Knes 259 Skeletal System & Upper Extremity Bones Lecture
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Skeletal system includes:
Bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, musculoskeletal system
5 Primary functions of the skeletal system and bones
Support
Protection
Leverage and Movement
Storage of minerals (like calcium) and lipids
Blood cell production
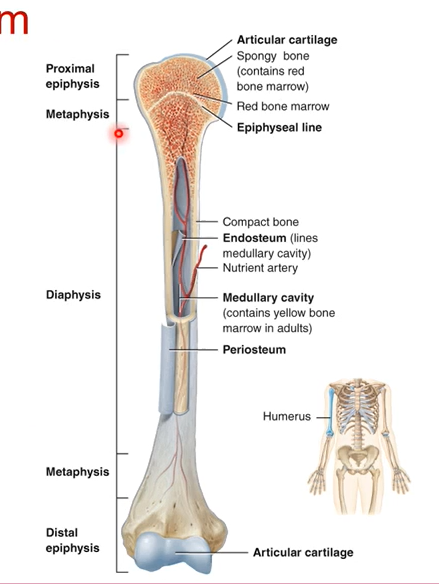
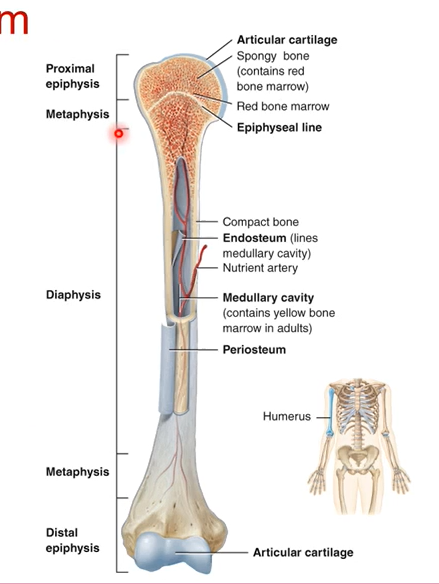
The longest part of the bone is known as the ____
diaphysis is the longest part of the shaft of the bone
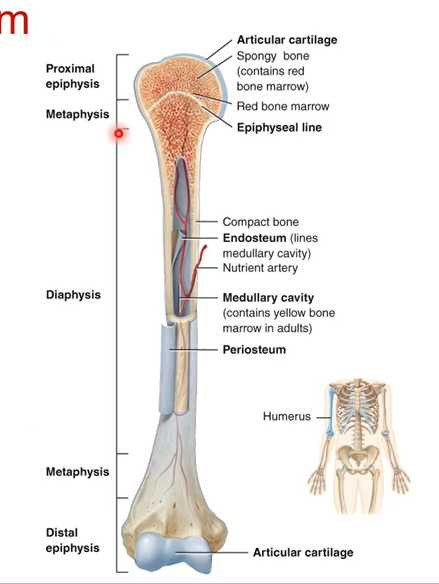
Define these:
Articular cartilage-
Spongy bone-
Endosteum-
Medullary cavity-
Periosteum-
Articular cartilage- smooth surface for bones to articulate together
Spongy bone- blood cell production occurs .bone marrow found
Endosteum- lines medullary cavity
Medullary cavity- storage and production of lipids and blood vessels run through here.
Periosteum- outside the bone. outer shell of bone that protects the bone and has blood vessels.
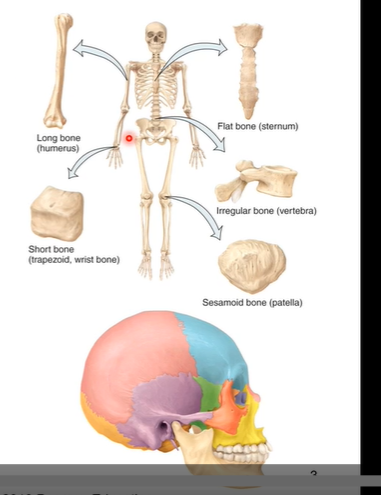
Types of bones in the body
Long (greater in length than width)- ex humerus, fibula, etc. primarily in upper and lower extremities
Flat- like a protective shield like ex sternum.
Sutural- found in skull. typically fuse together. make skull serve as one big bone instead of many unfused parts
Irregular ( complex shapes)- like vertebra
Short (cube shaped)- in carpals of wrist or tarsals of feet. help with stability and subtle movements for gliding. ex trapezoid bone
Sesamoid (shaped like a sesame seed)- changes direction of forces from muscles. ex patella (knee cap).
