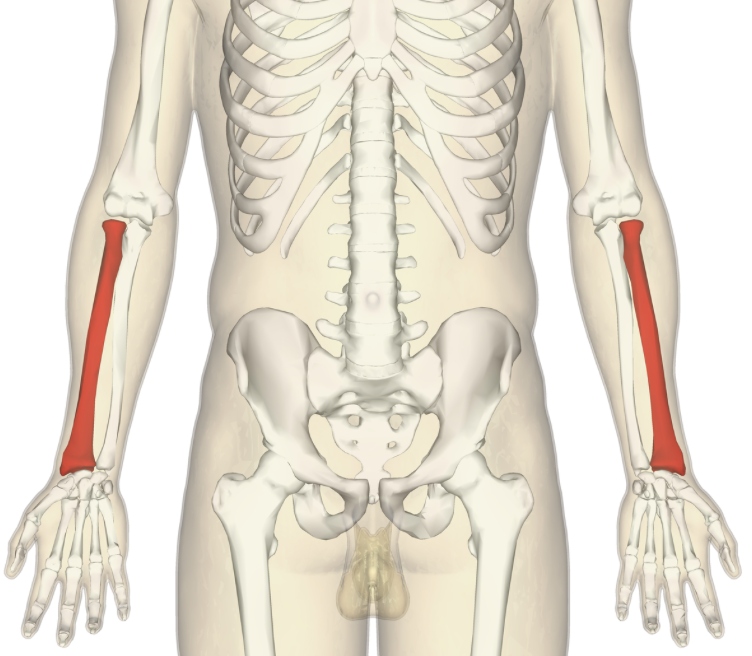
radius
What are the pelvic and pectoral girdles apart of? Which of the two is sturdier and less mobile?
apart of the appendicular skeleton
pelvic is sturdier but less mobile
what are the 4 parts of the axial skeleton?
skull, vertebral column, chest, and ribcage
osteocyte
the bone cells that maintain healthy bone structure and release chemical signals
