Lens and Vitreous
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
T/F nuclear sclerosis is a normal part of aging?
True
What is the effect of nuclear sclerosis on vision?
Minimal
What does nuclear sclerosis look like?
Grayish blue haze
What do you need to differentiate nuclear sclerosis from?
Cataracts
What can you do to differentiate nuclear sclerosis from a cataract?
Aim the light dorsally and use tapetal reflection
What is a cataract?
Opacity in the lens or capsule
What should the neuro things be with cataracts
Normal PLR and a dazzle reflex
Absent menace response
What are the 2 most common causes of cataracts in dogs?
Hereditary
Metabolic from Diabetes mellitus
What is the most common cause of cataracts in cats and horses?
Secondary to uveitis
What is a congenital cataract?
At birth
What is a juvenile catarac?
Young animal 1-5yrs
How do you classify cataracts?
Etiology
Age of onset
Location in lens
Stage of development
What are the cataract stages?
Incipient
Immature
Mature
Hypermature
What is an punctate opacity with <15% of the lens for a cateract?
Incipient
What is a cataract that is between 15% and 99% of the lens with some tapetal reflection?
Immature
What is a cataract with 100% opacification with no tapetal reflection and no menace response?
Mature
What is a resorption of some cataractous lens fibers causing a sparkling, wrinkled capsule with some tapetal reflection and some vision?
Hypermature
What stage of cataract do you lose menace response?
Mature
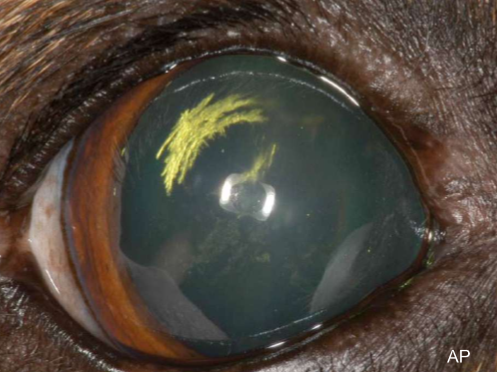
Incipient cataract
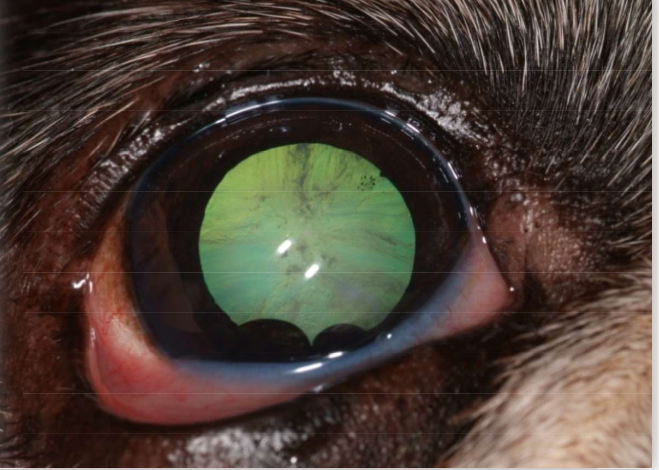
Immature cataract
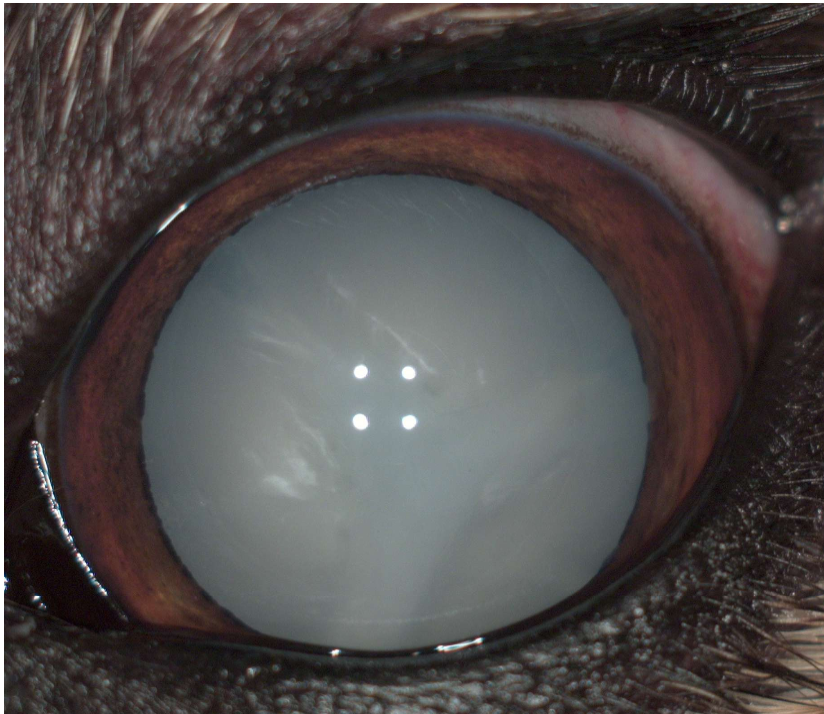
Mature cataract
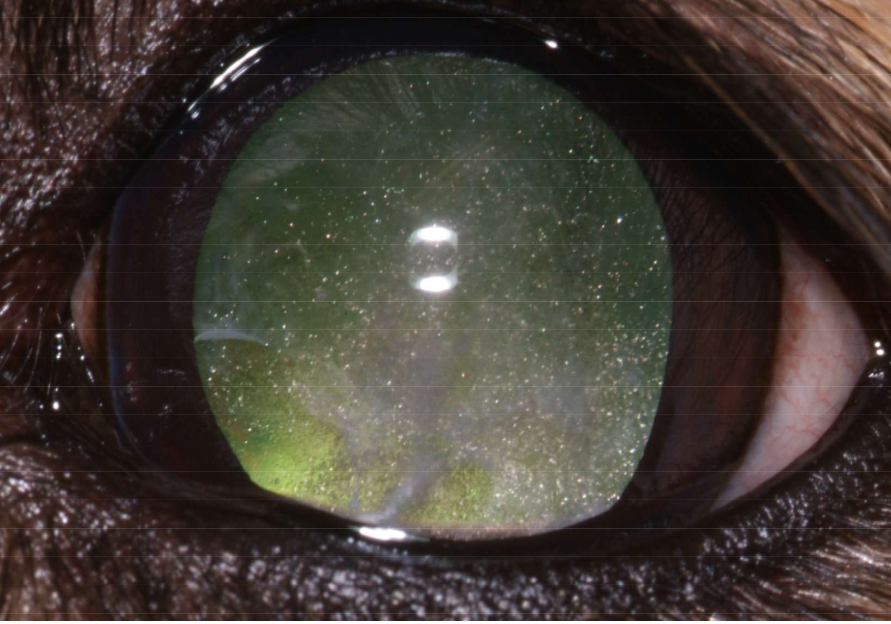
Hypermature cataract
Describe the steps of lens metabolism
High blood glucose causes elevated aqueous humor glucose, increasing lens glucose and overwhelming hexokinase enzyme
Excess glucose is metabolized by aldose reductase and converted to sorbitol
Sorbitol accumulates within the lens causing an osmotic effect
Fluid is drawn into the lens causing cataract
How is glucose normally metabolized in the lens?
Anaerobic glycolysis
What are two other concerns of cataracts that are not blindness?
Phacolytic uveitis
Phacoclasitc uveitis
What is phacolytic uveitis?
Leakage of lens proteins through intact lens capsule
What is phacoclastic uveitis?
Rupture of lens capsule exposing lens proteins acutely
How can you prevent lens-induced uveitis during cataract therapy?
Topical NSAIDs