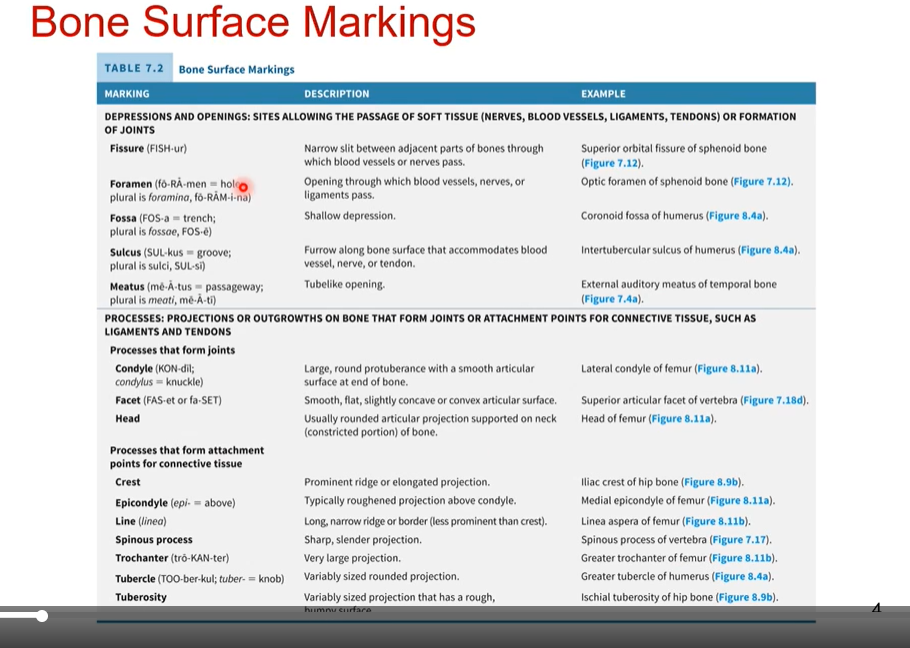
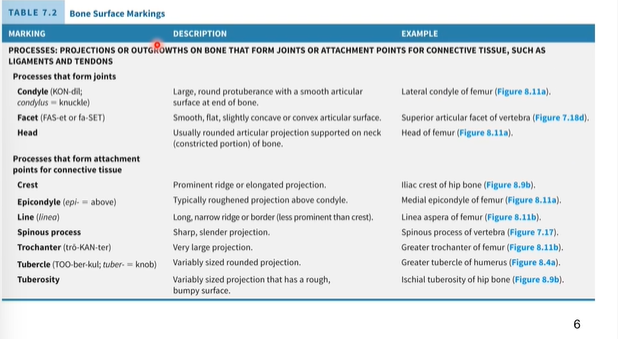
Bone Surface Markings 1
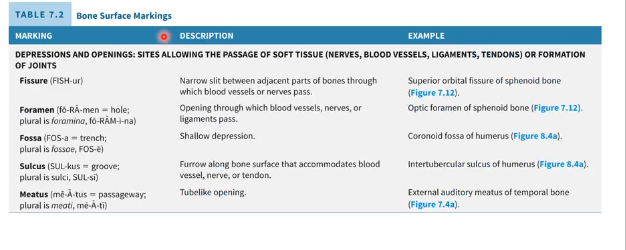
Bone Surface Markings 2
Bone Surface Markings 3
What are the skeletal divisions
Axial Skeleton- skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, vertebral columns, thorax. total bones =80
7
Appendicular Skeleton- pectoral, upper limbs, pelvic, lower limbs= 126
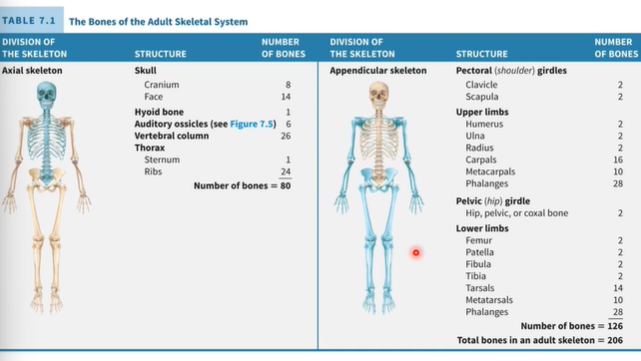
How many total bones in the adult skeletons
206
Upper extremity bones
each of these have a left and right version. there is a left ulna and right ulna for ex
Clavicle- the most proximal.
Scapula
Humerus
Ulna
Radius
Carpals
Metacarpals
Phalanges - most distal
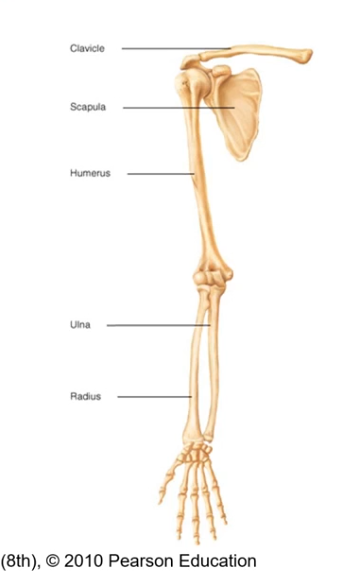
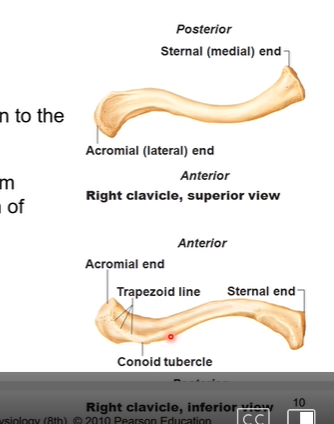
Define Clavicle Bone
joins axial skeleton to appendicular skeleton. articulates with sternum (medial) and acromion of scapula (lateral)
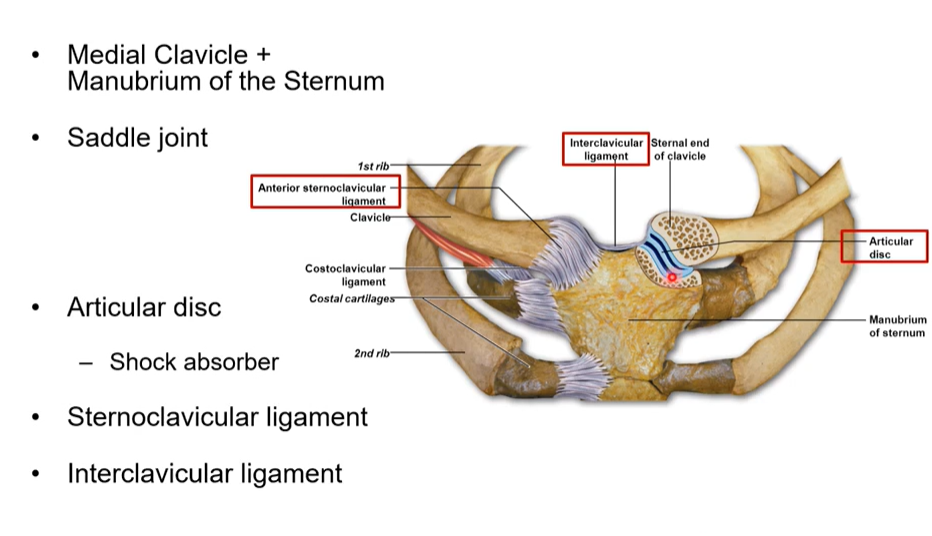
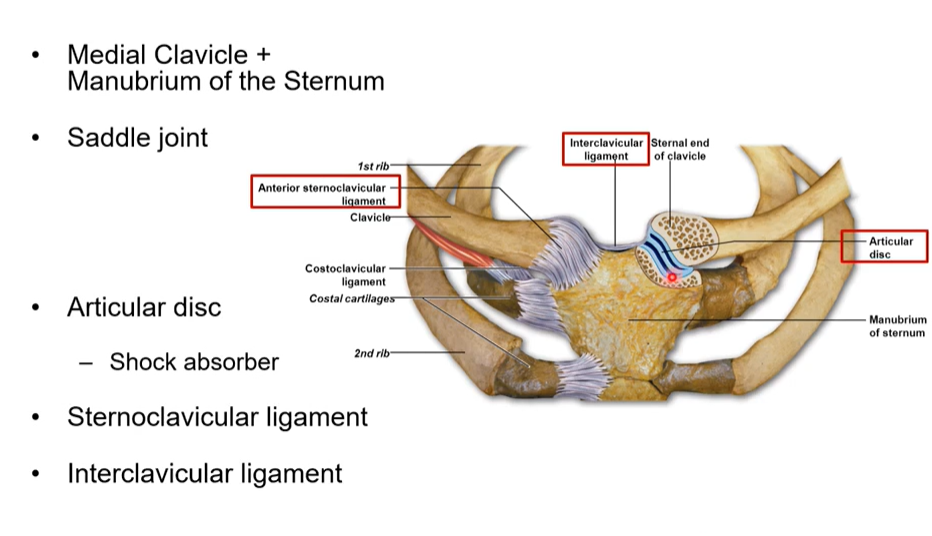
What is the sternoclavicular joint
where the medial clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum articulate together
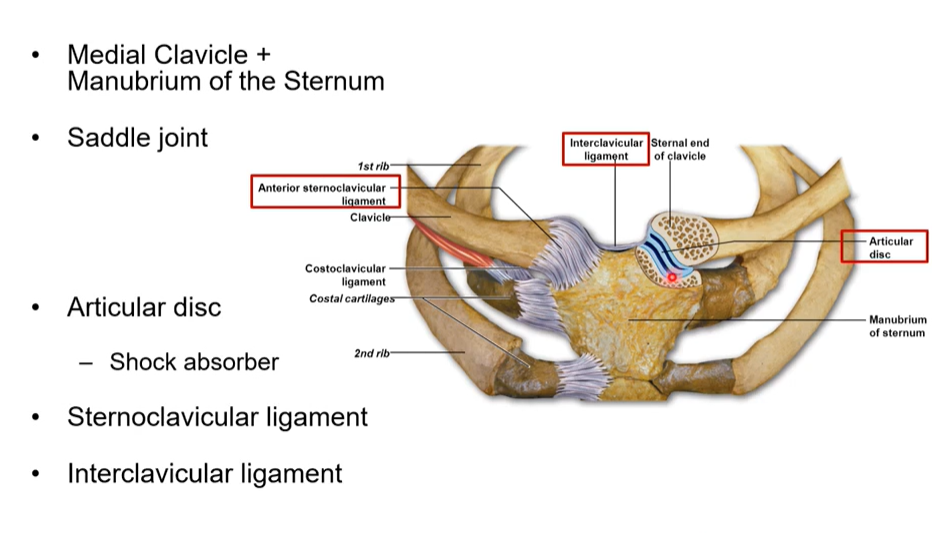
What does a ligament do
attaches bone to bone. reenforces joints so they’re stable and can have less movement