osteoblast
construct bones by calcifying them as they form
osteoclast
remodels bones by absorbing bone tissue
example of long bone and its function
femur; weight-bearing
example of short bone and function
carpals; hand and wrist movement
flat bone example and function
scapula; upper limb movement and stability
irregular bone example and function
hip bones; support and weight distrubution
synarthrosis
non-moving joint
amphiarthroses
slightly moving joint
diarthrosis
freely moving joint
gliding
when one flat bone surface glides or slips over another
Flexion
decreasing angle of joint
extension
increasing angle of joint
hyperextension
bending that goes beyond anatomical position
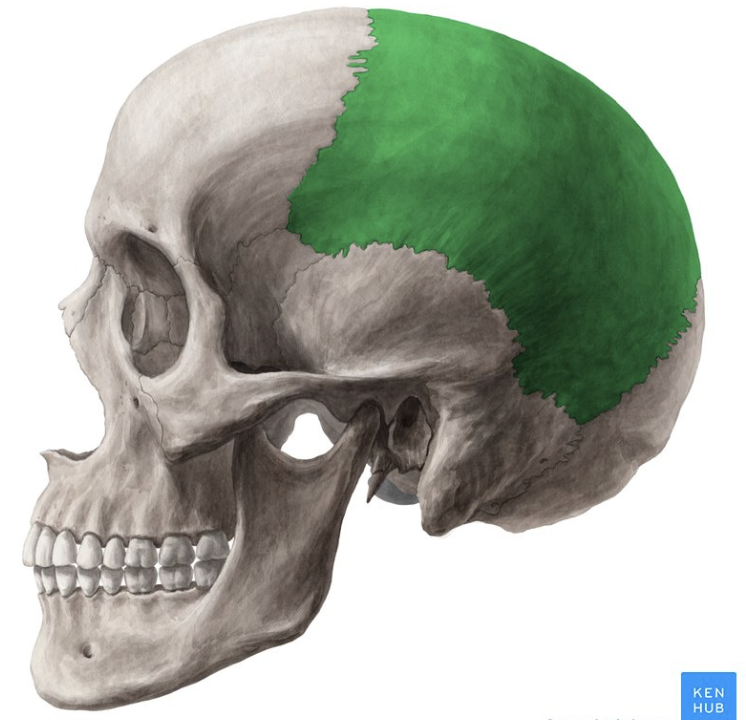
parietal
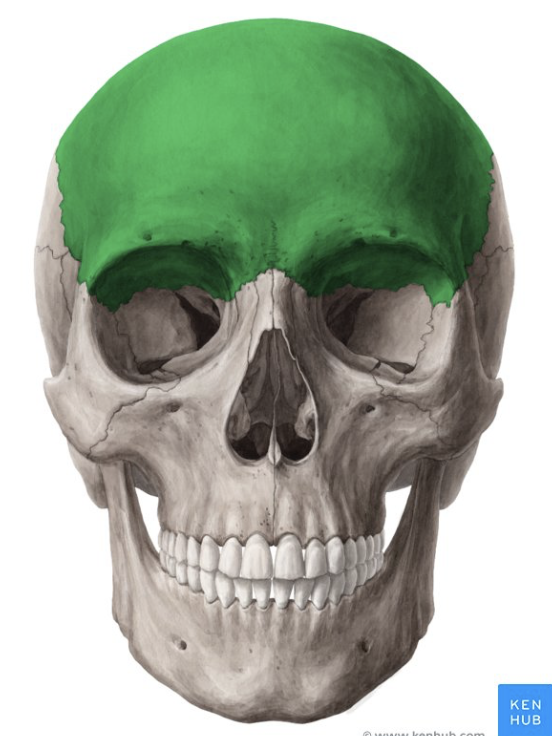