How do you treat active lens induced uveitis?
Topical steroid
Oral NSAID
When is the best time to do cataract surgery?
Mid-immature with no lens induced uveitis
What are some considerations for cataract surgery?
Uveitis must be controlled
General health needs to be good
Temperament of animal
Client commitment
What is the only way to cure cataractive?
Elective cataract surgery
What is LIU?
Lens induced uveitis
What is included in the work up for cataract surgery?
Complete ophthalmic exam
Physical exam to ensure it is safe
Gonioscopy
Electroretinogram
Ocular ultrasound
What is the rate of cataract surgery complications?
10-15%
What are the postoperative complications of cataract surgery?
Uveitis
Glaucoma
Retinal detachment
Endophthalmitis
What causes lens luxation?
The breakdown of zonules that holds the lens in place
What is subluxation of the lens?
Partial detachment of lens zonules
What is a lens luxation?
Complete detachment of lens zonules
What is an anterior lens luxation?
Lens is anterior to the iris
What is a posterior lens luxation?
Lens is posterior to iris, usually in vitreous chamber
What breeds are susceptible to primary lens luxation?
Terriers
What causes secondary lens luxation?
Chronic glaucoma
Uveitis
Trauma
Intraocular tumors
Hypermature cataracts
When is anterior lens luxation an emergency?
If it is recent and the dog is visual
How do you treat an emergency lens luxation?
Intracapsular lens extraction
How do you treat the secondary lens luxation with anterior lens luxation?
Mannitol IV or glycerin PO
Topical/oral carbonic anhydrase
Why should you not give miotics like pilocarpine or latanoprost to a patient with an anterior lens luxation?
It traps the lens in the anterior chamber
T/F secondary lens luxation is an emergency?
True, only if recent
What do you treat primary lens subluxation?
Proactive surgical lens removal
Medical therapy BID to keep pupil miotic and lens back with latonorpost
How do you manage posterior lens luxation?
Miotic therapy
How large is the vitreous?
>2/3 of globe volume
What is vitreous humor made of?
99% water 1% collagen
What does the vitreous do?
Support lens anteriorly and support retina posteriorly
Maintains globe shape
Transmits to retina
What are some vitreous abnormalities?
Vitreal degeneration
Vitreal cells
Vitreal hemorrhage
Asteroid hyalosis
What is ateroid hyalosis?
Small white particles in the vitreous that are Ca2+ or phospholipids that move with the eye
What is the significance of asteroid hyalosis?
Incidental