What is the articular disk purpose and where is it
it is in saddle reduces impact and absorbs shock
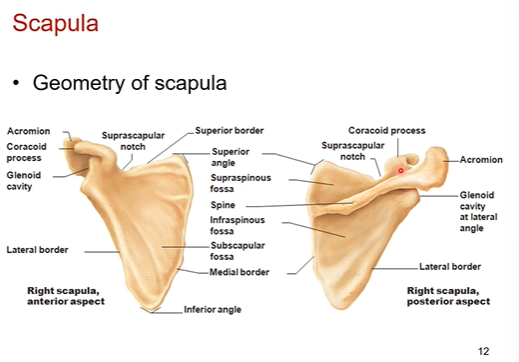
Scapula ( shoulder blades) purpose
acts like shield, insertion and attachment spots for muscles
Interclavicular ligament
in the jugular notch and connects both clavicles
Note clavicle in collar bone
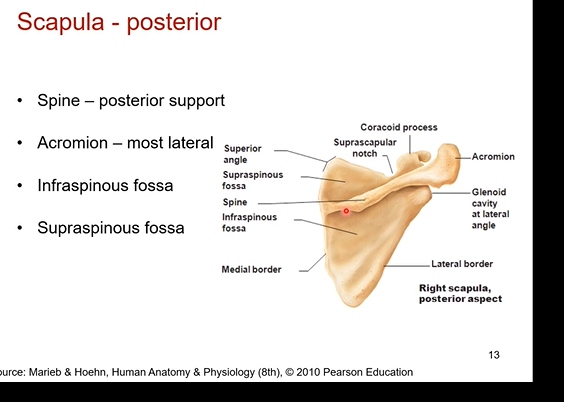
Posterior of right side of scapula. What’s in it? What is a distinguishing feature so you know you’re look at the posterior side of the scapula
Spine- posterior support
acromion - most lateral part of scapula bone
infraspinous fossa- under the spine. bony depression
supraspinous fossa= above the spine bony depression
seeing the spine is the distinguishing feature
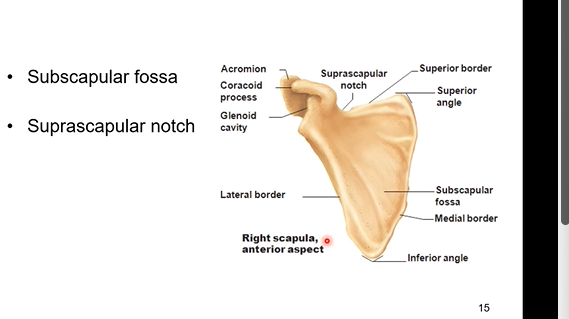
Lateral of right side of scapula. What’s in it? What is a distinguishing feature so you know you’re look at the lateral side of the scapula
With the lateral view you’re coming in from the sagittal view and looking at it from the side
Coracoid process - most anterior. good hook for multiple muscles including biceps, brachi muscle, and others
Glenoid fossa - articulates with head of humerus. its
distinguishing feature is the coracoid process seen