frontal
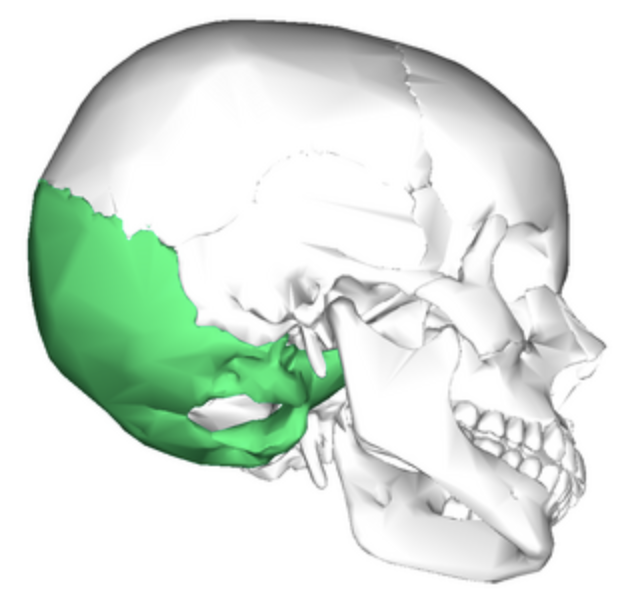
occipital
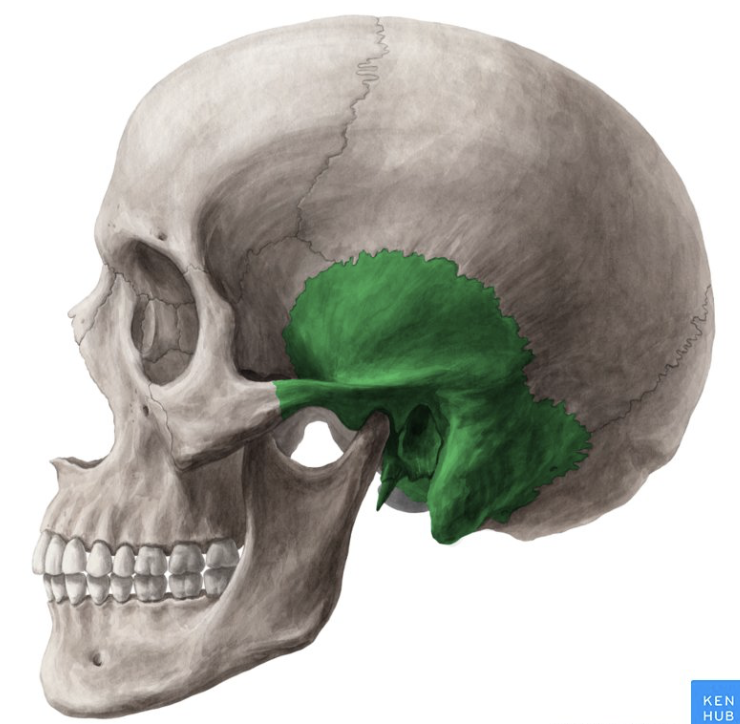
temporal
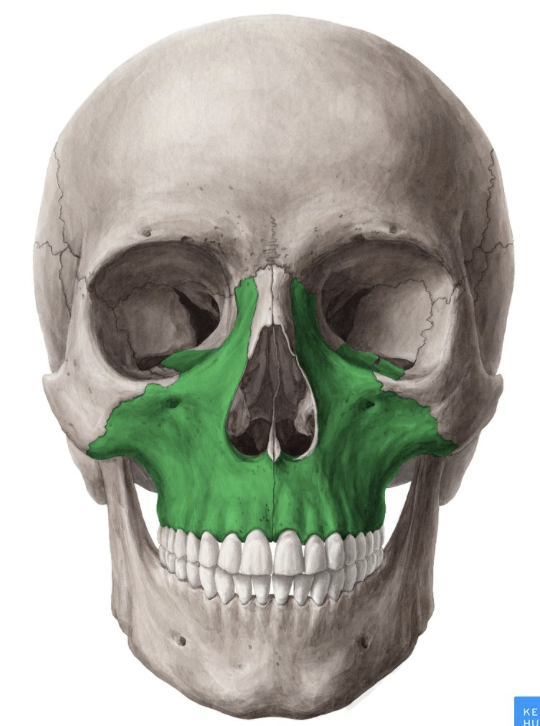
maxilla
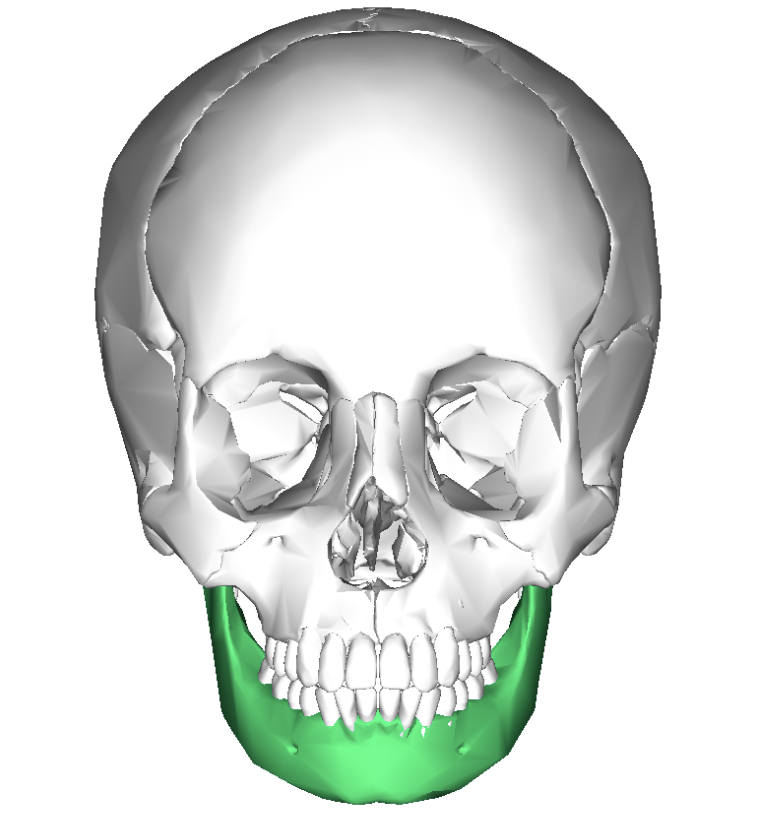
mandible
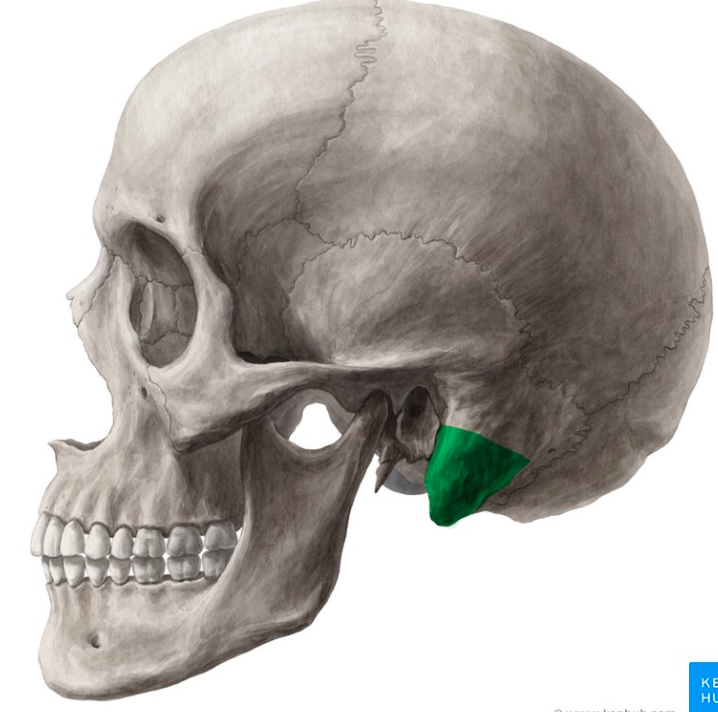
mastoid process
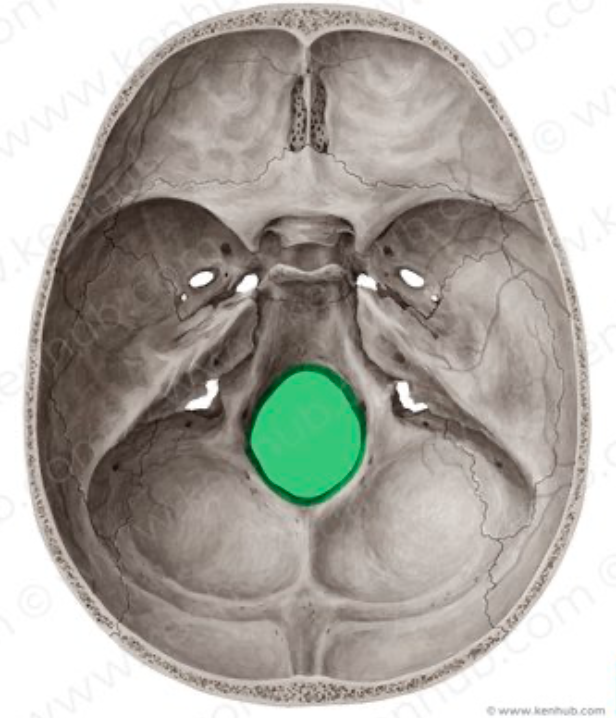
foremen magnum
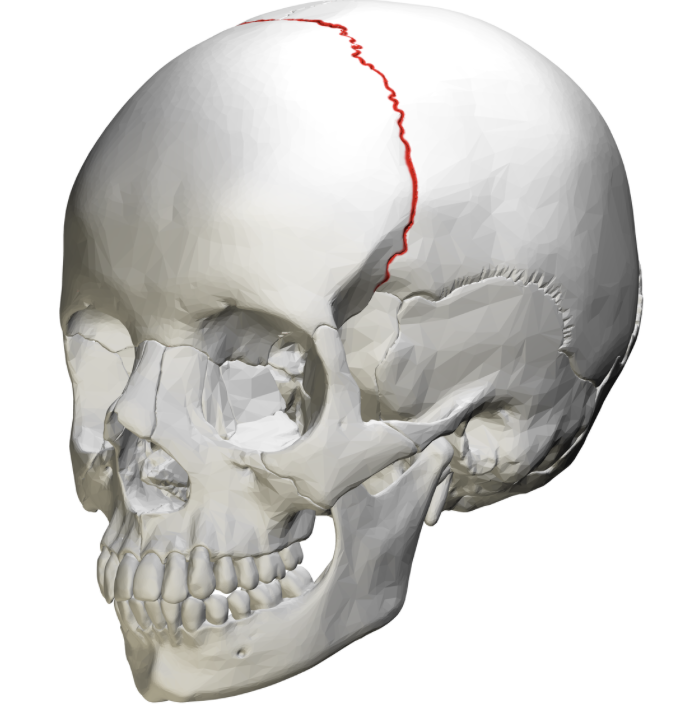
coronal suture
