1-Element Partitioning and Chemical Differentiation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What makes an element major, minor or trace?
Major >1 wt%, Na, Mg, Ca, Fe, Al, Si, O
Minor 0.1-1 wt% H, K, Ti, Cr, Mn, C, S
Trace elements <0.1 wt%
Why are trace elements used as tracers and resources?
not involved in chemical reaction
passive tracers in earth processes
relatively easy to measure by mass spectrometry
ore deposits occur where trace elements are highly concentrated
What is chemical differentiation?
Separation of larger bodies into chemically distinct parts.
Earth and solar system are differentiated.
trace elements track differentiation
How do we know about solar element abundances?
estimates from solar spectroscopy and analyses of CI chondrites (same as sun and so same as solar system)
nucleosynthesis mechanisms, H & He from Big Bang, Li B Be from cosmic ray spallation, C to Fe from stellar fusion, Ni to Bi from neutron capture
What is Odoo-Harkins rule?
Odd-even effect.
Paired protons, even elements are more stable and more abundant
What is siderophile, chalcophile, lithophile, atmophile?
Siderophile = iron liquid, core
Chalcophile = sulfide liquid, core
Lithophile = silicate liquid, mantle and crust
Atmophile = gas, atmosphere
Phile means loving
Partitioning affinity depends on conditions.
What is symbols for partition coefficients, and when is it compatible or incompatible?
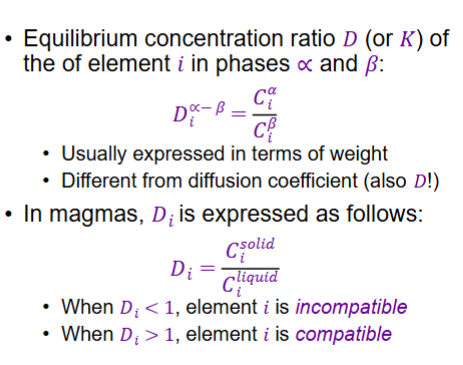
What is meant by compatible and incompatible?
When D < 1, element is incompatible. Element prefers the liquid
When D > 1, element is compatible. Element prefers the solid
What factors affect trace element partitioning? What are the general rules of partitioning?
ionic radius - avoid inducing lattice strain by introducing ions of different sizes
charge - avoid introducing highly charged ions, and avoid introducing charge imbalance
large cations are typically incompatible
small divalent cations are often more compatible than small univalent cations
ionic radius more important than charge
What is Goldschmidt’s Rules for element substitution?
ions of one element can extensively substitute for those of another if their radii differ by less than 15%
two ions have similar radii and the same charge, the smaller ion is preferentially incorporated into the solid
if two ions have similar radii but different charges, the ion with the higher charge is preferentially incorporated into the solid
What are the types of incompatible trace element?

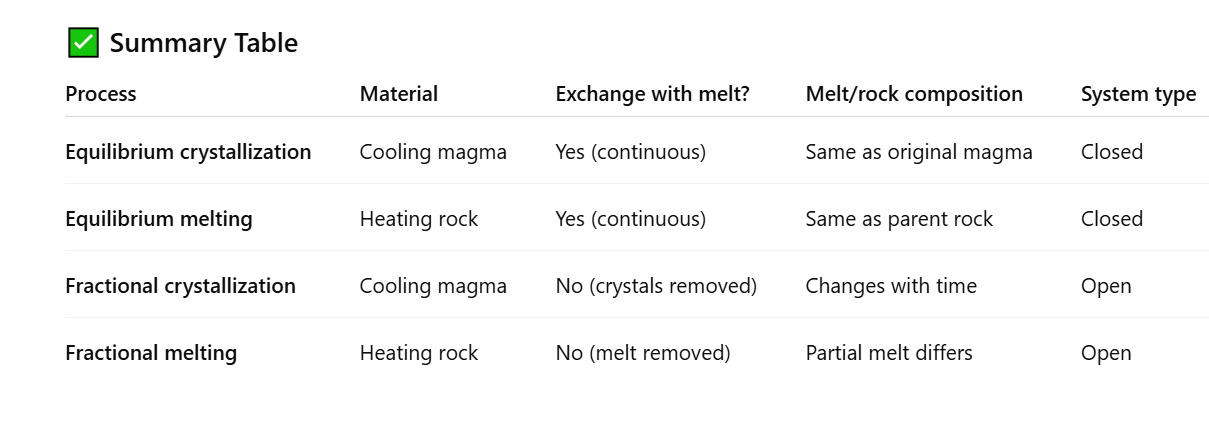
What are the four different magmatic processes to consider?
Equilibrium melting
Equilibrium crystallisation
Fractional melting
Fractional crystallisation