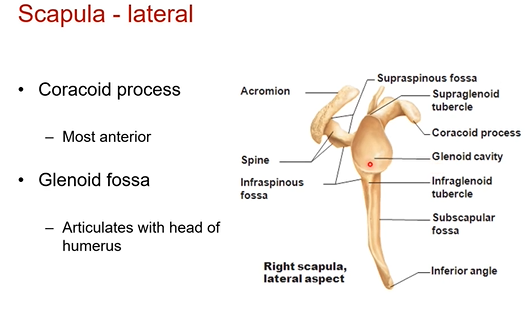
Anterior of right side of scapula. What’s in it? What is a distinguishing feature so you know you’re look at the anterior side of the scapula
Subscapular fossa- it’s a depression. a muscle fits in there. the subscapularis muscle
Suprascapular notch- good for blood supply and nerves to pass through
distinguishing feature is the subscapular fossa,
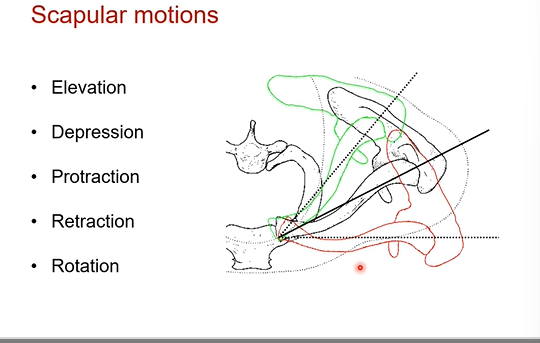
Scapular motions. What is the scapular in anatomical position?
side note motions don’t fit in the three planes of motion. you can use both palms of ur hand to mimic the scapula in each of ur shoulders
= depressed in anatomical
the scapular motions:
elevation, depression, protraction, retraction, rotation ( rotation is not the one in transverse plane),
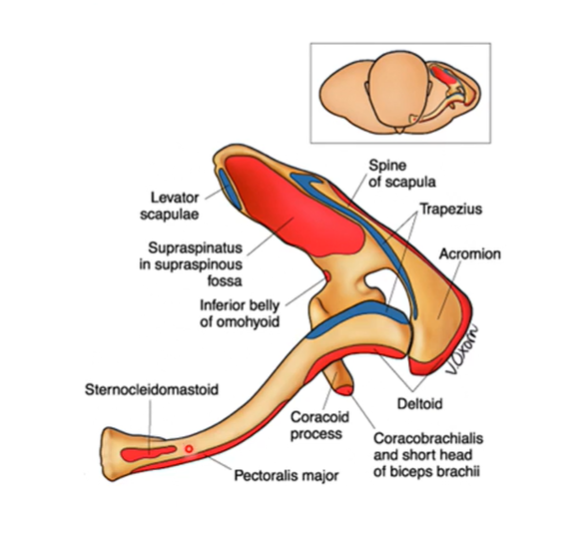
Clavicle is the only bone to do that in regards to the skeleton?
only bone that holds appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton
note pic is the superior view of the left side of clavicle/scapula
red/blue are where muscles insert or attach to or sit in
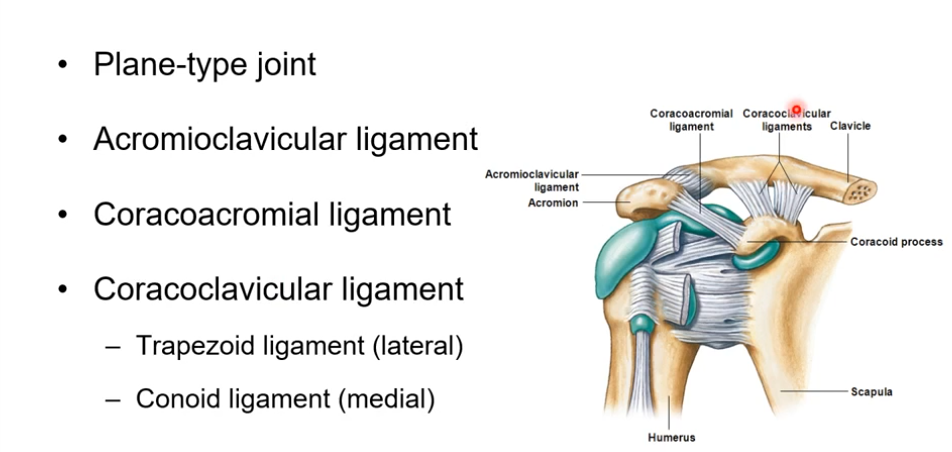
Joint associated with clavicle and scapula is the acromioclavicular joint. What does it articulate with? Parts in it?