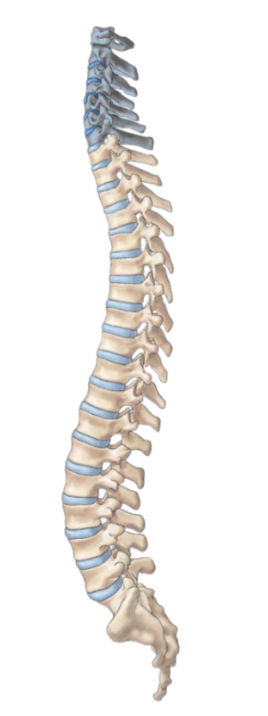
cervical
thoracic
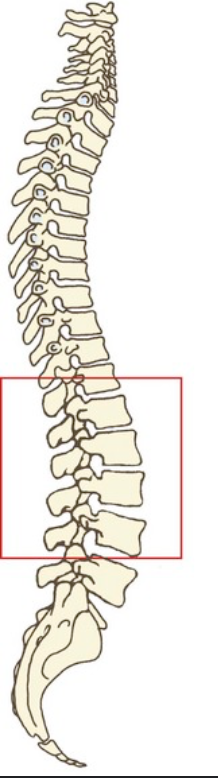
lumbar
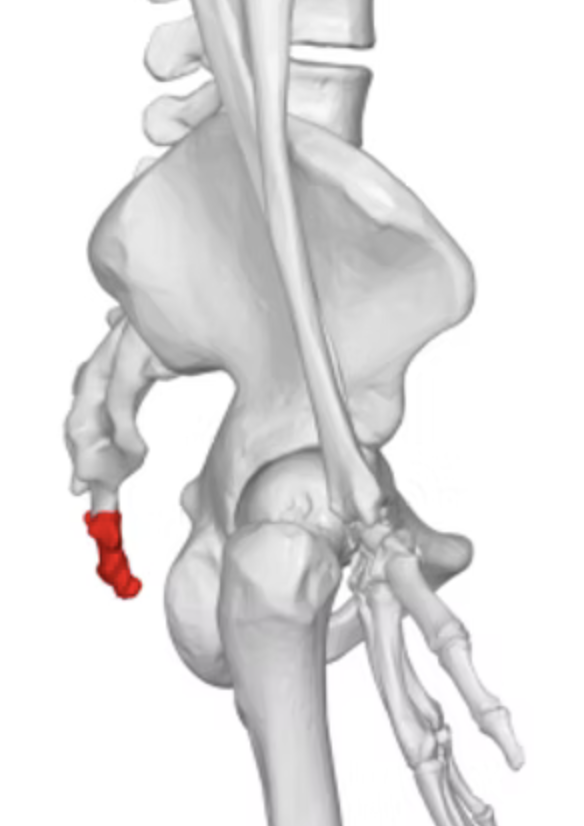
coccyx
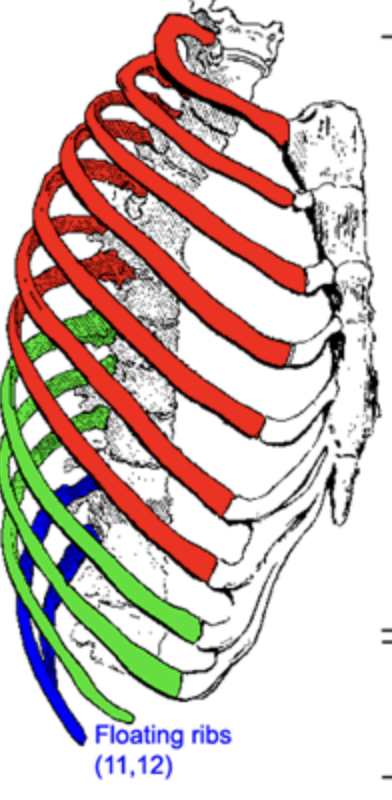
true and false ribs
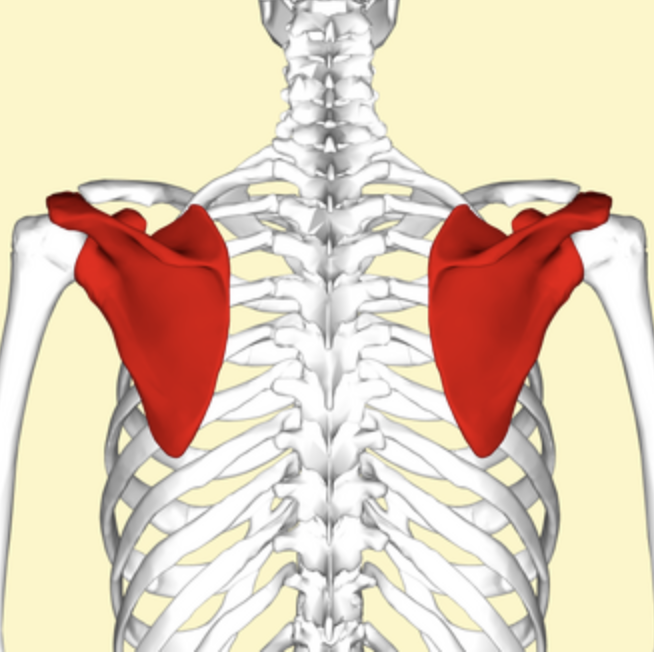
scapula
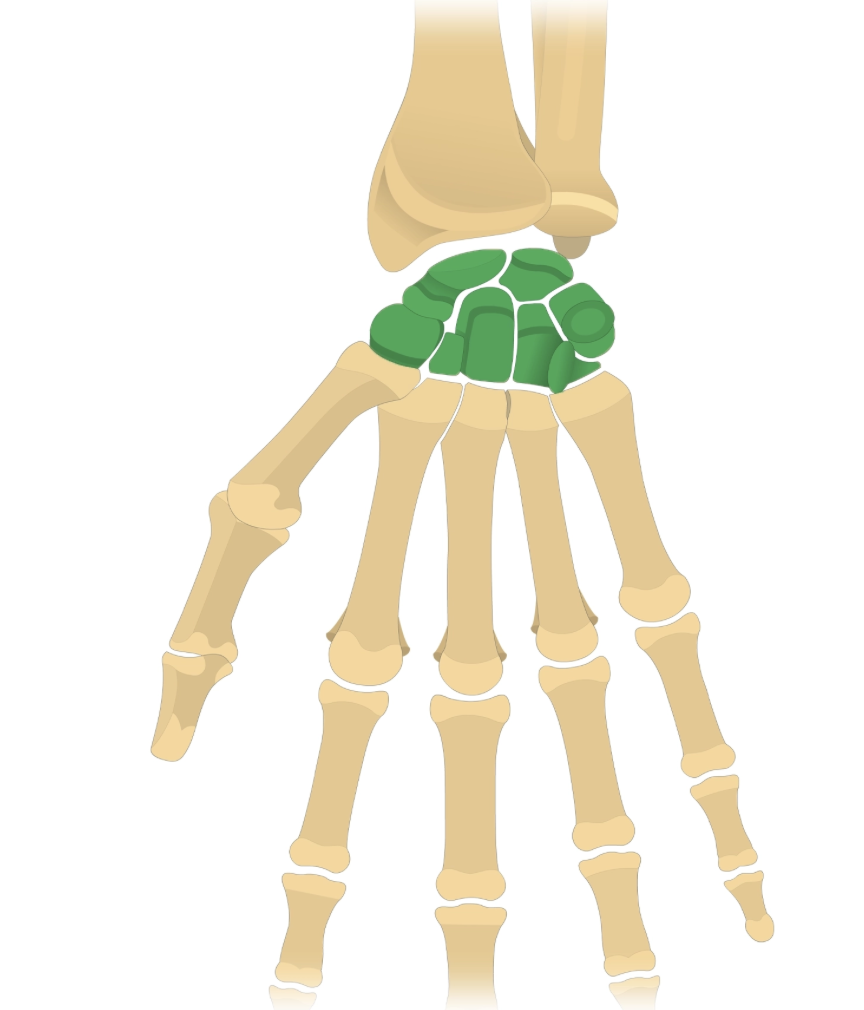
carpals
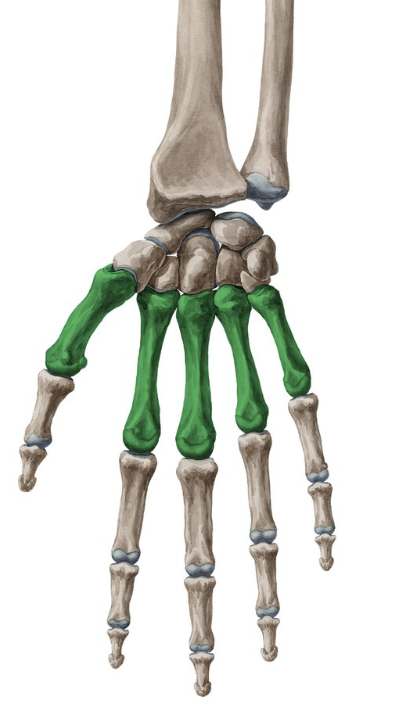
metacarpals
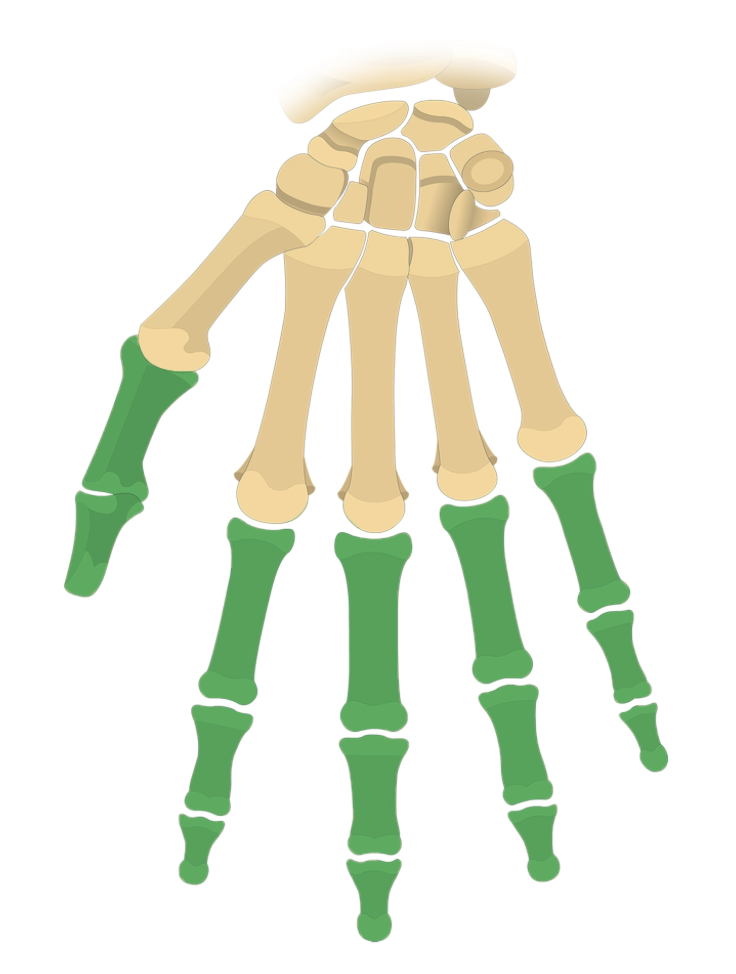