Explain equilbrium melting
Incompatible elements (prefer the liquid) are highly concentrated in the melt, at low F, and are diluted as F increases.
Compatible elements (prefer the solid) have very low concentrations in melts, especially at low F

What is meant by F and X?
The proportion of liquid is denoted F
Proportion of solid is often expressed as X, where X = 1 - F
What is difference between equilibrium crystallisation, melting, and fractional crystallisation and melting
Equilibrium crystallisation - Occurs when a magma cools and crystals form, but the crystals remain in contact with the melt and can exchange elements freely.
Equilibrium melting - The reverse process — when a solid rock melts and the melt stays in equilibrium with the remaining solid.
Fractional crystallization: crystals are removed from melt → melt composition changes rapidly.
Fractional melting: melt is removed from the solid → melt is different from the bulk rock.
What is equilibrium crystallisation?

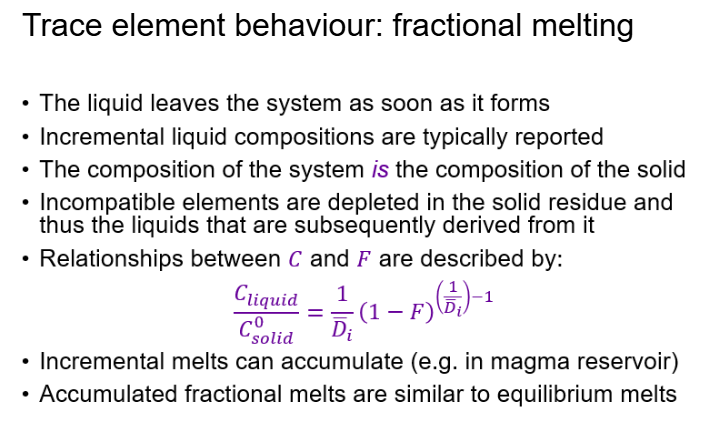
What is meant by fractional melting?
Incompatible elements (prefer the liquid) are rapidly depleted in the solid residue, so liquids are also rapidly depleted.
Compatible elements (prefer the solid) are initially retained in the solid, so the last liquids are relatively enriched.
What is fractional crystallisation?
Incompatible elements (prefer the liquid) remain in the system, so liquids become highly enriched.
Compatible elements (prefer the solid) are rapidly removed from the system, leaving highly depleted residual liquids

What is the composition of the core like?
16% of earth’s volume, 31% of earth’s mass
Fe 90 and Ni 5wt%, Fe/Ni core is similar to chondrites
Density is lower than pure alloy due to light elements present, H, C, S, O, Si
siderophile elements are depleted in the mantle but rich in the core
What is the composition of the mantle like?
83% of earth’s volume, 68.3% of earth’s mass
Bulk silicate earth BSE = CI chondrite - core
O, Si, Mg, and Fe dominate alongside Ca, Al
Mantle composition determined by meteorites, xenoliths, and ophiolites
What is the composition of the crust?
insignificant to earth’s volume, 0.7% of earth’s mass
composed of O, Si, Al, Fe, Mg, Na, K
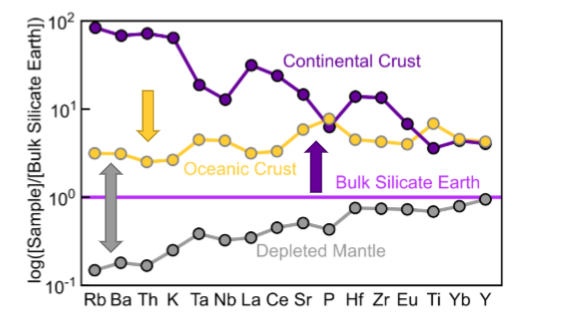
oceanic crust = rich in Ca, Mg, Fe, cover 70% of surface
continental crust = rich in Si, Na, K, and incompatible elements
How does the composition of the continental crust change?
Mean composition is andesitic.
Grades from basaltic at the base to granitic at the top.
What is the oceanic crust like?
Mean composition is basaltic, but stratified from ultramafic at base, to basaltic at top.
How is the continental crust and oceanic crust difference when it comes to having incompatible elements?
Continental crust has a lot more incompatible elements.
Oceanic crust is relatively depleted in high incompatible elements.