acromial process of scapular articulates with clavicle.
plane type joint
acromioclavicular ligament- hold acromial end of clavicle with acromial process of scapula to allow attachment. some sliding and gliding here but not a lot as it ensures stability
coracoacromial ligament- more reinforcement to make sure clavicle and scapula stay close together. coracoid process and acromial process of scapula. humerus lies in there. serves for anterior stability so nothing moves anteriorly
coracoclavicular ligament- where clavicle and sternum meet again and hook onto coracoid process and inferior process of clavicle. trapezoid ligament (lateral) and conoid ligament (medial) here too
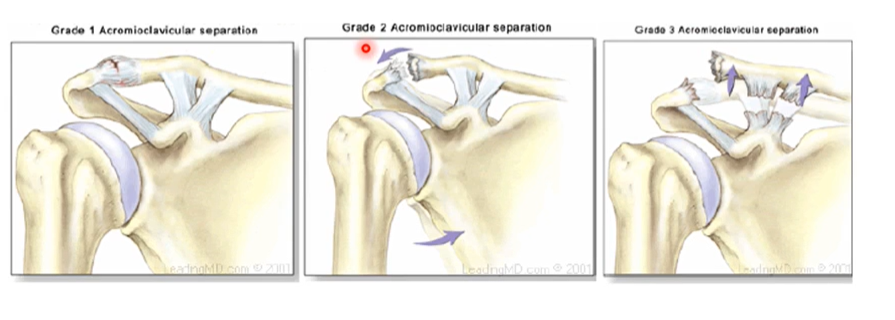
AC (acromioclavicular ) Joint Separation Grades meaning and what are they, which is most severe grade
the levels of tear and the number of ligaments damaged in the separation of the joint
Grade 1- partial tear of acromioclavicular ligament
Grade 2 - bones are detached from one another
Grade 3- separation of the acromioclavicular ligament and separation of the coracoclavicular ligament.
Grade 3 most severe type of separation cause we’ve completely detached the clavicle from the scapula
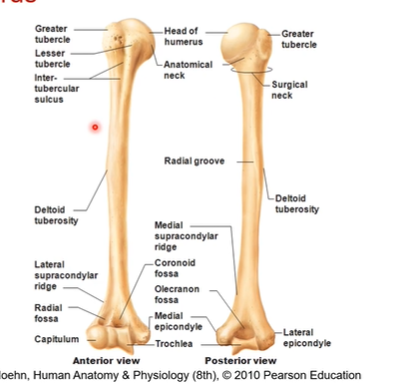
Humerus location? What is the most proximal end, what about distal. Which tubercle is on the anterior side?
located in the upper arm of the upper extremity. head of humerus is most proximal and medial. trochlea is most distal
lesser tubercle is on anterior side
side note greater tubercle is lateral, capitulum is lateral too
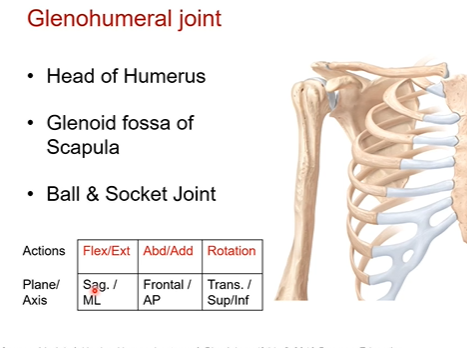
Glenohumeral joint (shoulder)- what does it articulate with? Is there lots of movement or stability? What increases the the glenoid fossa debt?
glenoid fossa of scapula and head of humerus articulate together as its a ball and socket joint. ball would be head of humerus and socket is the glenoid fossa
Yes lots of movement/mobility here in all three planes of motion resulting in all 3 types of actions
Not designed for stability so lots of ligaments around to help reenforce. like the coracoacromial ligaments prevents any superior dislocation.
Glenoid labrum is a tissue surrounding the glenoid fossa that increases the glenoid fossa debt
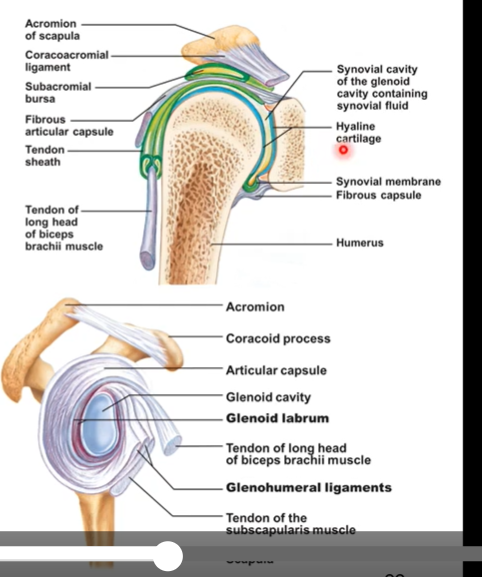
Ligaments in the glenohumeral joint
glenohumeral ligament - most anterior capsule
coracohumeral ligament
coracoacromial ligament
all reenforce and provide extra support for the ball and socket joint
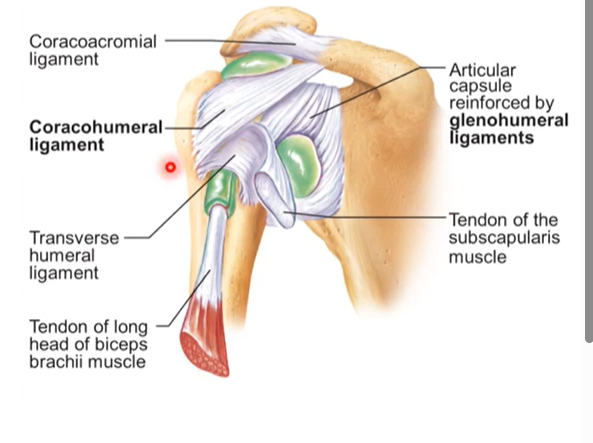
Radius and ulna- which side is each of them on? Where do you se olecranon process? What does trochlear notch allow for? Where is the distal end? What is the proximal end? What does the radial notch articulate with? What does the ulnar notch articulate with?