phalanges
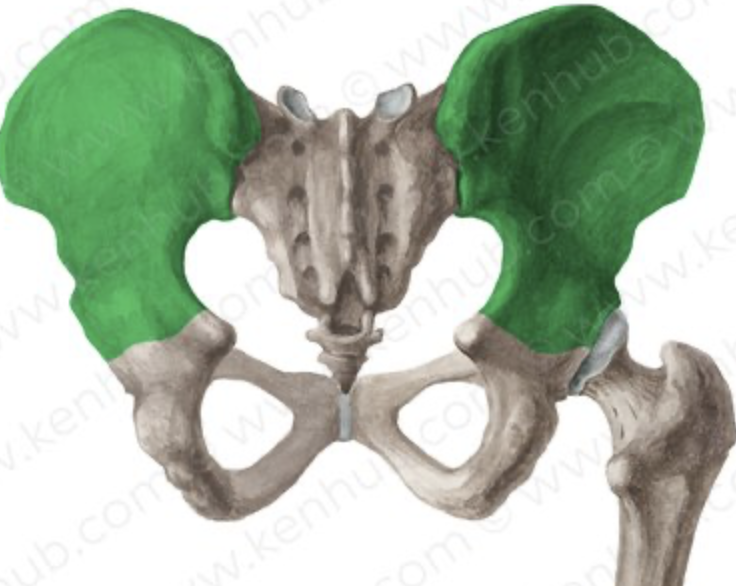
illium
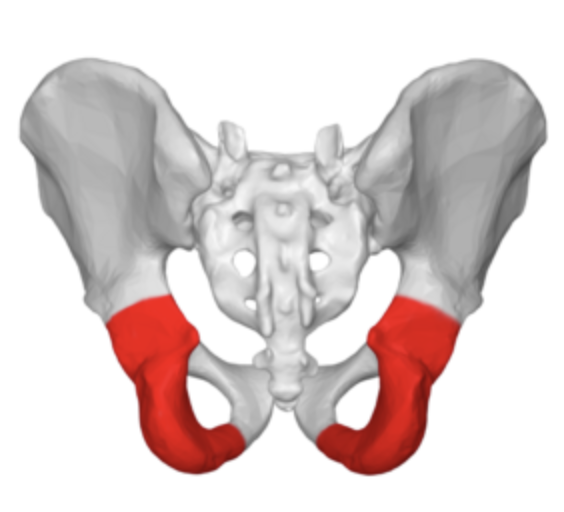
ischium
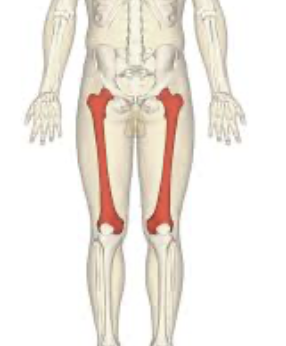
femur
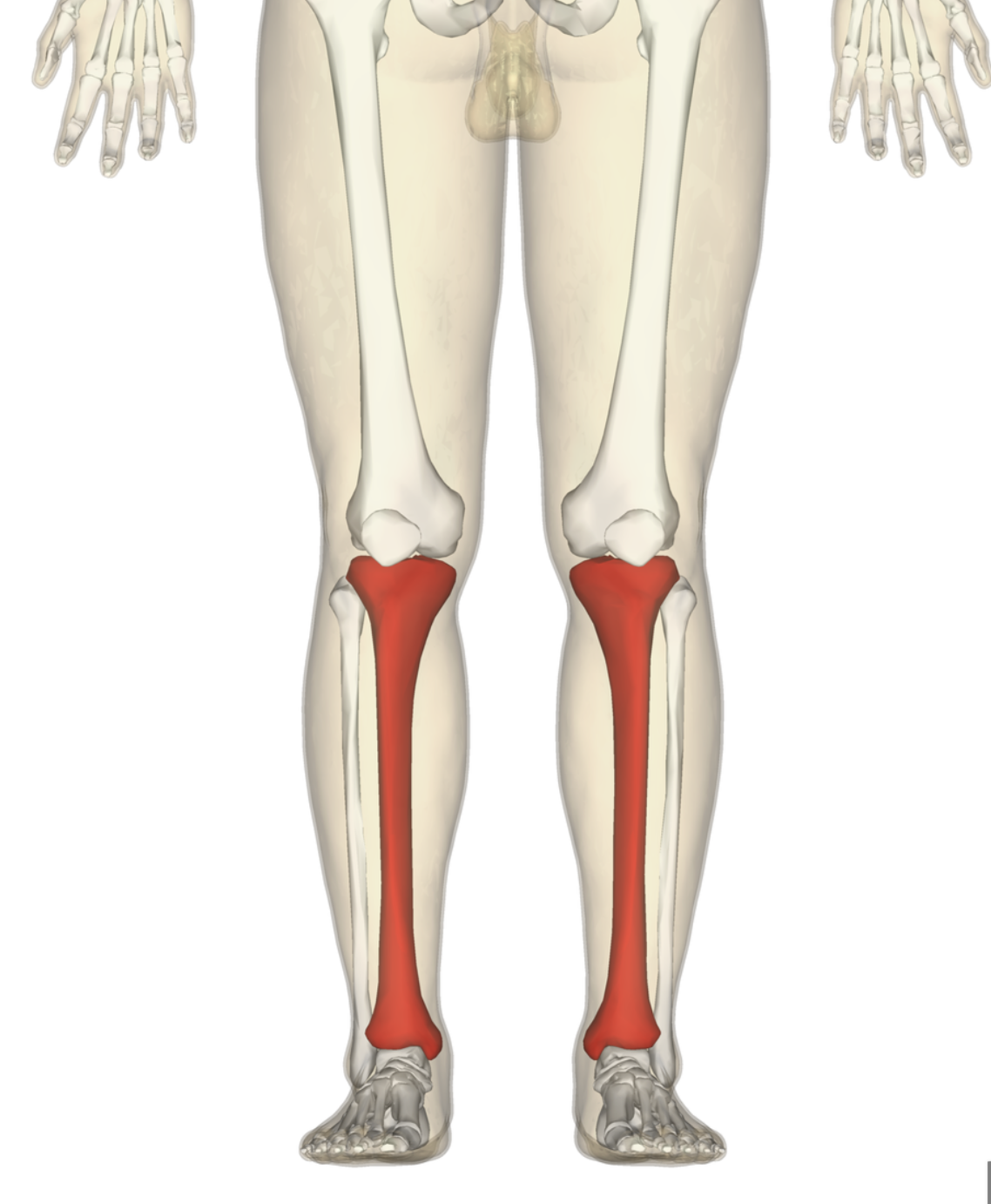
tibia
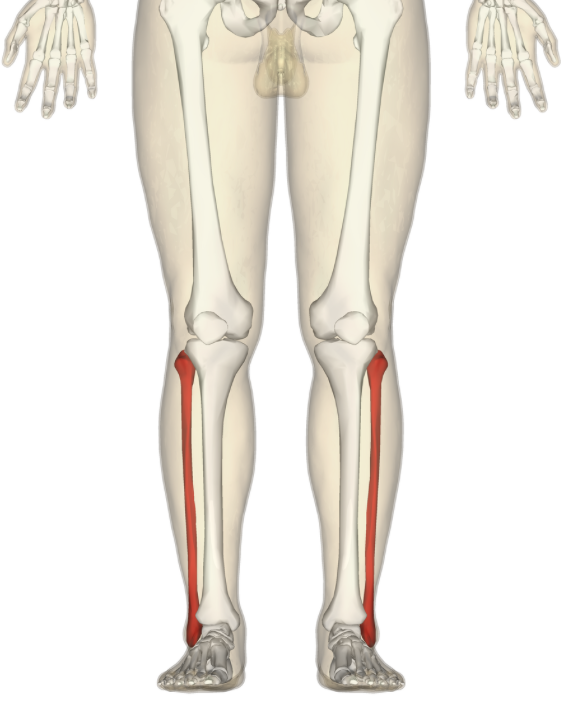
fibula
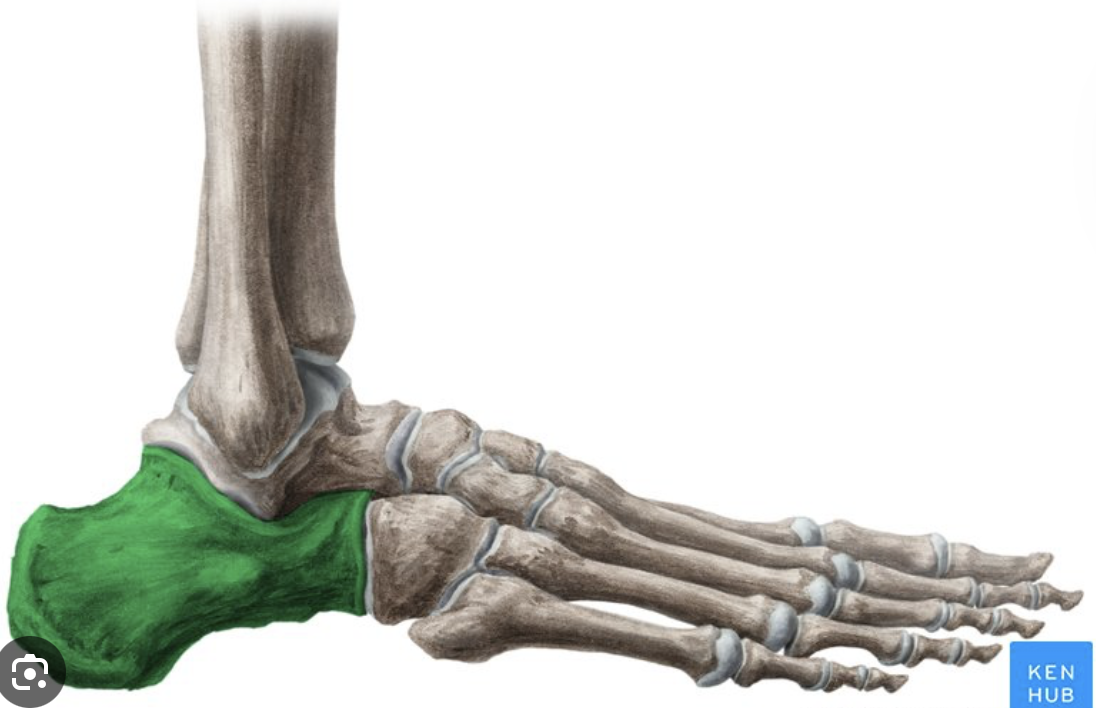
calcaneous
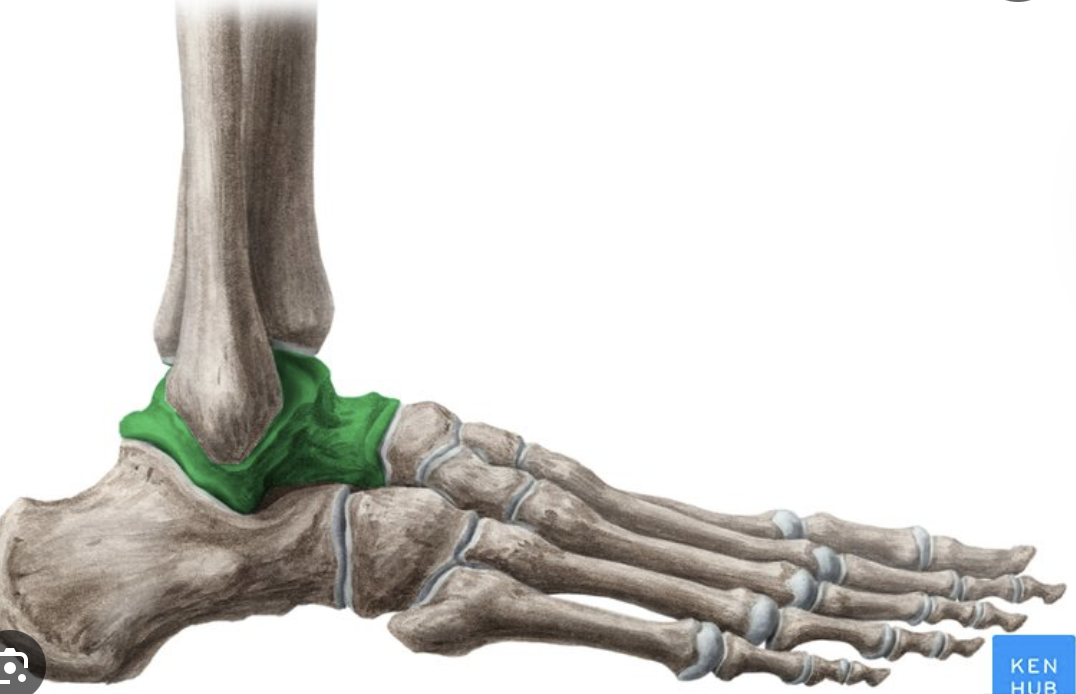
talus
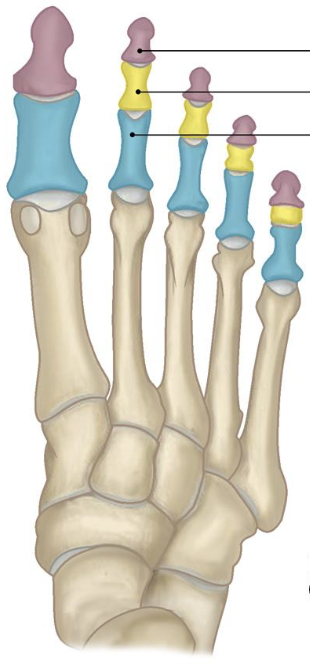