radius is the most lateral bone in the anatomical position on the thumb side.
ulna is on medial side
you see the olecranon process on posterior side
trochlear notch- allows for flexion and extension at the elbow
distal end= head of ulna
head of radius= proximal
radial notch of the ulna articulates with head of radius
ulnar notch of radius articulates with head of ulna
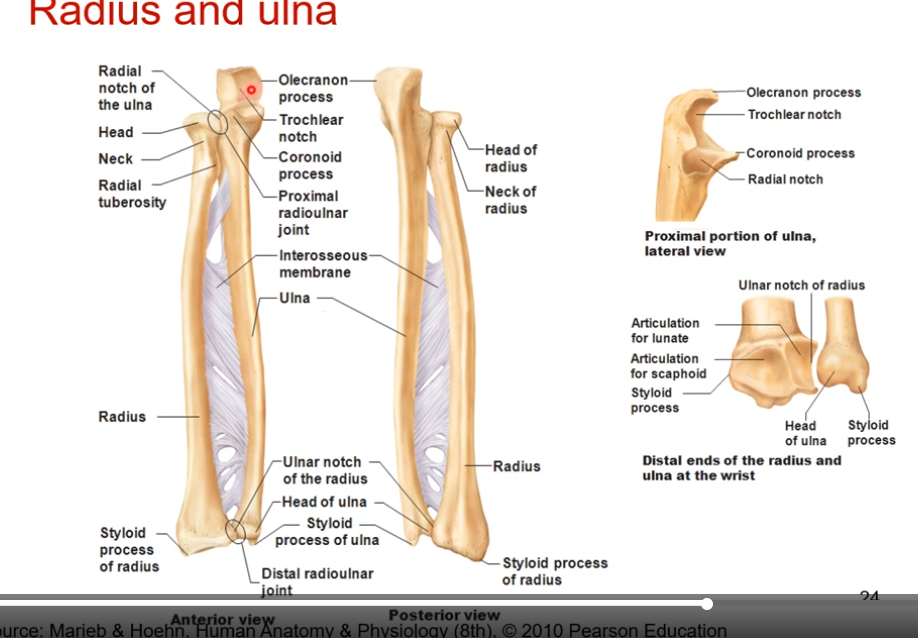
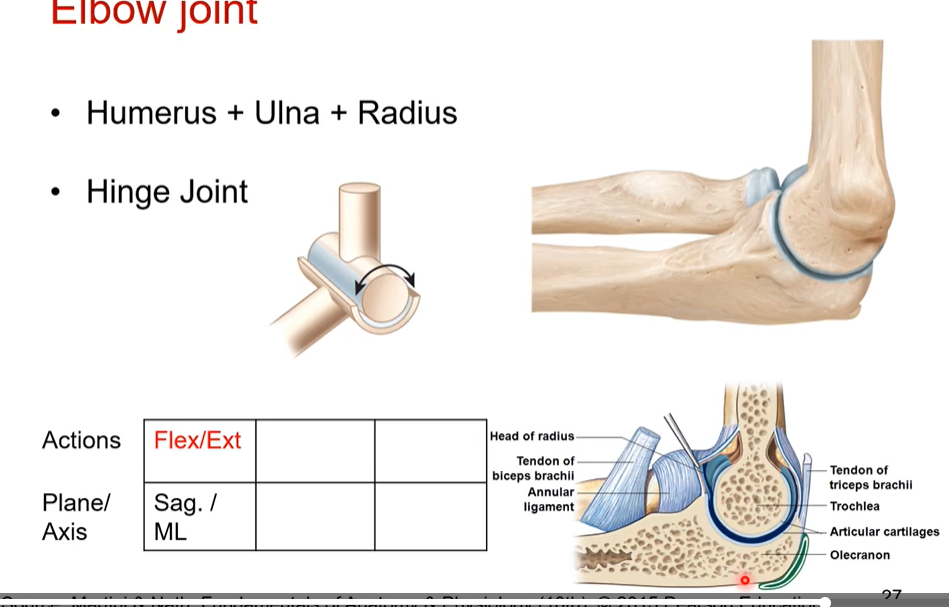
Humeroradial joint (combining humerus bone and radial bone) is what type of joint? what does it do? What plane does it do its actions? what articulates together? what ligament supports/stabilizes it
a hinge joint
flexion and extension in sagittal/ ML (medial lateral axis)
capitulum of humerus ( most lateral cap) articulates with head of radius
radial collateral ligament - on top of the articulation above. reenforces humeroradial joint.
Humeroulnar joint- is what type of joint? what does it do? What plane does it do its actions? what articulates together? what ligament supports/stabilizes it
hinge joint
flexion and extension
sag. or sagittal /ML ( medial lateral axis)
trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of ulna articulate together
ulnar collateral ligament
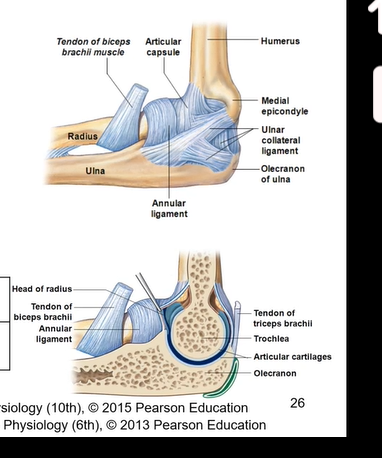
Elbow joint is made up of?
humerus + ulna + radius
hinge joint which includes trochlear notch and colleateral ligaments
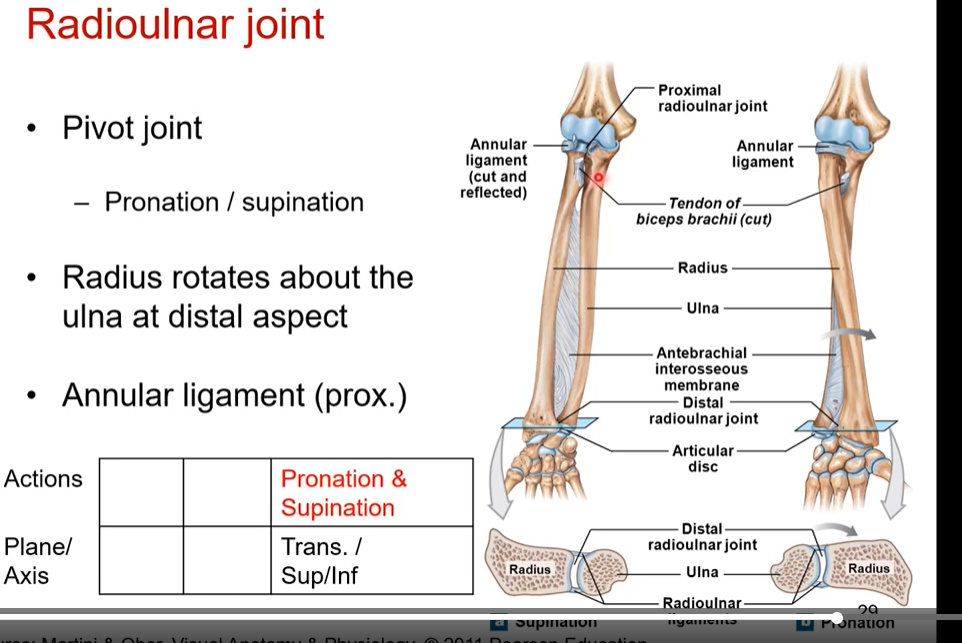
Radioulnar joint - what does the same imply is articulating together? Radioulnar joint articulates at the proximal and distal end, describe each end
the radius and ulna articulating together with the notches on each of them
at proximal end - we have head of radius that is articulating with capitulum on lateral side of radius and it’s articulating with radial notch of the ulna
at the distal end- head of ulna articulates with ulnar notch of radius
What does the radioulnar joint allow for and in which plane? what type of joint is it? what end does it pivot? what ligament is involved?
pronation/supination in the transverse plane of motion in the superior and inferior axis
it is a pivot joint
it pivots at proximal end
radius rotates about the ulna distal aspect
annular ligament (proximal)- doesn’t allow radius to roll over at the proximal end. only at distal end
Radiocarpal joint ( carpals are wrist bones) . What type of joint is it? what does the distal end of radius articulate with? What does the articulation allow for? What movements are associated with the radiocarpal joint?
condyloid joint - kind of a knuckle. knuckles of carpals articulate with the radius
distal end of radius articulates with scaphoid and lunate to connect our wrist and allows for movements like flexion and extension
movements associated are flexion and extension in the sagittal and medial lateral plants, abduction and adduction in frontal / AP plane
we have grater ulnar devaition ( adduction) vs radial deviation (abduction) because of gap present near wrist (space btw head of ulna and rest of carpal bones)
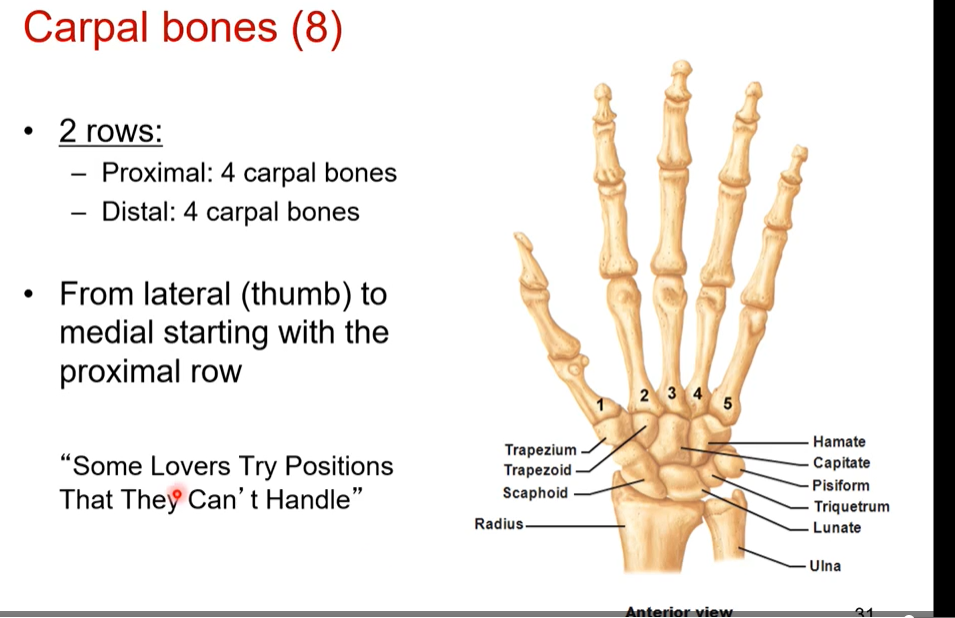
Carpal bones ( wrist bones)- how many carpal bones we have? What is in each of the 2 rows of carpal bones? Where do you start in naming? Does each carpal have a unique shape. What is hamate
we have 8 carpal bones. 2 rows of 4.