blue
proximal phalanges
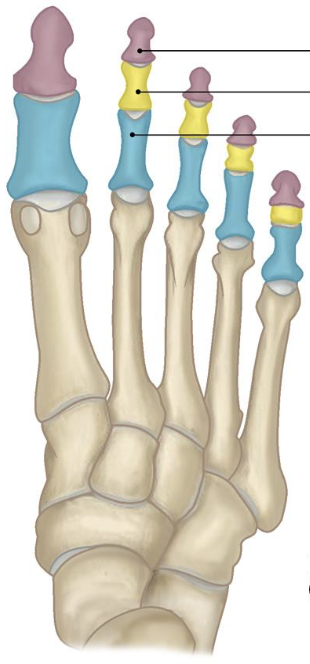
yellow
middle phalanges
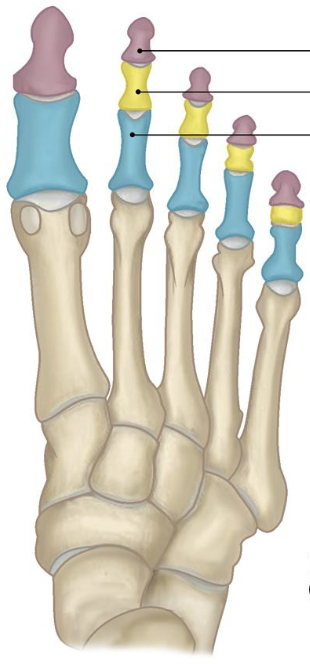
purple
distal phalanges
2 types of synovial joints and the movement they allow
intercarpal and allows gliding
intertarsal and allows gliding
synovial
allows most movement and connect with dense connective tissue
process of bone remodeling
Osteocytes release chemical signals to tell osteoclasts
Osteoclasts release enzymes for resorption
Macrophages promote bone tissue
Osteoblasts come in and build new bone
point if attachment for pelvic girdle
sacroiliac joint
point of attachment for the pectoral girdle
the sternoclavicular joint
why do the pelvic girdles of females differ from those in male?
wider pelvis for the need of childbirth