Proximal row: 4 carpal bones
distal row: 4 carpal bones
from lateral (thumb) to medial starting with proximal row
each carpal has a unique shape
hamate= carpal bone shaped like a hook
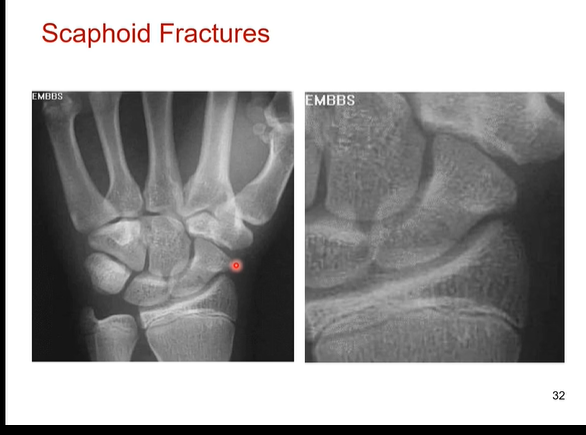
Does the scaphoid bone have poor blood supply? What does this mean for healing if you have a scaphoid fracture
Yes scaphoid bone has poor blood supply. it takes a long time to heal cause it gets only a little bit of oxygen
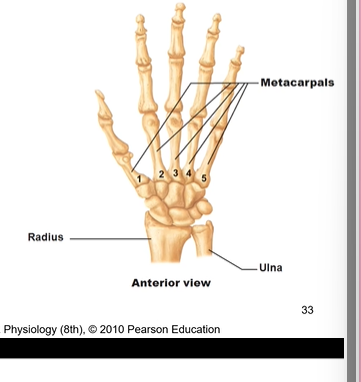
Metacarpal bones (meta= above, carpal= wrist bone). How are they numbered? Where are these bones? Each metacarpal has 3 things, what are they?
numbered 1-5. thumb is #1, pinky #5,
bones in the palm of your hand
each ( all 5) metacarpal bone has a:
base- most proximal
shaft- diaphasis of carpal bone
head- most distal
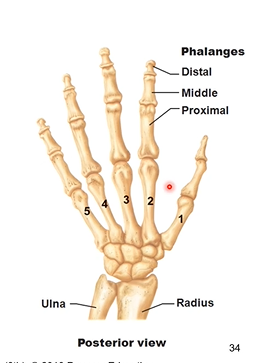
Phalanges ( digits/fingers). each phalange has how many bones to it. name the bones for each digit
each phalange has 2-3 bones to it. thumb or the 1 digit has 2 bones. digits 2-5 have 3 bones
first digit has proximal and distal phalanx
digits 2-5 have proximal (closer to metacarpal/wrist). middle, and distal phalanx
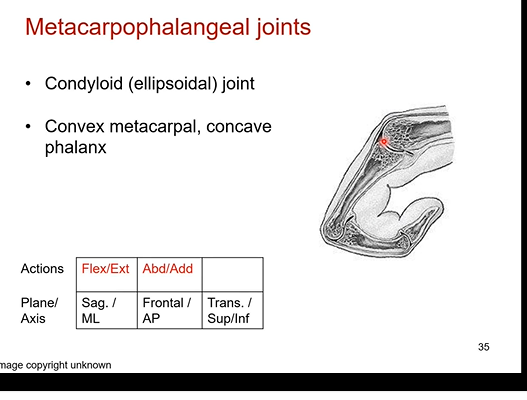
Metacarpophalangeal joints are what type of joints? What two types are present in here? What motions and planes are involved?
condyloid (ellipsoidal) joint is the type. condyloid means knuckles
we have a convex metacarpal ( outward curvature) and a concave phalanx
flexion and extension n the sagittal and medial lateral plane. abduction (spread ur fingers) and adduction ( bring fingers closer to middle finger) in the frontal/AP plane
we can circumduction / circumduct each of the fingers as well
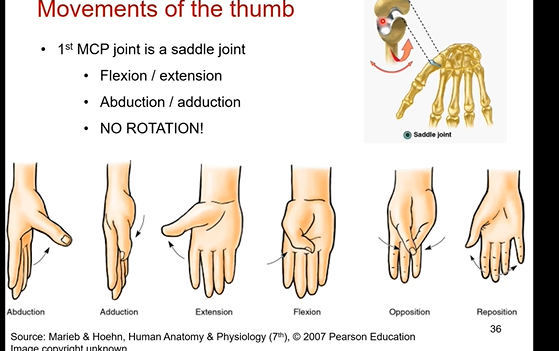
Movements of the thumb. what type of joint is it? its motions it can do? what motion CAN’T it do?
its the 1st MCP joint (metacarpal phalangeal)
it’s a saddle joint
has its own unique flexion/extension and abduction/adduction. the thumb does it have the planes that go with the motions like everything else
WE CAN’T ROTATE IT. NO ROTATION IN THUMB OR ANY DIGITS.
circumduction present in any digit inclduing thumb